HotSpot源码分析之类模型
HotSpot采用了OOP-Klass模型描述Java的类和对象。Klass模型采用Klass类及相关子类的对象来描述具体的Java类。一般HotSpot JVM 在加载Java的Class 文件时,会在方法区创建 Klass ,用来保存Java类的元数据,包括常量池、字段、方法等。
Klass模型中相关类的继承体系如下图所示。
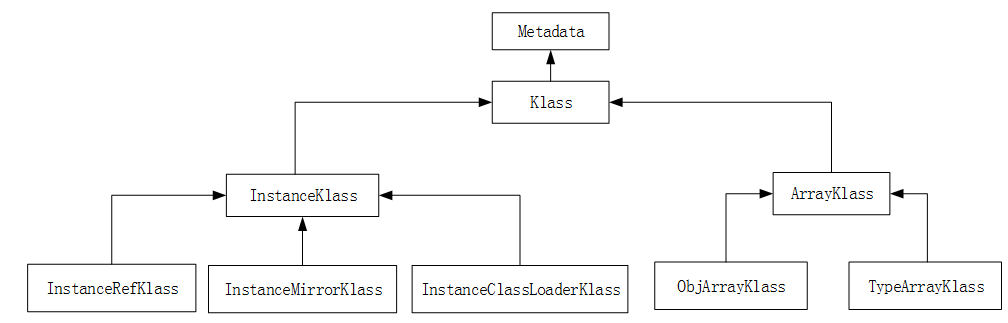
Metadata是元数据类的基础类型,除了Klass会直接继承外,表示方法的Method与表示常量池的ConstantPool也会继承,这里只讨论Klass继承体系中涉及到的相关类。
整个Klass模型中涉及到的C++类主要提供了2个功能:
(1)提供C++层面的Java类型(包括Java类和Java数组)表示,也就是用C++类的对象来描述Java类型。
(2)方法分派
这一篇文章重点介绍一下Klass这个基础类型。
一个Klass对象(注意是Klass对象表示Java类的元数据,所以不同的Java类就用不同的Klass对象表示)代表一个Java类的元数据(相当于java.lang.Class对象)。所以Klass中要有描述Java类中常量池、字段、方法的能力,也就是能保存这些信息,同时还能提供一些方法供HotSpot JVM的开发者操作这些信息。
Klass类及重要属性的定义如下:
- 源代码位置:hotspot/src/share/vm/oops/klass.hpp
class Klass : public Metadata {- // ...
- protected:
- // note: put frequently-used fields together at start of klass structure
- // for better cache behavior (may not make much of a difference but sure won't hurt)
- enum { _primary_super_limit = 8 };
- // The "layout helper" is a combined descriptor of object layout.
- // For klasses which are neither instance nor array, the value is zero.
- //
- // For instances, layout helper is a positive number, the instance size.
- // This size is already passed through align_object_size and scaled to bytes.
- // The low order bit is set if instances of this class cannot be
- // allocated using the fastpath.
- //
- // For arrays, layout helper is a negative number, containing four
- // distinct bytes, as follows:
- // MSB:[tag, hsz, ebt, log2(esz)]:LSB
- // where:
- // tag is 0x80 if the elements are oops, 0xC0 if non-oops
- // hsz is array header size in bytes (i.e., offset of first element)
- // ebt is the BasicType of the elements
- // esz is the element size in bytes
- // This packed word is arranged so as to be quickly unpacked by the
- // various fast paths that use the various subfields.
- //
- // The esz bits can be used directly by a SLL instruction, without masking.
- //
- // Note that the array-kind tag looks like 0x00 for instance klasses,
- // since their length in bytes is always less than 24Mb.
- //
- // Final note: This comes first, immediately after C++ vtable,
- // because it is frequently queried.
- jint _layout_helper;
- // The fields _super_check_offset, _secondary_super_cache, _secondary_supers
- // and _primary_supers all help make fast subtype checks. See big discussion
- // in doc/server_compiler/checktype.txt
- //
- // Where to look to observe a supertype (it is &_secondary_super_cache for
- // secondary supers, else is &_primary_supers[depth()].
