B-Tree算法分析与实现
在数据库系统中,或者说在文件系统中,针对存储在磁盘上的数据读取和在内存中是有非常大的区别的,因为内存针对任意在其中的数据是随机访问的,然而从磁盘中读取数据是需要通过机械的方式来读取一个block,不能指定的只读取我们期望的数值,比如文件中的某个int。那么针对存储在磁盘中数据结构的组织就很重要,为了提高访问数据的效率,在多种数据库系统中,采用B-Tree及其变种形式来保存数据,比如B+-Tree。我们这里先主要针对B-Tree的算法进行分析和实现。
一、 B-Tree的定义与意义
B-Tree的定义是这样的:
1、using the SEARCH procedure for M-way trees (described above) find the leaf node to which X should be added.
2、add X to this node in the appropriate place among the values already there. Being a leaf node there are no subtrees to worry about.
3、if there are M-1 or fewer values in the node after adding X, then we are finished.
If there are M nodes after adding X, we say the node has overflowed. To repair this, we split the node into three parts: Left:
the first (M-1)/2 values
Middle:
the middle value (position 1+((M-1)/2)
Right:
the last (M-1)/2 values
简单来说分为3步:
1、首先查找需要插入的key在哪个叶节点中
2、然后将关键字插入到指定的叶节点中
3、如果叶节点没有overflow,那么就结束了,非常简单。如果叶节点overflow了,也就是满了,那么就拆分(split)此节点,将节点中间的关键字放到其父节点中,剩余部分拆分为左右子节点。如果拆分出来放到父节点后,父节点也overflow了,那么继续拆分父节点,父节点当做当前,直到当前节点不再overflow。
实现的代码如下:btree.h
#ifndef BTREE_BTREE_H
#define BTREE_BTREE_H #define NULL 0
#include <algorithm> // btree节点
struct b_node {
int num; // 当前节点key的数量
int dim;
int* keys;
b_node* parent; // 父节点
b_node** childs; // 所有子节点 b_node() {
} b_node (int _dim) : num(), parent(NULL) {
dim = _dim;
keys = new int[dim + ]; // 预留一个位置,方便处理节点满了的时候插入操作
childs = new b_node*[dim + ]; // 扇出肯定需要比key还多一个
for (int i=; i<dim+; ++i) {
keys[i] = ;
childs[i] = NULL;
}
childs[dim+] = NULL;
} // 返回插入的位置
int insert(int key) {
int i = ;
keys[num] = key;
for (i = num; i > ; --i)
{
if (keys[i-] > keys[i])
{
std::swap(keys[i-], keys[i]);
continue;
}
break;
}
++num; // 数量添加
return i;
} bool is_full() {
if (num < dim) {
return false;
}
return true;
} // 获取需要插入的位置
int get_ins_pos(int key) {
int i = ;
for (i=; i<dim; ++i) {
if (key > keys[i] && keys[i]) {
continue;
}
} return i;
}
}; // 表达某个值的位置
struct pos {
b_node* node; // 所在位置的node指针
int index; // 所在node节点的索引
pos() : node(NULL), index(-) {
}
}; class btree {
public:
btree (int _dim) : dim(_dim), root(NULL) {
} pos query(int key); // 查找某个某个key
void insert(int key); // 插入某个key
void print(); // 分层打印btree private:
pos _query(b_node* root, int key); void _print(b_node* node, int level); void _insert(b_node* node, int key);
void _split_node(b_node* node);
void _link_node(b_node* parent, int pos, b_node* left_child, b_node* right_child); private:
int dim; // 维度
b_node* root; // 根节点
}; #endif
所有函数以"_"为开头的,都是内部函数,对外不可见。将针对节点本身的插入操作和基础判断都放在b_node结构中,增加代码的可读性。
btree.cpp 代码如下
#include "btree.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; void btree::insert(int key) {
_insert(root, key);
} void btree::_insert(b_node* node, int key) { // 根节点为空
if (root == NULL)
{
root = new b_node(dim);
root->insert(key);
return;
} int index = node->num;
while (index > && node->keys[index-] > key) // 找到对应的子节点
{
--index;
} // 如果当前node插入节点已经没有左右儿子了,那么就在当前节点中插入
if (!node->childs[index]) // 因为btree一定是既有左儿子,又有右儿子,所以只判断其中一个是否存在就可以了
{
// 如果节点没有满
if (!node->is_full())
{
node->insert(key);
return;
} // 如果当前节点已经满了,需要将中间节点拆分,然后加入到父节点中,将剩余的2个部分,作为新节点的左右子节点
