Volley(二)—— 基本Request对象 & RequestQueue&请求取消
详细解读Volley(一)—— 基本Request对象 & RequestQueue&请求取消

Volley它非常适合去进行数据量不大,但通信频繁的网络操作,而对于大数据量的网络操作,比如说下载文件等,Volley的表现就会非常糟糕。 所以不建议用它去进行下载文件、加载大图的操作。有人可能会问,如果我服务器中的图片都挺大的,activity中listview要加载这些图片,是不 是不能用这个框架呢?其实这个问题本身就是错误的,你想如果你服务器的图片都是大图,你要在手机上用照片墙进行展示,下载图片都会慢的要死,这个本身就是 不可行的。所以在项目初期就应该建立好服务器端的小图,照片墙用加载小图,点击后再从网络上下载大图,这才是正确思路。这时你就可以用volley加载小 图了,如果是要加载大图,可以用别的算法,强烈建议手动完成大图清除的工作,否则很可能会出现OOM。Volley本身没有做什么回收算法,还是用最基本 的GC,实际使用中可以根据需要自定义一下。
零、准备工作
Git项目,添加为lib,申请权限
git clone https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/volley
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
一、初始化请求对象——RequestQueue

public class MyApplication extends Application {
public static RequestQueue requestQueue;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
// 不必为每一次HTTP请求都创建一个RequestQueue对象,推荐在application中初始化
requestQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(this);
}
}

既然是Http操作,自然有请求和响应,RequestQueue是一个请求队列 对象,它可以缓存所有的HTTP请求,然后按照一定的算法并发地发出这些请求。RequestQueue内部的设计就是非常合适高并发的,因此我们不必为 每一次HTTP请求都创建一个RequestQueue对象,这是非常浪费资源的。所以在这里我建立了一个application,然后用单例模式定义了 这个对象。当然,你可以选择在一个activity中定义一个RequestQueue对象,但这样可能会比较麻烦,而且还可能出现请求队列包含 activity强引用的问题,因此我还是推荐在application中定义。
二、使用StringRequest接收String类型的响应
前 面定义了请求对象,那么自然就有接收响应的对象了,这个框架中有多个响应对象,像StringRequest接受到的响应就是string类型 的;JsonRequest接收的响应就是Json类型对象。其实它们都是继承自Request<T>,然后根据不同的响应数据来进行特殊的 处理。
2.1 初始化

/**
* Creates a new request with the given method.
*
* @param method the request {@link Method} to use
* @param url URL to fetch the string at
* @param listener Listener to receive the String response
* @param errorListener Error listener, or null to ignore errors
*/
public StringRequest(int method, String url, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener)


/**
* Creates a new GET request.
*
* @param url URL to fetch the string at
* @param listener Listener to receive the String response
* @param errorListener Error listener, or null to ignore errors
*/
public StringRequest(String url, Listener<String> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
this(Method.GET, url, listener, errorListener);
}

这就是StringRequest的两个构造函数,不同之处是一个传入了一个method的参数,一个没有。其实看上面的源码就知道,如果你不传入method,默认会调用GET方式进行请求。当你传入了Method.POST就会用post来请求。
【参数解释】
url:请求的地址
listener:响应成功的监听器
errorListener:出错时的监听器
StringRequest getStringRequest = new StringRequest("http://www.baidu.com", new ResponseListener(), new ResponseErrorListener());
StringRequest postStringRequest = new StringRequest(Method.POST, "http://www.baidu.com", new ResponseListener(),null);
2.2 配置监听器

/**
* @author:Jack Tony
* @description :设置响应结果监听器,因为用的是StringRequest,所以这里的结果我定义为string类型
* @date :2015年1月24日
*/
private class ResponseListener implements Response.Listener<String>{ @Override
public void onResponse(String response) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Log.d("TAG", "-------------\n" + response);
}
} /**
* @author:Jack Tony
* @description :访问出错时触发的监听器
* @date :2015年1月28日
*/
private class ResponseErrorListener implements Response.ErrorListener{ @Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);
} }

这两个监听器没啥可说的,因为是StringRequest调用的,所以成功时触发的监听器中得到的response就是String类型。如果访问出错,那么就打印出错信息。
2.3 执行GET请求
现在我们有了请求对象和响应对象,外加处理响应结果的监听器,那么就执行最后一步——发送请求。发送请求很简单,将响应对象添加到请求队列即可。
mQueue.add(getStringRequest);
完整代码:

