codewar代码练习2——7级晋升6级
7级晋升到6级的过程中以做6级题以及以前未完成的题目为主,一般选择算法题或者基础题。相比之前从8级升级7级(参见此博客:http://blog.csdn.net/m0_37324740/article/details/78408249)的难度有所提前,并且一些题目结合了一些简单的场景,也很有意思。
No.8
Topic:Vasya - Clerk
Instruction:
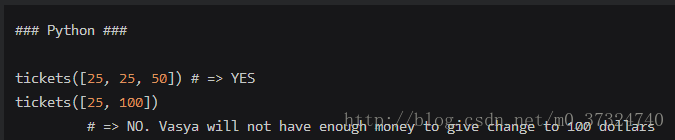
The new “Avengers” movie has just been released! There are a lot of people at the cinema box office standing in a huge line. Each of them has a single 100, 50 or 25 dollars bill. An “Avengers” ticket costs 25 dollars.
Vasya is currently working as a clerk. He wants to sell a ticket to every single person in this line.
Can Vasya sell a ticket to each person and give the change if he initially has no money and sells the tickets strictly in the order people follow in the line?
Return YES, if Vasya can sell a ticket to each person and give the change with the bills he has at hand at that moment. Otherwise return NO.
Examples:
My solution:
def tickets(people):
if people[0] != 25:
ans = 'NO'
else:
i = 1
a = [25]
while i < len(people):
try:
if people[i] == 25:
a.append(25)
i+=1
elif people[i] == 50:
if 25 in a:
a.remove(25)
a.append(50)
i+=1
else:
ans = 'NO'
return ans
else:
if 25 and 50 in a:
a.remove(25)
a.remove(50)
a.append(100)
i+=1
elif a.count(25) >= 3:
a.remove(25)
a.remove(25)
a.remove(25)
a.append(100)
i+=1
else:
ans = 'NO'
return ans
except ValueError:
ans = 'NO'
return ans
ans = 'YES'
return ansBest solutions from others:
def tickets(people):
till = {100.0:0, 50.0:0, 25.0:0}
for paid in people:
till[paid] += 1
change = paid-25.0
for bill in (50,25):
while (bill <= change and till[bill] > 0):
till[bill] -= 1
change -= bill
if change != 0:
return 'NO'
return 'YES'and
def tickets(a):
n25 = n50 = n100 = 0
for e in a:
if e==25 : n25+=1
elif e==50 : n25-=1; n50+=1
elif e==100 and n50>0 : n25-=1; n50-=1
elif e==100 and n50==0: n25-=3
if n25<0 or n50<0:
return 'NO'
return 'YES'貌似我当时跑程序的时候出现了valueerror,但是一下子找不到原因,所以用了try语句。
No.9
Topic:Simple Pig Latin
Instruction:Move the first letter of each word to the end of it, then add “ay” to the end of the word. Leave punctuation marks untouched.
Examples:
pig_it('Pig latin is cool') # igPay atinlay siay oolcay
pig_it('Hello world !') # elloHay orldWay !My solution:
def pig_it(text):
a = text.split()
b = list(map(lambda x: x[1:len(x)] + x[0] + 'ay', a))
if len(b[len(b)-1]) == 3:
b[len(b)-1] = a[len(a)-1]
else:
pass
c = ' '.join(b)
return cBest solution from others:
def pig_it(text):
lst = text.split()
return ' '.join( [word[1:] + word[:1] +
'ay' if word.isalpha() else word for word in lst])No.10
Topic:Decode the Morse code
Instruction:
In this kata you have to write a simple Morse code decoder. While the Morse code is now mostly superceded by voice and digital data communication channels, it still has its use in some applications around the world.
The Morse code encodes every character as a sequence of “dots” and “dashes”. For example, the letter A is coded as ·−, letter Q is coded as −−·−, and digit 1 is coded as ·−−−. The Morse code is case-insensitive, traditionally capital letters are used. When the message is written in Morse code, a single space is used to separate the character codes and 3 spaces are used to separate words. For example, the message HEY JUDE in Morse code is ···· · −·−− ·−−− ··− −·· ·.
