PAT 甲级 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(dijstra+dfs,dfs记录路径,做了两天)
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
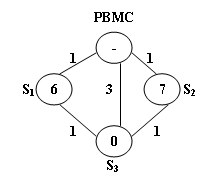
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex S is the current number of bikes stored at S. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
PBMC -> S1 -> S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
PBMC -> S2 -> S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: Cmax (≤), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; N (≤), the total number of stations; Sp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to N, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and M, the number of roads. The second line contains N non-negative numbers Ci (,) where each Ci is the current number of bikes at Si respectively. Then M lines follow, each contains 3 numbers: Si, Sj, and Tij which describe the time Tij taken to move betwen stations Si and Sj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of Sp is adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
Sample Input:
10 3 3 5
6 7 0
0 1 1
0 2 1
0 3 3
1 3 1
2 3 1
Sample Output:
3 0->2->3 0题意:
每个自行车车站的最大容量为一个偶数cmax,如果一个车站里面自行车的数量恰好为cmax / 2,那么称处于完美状态。如果一个车展容量是满的或者空的,控制中心(处于结点0处)就会携带或者从路上手机一定数量的自行车前往该车站,一路上会让所有的车展沿途都达到完美。现在给出cmax,车站的数量n,问题车站sp,m条边,还有距离,求最短路径。如果最短路径有多个,求能带的最少的自行车数目的那条。如果还是有很多条不同的路,那么就找一个从车站带回的自行车数目最少的。带回的时候是不调整的
思路:
首先用dijkstra算法求出PBMC(0点)到目标点的最短距离。然后深搜穷举,每次深搜找到一条最短路径后依次记录路径上的各点,然后扫描,如果有的station少于最大容量的一半,带出的车数就加到take中;如果多了,带回去的车数加到back中。注意,每一站多的车辆只能放到后面一站去,而不能补充前面车站中少的数目。
在dfs中借助栈记录下最好的路径
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std; int maze[][];//迷宫
int vis[][];//记录迷宫中的某个位置是否访问过
int n,m; int dir[][] = {{,},{,-},{,},{-,}};//四个方向 struct point//位置
{
int x,y;
} p; stack<point> path,temp;//记录路径,temp是一个临时变量,和path一起处理路径 int count;//路径条数 void dfs(int x,int y)//x,y:当前位置
{
if(x==n- && y==m-)//成功---下面处理路径问题
{
cout << "******************路径"<< ++count << "******************" << endl;
while(!path.empty())//将path里面的点取出来,放在temp里面
{//path从栈顶-栈底的方向,路径是从终点-起点的顺序
point p1 = path.top();
path.pop();
temp.push(p1);
}
while(!temp.empty())
{//输出temp里面的路径,这样刚好是从起点到终点的顺序
point p1 = temp.top();
temp.pop();
path.push(p1);//将路径放回path里面,因为后面还要回溯!!!
cout << "(" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << ")" << endl;
}
return;
} if(x< || x>=n || y< || y>=m)//越界
return; //如果到了这一步,说明还没有成功,没有出界
for(int i=;i<;i++)//从4个方向探测
{
int nx = x + dir[i][];
int ny = y + dir[i][];//nx,ny:选择一个方向,前进一步之后,新的坐标
if(<=nx && nx<n && <=ny && ny<m && maze[nx][ny]== && vis[nx][ny]==)
{//条件:nx,ny没有出界,maze[nx][ny]=0这个点不是障碍可以走,vis[nx][ny]=0说明(nx,ny)没有访问过,可以访问 vis[nx][ny]=;//设为访问过
p.x = nx;
p.y = ny;
path.push(p);//让当前点进栈 dfs(nx,ny);//进一步探测 vis[nx][ny]=;//回溯
path.pop();//由于是回溯,所以当前点属于退回去的点,需要出栈
}
}
} int main()
{
count = ;
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);//读取.cpp文件同目录下的名为in.txt的文件 p.x = ;
p.y = ;
path.push(p);//起点先入栈 cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<m;j++)
{
vis[i][j] = ;
cin >> maze[i][j];
}
}
dfs(,); return ;
}
这个题目有两个比较坑的点:
1.仔细阅读题目,会发现其实有三个优先级判断点:题目正文中要求第一优先级为最短路径,第二优先级为派出自行车最少,而在结果输出中有第三优先级,即收回自行车最少。遗漏后两个优先级会导致有的点通不过;
2.在统计派出数和收回数时,要注意一个站点中多出来的自行车只能向后面的站点补充,而不能向前面的站点补充,这也是很容易忽视的问题。
我的样例:
->-> ->->-> ->->-> ->->->-> ->-> ->->->->
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int INF = ;
int C,SP,N,M;
int h[];//拥有多少自行车
int e[][];
int d[];
int v[];
int min_go=INF;//带去的越少越好
int min_back=INF;//带回来的越少越好
vector<int>p[];//记录所有最短路径中各个点的前一个有哪些
stack<int>route;
stack<int>final_route;
void clear(stack<int> &s){//清空栈
stack<int> empty;
swap(empty,s);
}
void dijstra()
{
d[]=;
memset(v,,sizeof(v));
for(int i=;i<=N;i++){
d[i]=e[][i];
if(d[i]!=INF)
{
p[i].push_back();
}
}
for(int i=;i<=N-;i++){
int k=-;
int min=INF;
for(int j=;j<=N;j++){
if(v[j]== && min>d[j]){
k=j;
min=d[j];
}
}
if(k==-){
break;
}
v[k]=;
for(int j=;j<=N;j++){
if(v[j]==){
continue;
}
if(d[j]>d[k]+e[k][j])
{
p[j].clear();
p[j].push_back(k);
d[j]=d[k]+e[k][j];
}
else if(d[j]==d[k]+e[k][j]){
p[j].push_back(k);
}
}
}
}
void dfs(int s,int go,int back){
for(int i=;i<p[s].size();i++){
int x=p[s].at(i);
if(x==){
if(min_go>go){//根据优先级更新!