RequestQueue mQueue = MyApplication.requestQueue;
StringRequest getStringRequest = new StringRequest("http://www.baidu.com", new ResponseListener(), new ResponseErrorListener());
mQueue.add(getStringRequest);

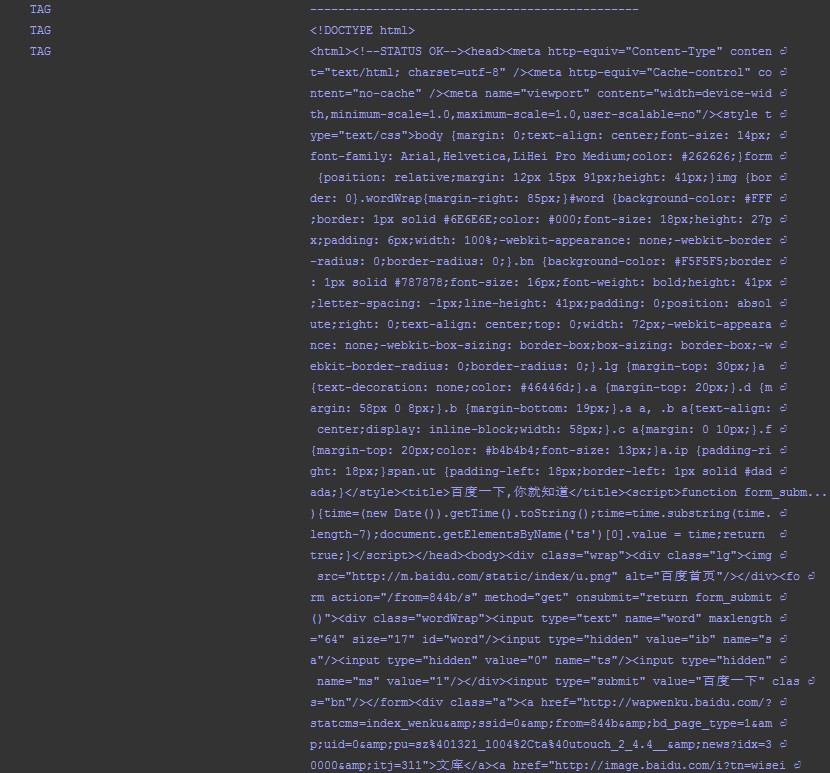
通过简单的add()方法就直接发送了请求,如果服务器响应了请求就会触发我们的结果监听器,然后被打印出啦。现在请求的是百度,所以得到了网页的源码:
2.4 执行POST请求
POST和GET一样,仅仅是传入的方法不同。但一般我们的post都是要带一些参数的,volley没有提供附加参数的方法,所以我们必须要在StringRequest的匿名类中重写getParams()方法:

StringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest(Method.POST, url, listener, errorListener) {
@Override
protected Map<String, String> getParams() throws AuthFailureError {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("params1", "value1");
map.put("params2", "value2");
return map;
}
};

这 样就传入了value1和value2两个参数了。现在可能有人会问为啥这个框架不提供这个传参的方法,还非得让我们重写。我个人觉得这个框架本身的目的 就是执行频繁的网络请求,比如下载图片,解析json数据什么的,用GET就能很好的实现了,所以就没有提供传参的POST方法。为了简单起见,我重写了 Request类中的getParams(),添加了传参的方法,以后通过setParams()就可以传参数了。
重写的代码块:

Map<String, String> mParams = null;
/**
* Returns a Map of parameters to be used for a POST or PUT request. Can throw
* {@link AuthFailureError} as authentication may be required to provide these values.
*
* <p>Note that you can directly override {@link #getBody()} for custom data.</p>
*
* @throws AuthFailureError in the event of auth failure
*/
protected Map<String, String> getParams() throws AuthFailureError {
return mParams;
}
public void setParams(Map<String, String> params){
mParams = params;
}