- juint _super_check_offset;
- // Class name. Instance classes: java/lang/String, etc. Array classes: [I,
- // [Ljava/lang/String;, etc. Set to zero for all other kinds of classes.
- Symbol* _name;
- // Cache of last observed secondary supertype
- Klass* _secondary_super_cache;
- // Array of all secondary supertypes
- Array<Klass*>* _secondary_supers;
- // Ordered list of all primary supertypes
- Klass* _primary_supers[_primary_super_limit];
- // java/lang/Class instance mirroring this class
- oop _java_mirror;
- // Superclass
- Klass* _super;
- // First subclass (NULL if none); _subklass->next_sibling() is next one
- Klass* _subklass;
- // Sibling link (or NULL); links all subklasses of a klass
- Klass* _next_sibling;
- // All klasses loaded by a class loader are chained through these links
- Klass* _next_link;
- // The VM's representation of the ClassLoader used to load this class.
- // Provide access the corresponding instance java.lang.ClassLoader.
- ClassLoaderData* _class_loader_data;
- AccessFlags _access_flags; // Access flags. The class/interface distinction is stored here.
- markOop _prototype_header; // Used when biased locking is both enabled and disabled for this type
- ...
- }
下表对各个属性进行了简单的介绍。
| 字段名 | 作用 |
| _layout_helper |
对象布局的综合描述符。如果不是InstanceKlass或ArrayKlass,值为0。如果是InstantceKlass或 ArrayKlass时,这个值是个组合数字。 (1)对InstanceKlass而言,组合数字中包含有表示对象的、以字节为单位的内存占用大小,也就是说InstanceKlass对象表示Java类,由这个Java类创建的对象所需要的大小。 (2)对ArrayKlass而言,该值是一个组合数字,包含4部分,具体怎么组合和解析由子类实现:
|
| _name | 类名,如java/lang/String,[Ljava/lang/String |
| _primary_supers |
_primary_supers代表了这个类的父类,其类型是个Klass指针数组,大小固定为8。例如IOException是Exception的子类, 而Exception又是Throwable的子类。所以表示IOException类的_primary_supers属性值为: [Throwable, Exception, IOException]。如果继承链过长,也就是当前类加上继承的类多于8个(默认值,可通过命令更改)时, 会将多出来的类存储到secondary_supers数组中 |
| _super_check_offset |
快速查找supertype的一个偏移量,这个偏移量是相对于Klass对象起始地址的偏移量。如果当前类是IOException, 那么这个属性就指向_primary_supers数组中存储IOException的位置。当存储的类多于8个时,值与secondary_super_cache 相等 |
| _secondary_supers |
Klass指针数组,一般存储Java类实现的接口,偶尔还会存储Java类的父类 |
| _secondary_super_cache |
Klass指针,保存上一次查询父类的结果 |
| _java_mirror | oopDesc类型的指针,保存的是当前Klass对象表示的Java类所对应的java.lang.Class对象,可以据此访问类的静态属性 |
| _super | Klass指针,指向Java类的直接父类 |
| _subklass | Klass指针,指向Java类的直接子类,由于直接子类可能有多个,所以通过_next_sibling连接起来 |
| _next_sibling | Klass指针,该类的下一个子类,也就是通过_subklass->next_sibling()获取_subklass的兄弟子类 |
| _next_link | Klass指针,ClassLoader加载的下一个Klass |
| _class_loader_data | ClassLoaderData指针,可以通过此属性找到加载该Java类的ClassLoader |
| _access_flags | 获取Java类的修饰符,如private、final、static、abstract 、native等 |
| _prototype_header | 在锁的实现过程中非常重要,后续在介绍锁时会介绍 |
可以看到,能够通过Klass类中的相关属性保存Java类定义的一些信息,如_name保存Java类的名称、_super保存Java类实现的类型等。Klass类是Klass模型中定义的C++类的基类,所以此类对象只保存了Java类的一些必要信息,其它如常量池、方法、字段等会通过Klass类的具体子类的相关属性来保存。
类的属性比较多,我们在后面解释类的过程中可以看到对相关属性的赋值操作。
1、_layout_helper
_layout_helper是一个组合属性。如果当前的类表示一个Java数组类型时,这个属性的值比较复杂。通常会调用如下函数生成值:
- jint Klass::array_layout_helper(BasicType etype) {
- assert(etype >= T_BOOLEAN && etype <= T_OBJECT, "valid etype");
- bool isobj = (etype == T_OBJECT);
- int tag = isobj ? _lh_array_tag_obj_value : _lh_array_tag_type_value;
- // Note that T_ARRAY is not allowed here.