NOTE: Extra spaces before or after the code have no meaning and should be ignored.
In addition to letters, digits and some punctuation, there are some special service codes, the most notorious of those is the international distress signal SOS (that was first issued by Titanic), that is coded as ···−−−···. These special codes are treated as single special characters, and usually are transmitted as separate words.
Your task is to implement a function decodeMorse(morseCode), that would take the morse code as input and return a decoded human-readable string.
For example:
decodeMorse('.... . -.-- .--- ..- -.. .')
#should return "HEY JUDE"The Morse code table is preloaded for you as a dictionary, feel free to use it. In CoffeeScript, C++, Go, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Ruby and TypeScript, the table can be accessed like this: MORSE_CODE[‘.–’], in Java it is MorseCode.get(‘.–’), in C# it is MorseCode.Get(‘.–’), in Haskell the codes are in a Map String String and can be accessed like this: morseCodes ! “.–”, in Elixir it is morse_codes variable.
All the test strings would contain valid Morse code, so you may skip checking for errors and exceptions. In C#, tests will fail if the solution code throws an exception, please keep that in mind. This is mostly because otherwise the engine would simply ignore the tests, resulting in a “valid” solution.
这道题我当时写的代码没有通过,很可惜没有保存下载,题目的思路不难,嵌套循环并用到替换。
Best solution from others:
def decodeMorse(morseCode):
return ' '.join(''.join(MORSE_CODE[letter] for letter in word.split(' ')) for word in morseCode.strip().split(' '))No.11
Topic:Who likes it?
Instruction:
You probably know the “like” system from Facebook and other pages. People can “like” blog posts, pictures or other items. We want to create the text that should be displayed next to such an item.
Implement a function likes :: [String] -> String, which must take in input array, containing the names of people who like an item. It must return the display text as shown in the examples:
likes [] // must be "no one likes this"
likes ["Peter"] // must be "Peter likes this"
likes ["Jacob", "Alex"] // must be "Jacob and Alex like this"
likes ["Max", "John", "Mark"] // must be "Max, John and Mark like this"
likes ["Alex", "Jacob", "Mark", "Max"] // must be "Alex, Jacob and 2 others like this"My solution:
def likes(names):
if len(names) == 0:
a = 'no one likes this'
elif len(names) == 1:
a = names[0] + ' ' + 'likes this'
elif len(names) == 2:
a = names[0] + ' ' +'and' + ' ' + names[1] + ' ' +'like this'
elif len(names) == 3:
a = names[0] + ',' + ' ' + names[1] + ' ' + 'and' +' ' + names[2] + ' ' + 'like this'
else:
a = names[0] + ',' + ' ' + names[1] + ' ' + 'and' +' ' + str((len(names)-2)) + ' ' + 'others like this'
return aBest solutions from others:
def likes(names):
n = len(names)
return {
0: 'no one likes this',
1: '{} likes this',
2: '{} and {} like this',
3: '{}, {} and {} like this',
4: '{}, {} and {others} others like this'
}[min(4, n)].format(*names[:3], others=n-2)and
def likes(names):
if len(names) == 0:
return "no one likes this"
elif len(names) == 1:
return "%s likes this" % names[0]
elif len(names) == 2:
return "%s and %s like this" % (names[0], names[1])
elif len(names) == 3:
return "%s, %s and %s like this" % (names[0], names[1], names[2])
else:
return "%s, %s and %s others like this" % (names[0], names[1], len(names)-2)No.12
Topic:Unique In Order
Instruction:Implement the function unique_in_order which takes as argument a sequence and returns a list of items without any elements with the same value next to each other and preserving the original order of elements.