完整代码:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package com.android.volley; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Map; import android.net.TrafficStats;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.text.TextUtils; import com.android.volley.VolleyLog.MarkerLog; /**
* Base class for all network requests.
*
* @param <T> The type of parsed response this request expects.
*/
public abstract class Request<T> implements Comparable<Request<T>> { /**
* Default encoding for POST or PUT parameters. See {@link #getParamsEncoding()}.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_PARAMS_ENCODING = "UTF-8"; /**
* Supported request methods.
*/
public interface Method {
int DEPRECATED_GET_OR_POST = -1;
int GET = 0;
int POST = 1;
int PUT = 2;
int DELETE = 3;
int HEAD = 4;
int OPTIONS = 5;
int TRACE = 6;
int PATCH = 7;
} /** An event log tracing the lifetime of this request; for debugging. */
private final MarkerLog mEventLog = MarkerLog.ENABLED ? new MarkerLog() : null; /**
* Request method of this request. Currently supports GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS,
* TRACE, and PATCH.
*/
private final int mMethod; /** URL of this request. */
private final String mUrl; /** Default tag for {@link TrafficStats}. */
private final int mDefaultTrafficStatsTag; /** Listener interface for errors. */
private final Response.ErrorListener mErrorListener; /** Sequence number of this request, used to enforce FIFO ordering. */
private Integer mSequence; /** The request queue this request is associated with. */
private RequestQueue mRequestQueue; /** Whether or not responses to this request should be cached. */
private boolean mShouldCache = true; /** Whether or not this request has been canceled. */
private boolean mCanceled = false; /** Whether or not a response has been delivered for this request yet. */
private boolean mResponseDelivered = false; // A cheap variant of request tracing used to dump slow requests.
private long mRequestBirthTime = 0; /** Threshold at which we should log the request (even when debug logging is not enabled). */
private static final long SLOW_REQUEST_THRESHOLD_MS = 3000; /** The retry policy for this request. */
private RetryPolicy mRetryPolicy; /**
* When a request can be retrieved from cache but must be refreshed from
* the network, the cache entry will be stored here so that in the event of
* a "Not Modified" response, we can be sure it hasn't been evicted from cache.
*/
private Cache.Entry mCacheEntry = null; /** An opaque token tagging this request; used for bulk cancellation. */
private Object mTag; /**
* Creates a new request with the given URL and error listener. Note that
* the normal response listener is not provided here as delivery of responses
* is provided by subclasses, who have a better idea of how to deliver an
* already-parsed response.
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #Request(int, String, com.android.volley.Response.ErrorListener)}.
*/
@Deprecated
public Request(String url, Response.ErrorListener listener) {
this(Method.DEPRECATED_GET_OR_POST, url, listener);
} /**
* Creates a new request with the given method (one of the values from {@link Method}),
* URL, and error listener. Note that the normal response listener is not provided here as
* delivery of responses is provided by subclasses, who have a better idea of how to deliver
* an already-parsed response.
*/
public Request(int method, String url, Response.ErrorListener listener) {
mMethod = method;
mUrl = url;
mErrorListener = listener;
setRetryPolicy(new DefaultRetryPolicy()); mDefaultTrafficStatsTag = findDefaultTrafficStatsTag(url);
} /**
* Return the method for this request. Can be one of the values in {@link Method}.
*/
public int getMethod() {
return mMethod;
} /**
* Set a tag on this request. Can be used to cancel all requests with this
* tag by {@link RequestQueue#cancelAll(Object)}.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public Request<?> setTag(Object tag) {
mTag = tag;
return this;
} /**
* Returns this request's tag.
* @see Request#setTag(Object)
*/
public Object getTag() {
return mTag;
} /**
* @return this request's {@link com.android.volley.Response.ErrorListener}.
*/
public Response.ErrorListener getErrorListener() {
return mErrorListener;
} /**
* @return A tag for use with {@link TrafficStats#setThreadStatsTag(int)}
*/
public int getTrafficStatsTag() {
return mDefaultTrafficStatsTag;
} /**
* @return The hashcode of the URL's host component, or 0 if there is none.
*/
private static int findDefaultTrafficStatsTag(String url) {
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(url)) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse(url);
if (uri != null) {
String host = uri.getHost();
if (host != null) {
return host.hashCode();
}
}
}
return 0;
} /**
* Sets the retry policy for this request.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public Request<?> setRetryPolicy(RetryPolicy retryPolicy) {
mRetryPolicy = retryPolicy;
return this;
} /**
* Adds an event to this request's event log; for debugging.
*/
public void addMarker(String tag) {
if (MarkerLog.ENABLED) {
mEventLog.add(tag, Thread.currentThread().getId());
} else if (mRequestBirthTime == 0) {
mRequestBirthTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
}
} /**
* Notifies the request queue that this request has finished (successfully or with error).
*
* <p>Also dumps all events from this request's event log; for debugging.</p>
*/