- // 在64位系统下,存放_metadata的空间大小是8字节,_mark是8字节,
- // length是4字节,对象头为20字节,由于要按8字节对齐,所以会填充4字节,最终占用24字节
- int hsize = arrayOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes(etype); // hsize表示数组头部大小
- int esize = type2aelembytes(etype); // Java基本类型元素需要占用的字节数
- int esz = exact_log2(esize); // 例如Java基本类型元素占用4个字节,则存储的是2
- int lh = array_layout_helper(tag, hsize, etype, esz);
- return lh;
- }
其中用到2个枚举常量,如下:
- _lh_array_tag_type_value = ~0x00,
- _lh_array_tag_obj_value = ~0x01
_lh_array_tag_type_value的二进制表示为32个1:11111111111111111111111111111111,其实也就是0xC0000000 >> 30,做算术右移,负数的最高位补1。
_lh_array_tag_obj_value的二进制表示为最高位31个1:11111111111111111111111111111110,其实也就是0x80000000 >> 30,做自述右移,负数的最高位补1。
调用的arrayOopDesc::base_offset_in_bytes()函数及调用的相关函数的实现如下:
- // Returns the offset of the first element.
- static int base_offset_in_bytes(BasicType type) {
- return header_size(type) * HeapWordSize;
- }
- // Should only be called with constants as argument (will not constant fold otherwise)
- // Returns the header size in words aligned to the requirements of the array object type.
- static int header_size(BasicType type) {
- size_t typesize_in_bytes = header_size_in_bytes();
- if( Universe::element_type_should_be_aligned(type) ){
- return (int)align_object_offset( typesize_in_bytes/HeapWordSize );
- }else {
- return (int)typesize_in_bytes/HeapWordSize;
- }
- }
- // 在64位系统下,存放_metadata的空间大小是8字节,_mark是8字节,length是4字节,对象头为20字节,
- // 由于要按8字节对齐,所以会填充4字节,最终占用24字节
- static int header_size_in_bytes() {
- intptr_t temp = length_offset_in_bytes() + sizeof(int); // sizeof(int)
- size_t hs = align_size_up(temp,HeapWordSize);
- return (int)hs;
- }
- // The _length field is not declared in C++. It is allocated after the
- // declared nonstatic fields in arrayOopDesc if not compressed, otherwise
- // it occupies the second half 下半场 of the _klass field in oopDesc.
