Shell编程之运算
一、变量的数值计算
1.算术运算符
常用的运算符号
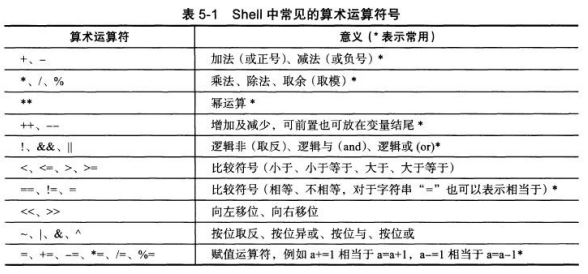
常用的运算命令

(1)双小括号
基本语法
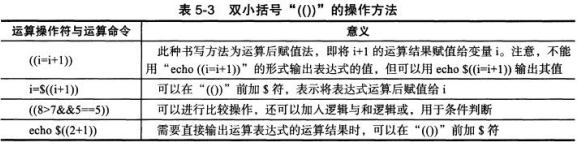
1)利用“(())”进行简单运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((1+1))
2
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6-3))
3
[root@codis-178 ~]# ((i=5))
[root@codis-178 ~]# ((i=i*2))
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
10
2)利用“(())”进行复杂运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# ((a=1+2**3-4%3))
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
8
[root@codis-178 ~]# b=$((1+2**3-4%3))
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $b
8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((1+2**3-4%3))
8
[root@codis-178 ~]# a=$((100*(100+1)/2))
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
5050
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((100*(100+1)/2))
5050
3)特殊运算符的运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# a=8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((a=a+1))
9
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((a+=1))
10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((a**2))
100
4)比较和判断
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((3<8))
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((8<3))
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((8==8))
1
[root@codis-178 ~]# if ((8>7&&5==5))
> then
> echo yes
> fi
yes
5)在变量前后使用--和++特殊运算符的表达式
[root@codis-178 ~]# a=10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((a++))
10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
11
[root@codis-178 ~]# a=11
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((a--))
11
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
10
[root@codis-178 ~]# a=10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((--a))
9
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((++a))
10
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a
10
6)通过“(())”运算后赋值给变量
[root@codis-178 ~]# myvar=99
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((myvar+1))
100
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $(( myvar+1 ))
100
[root@codis-178 ~]# myvar=$((myvar+1))
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $myvar
100
7)包含“(())”的各种常见运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6+2))
8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6-2))
4
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6*2))
12
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6/2))
3
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6%2))
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $((6**2))
36
8)在shell脚本中的示例
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
a=6
b=2
echo "a-b=$(($a-$b))"
echo "a+b=$(($a+$b))"
echo "a*b=$(($a*$b))"
echo "a/b=$(($a/$b))"
echo "a**b=$(($a**$b))"
echo "a%b=$(($a%$b))"
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh test.sh
a-b=4
a+b=8
a*b=12
a/b=3
a**b=36
a%b=0
9)将上面的脚本中a、b两个变量通过命令行脚本传参,以实现混合运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
a=$1
b=$2
echo "a-b=$(($a-$b))"
echo "a+b=$(($a+$b))"
echo "a*b=$(($a*$b))"
echo "a/b=$(($a/$b))"
echo "a**b=$(($a**$b))"
echo "a%b=$(($a%$b))"
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh test.sh 8 3
a-b=5
a+b=11
a*b=24
a/b=2
a**b=512
a%b=2
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh test.sh 3 6
a-b=-3
a+b=9
a*b=18
a/b=0
a**b=729
a%b=3
10)实现输入2个数进行运算的计算器
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat yunsuan.sh
#!/bin/bash
print_usage(){
printf "Please enter an integer\n"
exit 1
}
read -p "Please input first number: " firstnum
if [ -n "`echo $firstnum|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ];then
print_usage
fi
read -p "Please input the operators: " operators
if [ "${operators}" != "+" ] && [ "${operators}" != "-" ] && [ "${operators}" != "*" ] && [ "${operators}" != "/" ];then
echo "please use (+|-|*|/)"
exit 2
fi
read -p "Please input second number: " secondnum
if [ -n "`echo $secondnum|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ];then
printf_usage
fi
echo "${firstnum}${operators}${secondnum}=$((${firstnum}${operators}${secondnum}))"
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan.sh
Please input first number: 5
Please input the operators: +
Please input second number: 16
5+16=21
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan.sh
Please input first number: 9
Please input the operators: *
Please input second number: 24
9*24=216
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan.sh
Please input first number: 76
Please input the operators: -
Please input second number: 24
76-24=52
改良版
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat yunsuan1.sh
#!/bin/bash
print_usage(){
printf $"USAGE:$0 NUM1 {+|-|*|/} NUM2\n"
exit 1
}
if [ $# -ne 3 ]
then
print_usage
fi
firstnum=$1
secondnum=$3
op=$2
if [ -n "`echo $firstnum|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ];then
print_usage
fi