void finish(final String tag) {
if (mRequestQueue != null) {
mRequestQueue.finish(this);
}
if (MarkerLog.ENABLED) {
final long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
if (Looper.myLooper() != Looper.getMainLooper()) {
// If we finish marking off of the main thread, we need to
// actually do it on the main thread to ensure correct ordering.
Handler mainThread = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
mainThread.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mEventLog.add(tag, threadId);
mEventLog.finish(this.toString());
}
});
return;
} mEventLog.add(tag, threadId);
mEventLog.finish(this.toString());
} else {
long requestTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - mRequestBirthTime;
if (requestTime >= SLOW_REQUEST_THRESHOLD_MS) {
VolleyLog.d("%d ms: %s", requestTime, this.toString());
}
}
} /**
* Associates this request with the given queue. The request queue will be notified when this
* request has finished.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public Request<?> setRequestQueue(RequestQueue requestQueue) {
mRequestQueue = requestQueue;
return this;
} /**
* Sets the sequence number of this request. Used by {@link RequestQueue}.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public final Request<?> setSequence(int sequence) {
mSequence = sequence;
return this;
} /**
* Returns the sequence number of this request.
*/
public final int getSequence() {
if (mSequence == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("getSequence called before setSequence");
}
return mSequence;
} /**
* Returns the URL of this request.
*/
public String getUrl() {
return mUrl;
} /**
* Returns the cache key for this request. By default, this is the URL.
*/
public String getCacheKey() {
return getUrl();
} /**
* Annotates this request with an entry retrieved for it from cache.
* Used for cache coherency support.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public Request<?> setCacheEntry(Cache.Entry entry) {
mCacheEntry = entry;
return this;
} /**
* Returns the annotated cache entry, or null if there isn't one.
*/
public Cache.Entry getCacheEntry() {
return mCacheEntry;
} /**
* Mark this request as canceled. No callback will be delivered.
*/
public void cancel() {
mCanceled = true;
} /**
* Returns true if this request has been canceled.
*/
public boolean isCanceled() {
return mCanceled;
} /**
* Returns a list of extra HTTP headers to go along with this request. Can
* throw {@link AuthFailureError} as authentication may be required to
* provide these values.
* @throws AuthFailureError In the event of auth failure
*/
public Map<String, String> getHeaders() throws AuthFailureError {
return Collections.emptyMap();
} /**
* Returns a Map of POST parameters to be used for this request, or null if
* a simple GET should be used. Can throw {@link AuthFailureError} as
* authentication may be required to provide these values.
*
* <p>Note that only one of getPostParams() and getPostBody() can return a non-null
* value.</p>
* @throws AuthFailureError In the event of auth failure
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #getParams()} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
protected Map<String, String> getPostParams() throws AuthFailureError {
return getParams();
} /**
* Returns which encoding should be used when converting POST parameters returned by
* {@link #getPostParams()} into a raw POST body.
*
* <p>This controls both encodings:
* <ol>
* <li>The string encoding used when converting parameter names and values into bytes prior
* to URL encoding them.</li>
* <li>The string encoding used when converting the URL encoded parameters into a raw
* byte array.</li>
* </ol>
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #getParamsEncoding()} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
protected String getPostParamsEncoding() {
return getParamsEncoding();
} /**
* @deprecated Use {@link #getBodyContentType()} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public String getPostBodyContentType() {
return getBodyContentType();
} /**
* Returns the raw POST body to be sent.
*
* @throws AuthFailureError In the event of auth failure
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #getBody()} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public byte[] getPostBody() throws AuthFailureError {
// Note: For compatibility with legacy clients of volley, this implementation must remain
// here instead of simply calling the getBody() function because this function must
// call getPostParams() and getPostParamsEncoding() since legacy clients would have
// overridden these two member functions for POST requests.
Map<String, String> postParams = getPostParams();
if (postParams != null && postParams.size() > 0) {
return encodeParameters(postParams, getPostParamsEncoding());
}
return null;
} Map<String, String> mParams = null; /**
* Returns a Map of parameters to be used for a POST or PUT request. Can throw
* {@link AuthFailureError} as authentication may be required to provide these values.
*
* <p>Note that you can directly override {@link #getBody()} for custom data.</p>
*
* @throws AuthFailureError in the event of auth failure
*/
protected Map<String, String> getParams() throws AuthFailureError {
return mParams;
} public void setParams(Map<String, String> params){
mParams = params;
} /**
* Returns which encoding should be used when converting POST or PUT parameters returned by
* {@link #getParams()} into a raw POST or PUT body.
*