- static int length_offset_in_bytes() {
- if(UseCompressedClassPointers){
- return klass_gap_offset_in_bytes();
- }else{
- sizeof(arrayOopDesc);
- }
- }
代码的逻辑非常清晰,这里不过多介绍。最终会在Klass::array_layout_helper()函数中调用array_layout_helper()函数完成属性值的计算。这个函数的实现如下:
- static jint array_layout_helper(jint tag, int hsize, BasicType etype, int log2_esize) {
- return (tag << _lh_array_tag_shift) // 左移30位
- | (hsize << _lh_header_size_shift) // 左移16位
- | ((int)etype << _lh_element_type_shift) // 左移1位
- | (log2_esize << _lh_log2_element_size_shift); // 左移0位
- }
对_lh_array_tag_type_value与_lh_array_tag_obj_value值左移30位后,第32位上肯定为1,所以最终计算出的值是一个小于0的数。而非数组类型,一般由InstanceKlass对象表示的Java类来说,计算的属性值如下:
- static jint instance_layout_helper(jint size, bool slow_path_flag) {
- if(slow_path_flag){
- return (size << LogHeapWordSize) | _lh_instance_slow_path_bit;
- }else{
- return (size << LogHeapWordSize) | 0; // LogHeapWordSize=3
- }
- }
size为对象的、以字节为单位的内存占用大小,所以肯定是一个正数。这样就可以通过_layout_helper来判断类型了。
2、_primary_supers、_super_check_offset、_secondary_supers与_secondary_super_cache
这几个属性完全是为了加快判定父子关系等逻辑而加入的。下面看initialize_supers()函数中是如何初始化这几个属性的。函数的第1部分实现如下:
- 源代码位置:hotspot/src/share/vm/oops/klass.cpp
- void Klass::initialize_supers(Klass* k, TRAPS) { //
- // 当前类的父类k可能为NULL,例如Object的父类为NULL
- if (k == NULL) {
- set_super(NULL);
- _primary_supers[0] = this;
- }
- // k就是当前类的直接父类,如果有父类,那么super()一般为NULL,如果k为NULL,那么就是Object类,从下面的断言也可以看出
- else if (k != super() || k == SystemDictionary::Object_klass()) {
- set_super(k); // 设置Klass的_super属性
- Klass* sup = k;
- int sup_depth = sup->super_depth();
- juint my_depth = MIN2(sup_depth + 1, (int)primary_super_limit()); // primary_super_limit()方法得到的值一般默认为8
- // 当父类的的继承链长度大于等于primary_super_limit()时,当前的深度只能是primary_super_limit(),也就是8,因为_primary_supers中只存储8个类
- if (!can_be_primary_super_slow()){
- my_depth = primary_super_limit(); // 8
- }
- for (juint i = 0; i < my_depth; i++) { // my_depth默认的值为8
- _primary_supers[i] = sup->_primary_supers[i];
- }
- Klass* *super_check_cell;
- if (my_depth < primary_super_limit()) { // primary_super_limit()的默认为8
- _primary_supers[my_depth] = this;
- super_check_cell = &_primary_supers[my_depth];
- } else {
- // Overflow of the primary_supers array forces me to be secondary.
- super_check_cell = &_secondary_super_cache;
- }
- // 通过_super_check_offset这个偏移量可以快速定义到当前在_primary_supers中的位置
- juint _super_check_offset = (address)super_check_cell - (address) this;
- set_super_check_offset( _super_check_offset ); // 设置Klass中的_super_check_offset属性
- }
- // 第2部分代码在下面
- }
在设置当前类的父类时通常都会调用initialize_supers方法,同时也会设置_primary_supers、super_check_offset,如果继承链过长,还有可能设置secondary_supers、secondary_super_cache等值。这此属性中存储继承链中涉及到的类以方便快速的进行类关系之间的判断,例如父子关系的判断。
方法的第2部分代码实现如下:
- if (secondary_supers() == NULL) {
- KlassHandle this_kh (THREAD, this);
- // Now compute the list of secondary supertypes.
- // Secondaries can occasionally be on the super chain,
- // if the inline "_primary_supers" array overflows.
- int extras = 0;
- Klass* p;
- for (p = super();
- // 当p不为NULL并且p已经存储在了_secondary_supers数组中时,条件为true
- // 也就是当前类的父类多于8个,将多出来的存储到了_secondary_supers数组中了
- !(p == NULL || p->can_be_primary_super());
- p = p->super()) {
- ++extras;
- }
- // 计算secondaries需要的大小,因为secondaries数组中还需要存储当前类的所有实现接口(包括直接和间接实现的接口)
- // Compute the "real" non-extra secondaries.
- GrowableArray<Klass*>* secondaries = compute_secondary_supers(extras);
- if (secondaries == NULL) { // extras为0时直接返回,不需要额外的处理
- // secondary_supers set by compute_secondary_supers
- return;
- }
- GrowableArray<Klass*>* primaries = new GrowableArray<Klass*>(extras);
- for ( p = this_kh->super();
- !(p == NULL || p->can_be_primary_super());
- p = p->super()
- ){
- primaries->push(p);
- }
- // Combine the two arrays into a metadata object to pack the array.
- // The primaries are added in the reverse order, then the secondaries.