if [ "$op" != "+" ] && [ "$op" != "-" ] && [ "$op" != "*" ] && [ "$op" != "/" ]
then
print_usage
fi
if [ -n "`echo $secondnum|sed 's/[0-9]//g'`" ];then
printf_usage
fi
echo "${firstnum}${op}${secondnum}=$((${firstnum}${op}${secondnum}))"
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 6 + 8
6+8=14
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 56 + 13
56+13=69
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 56 - 13
56-13=43
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 2 * 2
USAGE:yunsuan1.sh NUM1 {+|-|*|/} NUM2
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 9 / 3
9/3=3
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh yunsuan1.sh 2 \* 2 # 乘号需要转义
2*2=4
(2)let运算命令
1)给自变量加8
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=2
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=i+8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
i+8
[root@codis-178 ~]# unset i
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=2
[root@codis-178 ~]# let i=i+8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
10
2)监控Web服务状态,如果访问两次均失败,则报警
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat web.sh
#!/bin/bash
CheckUrl(){
timeout=5
fails=0
success=0
while true
do
wget --timeout=$timeout --tries=1 http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com -q -O /dev/null
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
let fails=fails+1
else
let success+=1
fi
if [ $success -ge 1 ]
then
echo success
exit 0
fi
if [ $fails -ge 2 ]
then
Critical="sys is down."
echo $Critical|tee|mail -s "$Critical" tongxiaoda@anzhi.com
exit 2
fi
done
}
CheckUrl
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh web.sh
success
(3)expr命令
1)expr用于计算
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 2 + 2
4
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 2 - 2
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 2 * 2 # 需要转义
expr: syntax error
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 2 \* 2
4
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr 2 / 2
1
2)expr配合变量计算
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=5
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=`expr $i + 6`
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
11
3)判断一个变量或字符串是否为整数
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=5
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr $i + 6 &>/dev/null
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $?
0
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=oldboy
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr $i + 6 &>/dev/null
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $?
2
4)通过传参判断输出内容是否为整数
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat expr.sh
#!/bin/bash
expr $1 + 1 > /dev/null 2>&1
[ $? -eq 0 ] && echo int || echo chars
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh expr.sh oldboy
chars
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh expr.sh 119
int
5)通过read读入持续等待输入
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat judge_int.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true
do
read -p "Pls input:" a
expr $a + 0 >/dev/null 2>&1
[ $? -eq 0 ] && echo int || echo chars
done
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh judge_int.sh
Pls input:oldgirl
chars
Pls input:76
int
Pls input:76sd
chars
6)通过expr判断文件扩展名是否符合要求
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat expr1.sh
#!/bin/bash
if expr "$1" : ".*\.pub" &>/dev/null
then
echo "you are using $1"
else
echo "Pls use *.pub file"
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh expr1.sh ttt.pub
you are using ttt.pub
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh expr1.sh ttt.py
Pls use *.pub file
7)使用expr命令实现ssh服务自带的ssh-copy-id公钥分发脚本
[root@codis-178 ~]# sed -n '10,20p' which /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id
sed: can't read which: No such file or directory
if [ "-i" = "$1" ]; then
shift
# check if we have 2 parameters left, if so the first is the new ID file
if [ -n "$2" ]; then
if expr "$1" : ".*\.pub" > /dev/null ; then
ID_FILE="$1"
else
ID_FILE="$1.pub"
fi
shift # and this should leave $1 as the target name
fi
8)通过expr计算字符串长度
[root@codis-178 ~]# char="I am oldboy"
[root@codis-178 ~]# expr length "$char"
11
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo ${char}
I am oldboy
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo ${char}|wc -L
11
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo ${char}|awk '{print length($0)}'
11
9)请编写shell脚本,打印下面语句中字符数不大于6的单词
I am oldboy linux welcome to our training
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat word_length.sh
#!/bin/bash
for n in I am oldboy linux welcome to our training
do
if [ `expr length $n` -le 6 ]
then
echo $n
fi
done
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh word_length.sh
I
am
oldboy
linux
to
our
(4)bc命令
Linux内部计算器
[root@codis-178 ~]# bc
bc 1.06.95
Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
For details type `warranty'.