* <p>This controls both encodings:
* <ol>
* <li>The string encoding used when converting parameter names and values into bytes prior
* to URL encoding them.</li>
* <li>The string encoding used when converting the URL encoded parameters into a raw
* byte array.</li>
* </ol>
*/
protected String getParamsEncoding() {
return DEFAULT_PARAMS_ENCODING;
} /**
* Returns the content type of the POST or PUT body.
*/
public String getBodyContentType() {
return "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=" + getParamsEncoding();
} /**
* Returns the raw POST or PUT body to be sent.
*
* <p>By default, the body consists of the request parameters in
* application/x-www-form-urlencoded format. When overriding this method, consider overriding
* {@link #getBodyContentType()} as well to match the new body format.
*
* @throws AuthFailureError in the event of auth failure
*/
public byte[] getBody() throws AuthFailureError {
Map<String, String> params = getParams();
if (params != null && params.size() > 0) {
return encodeParameters(params, getParamsEncoding());
}
return null;
} /**
* Converts <code>params</code> into an application/x-www-form-urlencoded encoded string.
*/
private byte[] encodeParameters(Map<String, String> params, String paramsEncoding) {
StringBuilder encodedParams = new StringBuilder();
try {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
encodedParams.append(URLEncoder.encode(entry.getKey(), paramsEncoding));
encodedParams.append('=');
encodedParams.append(URLEncoder.encode(entry.getValue(), paramsEncoding));
encodedParams.append('&');
}
return encodedParams.toString().getBytes(paramsEncoding);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException uee) {
throw new RuntimeException("Encoding not supported: " + paramsEncoding, uee);
}
} /**
* Set whether or not responses to this request should be cached.
*
* @return This Request object to allow for chaining.
*/
public final Request<?> setShouldCache(boolean shouldCache) {
mShouldCache = shouldCache;
return this;
} /**
* Returns true if responses to this request should be cached.
*/
public final boolean shouldCache() {
return mShouldCache;
} /**
* Priority values. Requests will be processed from higher priorities to
* lower priorities, in FIFO order.
*/
public enum Priority {
LOW,
NORMAL,
HIGH,
IMMEDIATE
} /**
* Returns the {@link Priority} of this request; {@link Priority#NORMAL} by default.
*/
public Priority getPriority() {
return Priority.NORMAL;
} /**
* Returns the socket timeout in milliseconds per retry attempt. (This value can be changed
* per retry attempt if a backoff is specified via backoffTimeout()). If there are no retry
* attempts remaining, this will cause delivery of a {@link TimeoutError} error.
*/
public final int getTimeoutMs() {
return mRetryPolicy.getCurrentTimeout();
} /**
* Returns the retry policy that should be used for this request.
*/
public RetryPolicy getRetryPolicy() {
return mRetryPolicy;
} /**
* Mark this request as having a response delivered on it. This can be used
* later in the request's lifetime for suppressing identical responses.
*/
public void markDelivered() {
mResponseDelivered = true;
} /**
* Returns true if this request has had a response delivered for it.
*/
public boolean hasHadResponseDelivered() {
return mResponseDelivered;
} /**
* Subclasses must implement this to parse the raw network response
* and return an appropriate response type. This method will be
* called from a worker thread. The response will not be delivered
* if you return null.
* @param response Response from the network
* @return The parsed response, or null in the case of an error
*/
abstract protected Response<T> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response); /**
* Subclasses can override this method to parse 'networkError' and return a more specific error.
*
* <p>The default implementation just returns the passed 'networkError'.</p>
*
* @param volleyError the error retrieved from the network
* @return an NetworkError augmented with additional information
*/
protected VolleyError parseNetworkError(VolleyError volleyError) {
return volleyError;
} /**
* Subclasses must implement this to perform delivery of the parsed
* response to their listeners. The given response is guaranteed to
* be non-null; responses that fail to parse are not delivered.
* @param response The parsed response returned by
* {@link #parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse)}
*/
abstract protected void deliverResponse(T response); /**
* Delivers error message to the ErrorListener that the Request was
* initialized with.
*
* @param error Error details
*/
public void deliverError(VolleyError error) {
if (mErrorListener != null) {
mErrorListener.onErrorResponse(error);
}
} /**
* Our comparator sorts from high to low priority, and secondarily by
* sequence number to provide FIFO ordering.
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Request<T> other) {
Priority left = this.getPriority();
Priority right = other.getPriority(); // High-priority requests are "lesser" so they are sorted to the front.
// Equal priorities are sorted by sequence number to provide FIFO ordering.
return left == right ?
this.mSequence - other.mSequence :
right.ordinal() - left.ordinal();
} @Override
public String toString() {
String trafficStatsTag = "0x" + Integer.toHexString(getTrafficStatsTag());
return (mCanceled ? "[X] " : "[ ] ") + getUrl() + " " + trafficStatsTag + " "
+ getPriority() + " " + mSequence;
}
}
使用示例:

StringRequest postStringRequest = new StringRequest(Method.POST, "http://m.weather.com.cn/data/101010100.html",
new ResponseListener(), null);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("params1", "value1");
map.put("params2", "value2");
postStringRequest.setParams(map);
mQueue.add(postStringRequest);

结果:
三、使用JsonObjectRequest接收Json类型的响应
类似于StringRequest,JsonRequest也是继承自Request类的,不过由于JsonRequest是一个抽象类,因此我们无法直接创建它的实例,那么只能从它的子类入手了。JsonRequest有两个直接的子类,JsonObjectRequest和JsonArrayRequest,从名字上你应该能就看出它们的区别了吧?一个是用于请求一段JSON数据的,一个是用于请求一段JSON数组的。
3.1 构造函数

/**
* Creates a new request.
* @param method the HTTP method to use
* @param url URL to fetch the JSON from
* @param jsonRequest A {@link JSONObject} to post with the request. Null is allowed and
* indicates no parameters will be posted along with request.
* @param listener Listener to receive the JSON response
* @param errorListener Error listener, or null to ignore errors.
*/
public JsonObjectRequest(int method, String url, JSONObject jsonRequest,
Listener<JSONObject> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(method, url, (jsonRequest == null) ? null : jsonRequest.toString(), listener,
errorListener);
} /**
* Constructor which defaults to <code>GET</code> if <code>jsonRequest</code> is
* <code>null</code>, <code>POST</code> otherwise.
*
* @see #JsonObjectRequest(int, String, JSONObject, Listener, ErrorListener)
*/
public JsonObjectRequest(String url, JSONObject jsonRequest, Listener<JSONObject> listener,
ErrorListener errorListener) {
this(jsonRequest == null ? Method.GET : Method.POST, url, jsonRequest,
listener, errorListener);
}

3.2 发送请求
和之前讲过的StringRequest一样,可以传入请求的类型,如果没传就默认是GET请求。参数也是如出一辙,就是泛型变了下。定义和使用的方式也完全一致,初始化对象后,添加到请求队列即可。

JsonObjectRequest request = new JsonObjectRequest("http://m.weather.com.cn/data/101010100.html",
null, new ResponseListener(), new ResponseErrorListener());
mQueue.add(request);


/**
* @author:Jack Tony
* @description :设置响应结果监听器,这里用的是JsonObjectRequest,所以返回的结果是JSONObject
* @date :2015年1月24日
*/
private class ResponseListener implements Response.Listener<JSONObject> { @Override
public void onResponse(JSONObject response) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Log.d("TAG", "-------------\n" + response.toString());
} } /**
* @author:Jack Tony
* @description :访问出错时触发的监听器
* @date :2015年1月28日
*/
private class ResponseErrorListener implements Response.ErrorListener { @Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);
}
}

结果:
你怎么查看解析是否成功了呢?服务器端的数据:

{"weatherinfo":{"city":"北京","city_en":"beijing","date_y":"2014年3月4日","date":"","week":"星期二","fchh":"11","cityid":"101010100","temp1":"8℃~-3℃","temp2":"8℃~-3℃","temp3":"7℃~-3℃","temp4":"8℃~-1℃","temp5":"10℃~1℃","temp6":"10℃~2℃","tempF1":"46.4℉~26.6℉","tempF2":"46.4℉~26.6℉","tempF3":"44.6℉~26.6℉","tempF4":"46.4℉~30.2℉","tempF5":"50℉~33.8℉","tempF6":"50℉~35.6℉","weather1":"晴","weather2":"晴","weather3":"晴","weather4":"晴转多云","weather5":"多云","weather6":"多云","img1":"0","img2":"99","img3":"0","img4":"99","img5":"0","img6":"99","img7":"0","img8":"1","img9":"1","img10":"99","img11":"1","img12":"99","img_single":"0","img_title1":"晴","img_title2":"晴","img_title3":"晴","img_title4":"晴","img_title5":"晴","img_title6":"晴","img_title7":"晴","img_title8":"多云","img_title9":"多云","img_title10":"多云","img_title11":"多云","img_title12":"多云","img_title_single":"晴","wind1":"北风4-5级转微风","wind2":"微风","wind3":"微风","wind4":"微风","wind5":"微风","wind6":"微风","fx1":"北风","fx2":"微风","fl1":"4-5级转小于3级","fl2":"小于3级","fl3":"小于3级","fl4":"小于3级","fl5":"小于3级","fl6":"小于3级","index":"寒冷","index_d":"天气寒冷,建议着厚羽绒服、毛皮大衣加厚毛衣等隆冬服装。年老体弱者尤其要注意保暖防冻。","index48":"冷","index48_d":"天气冷,建议着棉服、羽绒服、皮夹克加羊毛衫等冬季服装。年老体弱者宜着厚棉衣、冬大衣或厚羽绒服。","index_uv":"中等","index48_uv":"中等","index_xc":"较适宜","index_tr":"一般","index_co":"较舒适","st1":"7","st2":"-3","st3":"8","st4":"0","st5":"7","st6":"-1","index_cl":"较不宜","index_ls":"基本适宜","index_ag":"易发"}}