// 如果父节点加入新的key之后也满了,那么递归上一个步骤
node->insert(key);
_split_node(node);
return;
} // 已经遍历到最右key了
if (index == node->num)
{
_insert(node->childs[index], key);
return;
} _insert(node->childs[index], key);
return;
} void btree::_split_node(b_node* node) {
if (!node || !node->is_full()) {
return;
} int split_pos = (node->dim-)/ + ; // 分割点
int split_value = node->keys[split_pos];
b_node* split_left_node = new b_node(dim);
b_node* split_right_node = new b_node(dim); // 处理左儿子节点
int i = ;
int j = ;
for (; i<split_pos; ++i, ++j) {
split_left_node->keys[i] = node->keys[j];
split_left_node->childs[i] = node->childs[j];
}
split_left_node->childs[i] = node->childs[j];
split_left_node->num = split_pos; // 处理右儿子节点
for (i = , j=split_pos+; i < dim - split_pos; ++i, ++j) {
split_right_node->keys[i] = node->keys[j];
split_right_node->childs[i] = node->childs[j];
}
split_right_node->childs[i] = node->childs[j];
split_right_node->num = dim - split_pos; // 将分割的节点上升到父节点中
b_node* parent = node->parent;
if (!parent) { // 父节点不存在
b_node* new_parent = new b_node(dim);
new_parent->insert(split_value); _link_node(new_parent, , split_left_node, split_right_node); // 重置根节点
root = new_parent;
return;
} // 如果父节点也满了,那么先将split出来的节点加入父节点,然后再对父节点split
if (parent->is_full()) {
int new_pos = parent->insert(split_value); _link_node(parent, new_pos, split_left_node, split_right_node);
_split_node(parent); // 如果父节点也满了, 那么继续split父节点
}
else {
int pos = parent->insert(split_value);
_link_node(parent, pos, split_left_node, split_right_node);
} return;
} void btree::_link_node(b_node* parent, int pos, b_node* left_child, b_node* right_child) {
parent->childs[pos] = left_child;
left_child->parent = parent; parent->childs[pos+] = right_child;
right_child->parent = parent;
} void btree::print() {
cout << "==================================" << endl;
_print(root, );
cout << "==================================" << endl;
} void btree::_print(b_node* node, int level) {
if (!node) {
return;
} cout << level << ":";
for (int i=; i<node->num; ++i) {
cout << node->keys[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl; for (int i=; i<node->num+; ++i) {
_print(node->childs[i], level+);
}
return;
}
(1) insert接口调用内部的_insert函数。
(2) _insert中首先判断B-Tree是否为空,要是空的话,先创建根节点,然后简单的将key插入就可以了。
(3)如果不是空的话,判断key在当前节点是否可以插入,如果当前节点就是叶子节点,那么肯定是没有子节点了,也就是childs是空了。如果不是叶子节点,那么就需要递归下层子节点做判断,直到直到可以插入的叶子节点,然后做插入操作。
(4)插入的时候先判断当前节点是否已经满了,如果没有满,那么就简单的直接插入,调用b_node的insert就结束了。否则先将key插入,然后_split_node针对节点进行分裂。
(5)在_split_node中,先找到需要上升到父节点的key,然后将key左边的所有key变成左子树,将key右边的所有key变成右子树,对里面的key和子节点指针做复制。然后将split_value添加到父节点中,没有父节点就先创建一个父节点,有就加入。如果父节点也overflow了,就递归的进行_split_node,直到当前节点没有overflow为止。
代码中的dim是维度的意思,维度为3,就是指fan-out为4,也就是一个node可以保持3个key,拥有最多4个子节点。这个概念可能不同的地方略有差异,需要根据实际的说明注意一下。
测试代码:
#include "btree.h"
int main() {
btree btr();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.insert();
btr.print();
return ;
}
三、BTree删除
BTree删除的算法,比插入还要稍微的复杂一点。通常的做法是,当删除一个key的时候,如果被删除的key不在叶子节点中,那么我们使用其最大左子树的key来替代它,交换值,然后在最大左子树中删除。
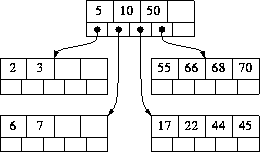
以上图为例,如果需要删除10,那么我们使用7和10进行交换,然后原来的[6,7]变成[6,10],删除10.