Examples:
unique_in_order('AAAABBBCCDAABBB') == ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'A', 'B']
unique_in_order('ABBCcAD') == ['A', 'B', 'C', 'c', 'A', 'D']
unique_in_order([1,2,2,3,3]) == [1,2,3]My solution:
def unique_in_order(iterable):
list = []
pre = None
for i in iterable:
if i != pre:
list.append(i)
pre = i
return listBest solution from others:
def unique_in_order(iterable):
result = []
prev = None
for char in iterable[0:]:
if char != prev:
result.append(char)
prev = char
return resultNo.13
Topic:Dubstep
Instruction:
Polycarpus works as a DJ in the best Berland nightclub, and he often uses dubstep music in his performance. Recently, he has decided to take a couple of old songs and make dubstep remixes from them.
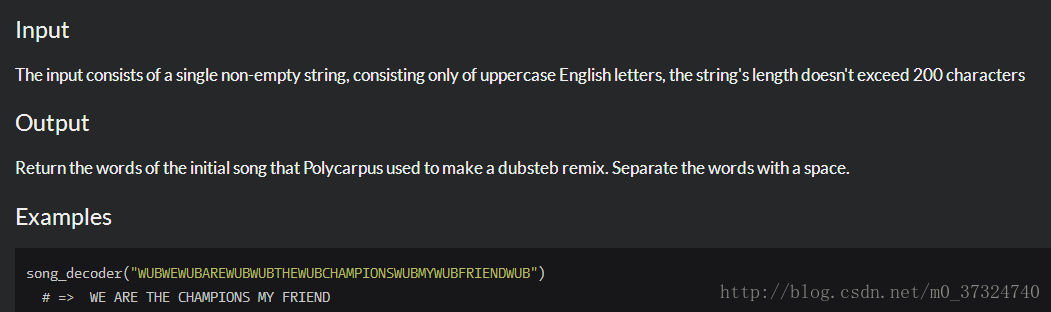
Let’s assume that a song consists of some number of words. To make the dubstep remix of this song, Polycarpus inserts a certain number of words “WUB” before the first word of the song (the number may be zero), after the last word (the number may be zero), and between words (at least one between any pair of neighbouring words), and then the boy glues together all the words, including “WUB”, in one string and plays the song at the club.
For example, a song with words “I AM X” can transform into a dubstep remix as “WUBWUBIWUBAMWUBWUBX” and cannot transform into “WUBWUBIAMWUBX”.
Recently, Jonny has heard Polycarpus’s new dubstep track, but since he isn’t into modern music, he decided to find out what was the initial song that Polycarpus remixed. Help Jonny restore the original song.
Examples:
My solution:
def song_decoder(song):
a = song.replace('WUB',' ').strip()
b = ' '.join(a.split())
return bBest solution from others:
def song_decoder(song):
return " ".join(song.replace('WUB', ' ').split())总结:
1. 如何写嵌套循环
2. 格式化字符串的使用
3. 多个空格合并单个空格
4. strip函数删除字符串两端空格
5. 用lambda和map对列表中每个元素做相同的操作
6. Practice makes perfect.
codewar代码练习2——7级晋升6级的更多相关文章
- codewar代码练习1——8级晋升7级
最近发现一个不错的代码练习网站codewar(http://www.codewars.com).注册了一个账号,花了几天的茶余饭后时间做题,把等级从8级升到了7级.本文的目的主要介绍使用感受及相应题目 ...
- 行为级和RTL级的区别(转)
转自:http://hi.baidu.com/renmeman/item/5bd83496e3fc816bf14215db RTL级,registertransferlevel,指的是用寄存器这一级别 ...
- CSS 各类 块级元素 行级元素 水平 垂直 居中问题
元素的居中问题是每个初学者碰到的第一个大问题,在此我总结了下各种块级 行级 水平 垂直 的居中方法,并尽量给出代码实例. 首先请先明白块级元素和行级元素的区别 行级元素 一块级元素 1 水平居中: ( ...