如果解析错误,就会出现警告,这时错误监听器就会被触发:
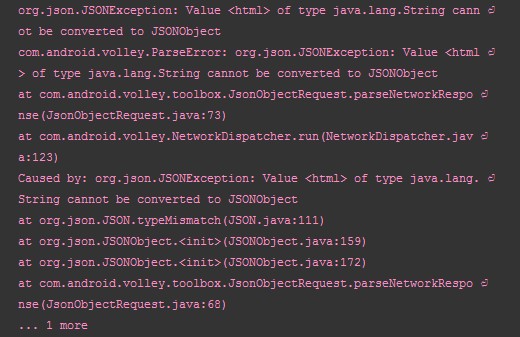
如果解析成功,就不会出现错误,这就是泛型的好处,保证了程序的正确性。

最终我们就可以在Response.Listener<JSONObject>中得到JSONObject对象,通过这个对象就能进行下一步的处理了。
3.3 解析Json
比如要解析出上面Json数据中city的字段,就可以按照如下方式编码:

try {
response = response.getJSONObject("weatherinfo");
Log.i(TAG, "City = " + response.getString("city"));
} catch (JSONException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}

完整监听器代码:

private class ResponseListener implements Response.Listener<JSONObject> {
@Override
public void onResponse(JSONObject response) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
Log.d("TAG", "-------------\n" + response.toString());
try {
response = response.getJSONObject("weatherinfo");
Log.i(TAG, "City = " + response.getString("city"));
} catch (JSONException e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

结果:
四、JsonArrayRequest简介
除此之外,还有一个相关的响应对象叫做JsonArrayRequest,这个获得的就是一个Json序列,使用方式没有任何改变,这里就不做过多介绍了,因为剩下的就是Json的知识了,和Volley没有任何关系。
源码:

/*
* Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package com.android.volley.toolbox; import com.android.volley.NetworkResponse;
import com.android.volley.ParseError;
import com.android.volley.Response;
import com.android.volley.Response.ErrorListener;
import com.android.volley.Response.Listener; import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; /**
* A request for retrieving a {@link JSONArray} response body at a given URL.
*/
public class JsonArrayRequest extends JsonRequest<JSONArray> { /**
* Creates a new request.
* @param url URL to fetch the JSON from
* @param listener Listener to receive the JSON response
* @param errorListener Error listener, or null to ignore errors.
*/
public JsonArrayRequest(String url, Listener<JSONArray> listener, ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(Method.GET, url, null, listener, errorListener);
} @Override
protected Response<JSONArray> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
try {
String jsonString =
new String(response.data, HttpHeaderParser.parseCharset(response.headers));
return Response.success(new JSONArray(jsonString),
HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(e));
} catch (JSONException je) {
return Response.error(new ParseError(je));
}
}
}