从BTree中删除key就可以保证一定是在叶子节点中进行的了。删除主要分为2步操作:
1、将key从当前节点删除,由于一定是在叶子节点中,那么根本不需要考虑左右子树的问题。
2、由于从节点中删除了key,那么节点中key的数量肯定减少了。如果节点中key的数量小于(M-1)/2了,我们就认为其underflowed了。如果underflowed没有发生,那么这次删除操作就简单的结束了,如果发生了,那么就需要修复这种问题(这是由于BTree的自平衡特性决定的,可以回头看下一开始说的BTree定义)。
针对BTree的删除,复杂的部分就是修复underflowed的问题。如何修复这种问题呢?做法是从被删除节点的邻居“借”key来修复,那么一个节点可能有2个邻居,我们选择key数量更多的邻居来“借”。那么借完之后,我们将被删除节点,其邻居,以及其父节点中key来生成一个新的node,“combined node”(连接节点)。生成新的节点之后,如果其数量大于(M-1),或者等于(M-1)的做法是不一样的,分为2中做法。
(1)如果大于(M-1),那么处理方法也比较简单,将新的combined node分裂成3个部分,Left,Middle,Right,Middle就是combined node正中间的key,用来替代原来的父节点值,Left和Right作为新的左右子树。由于大于(M-1),那么可以保证新的Left和Right都是满足BTree要求的。
(2)如果等于(M-1)就比较复杂了。由于新的Combined node的节点数量刚好满足BTree要求,而且也不能像(1)的情况那样进行分裂,那么就等于新节点从父节点“借”了一个值,如果父节点被借了值之后,数量大于等于(M-1)/2,那么没问题,修复结束。如果父节点的值也小于(M-1)/2了,那么就需要再修复父节点,重复这个步骤,直到根节点为止。
比如上面的树,删除key=3,那么删除后的树为
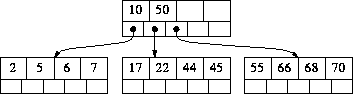
由于BTree根节点的特殊性,它只需要最少有一个节点就可以了,如果修复到根节点还有至少一个节点,那么修复结束,否则删除现有根节点,使用其左子树替代,左子树可能为空,那么整棵BTree就是空了!
代码如下:
void btree::del(int key) {
_del(root, key);
}
void btree::_del(b_node* node, int key) {
// 先找到删除节点所在的位置
pos p = query(key);
// 查找其最大左子树key
pos left_max_p = _get_left_max_key(key);
b_node* del_node = p.node;
if (left_max_p.node != NULL)
{
del_node = left_max_p.node;
std::swap(p.node->keys[p.index], left_max_p.node->keys[left_max_p.index]); // 将最大左子树key和当前key进行交换
}
// 现在针对key进行删除
del_node->del(key);
// 先判断如果没有underflowed,就直接结束了
if (!del_node->is_underflowed()) {
return;
}
_merge_node(del_node);
}
void btree::_merge_node(b_node* del_node) {
// 如果underflowed了,那么先判断是否为根节点,根节点只要最少有一个key就可以了,其他非根节点最少要有(M-1)/2个key
if (del_node->is_root())
{
if (del_node->num == ) // 根节点已经没有key了
{
root = del_node->childs[];
}
return;
}
// 如果是叶子节点并且underflowed了,那么就需要从其“邻居”来“借”了
b_node* ngb_node = del_node->get_pop_ngb();
if (ngb_node == NULL)
{
return;
}
int p_key_pos = (del_node->pos_in_parent + ngb_node->pos_in_parent) / ;
int parent_key = del_node->parent->keys[p_key_pos];
// 处理组合后的节点
b_node* combined_node = new b_node(del_node->num + + ngb_node->num);
if (del_node->pos_in_parent < ngb_node->pos_in_parent)
{
int combined_n = ;
_realloc(combined_node, del_node, del_node->num);
combined_n += del_node->num;
combined_node->insert(parent_key); ++combined_n;
_realloc(combined_node, ngb_node, ngb_node->num, combined_n);
}
else
{
int combined_n = ;
_realloc(combined_node, ngb_node, ngb_node->num);
combined_n += ngb_node->num;
combined_node->insert(parent_key); ++combined_n;
