2.5 References & Borrowing
Here is how you would define and use a calculate_length function that has a reference to an object as a parameter instead of taking ownership of the value:
- [root@itoracle test]# cargo new references
- Created binary (application) `references` package
- [root@itoracle test]# cd references/
- [root@itoracle references]# vim src/main.rs
- fn main() {
- let s1 = String::from("wa ka ka ");
- let _len = get_length(&s1);
- println!("The length of '{}' is {}",s1,_len);
- }
- fn get_length(ss: &String) -> usize{
- ss.len()
- }
- [root@itoracle references]# cargo run
- Compiling references v0.1.0 (/usr/local/automng/src/rust/test/references)
- Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in .50s
- Running `target/debug/references`
- The length of 'wa ka ka ' is
These ampersands are references, and they allow you to refer to some value without taking ownership of it.
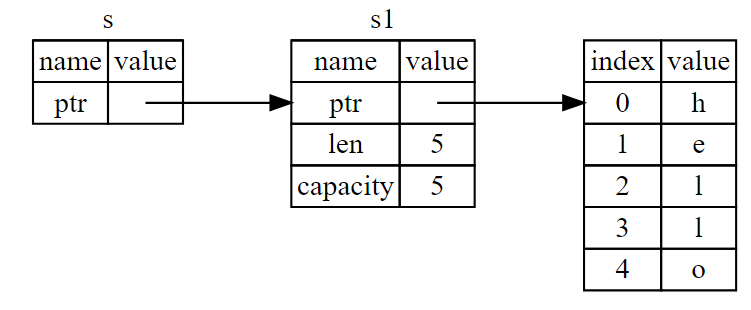
The &s1 syntax lets us create a reference that refers to the value of s1 but does not own it. Because it does not own it, the value it points to will not be dropped when the reference goes out of scope.
Likewise, the signature of the function uses & to indicate that the type of the parameter s is a reference. Let’s add some explanatory annotations:
- fn get_length(s: &String) -> usize { // s is a reference to a String
- s.len()
- } // Here, s goes out of scope. But because it does not have ownership of what
- // it refers to, nothing happens.
如果使用ownership方式求字符串长度,s1的作用范围就立即变化,引用的方式不会使变量作用域发生变化,以下是ownership的实现方式
- fn main() {
- let s1 = String::from("wa ka ka ");
- let _len = get_length(s1); //基于ownership 时s1 move到了方法中,作用域虽然没有变,但后续不能再使用s1变量了
- // println!("The length of '{}' is {}",s1,_len);
- println!("The length is {}",_len);
- }
- fn get_length(ss: String) -> usize{
- ss.len()
- }
Mutable References
- fn main() {
- let mut s1 = String::from("wa ka ka ");
- change(&mut s1);
- println!("s1={}",s1);
- }
- fn change(my_str: &mut String){
- my_str.push_str("!!!");
- }
- [root@itoracle references]# cargo run
- Compiling references v0.1.0 (/usr/local/automng/src/rust/test/references)
- Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in .06s
- Running `target/debug/references`
- s1=wa ka ka !!!
First, we had to change s to be mut. Then we had to create a mutable reference with &mut s and accept a mutable reference with some_string: &mut String.
But mutable references have one big restriction: you can have only one mutable reference to a particular piece of data in a particular scope. This code will fail:
下面代码是错误的
- let mut s = String::from("hello");
- let r1 = &mut s;
- let r2 = &mut s;
- println!("{}, {}", r1, r2);
This restriction allows for mutation but in a very controlled fashion. It’s something that new Rustaceans struggle with, because most languages let you mutate whenever you’d like.
The benefit of having this restriction is that Rust can prevent data races at compile time. A data raceis similar to a race condition and happens when these three behaviors occur:
- Two or more pointers access the same data at the same time.
- At least one of the pointers is being used to write to the data.
- There’s no mechanism being used to synchronize access to the data.
Data races cause undefined behavior and can be difficult to diagnose and fix when you’re trying to track them down at runtime; Rust prevents this problem from happening because it won’t even compile code with data races!
As always, we can use curly brackets to create a new scope, allowing for multiple mutable references, just not simultaneous ones:
- let mut s = String::from("hello");
- {
- let r1 = &mut s;
- } // r1 goes out of scope here, so we can make a new reference with no problems.
- let r2 = &mut s;
下一次的可变引用,要建立在上一次的引用“不可用”的基础的上,下面的做法也可以
这里的 不可用,是指作用域可能还没消失,但运行时不可调用了,代码中不可使用了
- fn main() {
- let mut s1 = String::from("wa ka ka ");
- change(&mut s1);
- println!("s1={}",s1);
- {
- let _r1 = &mut s1;
- } // r1 goes out of scope here, so we can make a new reference with no problems.
- let _r2 = &mut s1;
- change(&mut s1); //_r2在可变s1被第二次引用时不可再使用,后面不能再对_r2使用了
- }
- fn change(my_str: &mut String){
- my_str.push_str("!!!");
- }
对于可变引用,如果代码中有一个以上的地方引用,那就表示至少有两处地方可以对该变量修改,不符合rust可变变量只能有一处地方可修改的规则,编辑阶段就会报错。
一个可变变量同一作用域中只能有一处可用引用,新的引用生效时,已有引用失效,后续无法再次使用。
将已经用过一次的可变引用以方法参数传递时,之前对该可变变量的引用自动失效,只要后续不再使用之前的引用变量,代码可以正常运行;
如果是直接将可变引用第二次赋值到新变量,则是编译阶段报错。
- fn main() {
- let mut s1 = String::from("wa ka ka ");
- change(&mut s1);
- println!("s1={}",s1);
- {
- let _r1 = &mut s1;
- } // r1 goes out of scope here, so we can make a new reference with no problems.