1+1
2
3*3
9
1)将bc用在命令行实现运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo 3+5|bc
8
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo 3.3+5.6|bc
8.9
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo 7.28-5.62|bc
1.66
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo "scale=2;355/113"|bc # scale保留几位小数
3.14
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo "scale=4;355/113"|bc
3.1415
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=5
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=`echo $i+6|bc`
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
11
2)通过一条命令计算输出1+2+3+...+10的表达式,并计算结果
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo `seq -s '+' 10`=`seq -s "+" 10|bc`
1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10=55
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo `seq -s '+' 10`=$((`seq -s "+" 10`))
1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10=55
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo `seq -s "+" 10`=`seq -s " + " 10|xargs expr`
1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9+10=55
(5)awk实现计算
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo "7.73 3.854" |awk '{print ($1-$2)}'
3.876
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo "367 131" |awk '{print ($1-3)/$2}'
2.77863
(6)$[]符号的运算
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=5
[root@codis-178 ~]# i=$[i+6]
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $i
11
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $[2*3]
6
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $[3%5]
3
打印数学杨辉三角
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat shuxue.sh
#!/bin/bash
if (test -z $1);then
read -p "Input Max Lines:" MAX
else
MAX=$1
fi
i=1
while [ $i -le $MAX ]
do
j=1
while [ $j -le $i ]
do
f=$[i-1]
g=$[j-1]
if [ $j -eq $i ] || [ $j -eq 1 ];then
declare SUM_${i}_$j=1
else
declare A=$[SUM_${f}_$j]
declare B=$[SUM_${f}_$g]
declare SUM_${i}_$j=`expr $A + $B`
fi
echo -en $[SUM_${i}_$j]" "
let j++
done
echo
let i++
done
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh shuxue.sh
Input Max Lines:4
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
2.基于Shell变量输入read命令的运算
(1)read命令
语法格式:read [参数] [变量名]
参数:
- -p prompt 设置提示信息
- -t timeout 设置输入等待时间,单位秒
[root@codis-178 ~]# read -t 10 -p "Pls input one num:" num
Pls input one num:18
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $num
18
[root@codis-178 ~]# read -t 10 -p "Pls input two num:" a1 a2
Pls input two num:5 6
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a1
5
[root@codis-178 ~]# echo $a2
6
(2)以read命令读取及传参的综合案例
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat read_size01.sh
#!/bin/bash
read -t 15 -p "Please input two number:" a b
[ ${#a} -le 0 ] && {
echo "the first num is null"
exit 1
}
[ ${#b} -le 0 ] && {
echo "the second num is null"
exit 1
}
expr $a + 1 &>/dev/null
RETVAL_A=$?
expr $b + 1 &>/dev/null
RETVAL_B=$?
if [ $RETVAL_A -ne 0 -o $RETVAL_B -ne 0 ];then
echo "one of the num is not num,pls input again."
exit 1
fi
echo "a-b=$(($a-$b))"
echo "a+b=$(($a+$b))"
echo "a*b=$(($a*$b))"
echo "a/b=$(($a/$b))"
echo "a**b=$(($a**$b))"
echo "a%b=$(($a%$b))"
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh read_size01.sh
Please input two number:qq
the second num is null
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh read_size01.sh
Please input two number:12 6
a-b=6
a+b=18
a*b=72
a/b=2
a**b=2985984
a%b=0
通过传参方式
[root@codis-178 ~]# cat read_size02.sh
#!/bin/bash
a=$1
b=$2
Usage(){
echo $"USAGE:sh $0 num1 num2"
exit 1
}
if [ $# -ne 2 ];then
Usage
fi
expr $a + 1 >/dev/null 2>&1
[ $? -ne 0 ] && Usage
echo "a-b=$(($a-$b))"
echo "a+b=$(($a+$b))"
echo "a*b=$(($a*$b))"
echo "a**b=$(($a**$b))"
if [ $b -eq 0 ]
then
echo "your input does not allow to run"
echo "a/b =error"
echo "a%b =error"
else
echo "a/b =$(($a/$b))"
echo "a%b =$(($a%$b))"
fi
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh read_size02.sh
USAGE:sh read_size02.sh num1 num2
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh read_size02.sh 7 old
USAGE:sh read_size02.sh num1 num2
[root@codis-178 ~]# sh read_size02.sh 7 3
a-b=4
a+b=10
a*b=21
a**b=343
a/b =2
a%b =1
Shell编程之运算的更多相关文章
- shell编程系列5--数学运算
shell编程系列5--数学运算 方法1 expr $num1 operator $num2 方法2 $(($num1 operator $num2)) expr操作符对照表1 操作符 含义 num1 ...