min_go=go;
min_back=back;
final_route=route;//更新最终路线
final_route.push(x);
}else if(min_go==go && min_back>back){
min_go=go;
min_back=back;
final_route=route;//更新最终路线
final_route.push(x);
}
}else{
int g=go+C-h[x];
int b=back;//后面多的不能补到前面!
if(g<){//需要送去的为负数了
b+=(-*g);//反而还要带点回来
g=;//那就不送了
}
route.push(x);
dfs(x,g,b);
route.pop();
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>C>>N>>SP>>M;
C/=;
for(int i=;i<=N;i++){
cin>>h[i];
p[i].clear();
}
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=N;j++)
{
if (i==j) e[i][j]=;
else e[i][j]=INF;
}
}
for(int i=;i<=M;i++){
int u,v,t;
cin>>u>>v>>t;
e[u][v]=e[v][u]=t;
}
dijstra(); int go=C-h[SP];
int back=;
if(go<){
back=-*go;
go=;
}
clear(route);
clear(final_route);
route.push(SP); dfs(SP,go,back);
//输出
cout<<min_go<<" ";
while(!final_route.empty()){
cout<<final_route.top();
final_route.pop();
if(!final_route.empty()){
cout<<"->";
}
}
cout<<" "<<min_back<<endl; return ;
}
PAT 甲级 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(dijstra+dfs,dfs记录路径,做了两天)的更多相关文章
- 【PAT甲级】1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(SPFA,DFS)
题意: 输入四个正整数C,N,S,M(c<=100,n<=500),分别表示每个自行车站的最大容量,车站个数,此次行动的终点站以及接下来的M行输入即通路.接下来输入一行N个正整数表示每个自 ...
- PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management
PAT甲级1018. Public Bike Management 题意: 杭州市有公共自行车服务,为世界各地的游客提供了极大的便利.人们可以在任何一个车站租一辆自行车,并将其送回城市的任何其他车站. ...
- PAT Advanced 1018 Public Bike Management (30) [Dijkstra算法 + DFS]
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists fro ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) 思路分析 + 满分代码
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) PAT甲级真题 dijkstra + dfs
前言: 本题是我在浏览了柳神的代码后,记下的一次半转载式笔记,不经感叹柳神的强大orz,这里给出柳神的题解地址:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuo/article/detail ...
- PAT A 1018. Public Bike Management (30)【最短路径】
https://www.patest.cn/contests/pat-a-practise/1018 先用Dijkstra算出最短路,然后二分答案来验证,顺便求出剩余最小,然后再从终点dfs回去求出路 ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) (迪杰斯特拉+dfs)
思路就是dijkstra找出最短路,dfs比较每一个最短路. dijkstra可以找出每个点的前一个点, 所以dfs搜索比较的时候怎么处理携带和带走的数量就是关键,考虑到这个携带和带走和路径顺序有关, ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30)(30 分)
时间限制400 ms 内存限制65536 kB 代码长度限制16000 B There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
随机推荐
- 在linux中安装VM tools
step 1:虚拟机选择安装 Vmware tools ,在DVD中将.tar.gz的文件包拖到桌面中: step 2:打开终端,切换到桌面,cd /home/whoami/桌面 cd /home/u ...
- Java 基础 - 泛型类/泛型方法/类型通配符'?' 的用法及栗子
笔记: /**1.定义一个PairTest泛型类, 测试泛型 类 Pair的用法 * class Pair<T>{ * private T first; * private T secon ...
- Java锁--LockSupport
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3505784.html LockSupport介绍 LockSupport是用来创建锁和其他同步类的基本线 ...
- Vue基础认识
一:什么是Vue? vue是一个渐进式的JavaScript框架,采用的是MVVM模式.Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用.Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整 ...
- maven 安装第三方jar到本地 出现 The goal you specified requires a project to execute but there is no POM in this directory 错误
原因是因为操作系统的差异导致,把所有参数加上引号即可. 如下所示: mvn install:install-file "-Dfile=cobra.jar" "-Dgrou ...
- 为什么Object.prototype在Function的原型链上与Function.prototype在Object的原型链上都为true
关于javascript的原型链有一个问题我一直很疑惑:为什么 Function instanceof Object 与 Object instanceof Function都为true呢? Func ...
- PHP基础--traits的应用
Traits 在PHP中实现在方法的重复使用:Traits与Class相似,但是它能够在Class中使用自己的方法而不用继承: Traits在Class中优先于原Class中的方法,引用PHP Doc ...
- webpack+vue+Eslint+husky+lint-staged 统一项目编码规范
一. Eslint: 为什么我们要在项目中使用ESLint ESLint可以校验我们写的代码,给代码定义一个规范,项目里的代码必须按照这个规范写. 加入ESLint有非常多的好处,比如说可以帮助我们避 ...
- luogu2885
P2885 [USACO07NOV]电话线Telephone Wire 给出若干棵树的高度,你可以进行一种操作:把某棵树增高h,花费为h*h. 操作完成后连线,两棵树间花费为高度差*定值c. 求两种花 ...
- classpath详解
在dos下编译java程序,就要用到classpath这个概念,尤其是在没有设置环境变量的时候.classpath就是存放.class等编译后文件的路径. javac:如果当前你要编译的java文件中 ...