Introduction to Functional Interfaces – A concept recreated in Java 8
Any java developer around the world would have used at least one of the following interfaces: java.lang.Runnable,java.awt.event.ActionListener, java.util.Comparator,java.util.concurrent.Callable. There is some common feature among the stated interfaces and that feature is they have only one method declared in their interface definition. There are lot more such interfaces in JDK and also lot more created by java developers. These interfaces are also called Single Abstract Method interfaces (SAM Interfaces). And a popular way in which these are used is by creating Anonymous Inner classes using these interfaces, something like:
[java]
public class AnonymousInnerClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Aad created and running …");
}
}).start();
}
}
[/java]
With Java 8 the same concept of SAM interfaces is recreated and are called Functional interfaces. These can be represented using Lambda expressions, Method reference and constructor references(I will cover these two topics in the upcoming blog posts). There’s an annotation introduced- @FunctionalInterface which can be used for compiler level errors when the interface you have annotated is not a valid Functional Interface. Lets try to have a look at a simple functional interface with only one abstract method:
[java]
@FunctionalInterface
public interface SimpleFuncInterface {
public void doWork();
}
[/java]
The interface can also declare the abstract methods from thejava.lang.Object class, but still the interface can be called as a Functional Interface:
[java]
@FunctionalInterface
public interface SimpleFuncInterface {
public void doWork();
public String toString();
public boolean equals(Object o);
}
[/java]
Once you add another abstract method to the interface then the compiler/IDE will flag it as an error as shown in the screenshot below:
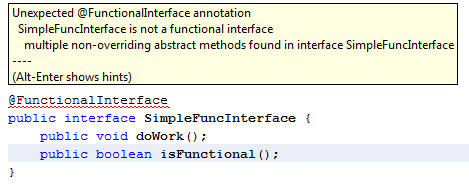
Interface can extend another interface and in case the Interface it is extending in functional and it doesn’t declare any new abstract methods then the new interface is also functional. But an interface can have one abstract method and any number of default methods and the interface would still be called an functional interface. To get an idea of default methods please read here.
[java]
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ComplexFunctionalInterface extends SimpleFuncInterface {
default public void doSomeWork(){
System.out.println("Doing work in interface impl…");
}
default public void doSomeOtherWork(){
System.out.println("Doing other work in interface impl…");
}
}
[/java]
The above interface is still a valid functional interface. Now lets see how we can use the lambda expression as against anonymous inner class for implementing functional interfaces:
[java]
/*
* Implementing the interface by creating an
* anonymous inner class versus using
* lambda expression.
*/
public class SimpleFunInterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
carryOutWork(new SimpleFuncInterface() {
@Override
public void doWork() {
System.out.println("Do in SimpleFun impl…");
}
});
carryOutWork(() -> System.out.println("Do in lambda exp impl…"));
}
public static void carryOutWork(SimpleFuncInterface sfi){
sfi.doWork();
}
}
[/java]
And the output would be …
[shell]
Do work in SimpleFun impl…
Do work in lambda exp impl…
[/shell]
In case you are using an IDE which supports the Java Lambda expression syntax(Netbeans 8 Nightly builds) then it provides an hint when you use an anonymous inner class as used above
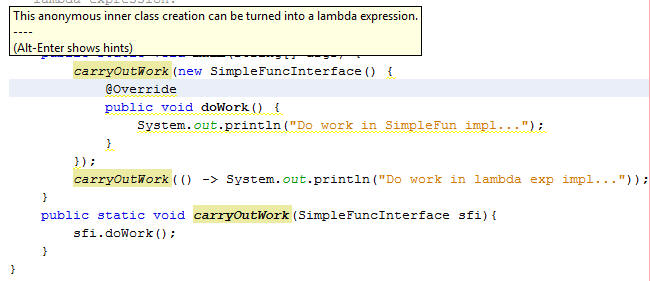
This was a brief introduction to the concept of functional interfaces in java 8 and also how they can be implemented using Lambda expressions.
如果你正在浏览Java8的API,你会发现java.util.function中 Function, Supplier, Consumer, Predicate和其他函数式接口广泛用在支持lambda表达式的API中。这些接口有一个抽象方法,会被lambda表达式的定义所覆盖。在这篇文章中,我会简单描述Function接口,该接口目前已发布在java.util.function中。
Function接口的主要方法:
R apply(T t) – 将Function对象应用到输入的参数上,然后返回计算结果。
default ‹V› Function‹T,V› – 将两个Function整合,并返回一个能够执行两个Function对象功能的Function对象。
译者注:Function接口中除了apply()之外全部接口如下:
default <V> Function<T,V> andThen(Function<? super R,? extends V> after) 返回一个先执行当前函数对象apply方法再执行after函数对象apply方法的函数对象。
default <V> Function<T,V> compose(Function<? super V,? extends T> before)返回一个先执行before函数对象apply方法再执行当前函数对象apply方法的函数对象。
static <T> Function<T,T> identity() 返回一个执行了apply()方法之后只会返回输入参数的函数对象。
本章节将会通过创建接受Function接口和参数并调用相应方法的例子探讨apply方法的使用。我们同样能够看到API的调用者如何利用lambda表达式替代接口的实现。除了传递lambda表达式之外,API使用者同样可以传递方法的引用,但这样的例子不在本篇文章中。
如果你想把接受一些输入参数并将对输入参数处理过后的结果返回的功能封装到一个方法内,Function接口是一个不错的选择。输入的参数类型和输出的结果类型可以一致或者不一致。
一起来看看接受Function接口实现作为参数的方法的例子:
01 |
public class FunctionDemo { |
03 |
//API which accepts an implementation of |
07 |
static void modifyTheValue(int valueToBeOperated, Function<Integer, Integer> function){ |
09 |
int newValue = function.apply(valueToBeOperated); |
12 |
* Do some operations using the new value. |
15 |
System.out.println(newValue); |
下面是调用上述方法的例子:
01 |
public static void main(String[] args) { |
03 |
int incr = 20; int myNumber = 10; |
05 |
modifyTheValue(myNumber, val-> val + incr); |
07 |
myNumber = 15; modifyTheValue(myNumber, val-> val * 10); |
09 |
modifyTheValue(myNumber, val-> val - 100); |
11 |
modifyTheValue(myNumber, val-> "somestring".length() + val - 100); |
你可以看到,接受1个参数并返回执行结果的lambda表达式创建在例子中。这个例子的输入如下:
- Java中java.util.concurrent包下的4中线程池代码示例
先来看下ThreadPool的类结构 其中红色框住的是常用的接口和类(图片来自:https://blog.csdn.net/panweiwei1994/article/details/78617117 ...