- Shell编程菜鸟基础入门笔记
Shell编程基础入门 1.shell格式:例 shell脚本开发习惯 1.指定解释器 #!/bin/bash 2.脚本开头加版权等信息如:#DATE:时间,#author(作者)#mail: ...
- Linux Shell编程基础
在学习Linux BASH Shell编程的过程中,发现由于不经常用,所以很多东西很容易忘记,所以写篇文章来记录一下 ls 显示当前路径下的文件,常用的有 -l 显示长格式 -a 显示所有包括隐 ...
- 【转载】shell编程——if语句 if -z -n -f -eq -ne -lt
shell编程中条件表达式的使用 if 条件then Commandelse Commandfi 别忘了这个结尾 If语句忘了结尾fites ...
- shell编程基础练习
shell作为一个人机交互的接口,在Linux中发挥着很大的作用,而shell编程则是减轻系统工程师工作的利器,这里总结一下shell编程的主要内容(趁着程序运行的空档). 本文的基本结构是shell ...
- Linux Shell编程变量赋值和引用
我们可以使用任意一种文字编辑器,比如gedit.kedit.emacs.vi等来编写shell脚本,它必须以如下行开始(必须放在文件的第一行): #!/bin/sh ... 注意:最好使用“! ...
- shell编程基础(5)---循环指令
while类型的循环 while类型的循环是不定循环的一种,每一次循环都会验证给出的循环条件,判断是否要进行下一次循环.linux中while循环的写法和c语言中很想,但是条件给出的方式有些区别. 首 ...
- linux中shell编程
shell编程 1 echo -e 识别\转义符 \a \b \t \n \x十六进制 \0八进制 等等 #!/bin/bash echo -e "hello world" 执行脚 ...
- linux —— shell 编程(文本处理)
导读 本文为博文linux —— shell 编程(整体框架与基础笔记)的第4小点的拓展.(本文所有语句的测试均在 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 上进行) 目录 基本文本处理 流编辑器sed aw ...
随机推荐
- 第一百七十四节,jQuery,Ajax进阶
jQuery,Ajax进阶 学习要点: 1.加载请求 2.错误处理 3.请求全局事件 4.JSON 和 JSONP 5.jqXHR 对象 在 Ajax 课程中,我们了解了最基本的异步处理方式.本章,我 ...
- staticmethod classmethod修饰符
一.staticmethod(function) Return a static method for function.A static method does not receive an imp ...
- 操作XML-dom4j
首先是到dom4j的官网dom4j文件包,下载之后解压如下所示. 在根目录中,找到dom4j-1.6.1jar包,加入到eclipse中的lib文件下,最后build path一下,即可使用相关的方法 ...
- day8笔记
一.上节回顾 1,id() 内存地址2, == 比较的是值 is 比较的是内存地址 数字,字符串,有小数据池, #内存地址一样的 int -5--256 str:1,不能有空格. 2,长度不能超过20 ...
- python 推荐算法
每个人都会有这样的经历:当你在电商网站购物时,你会看到天猫给你弹出的“和你买了同样物品的人还买了XXX”的信息:当你在SNS社交网站闲逛时,也会看到弹出的“你可能认识XXX“的信息:你在微博添加关注人 ...
- iOS开发笔记--如何实现程序长时间未操作退出
我们使用金融软件经常会发现手机锁屏或者长时间未操作就会退出程序或者需要重新输入密码等情况.下面让我们看一下如何实现这种功能.我们知道iOS有一个事件循环机制,也就是大家所说的runloop.我们在对程 ...
- 高通Quick Charge高速充电原理分析
1 QC 2.0 1.1 高通Quick Charge 2.0 高速充电原理分析 高通的QC2.0高速充电须要手机端和充电器都要支持才行. 当将充电器端通过数据线连到手机上时,充电器默认的是将D+和D ...
- codevs2894、2837、1669、2503、3231
6.25动态规划之背包回顾 2894 Txx考试 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 32000 KB 题目等级 : 黄金 Gold 题解 题目描述 Description Txx是一个 ...
- ACM至大二省赛小结
大一进acm坑的,大一上就学了个c,下才学c++,不过 c 学完后学 c++ 感觉很简单,应该是大一下开学左右才开始刷题的,前面都在水???然后因为acm协会有各种月赛校赛什么的,班主任的提醒较多,所 ...
- EasyNVR现场部署搭配EasyNVS云端集中控制应用于幼儿园直播场景的最佳方案!
在之前的介绍中,我们已经介绍了很多EasyNVR成功应用于幼儿园类教育直播的场景,例如<EasyDarwin幼教云视频平台在幼教平台领域大放异彩!>.<基于EasyDarwin云视频 ...