_realloc(combined_node, del_node, del_node->num, combined_n);
}
// 如果邻居key的数量大于(M-1)/2, 那么执行case1逻辑,将combined后的node中间值和parent中的值进行交换,然后分裂成2个节点
if (ngb_node->num > dim/)
{
int split_pos = (del_node->num + ngb_node->num + ) / ;
b_node* combined_left = new b_node(dim);
b_node* combined_right = new b_node(dim);
_realloc(combined_left, combined_node, split_pos);
_realloc(combined_right, combined_node, combined_node->num - split_pos - , , split_pos + );
combined_left->parent = del_node->parent;
combined_right->parent = del_node->parent;
b_node* parent = del_node->parent;
std::swap(combined_node->keys[split_pos], del_node->parent->keys[del_node->pos_in_parent]);
parent->childs[p_key_pos] = combined_left;
combined_left->pos_in_parent = p_key_pos;
parent->childs[p_key_pos + ] = combined_right;
combined_right->pos_in_parent = p_key_pos + ;
return;
}
// 如果邻居的key的数量刚好是(M-1)/2,那么合并之后就可能会发生underflowed情况
// 邻居key的数量不可能会发生小于(M-1)/2的,因为如果是这样,之前就已经做过fix处理了
del_node->parent->del(parent_key);
del_node->parent->childs[del_node->pos_in_parent] = combined_node;
combined_node->parent = del_node->parent;
combined_node->pos_in_parent = del_node->pos_in_parent;
// 如果parent去掉一个节点之后并没有underflowed,那么就结束
if (!del_node->parent->is_underflowed())
{
return;
}
// 否则继续对parent节点进行修复, 直到根节点
_merge_node(del_node->parent);
return;
}
void btree::_realloc(b_node* new_node, b_node* old_node, int num, int new_offset, int old_offset) {
int i = old_offset;
int n = new_offset;
for (; i<old_offset + num; ++i, ++n)
{
new_node->keys[n] = old_node->keys[i];
new_node->childs[n] = old_node->childs[i];
if (new_node->childs[n]) {
new_node->childs[n]->parent = new_node;
new_node->childs[n]->pos_in_parent = n;
}
}
new_node->childs[n] = old_node->childs[i];
if (new_node->childs[n]) {
new_node->childs[n]->parent = new_node;
new_node->childs[n]->pos_in_parent = n;
}
new_node->num += num;
return;
}
测试代码通过一个个的值插入,我们有意的数值安排,将我们的B-Tree从1层,最后扩展到了3层,可以通过print接口来更方便的观看一下B-Tree各层的数值。
如果想知道自己实现的是否正确,或者想了解B-Tree插入节点的流程,https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BTree.html 这个网址用动画的方式给我们展示B-Tree的插入和分裂过程,非常形象,很好理解。
B-Tree算法分析与实现的更多相关文章
- 数据结构与算法分析–Minimum Spanning Tree(最小生成树)
给定一个无向图,如果他的某个子图中,任意两个顶点都能互相连通并且是一棵树,那么这棵树就叫做生成树(spanning tree). 如果边上有权值,那么使得边权和最小的生成树叫做最小生成树(MST,Mi ...
- 《数据结构与算法分析——C语言描述》ADT实现(NO.03) : 二叉搜索树/二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree),又名二叉查找树.二叉排序树,是一种简单的二叉树.它的特点是每一个结点的左(右)子树各结点的元素一定小于(大于)该结点的元素.将该树用于查找时,由于二 ...