通过源码我们知道,这个响应对象发送的请求是Get,而且它是继承自JsonRequest,如果你想用POST来做,自行添加新的构造函数即可。
四、请求取消
1)可以针对某些个request做取消操作:
@Override
public void onStop() {
for (Request <?> req : mRequestQueue) {
req.cancel();
}
}
2)取消这个队列里的所有请求:
@Override
protected void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
mRequestQueue.cancelAll(this);
}
3)可以根据RequestFilter或者Tag来终止某些请求
给请求设置标签:
如果你想取消所有的请求,在onStop方法中添加如下代码:
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
mRequestQueue.cancelAll(new RequestQueue.RequestFilter() {
@Override
public boolean apply(Request<?> request) {
// do I have to cancel this?
return true; // -> always yes
}
});
}
这样你就不必担心在onResponse被调用的时候用户已经销毁Activity。这种情况下会抛出NullPointerException 异。但是post请求则需要继续,即使用户已经改变了Activity。我们可以通过使用tag来做到,在构造GET请求的时候,添加一个tag给它。
// after declaring your request
request.setTag("My Tag");
mRequestQueue.add(request);
如果要取消所有指定标记My Tag的请求,只需简单的添加下面的一行代码:
mRequestQueue.cancelAll("My Tag");
这样你就只会取消My Tag请求,让其它请求不受影响。注意你必须手动在销毁的Activity中处理这种情况。
@Override
rotected void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop(); mRequestQueue.cancelAll( new RequestFilter() {});
or
mRequestQueue.cancelAll(new Object());
Volley源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/shark0017/8404451
Volley(二)—— 基本Request对象 & RequestQueue&请求取消的更多相关文章
- request对象实现请求转发
request对象实现请求转发,请求转发指一个web资源收到客户端请求后,通知服务器去调用另外一个web资源进行处理.request对象提供了一个getRequestDispatcher方法,该方法返 ...
- 详细解读Volley(一)—— 基本Request对象 & RequestQueue
Volley它非常适合去进行数据量不大,但通信频繁的网络操作,而对于大数据量的网络操作,比如说下载文件等,Volley的表现就会非常糟糕.所以不建议用它去进行下载文件.加载大图的操作.有人可能会问,如 ...
- 常用Request对象获取请求信息
Request.ServerVariables(“REMOTE_ADDR”) ‘获取访问IPRequest.ServerVariables(“LOCAL_ADDR”) ‘同上Request.Serve ...
- Request对象实现请求转发区别
servlet请求转发与重定向的区别: request.setAttribute("test","hello"); request.getRequestDisp ...
- 通过Request对象获取请求的IP地址
/** * 标识要从哪些消息头中获取IP地址 */ private static final String[] getIpArray = {"HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR&quo ...
- java后端通过request对象获取请求的ip地址工具类
package cn.zgjkw.battalion.util; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServl ...
- Django整理(五) - 请求与响应 - request对象
请求对象 一.客户端传参的几种方式 1. 通过URL路径(path)传递,例如:http://127.0.0.1:8000/news/1/2,两个参数:id和page 2. 通过 query stri ...
- request 对象和 response 对象
Web服务器收到客户端的http请求,会针对每一次请求,分别创建一个用于代表请求的request对象.和代表响应的response对象 HttpServletResponse HttpServletR ...
- Asp.net内置对象之Request对象(概述及应用)
Request对象主要用于获取来自客户端的数据,如用户填入表单的数据.保存在客户端的Cookie等,本文将围绕Request对象,讲解其的主要作用:读取窗体变量.读取查询字符串变量.取得Web服务器端 ...
随机推荐
- iOS Apple Pay
iOS 苹果支付 需要证书支持支付功能 targets 打开支付功能按钮 //ApplePay#import <PassKit/PassKit.h> ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-对UIView进行截图
一,效果图. 二,工程图. 三,代码. RootViewController.m #import "RootViewController.h" @interface RootVie ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-3DES+Base64加密解密
一,工程目录. 二,代码. RootViewController.m #import "RootViewController.h" #import "NSString+T ...
- Android 中MyApplication
package liu.basedemo; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.Application; import java.lang. ...
- net2.0对于递归变量的处理方式不同引发的递归问题
同样的代码,用NET2.0执行产生的效果与其它框架使用的不同,导致报错. 认真查找原因后发现该程序的编写人员隐式的使用了一个公共变量,使之在递归过程中不断的被改写,使得1次递归后就破坏了原来的循环体, ...
- unity3D 常用快捷键
http://blog.csdn.net/ganlijianstyle/article/details/7985509 此页面提供了Unity3D默认的快捷键. shift +方向键 ...
- 使用AS3输出ByteArray为16进制
package { import flash.utils.ByteArray; /** * 输出ByteArray为16进制 * @author Rise */ public class Byte2H ...
- Windows下配置Git服务器和客户端 超全
为了配合Redmine使用,特地用Git来做版本控制. Git Candy© 是一个基于ASP.NET MVC的Git分布式版本控制平台,Git Candy的目标是轻松干掉Bonobo,逐渐追赶Git ...
- openstack数据库获取一个虚机的floating_ip, fix_ip, project_name, user_name, hostname, host
转载请注明 http://www.cnblogs.com/juandx/p/5418204.html openstack有3个库,nova,neutron,keystone,我现在需要做的是跨库联表 ...
- python之装饰器
一.简单装饰器: #定义装饰器函数 def W1(main_func): def outer(): print("before") main_func() print(" ...