- 学习总结:CSS(二)块级与行级元素特性、盒模型、层模型、BUG与BFC、浮动模型
一.元素的块级与行级特性 在CSS属性display控制元素是否及如何显示的特性,常用的值有none.inline.block.inline-block,在CSS3中还有一些新的特性状态,在这里不做讨 ...
- 51nod图论题解(4级,5级算法题)
51nod图论题解(4级,5级算法题) 1805 小树 基准时间限制:1.5 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 80 难度:5级算法题 她发现她的树的点上都有一个标号(从1到n),这些树都在空 ...
- js input复选框选中父级同时子级也选中
js实现复选框选中父级元素子级元素也选中,没有子级元素选中父级也不选中的效果 HTML <tr> <td> <label> <input name=" ...
- 操作系统学习笔记5 | 用户级线程 && 内核级线程
在上一部分中,我们了解到操作系统实现多进程图像需要组织.切换.考虑进程之间的影响,组织就是用PCB的队列实现,用到了一些简单的数据结构知识.而本部分重点就是进程之间的切换. 参考资料: 课程:哈工大操 ...
- [数据库事务与锁]详解五: MySQL中的行级锁,表级锁,页级锁
注明: 本文转载自http://www.hollischuang.com/archives/914 在计算机科学中,锁是在执行多线程时用于强行限制资源访问的同步机制,即用于在并发控制中保证对互斥要求的 ...
- MySQL行级锁,表级锁,页级锁详解
页级:引擎 BDB. 表级:引擎 MyISAM , 理解为锁住整个表,可以同时读,写不行 行级:引擎 INNODB , 单独的一行记录加锁 表级,直接锁定整张表,在你锁定期间,其它进程无法对该表进行写 ...
随机推荐
- vim插件快捷键
@1:winmanager: #1:打开winmanager的快捷键在.vimrc中配置,默认为":WMToggle",使用nmap可以将其映射到其他的命令. #2:netrw快捷 ...
- List Slice in Python(Compared with Java)
Python: 在Python中, 对于list, 切片会返回一个新的list, 而不会改变原有的list. 注意这儿说的"不会改变原有的list"指的是下面的这种情况: a = ...
- vs2015 安卓相关配置
vs2015的安卓相关配置百度不到,园子里也没人写.还是我没搜索到? 看来只能靠自己的英(pin)语(yin)能力一点点解决了 安装2015这个过程没啥可说的.都安装就OK了. 重要的就是选择安卓程序 ...
- Python 7 多线程及进程
进程与线程: 进程的概念: 1.程序的执行实例称为进程. 2.每个进程都提供执行程序所需的资源.一个进程有一个虚拟地址空间.可执行代码.对系统对象的开放句柄.一个安全上下文.一个独特的进程标识符.环境 ...
- commonAncestor
commonAncestor 光标或选区所在区域最外层的祖先节点
- Xshell访问kali配置
1.安装虚拟机VMware Workstation12 PRO 2.在虚拟机上安装kali2.0 3.查看liunx的ip地址ifconfig 4.端口 协议 (1)RDP协议(桌面协议)3389端口 ...
- json学习笔记--在JavaScript中的使用
1.字符串转换为JavaScript对象 var jsonStr = '[' + '{"name":"陶国荣","sex":"男& ...
- CMD mysql 备份脚本
创建.bat文件 echo. echo MySQL数据库备份脚本 echo ***************************** echo. echo 备份日期:%date% echo 备份时间 ...
- ucsc genome brower的用法和说明(一)
官网说明书:http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenpath/help/hgTracksHelp.html 1.genome brower的作用 a,展示任何尺度的基因组片段.比如, ...
- ResourceLoader笔记
Ant路径匹配 Ant路径通配符支持“?”.“*”.“**”,注意通配符匹配不包括目录分隔符“/”: “?”:匹配一个字符,如“config?.xml”将匹配“config1.xml”: “*”:匹配 ...