- int new_length = primaries->length() + secondaries->length();
- Array<Klass*>* s2 = MetadataFactory::new_array<Klass*>(class_loader_data(), new_length, CHECK);
- int fill_p = primaries->length();
- for (int j = 0; j < fill_p; j++) {
- s2->at_put(j, primaries->pop()); // add primaries in reverse order.也就是父类永远在数组前,子类永远在数组后
- }
- for( int j = 0; j < secondaries->length(); j++ ) {
- s2->at_put(j+fill_p, secondaries->at(j)); // add secondaries on the end.
- }
- this_kh->set_secondary_supers(s2); // 设置_secondary_supers属性
- }
可以看到,会将父亲继承链中多于8个的父类存储到secondary_supers数组中,不过因为继承链一般都不会多于8个,所以设置了默认值为8。
下面举个例子,看看这几个属性是如何存储值的,如下:
- interface IA{}
- interface IB{}
- class A{}
- class B extends A{}
- class C extends B{}
- class D extends C{}
- public class Test extends D implements IA,IB {}
配置-XX:FastSuperclassLimit=3后,_primary_supers数组中就最多只能存储3个类了。值如下:
- _primary_supers[Object,A,B]
- _secondary_supers[C,D,Test,IA,IB]
由于当前类Test的继承链过长,导致C、D和Test只能存储到_secondary_supers。所以此时_super_check_offset会指向C,也就是_secondary_supers中存储的第1个元素。
下面举个例子,看一下这几个属性如何应用。例如is_subtype_of()方法,实现如下:
- // subtype check: true if is_subclass_of, or if k is interface and receiver implements it
- bool is_subtype_of(Klass* k) const { // 判断当前类是否为k的子类
- juint off = k->super_check_offset();
- Klass* sup = *(Klass**)( (address)this + off );
- const juint secondary_offset = in_bytes(secondary_super_cache_offset());
- if (sup == k) {
- return true;
- } else if (off != secondary_offset) {
- return false;
- } else {
- return search_secondary_supers(k);
- }
- }
当通过_super_check_offset获取到的类与k相同时,那么k存在于当前类的继承链上,肯定有父子关系。
如果k存在于_primary_supers数组中,那么通过_super_check_offset就可快速判断,如果k存在于_secondary_supers中,那么需要调用search_secondary_supers()来判断。
调用的search_secondary_supers()方法的实现如下:
- bool Klass::search_secondary_supers(Klass* k) const {
- // Put some extra logic here out-of-line, before the search proper.
- // This cuts down the size of the inline method.
- // This is necessary, since I am never in my own secondary_super list.
- if (this == k){
- return true;
- }
- // Scan the array-of-objects for a match
- int cnt = secondary_supers()->length();
- for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
- if (secondary_supers()->at(i) == k) {
- ((Klass*)this)->set_secondary_super_cache(k); // 设置_secondary_super_cache属性,保存这次查询的结果
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
可以看到,属性_secondary_super_cache保存了这一次父类查询的结果。查询的逻辑很简单,遍历_secondary_supers数组中的值并比较即可。
3、_super、_subklass、_next_sibling
由于Java类是单继承,所以可通过_super、_subklass、_next_sibling属性可直接找到当前类的父类或所有子类。调用Klass::append_to_sibling_list()函数设置_next_sibling与_subklass的值,方法的实现如下:
- void Klass::append_to_sibling_list() {
- // add ourselves to superklass' subklass list
- InstanceKlass* super = superklass(); // 获取到_super属性的值
- if (super == NULL)
- return; // special case: class Object
- Klass* prev_first_subklass = super->subklass_oop(); // 获取_subklass属性的值
- if (prev_first_subklass != NULL) {
- // set our sibling to be the superklass' previous first subklass
- set_next_sibling(prev_first_subklass); // 设置_next_sibling属性的值
- }
- // make ourselves the superklass' first subklass
- super->set_subklass(this); // 设置_subklass属性的值
- }
方法的实现逻辑很简单,这里不过多介绍。
其它文章:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码(配视频)
搭建过程中如果有问题可直接评论留言或加作者微信mazhimazh。
作者持续维护的个人博客 classloading.com。
B站上有HotSpot源码分析相关视频 https://space.bilibili.com/27533329
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!