- let _r2 = &mut s1;
- change(&mut s1);
- let r3 = &s1; // no problem
- let r4 = &s1; // no problem
- let r5 = &mut s1; //前面还有引用(_r2)未失效,这里会报错
- println!("{},{}",r3,r4);
- }
- fn change(my_str: &mut String){
- my_str.push_str("!!!");
- }
- error[E0502]: cannot borrow `s1` as mutable because it is also borrowed as immutable
- --> src/main.rs::
- |
- | let r3 = &s1; // no problem
- | --- immutable borrow occurs here
- | let r4 = &s1; // no problem
- | let r5 = &mut s1;
- | ^^^^^^^ mutable borrow occurs here
- | println!("{},{}",r3,r4);
- | -- immutable borrow later used here
- error: aborting due to previous error
- For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0502`.
- error: Could not compile `references`.
2.5 References & Borrowing的更多相关文章
- 3.5 Rust Generic Types, Traits, and Lifetimes
Every programming language has tools for effectively handling the duplication of concepts. In Rust, ...
- JavaScript Patterns 6.7 Borrowing Methods
Scenario You want to use just the methods you like, without inheriting all the other methods that yo ...
- Oracle Created Database Users: Password, Usage and Files References (文档 ID 160861.1)
This document is no longer actively maintained, for info on specific (new) users in recent product e ...
- Atitit java方法引用(Method References) 与c#委托与脚本语言js的函数指针
Atitit java方法引用(Method References) 与c#委托与脚本语言js的函数指针 1.1. java方法引用(Method References) 与c#委托与脚本语言js ...
- object references an unsaved transient instance - save the transient instance before flushing错误
异常1:not-null property references a null or transient value解决方法:将“一对多”关系中的“一”方,not-null设置为false(参考资料: ...
- C++ 之 const references
extraction from The C++ Programming Language 4th. ed., Section 7.7 References, Bjarne Stroustrup To ...
- Notice: Only variable references should be returned by reference(PHP版本兼容性问题)
摘自:http://sushener.spaces.live.com/blog/cns!BB54050A5CFAFCDD!435.entry PHP5一个很让人恼火的一点就是BC(向后兼容)不是很理想 ...
- [翻译]Understanding Weak References(理解弱引用)
原文 Understanding Weak References Posted by enicholas on May 4, 2006 at 5:06 PM PDT 译文 我面试的这几个人怎么这么渣啊 ...
- ManyToMany【项目随笔】关于异常object references an unsaved transient instance
在保存ManyToMany 时出现异常: org.springframework.dao.InvalidDataAccessApiUsageException: org.hibernate.Tran ...
随机推荐
- Android Hander、Looper、Message三者之间的联系
1.首先Looper.prepare()在本线程中保存一个Looper实例,然后该实例中保存一个MessageQueue对象:因为Looper.prepare()在一个线程中只能调用一次,所以Mess ...
- 记.gitignore的一次惊心动魄
git rm -r --cached . #清除缓存 git add . #重新trace file git commit -m "update .gitignore" #提交和 ...
- windows phone制作引导页
适用于WP7 WP8+ 源码下载撸这里 制作动画gif小软件下载 小技巧 ①图片是纯色背景:将页面设置跟图片背景一样颜色 ②图片是渐变or其他,切图时候:单独切背景(页面设置这个为背景)跟图片里面元素 ...
- c#读取数据库内容
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.T ...
- [.net 多线程]SpinWait
<CLR via C#>读书笔记-线程同步(四) 混合线程同步构造简介 之前有用户模式构造和内核模式构造,前者快速,但耗费CPU:后者可以阻塞线程,但耗时.耗资源.因此.NET会有一些混合 ...
- [.net 多线程]Barrier
当需要[一组任务]并行地运行一连串的阶段,但是每一个阶段都要等待所有他任务完成前一阶段之后才能开始,可以通过Barrier实例来同步这一类协同工作.Barrier初始化后,将等待特定数量的信号到来,这 ...
- Unity5.5.2 CD旋转 顺时针逆时针
UGUI 下 Sprite_CD 在Inspector下 Image(Script) 下 Clock wise 勾选 决定 CD是顺时针还是逆时针 默认是顺时针 勾选则为逆时针
- Navicat premium连不上Oracle的问题解决
1.ORA-28547: 这是因为oci.dll版本不对.Navicat本地的OCI版本与Oracle服务器服务器不符造成的. 或者 打开Navicat premium客户端:Tool->Opt ...
- Kubernetes 集群部署(3) -- Flannel 集群
1. 下载包 wget https://github.com/coreos/flannel/releases/download/v0.11.0/flannel-v0.11.0-linux-amd64. ...
- 【转】分析.net中的object sender与EventArgs e
源地址:http://blog.csdn.net/feihu19851111/article/details/7523118
