Codeforces 716 E Digit Tree
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
ZS the Coder has a large tree. It can be represented as an undirected connected graph of n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1edges between them. There is a single nonzero digit written on each edge.
One day, ZS the Coder was bored and decided to investigate some properties of the tree. He chose a positive integer M, which is coprime to 10, i.e. 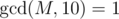 .
.
ZS consider an ordered pair of distinct vertices (u, v) interesting when if he would follow the shortest path from vertex u to vertex v and write down all the digits he encounters on his path in the same order, he will get a decimal representaion of an integer divisible by M.
Formally, ZS consider an ordered pair of distinct vertices (u, v) interesting if the following states true:
- Let a1 = u, a2, ..., ak = v be the sequence of vertices on the shortest path from u to v in the order of encountering them;
- Let di (1 ≤ i < k) be the digit written on the edge between vertices ai and ai + 1;
- The integer
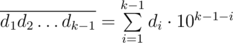 is divisible by M.
is divisible by M.
Help ZS the Coder find the number of interesting pairs!
The first line of the input contains two integers, n and M (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ M ≤ 109, 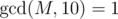 ) — the number of vertices and the number ZS has chosen respectively.
) — the number of vertices and the number ZS has chosen respectively.
The next n - 1 lines contain three integers each. i-th of them contains ui, vi and wi, denoting an edge between vertices ui and vi with digit wi written on it (0 ≤ ui, vi < n, 1 ≤ wi ≤ 9).
Print a single integer — the number of interesting (by ZS the Coder's consideration) pairs.
6 7
0 1 2
4 2 4
2 0 1
3 0 9
2 5 7
7
5 11
1 2 3
2 0 3
3 0 3
4 3 3
8 虽然不是很难想但是差点调死我hhhhh
首先这道题和常规点分治不太一样的地方是,普通的点分治一般是无向路径,我们往往不用考虑起点和终点而是直接考虑路径的两个端点就行了。
但是本题是有向路径,不同的方向意味着不同的数字。 而且本题还要一个坑爹的地方是知道终点好找起点,但是知道起点不好找终点。。。。。
当然有两种解决方法:
1.对于当前的重心选任意两条路径统计一遍,再把在同一颗子树内的减掉。
2.考虑到起点要么比终点先被扫到,要么晚被扫到,那么我们就正反两遍常规的calc,这样还不用去重。 我就是用的第二种方法。。。 然后千万别忘了起点或终点是重心的情况,,,,但这样不太可能,因为这样例都过不了hhhh 对于点分的每层我们用map记录一下起点的情况,然后用扫到的终点更新答案。
至于怎么更新答案,就是一个式子,推一下就好了也不难hhhh 当然如果你把向下和向上的路径写反了(就像一开始的我)是要调很久的hhhh,因为样例里并没有长度>=3的路径。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define maxn 100005
using namespace std;
map<int,int> mmp;
int ci[maxn],n,m,num=,b[maxn];
int to[maxn*],ne[maxn*];
int hd[maxn],sz,minn,root;
int d[maxn],tot,ni[maxn];
int siz[maxn],val[maxn*];
ll ans;
bool done[maxn]; inline void add(int uu,int vv,int ww){
to[++num]=vv,ne[num]=hd[uu],hd[uu]=num,val[num]=ww;
} void froot(int x,int fa){
siz[x]=;
int bal=;
for(int i=hd[x];i;i=ne[i]) if(!done[to[i]]&&to[i]!=fa){
froot(to[i],x);
siz[x]+=siz[to[i]];
bal=max(bal,siz[to[i]]);
} bal=max(bal,sz-siz[x]);
if(bal<minn) minn=bal,root=x;
} int fsiz(int x,int fa){
int an=;
for(int i=hd[x];i;i=ne[i]) if(!done[to[i]]&&to[i]!=fa){
an+=fsiz(to[i],x);
}
return an;
} void dfs(int x,int fa,int dep,int dx,int dy,int tmp){
int tox=(ll)(m-dy)*(ll)ni[dep]%m;
if(mmp.count(tox)) ans+=(ll)mmp[tox];
if(tmp){
if(!dx) ans++;
if(!dy) ans++;
} d[++tot]=dx; for(int i=hd[x];i;i=ne[i]) if(!done[to[i]]&&to[i]!=fa){
dfs(to[i],x,dep+,((ll)dx+(ll)val[i]*(ll)ci[dep])%m,((ll)dy*10ll+(ll)val[i])%m,tmp);
}
} inline void calc(int pos,int va,int tmp){
int pre=tot+;
dfs(pos,pos,,va,va,tmp);
for(;pre<=tot;pre++){
if(!mmp.count(d[pre])) mmp[d[pre]]=;
else mmp[d[pre]]++;
}
} inline void work(int x,int trsiz){
sz=trsiz,minn=<<;
froot(x,x);
done[root]=; int len=;
for(int i=hd[root];i;i=ne[i]) if(!done[to[i]]){
b[++len]=i;
calc(to[i],val[i],);
} mmp.clear(),tot=; for(;len;len--){
calc(to[b[len]],val[b[len]],);
} mmp.clear(),tot=;
for(int i=hd[root];i;i=ne[i]) if(!done[to[i]]){
work(to[i],fsiz(to[i],to[i]));
}
} void gcd(int aa,int bb,ll &xx,ll &yy){
if(!bb){
xx=,yy=;
return;
} gcd(bb,aa%bb,yy,xx);
yy-=xx*(ll)(aa/bb);
} inline int get_ni(int x){
ll xx,yy;
gcd(x,m,xx,yy);
return (xx+m)%m;
} int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
ci[]=ni[]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) ci[i]=(ll)ci[i-]*10ll%m,ni[i]=get_ni(ci[i]);
//printf("%d %d %d\n",i,ci[i],ni[i]); int uu,vv,ww;
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d",&uu,&vv,&ww),uu++,vv++;
ww%=m;
add(uu,vv,ww),add(vv,uu,ww);
} work(,n); cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
Codeforces 716 E Digit Tree的更多相关文章
- 【Codeforces 715C】Digit Tree(点分治)
Description 程序员 ZS 有一棵树,它可以表示为 \(n\) 个顶点的无向连通图,顶点编号从 \(0\) 到 \(n-1\),它们之间有 \(n-1\) 条边.每条边上都有一个非零的数字. ...
