HashMap不足性分析
不足性:
1.缺陷就在于其高度依赖hash算法,如果key是自定义类,你得自己重写hashcode方法,写hash算法。
而且hashmap要求,存入时的hashcode什么样,之后就不能在变更,如果一个类的hashcode与其成员变量name有关,而之后name又发生了变化,那么hashmap行为将不正常。
两个对象如果equals相同,那hashcode的值一定相同,如果hashcode值相同,对象不一定equals相同,只能证明两对象在散列存储中处于同一位置! 在散列存储中存放元素,通常先判断hash值,确定是不是在这个位置,再判断equals 和已存放的元素是否相等。
所以hash值又必须跟对象属性有关系,否则无法保证equals相等 hash就等,但和属性挂钩,一旦属性变化,hash就变化,处于散列存储的位置就会发生变化
2.hashmap的元素存储位置,除了元素key的hash值有关,还跟数组本身长度有关,如果扩容数组长度发生变化,必须把所有元素重新计算其index存放位置,所以尽可能事先确定hashmap的大小,防止扩容
1、基本概念:
Hash散列:通过hash算法转换成一个固定值
Map:x,y 地图
通过Hash值定位到Map,将Value存进去
存储方式:k:v方式。键值对
key可以为空,null当成一个key来存储
2、源码分析:
1、static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
默认的初始容量2的4次方
2、static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
最大容量为2的30次方
3、static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
加载因子:0.75f,是指容量达到容器的4分之3时,进行扩容
4、int threshold;
入口初始化--扩容的变量
5、transient Node<K,V>[] table;
第一次使用时初始化,并根据需要调整大小。当分配时,长度总是2的幂
6、transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
保存缓存entrySet (),用来存取key、values
7、transient int size;
此映射中包含的键值映射的数目
8、transient int modCount;
用来记录被修改的次数
9、final float loadFactor;
临时的加载因子
/**
*initialCapacity:初始容量
*loadFactor:加载因子
*/
10、public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
一个有参的构造方法
11、public HashMap(int initialCapacity)
12、public HashMap()
初始化加载因子
13、public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
实现了地图。putAll和Map构造函数。
14、 public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
将指定值与此映射中的指定键关联。如果映射以前包含键的映射,则替换旧值。
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
15、 public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
--键值参数实体类
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
--根据健查找容器中是否存在的key,有则返回V,无则返回null
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
Entry对象: Table:数组+链表 数据结构
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
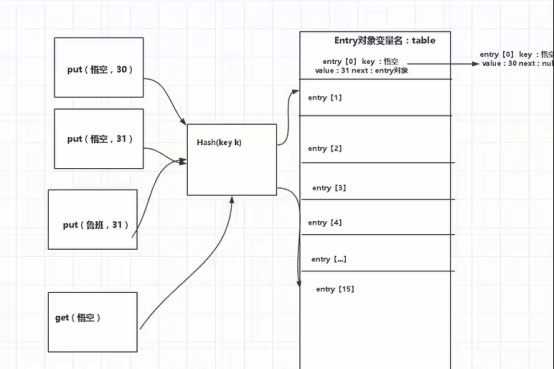
3、手写HashMap源码:
顶层接口Map:
package com.cq.hashmap;
/**
*
* @author M
*
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public interface Map<K,V> {
/**
* 内容添加
* @param k
* @param v
* @return
*/
public V put(K k,V v);
/**
* 根据key获取最新内容
* @param k
* @return
*/
public V get(K k);
/**
* 获取容器内容数量
* @return
*/
public int size();
/**
* 实体类接口
* @author Administrator
*
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public interface Entry<K, V>{
public K getKey();
public V getValue();
}
}
实现类HashMap<k,v>
package com.cq.hashmap;
public class HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K, V> {
// 默认容器
private static int defaultlegth = 1 << 4;
// 加载因子
private static float defaultLoder = 0.75f;
private Entry[] table = null;
private int size = 0;
public HashMap() {
this(defaultlegth, defaultLoder);
}
public HashMap(int length, float defaultLoder2) {
defaultlegth = length;
defaultLoder = defaultLoder2;
table = new Entry[defaultlegth];
}
public V put(K k, V v) {
size++;
int index = hash(k);
Entry<K, V> entry = table[index];
if (entry == null) {
table[index] = newEntry(k, v, null);
} else {
table[index] = newEntry(k, v, entry);
}
return (V) table[index].getValue();
}
public Entry<K, V> newEntry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> next) {
return new Entry<K,V>(k, v, next);
}
private Integer hash(K k) {
int len = defaultlegth;
int i = k.hashCode() % len;
return i >= 0 ? i : -i;
}
public V get(K key) {
int index = hash(key);
if (table[index] == null) {
return null;
}
return (V) find(key, table[index]);
}
private V find(K key, Entry<K, V> entry) {
if (key == entry || key.equals(entry.getKey())) {
if (entry.next != null) {
System.out.println("旧值:" + entry.next.getValue());
}
return entry.getValue();
} else {
if (entry.next != null) {
System.out.println("旧值:" + entry.next.getValue());
find(key, entry.next);
}
}
return null;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
K k;
V v;
Entry<K, V> next;
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> next) {
super();
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
this.next = next;
}
public K getKey() {
return k;
}
public V getValue() {
return v;
}
}
}
测试类:
package com.cq.hashmap;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestMap {
@Test
public void MapTest() {
Map<String, Integer> map=new HashMap<String, Integer>();
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
map.put("悟空"+i,i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println(map.get("悟空"+i));
}
long currentTimeMillis2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("大小:"+map.size()+"时间:"+(currentTimeMillis2-currentTimeMillis));
}
}
不足之处:(伸缩性)
1、伸缩性
2、时间复杂度:你的hash算法决定了你的效率
3、Key是否重复有关get(0)1
4、当hash扩容是,需要重新去add entry数组里面。
当需要多少容量时,最好先指定扩容大小,防止在put的时候进行扩容很多次
HashMap不足性分析的更多相关文章
- MINIX3 内核整体架构回顾及内核定 性分析
MINIX3 内核整体架构回顾及内核定 性分析 12.1 注意事项 由于本文档不对 I/O 文件系统做出分析,所以在此不对 MINIX3 整体做出一个分 析,本章主要是针对内核进程分析.并且这里的模 ...