- JAVA8的java.util.function包 @FunctionalInterface
1 函数式接口java.util.function https://www.cnblogs.com/CobwebSong/p/9593313.html 2 JAVA8的java.util.functi ...
- java.util.regex包下的Pattern类和Matcher类的使用总结
一.介绍 Java正则表达式通过java.util.regex包下的Pattern类与Matcher类实现1.Pattern类用于创建一个正则表达式,也可以说创建一个匹配模式,它的构造方法是私有的,不 ...
- java.util.regex包下的Pattern和Matcher详解(正则匹配)
java正则表达式通过java.util.regex包下的Pattern类与Matcher类实现(建议在阅读本文时,打开java API文档,当介绍到哪个方法时,查看java API中的方法说明,效果 ...
- java.util.concurrent包下集合类的特点与适用场景
java.util.concurrent包,此包下的集合都不允许添加null元素 序号 接口 类 特性 适用场景 1 Queue.Collection ArrayBlockingQueue 有界.阻塞 ...
- Java:concurrent包下面的Map接口框架图(ConcurrentMap接口、ConcurrentHashMap实现类)
Java集合大致可分为Set.List和Map三种体系,其中Set代表无序.不可重复的集合:List代表有序.重复的集合:而Map则代表具有映射关系的集合.Java 5之后,增加了Queue体系集合, ...
- Java:concurrent包下面的Collection接口框架图( CopyOnWriteArraySet, CopyOnWriteArrayList,ConcurrentLinkedQueue,BlockingQueue)
Java集合大致可分为Set.List和Map三种体系,其中Set代表无序.不可重复的集合:List代表有序.重复的集合:而Map则代表具有映射关系的集合.Java 5之后,增加了Queue体系集合, ...
- JAVA8的java.util.function包
一 概述 name type description Consumer Consumer< T > 接收T对象,不返回值 Predicate Predicate< T > 接收 ...
- jdk8中java.util.concurrent包分析
并发框架分类 1. Executor相关类 Interfaces. Executor is a simple standardized interface for defining custom th ...
随机推荐
- 关于Unity动态物体无法向使用使用custom shader和lightmap的物体投射阴影
最近在做unity shader forge和marmoset的优化,TA那边遇到了一个阴影显示的问题,具体如下: 在Forward Rendering状态下,静态场景使用了是shader for ...
- aufomaper Queryable Extensions ProjectTo
When using an ORM such as NHibernate or Entity Framework with AutoMapper's standard Mapper.Map funct ...
- 【转】SPDY协议
SPDY协议 - v3 原文:SPDY Protocol - Draft 3 翻译:邱鹏滔(QQ: 95350530,主页:www.fireflysource.com) 1 概述 HTTP协议的瓶颈在 ...
- Spring Ioc--Bean装配
继前一篇IoC概述.Spring容器总结,接下来总结下Bean的装配过程. 要使引用程序中的Spring容器成功启动,需要同时具备以下3个条件: 1.Spring框架的类包,放在应用程序的类路径下. ...
- 调整Linux磁盘分区的大小的方法
昨天数据入库时,一直报错,说磁盘满了,,df -h 一看,发现/目录下只有50G空间,已使用49G:我的程序和dbss都安装在/目录下,ftp到的数据放在/data下的一个子目录下,分解完的 ...
- fedora 23如何实现 让root用户自动登录?
没想到很简单: 只是修改一个文件的一个地方: 修改: /etc/gdm/custom.conf文件, 将自动登录 启用为true, 然后自动登录的名字设为root 即可:
- 我的linux桌面
经过几次尝试安装linux系统之后,终于把自己的系统安装成了linux系统. wangkongming@ThinkPad-T410 ~ $ lsb_release -a No LSB modules ...
- CF451C Predict Outcome of the Game 水题
Codeforces Round #258 (Div. 2) Predict Outcome of the Game C. Predict Outcome of the Game time limit ...
- Linux(Red Hat)-中安装Vmware Tools
0. 会弹出 ***1.在弹出的文件夹中找到"VMwwareTools9.6.2-1688356.tar.gz",右击"解压缩到"...我解压缩到了" ...
- 此请求的查询字符串的长度超过配置的 maxQueryStringLength 值 --不仅wen.fonfig一个地方需要设置
提示已经很明确了... 搜出来的都是: <system.webServer> <security> <requestFiltering> <requestLi ...