- 【题解】Digit Tree
[题解]Digit Tree CodeForces - 716E 呵呵以为是数据结构题然后是淀粉质还行... 题目就是给你一颗有边权的树,问你有多少路径,把路径上的数字顺次写出来,是\(m\)的倍数. ...
- 【Codeforces715C&716E】Digit Tree 数学 + 点分治
C. Digit Tree time limit per test:3 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input ...
- Codeforces 461B Appleman and Tree(木dp)
题目链接:Codeforces 461B Appleman and Tree 题目大意:一棵树,以0节点为根节点,给定每一个节点的父亲节点,以及每一个点的颜色(0表示白色,1表示黑色),切断这棵树的k ...
- Codeforces 1129 E.Legendary Tree
Codeforces 1129 E.Legendary Tree 解题思路: 这题好厉害,我来复读一下官方题解,顺便补充几句. 首先,可以通过询问 \(n-1\) 次 \((S=\{1\},T=\{ ...
- Codeforces 280C Game on tree【概率DP】
Codeforces 280C Game on tree LINK 题目大意:给你一棵树,1号节点是根,每次等概率选择没有被染黑的一个节点染黑其所有子树中的节点,问染黑所有节点的期望次数 #inclu ...
- Codeforces A. Game on Tree(期望dfs)
题目描述: Game on Tree time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- Codeforces Round #781(C. Tree Infection)
Codeforces Round #781 C. Tree Infection time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megab ...
- [Codeforces 715C] Digit Tree
[题目链接] https://codeforces.com/contest/715/problem/C [算法] 考虑点分治 一条路径(x , y)合法当且仅当 : d(x) * 10 ^ dep(x ...
随机推荐
- final变量属性小记
final 修饰符对于类成员变量来说,具备语法上不可变的特性:对于类成员方法来说,具备语法上子类不可覆盖重写的特性(能被继承的前提下). 但 final 并不限制子类对父类被修饰声明的成员变量进行覆盖 ...
- POJ 1050 To the Max 二维最大子段和
To the MaxTime Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000KTotal Submissions: 52281 Accepted: 27633Description ...
- MyBatis对象关联关系----多对多的保存与查询
模拟情景: 对象:学生,课程 关系:一个学生可选多个课程,一门课程可被多个学生选择 一.保存 1.创建数据库表,student,course,student_course,其中student_cour ...
- 【BZOJ】1725: [Usaco2006 Nov]Corn Fields牧场的安排
[算法]状压DP [题解]对于上一行的每个状态,每行进行DFS. #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstrin ...
- linux软件管理(Vim编辑器使用) ——(七)
windows : .exe 安装 .卸载 安装: mysql.exe cc.exe 卸载 : 该软件唯一的标识 ,包名 alibaba android : *.apk 卸载 包 ...
- 如何加快Eclipse的启动速度?
http://it.taocms.org/12/6457.htm 浅析配置更快的Eclipse方法 What is the Metadata GC Threshold and how do I tun ...
- HDU1142 (Dijkstra+记忆化搜索)
A Walk Through the Forest Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Jav ...
- 搭建git for windows服务器(100%可以成功)【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/code_style/article/details/38764203 既然Git在linux下面非常好用,为什么还要搭建git windows的服务器 ...
- python的算法:二分法查找(2)--bisect模块
Python 有一个 bisect 模块,用于维护有序列表.bisect 模块实现了一个算法用于插入元素到有序列表.在一些情况下,这比反复排序列表或构造一个大的列表再排序的效率更高.Bisect 是二 ...
- 在表达式和脚本中将bean实例暴露出来
默认情况下,在activiti.cfg.xml中的所有bean和Spring配置文件中的所有bean都可以用于表达式和脚本.如果要限制配置文件中的bean的可见性,可以在流程引擎配置文件中配置一个名为 ...