- 连续型变量的推断性分析——t检验
连续型变量的推断性分析方法主要有t检验和方差分析两种,这两种方法可以解决一些实际的分析问题,下面我们分别来介绍一下这两种方法 一.t检验(Student's t test) t检验也称student ...
- 【JAVA集合】HashMap源码分析(转载)
原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenpi/p/5280304.html 以下内容基于jdk1.7.0_79源码: 什么是HashMap 基于哈希表的一个Map接口实现,存储 ...
- Java中HashMap源码分析
一.HashMap概述 HashMap基于哈希表的Map接口的实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键.(除了不同步和允许使用null之外,HashMap类与Hashtab ...
- 基础进阶(一)之HashMap实现原理分析
HashMap实现原理分析 1. HashMap的数据结构 数据结构中有数组和链表来实现对数据的存储,但这两者基本上是两个极端. 数组 数组存储区间是连续的,占用内存严重,故空间复杂的很大.但数组的二 ...
- JDK1.8 HashMap源码分析
一.HashMap概述 在JDK1.8之前,HashMap采用数组+链表实现,即使用链表处理冲突,同一hash值的节点都存储在一个链表里.但是当位于一个桶中的元素较多,即hash值相等的元素较多时 ...
- HashMap源码分析和应用实例的介绍
1.HashMap介绍 HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射.HashMap 继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map.Cloneable.java.io.S ...
- 【Java】HashMap源码分析——常用方法详解
上一篇介绍了HashMap的基本概念,这一篇着重介绍HasHMap中的一些常用方法:put()get()**resize()** 首先介绍resize()这个方法,在我看来这是HashMap中一个非常 ...
- 【Java】HashMap源码分析——基本概念
在JDK1.8后,对HashMap源码进行了更改,引入了红黑树.在这之前,HashMap实际上就是就是数组+链表的结构,由于HashMap是一张哈希表,其会产生哈希冲突,为了解决哈希冲突,HashMa ...
随机推荐
- 转 linux 添加PHP环境变量,/etc/profile 不生效,每次都要 source /etc/profile
http://shanhuxueyuan.com/news/detail/46.html 执行php -v 提示未找到命令,这是因为没有将php路径添加到环境变量 方法一:直接运行命令export P ...
- ireport5.6.0分组显示
一,ireport中分组 二,java调用实现分组 一,ireport中分组: 1,新建模板文件,纸张随意,名称随意,路径随意 2,连接要分组的数据源 3,添加测试表和数据 CREATE TABLE ...
- Django Model 模型
参考: https://www.runoob.com/django/django-model.html https://www.cnblogs.com/taosiyu/p/11260000.html ...
- 仿简书MarkDown编辑器可同步滚动
模仿简书的MarkDown编辑器,使用Angular8写的示例 1.支持同步滚动 编辑的过程中,右侧预览界面会同步滚动.滚动右侧预览界面,左侧编辑区也会同步滚动哦 2.支持语法高亮 如下: using ...
- 【Docker学习之六】Docker容器互联
环境 docker-ce-19.03.1-3.el7.x86_64 centos 7 一.基于Volume的互联就是-v参数,将本机文件或目录挂载到容器目录,实现文件目录共享 二.基于Link的互联 ...
- CentOS7.5 使用 kubeadm 安装配置 Kubernetes1.12(四)
在之前的文章,我们已经演示了yum 和二进制方式的安装方式,本文我们将用官方推荐的kubeadm来进行安装部署. kubeadm是 Kubernetes 官方提供的用于快速安装Kubernetes集群 ...
- SQL Server表分区(转)
什么是表分区 一般情况下,我们建立数据库表时,表数据都存放在一个文件里. 但是如果是分区表的话,表数据就会按照你指定的规则分放到不同的文件里,把一个大的数据文件拆分为多个小文件,还可以把这些小文件放在 ...
- Go基础编程实践(七)—— 并发
同时运行多个函数 观察常规代码和并发代码的输出顺序. // 常规代码,顺序执行,依次输出 package main import ( "fmt" "time" ...
- Go基础编程实践(三)—— 日期和时间
日期和时间 package main import ( "fmt" "time" ) func main() { // 获取当前时间 current := ti ...
- CLRS10.2-7练习 - 翻转单向列表
要求: Give a Θ(n)-time nonrecursive procedure that reverses a singly linked list of nelements. The pro ...