HotSpot源码分析之类模型的更多相关文章
- HotSpot源码分析之C++对象的内存布局
HotSpot采用了OOP-Klass模型来描述Java类和对象.OOP(Ordinary Object Pointer)指的是普通对象指针,而Klass用来描述对象的具体类型.为了更好理解这个模型, ...
- Netty源码分析--内存模型(上)(十一)
前两节我们分别看了FastThreadLocal和ThreadLocal的源码分析,并且在第八节的时候讲到了处理一个客户端的接入请求,一个客户端是接入进来的,是怎么注册到多路复用器上的.那么这一节我们 ...
- 前端MVC框架Backbone 1.1.0源码分析(二) - 模型
模型是什么? Models are the heart of any JavaScript application, containing the interactive data as well a ...
- Netty源码分析--内存模型(下)(十二)
这一节我们一起看下分配过程 PooledByteBuf<T> allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacit ...
- Netty源码分析--Reactor模型(二)
这一节和我一起开始正式的去研究Netty源码.在研究之前,我想先介绍一下Reactor模型. 我先分享两篇文献,大家可以自行下载学习. 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Uty ...
- 源码分析HotSpot GC过程(三):TenuredGeneration的GC过程
老年代TenuredGeneration所使用的垃圾回收算法是标记-压缩-清理算法.在回收阶段,将标记对象越过堆的空闲区移动到堆的另一端,所有被移动的对象的引用也会被更新指向新的位置.看起来像是把杂陈 ...
- Hbase WAL线程模型源码分析
版权声明:本文由熊训德原创文章,转载请注明出处: 文章原文链接:https://www.qcloud.com/community/article/257 来源:腾云阁 https://www.qclo ...
- Memcached源码分析之线程模型
作者:Calix 一)模型分析 memcached到底是如何处理我们的网络连接的? memcached通过epoll(使用libevent,下面具体再讲)实现异步的服务器,但仍然使用多线程,主要有两种 ...
- quartz源码分析——执行引擎和线程模型
title: quartz源码分析--执行引擎和线程模型 date: 2017-09-09 23:14:48 categories: quartz tags: [quartz, 源码分析] --- - ...
随机推荐
- 【UR #9】App 管理器
UOJ小清新题表 题目内容 UOJ链接 一句话题意:给出一个强联通的混合图,有一些有向边和无向边.删除一些边使其维持强联通的状态,求删边方案. 数据范围 \(1\leq n\leq 5000,0\le ...
- elk-架构图
- go读取键盘输入两种方式
一种scanf var x intfmt.Println("input a int number")fmt.Scan(&x)fmt.Printf("读取到内容:% ...
- git的一些操作命令
一,如何修改一个commit的注释? root@kubuntu:/data/git/clog# git commit --amend 说明:架构森林是一个专注架构的博客,地址:https://www. ...
- selenium-窗口切换
方法一 # 获取打开的多个窗口句柄 windows = driver.window_handles # 切换到当前最新打开的窗口 driver.switch_to.window(windows[-1] ...
- windows搭建SVN服务
下载`TortoiseSVN 官网下载址:https://www.visualsvn.com/visualsvn/download/tortoisesvn/ 根据自己系统环境选择 安装Tortoise ...
- jquery $.ajax 获取josn数据
<script type="text/javascript" src="jquery-1.9.1.js"></script> <s ...
- Python中while循环初识
基本结构 while 条件: 循环体 基本原理: 1.先判断条件是否为True 2.如果是True进入循环体 3.执行到循环体的底部 4.继续判断条件,条件为True,再次进入 ...
- 反射(Reflection)
Java学习笔记--反射(Reflection) 关于反射 能够分析类能力的程序称之为反射(Reflection) 反射机制可以用来: 在运行时分析类的能力 在运行时检查对象,例如:编写一个适合所有类 ...
- Spring boot ConditionalOnClass原理解析
Spring boot如何自动加载 对于Springboot的ConditionalOnClass注解一直非常好奇,原因是我们的jar包里面可能没有对应的class,而使用ConditionalOnC ...