- poj 3237 Tree 树链剖分
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3237 You are given a tree with N nodes. The tree’s nodes are numbered ...
- RapidMiner的基本使用(一个医疗数据的简单决策树算法分析)
RapidMiner的基本使用(一个医疗数据的简单决策树算法分析) RapidMiner的基本使用(一个医疗数据的简单决策树算法分析) 需要分析的文件: 右键分别创建读取excel数据,选择属性,设置 ...
- Mysql B-Tree, B+Tree, B*树介绍
[摘要] 最近在看Mysql的存储引擎中索引的优化,神马是索引,支持啥索引.全是浮云,目前Mysql的MyISAM和InnoDB都支持B-Tree索引,InnoDB还支持B+Tree索引,Memory ...
- 【数据结构】B-Tree, B+Tree, B*树介绍
[摘要] 最近在看Mysql的存储引擎中索引的优化,神马是索引,支持啥索引.全是浮云,目前Mysql的MyISAM和InnoDB都支持B-Tree索引,InnoDB还支持B+Tree索引,Memory ...
- 【数据结构】B-Tree, B+Tree, B*树介绍 转
[数据结构]B-Tree, B+Tree, B*树介绍 [摘要] 最近在看Mysql的存储引擎中索引的优化,神马是索引,支持啥索引.全是浮云,目前Mysql的MyISAM和InnoDB都支持B-Tre ...
- webpack4 系列教程(九): CSS Tree Shaking
教程所示图片使用的是 github 仓库图片,网速过慢的朋友请移步原文地址 有空就来看看个人技术小站, 我一直都在 0. 课程介绍和资料 本次课程的代码目录(如下图所示): >>> ...
- <数据结构与算法分析>读书笔记--最大子序列和问题的求解
现在我们将要叙述四个算法来求解早先提出的最大子序列和问题. 第一个算法,它只是穷举式地尝试所有的可能.for循环中的循环变量反映了Java中数组从0开始而不是从1开始这样一个事实.还有,本算法并不计算 ...
- <数据结构与算法分析>读书笔记--运行时间计算
有几种方法估计一个程序的运行时间.前面的表是凭经验得到的(可以参考:<数据结构与算法分析>读书笔记--要分析的问题) 如果认为两个程序花费大致相同的时间,要确定哪个程序更快的最好方法很可能 ...
随机推荐
- netstat命令详解
它主要的用法和详解! (netstat -na 命令),本文主要是说Linux下的netstat工具,然后详细说明一下各种网络连接状态. netstat -nat |awk ‘{print $}’|s ...
- linux-ubuntu常用命令
常用命令 cd 目录 #跳转到指定目录 cp fileName pfileName #拷贝fileName到pfilename ll #显示目录下的所有文件和目录 uname -a #查看内核版本 c ...
- [转](三)unity4.6Ugui中文教程文档-------概要-UGUI Basic Layout
大家好,我是孙广东. 转载请注明出处:http://write.blog.csdn.net/postedit/38922399 更全的内容请看我的游戏蛮牛地址:http://www.unityma ...
- MYSQL转换JSON
http://51strive.com/ <!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- 手机测试pc端网页
在这个问题上徘徊了 一个钟头了,终于被我找到方法了,就赶紧记下来,以后好查阅!! 主要问题在防火墙,防火墙阻当了80端口,所以怎么用手机访问都是访问不了的.把防火墙关闭就好了! 贴上httpd-vho ...
- <hr/> 水平线样式
<hr style="width:490px;" /> <hr size=8 style="COLOR: #ffd306;border-style:ou ...
- python打怪之路【第二篇】:ImportError: No module named setuptools
在python安装第三方模块时出现如下错误: python错误:ImportError: No module named setuptools这句错误提示的表面意思是:没有setuptools的模块, ...
- #pragma once与 #ifndef的区别
为了避免同一个文件被include多次 1 #ifndef方式2 #pragma once方式 在能够支持这两种方式的编译器上,二者并没有太大的区别,但是两者仍然还是有一些细微的区别. ...
- Mybatis 开启事务@Transactional
- 能源项目xml文件 -- springMVC-servlet.xml -- default-lazy-init
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w ...
