Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A, B , C 水, map ,拓扑
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Misha and Vasya participated in a Codeforces contest. Unfortunately, each of them solved only one problem, though successfully submitted it at the first attempt. Misha solved the problem that costs a points and Vasya solved the problem that costs b points. Besides, Misha submitted the problem c minutes after the contest started and Vasya submitted the problem d minutes after the contest started. As you know, on Codeforces the cost of a problem reduces as a round continues. That is, if you submit a problem that costs p points tminutes after the contest started, you get 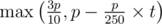 points.
points.
Misha and Vasya are having an argument trying to find out who got more points. Help them to find out the truth.
The first line contains four integers a, b, c, d (250 ≤ a, b ≤ 3500, 0 ≤ c, d ≤ 180).
It is guaranteed that numbers a and b are divisible by 250 (just like on any real Codeforces round).
Output on a single line:
"Misha" (without the quotes), if Misha got more points than Vasya.
"Vasya" (without the quotes), if Vasya got more points than Misha.
"Tie" (without the quotes), if both of them got the same number of points.
500 1000 20 30
Vasya
1000 1000 1 1
Tie
1500 1000 176 177
Misha
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
int main()
{
int a,b,c,d;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d);
int m1=max(*a/,a-(a*c)/);
int m2=max(*b/,b-(b*d)/);
if(m1>m2)
printf("Misha\n");
else if(m1==m2)
printf("Tie\n");
else
printf("Vasya\n");
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Misha hacked the Codeforces site. Then he decided to let all the users change their handles. A user can now change his handle any number of times. But each new handle must not be equal to any handle that is already used or that was used at some point.
Misha has a list of handle change requests. After completing the requests he wants to understand the relation between the original and the new handles of the users. Help him to do that.
The first line contains integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1000), the number of handle change requests.
Next q lines contain the descriptions of the requests, one per line.
Each query consists of two non-empty strings old and new, separated by a space. The strings consist of lowercase and uppercase Latin letters and digits. Strings old and new are distinct. The lengths of the strings do not exceed 20.
The requests are given chronologically. In other words, by the moment of a query there is a single person with handle old, and handlenew is not used and has not been used by anyone.
In the first line output the integer n — the number of users that changed their handles at least once.
In the next n lines print the mapping between the old and the new handles of the users. Each of them must contain two strings, old andnew, separated by a space, meaning that before the user had handle old, and after all the requests are completed, his handle is new. You may output lines in any order.
Each user who changes the handle must occur exactly once in this description.
5
Misha ILoveCodeforces
Vasya Petrov
Petrov VasyaPetrov123
ILoveCodeforces MikeMirzayanov
Petya Ivanov
3
Petya Ivanov
Misha MikeMirzayanov
Vasya VasyaPetrov123
思路:map模拟下就好;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e3+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
string a[N];
string b[N];
map<string,string>m;
int main()
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
for(int i=x;i>=;i--)
{
m[a[i]]=b[i];
while(m[b[i]]!="")
{
m[a[i]]=m[b[i]];
m[b[i]]="";
}
}
int ans=;
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
if(m[a[i]]!="")
ans++;
cout<<ans<<endl;
for(int i=;i<=x;i++)
if(m[a[i]]!="")
cout<<a[i]<<" "<<m[a[i]]<<endl;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Let's define a forest as a non-directed acyclic graph (also without loops and parallel edges). One day Misha played with the forest consisting of n vertices. For each vertex v from 0 to n - 1 he wrote down two integers, degreev and sv, were the first integer is the number of vertices adjacent to vertex v, and the second integer is the XOR sum of the numbers of vertices adjacent to v (if there were no adjacent vertices, he wrote down 0).
Next day Misha couldn't remember what graph he initially had. Misha has values degreev and sv left, though. Help him find the number of edges and the edges of the initial graph. It is guaranteed that there exists a forest that corresponds to the numbers written by Misha.
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 216), the number of vertices in the graph.
The i-th of the next lines contains numbers degreei and si (0 ≤ degreei ≤ n - 1, 0 ≤ si < 216), separated by a space.
In the first line print number m, the number of edges of the graph.
Next print m lines, each containing two distinct numbers, a and b (0 ≤ a ≤ n - 1, 0 ≤ b ≤ n - 1), corresponding to edge (a, b).
Edges can be printed in any order; vertices of the edge can also be printed in any order.
3
2 3
1 0
1 0
2
1 0
2 0
2
1 1
1 0
1
0 1
The XOR sum of numbers is the result of bitwise adding numbers modulo 2. This operation exists in many modern programming languages. For example, in languages C++, Java and Python it is represented as "^", and in Pascal — as "xor".
思路:总是有度数为1的节点,裸拓扑;
坑点,多个联通块;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=1e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+;
vector<int>v[N];
int du[N];
int sum[N];
priority_queue<int>q;
int main()
{
int n;
ll ans=;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&du[i],&sum[i]);
ans+=du[i];
if(du[i]==)
q.push(i);
}
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.top();
q.pop();
if(du[x]==)
continue;
du[x]--;
v[x].push_back(sum[x]);
du[sum[x]]--;
sum[sum[x]]^=x;
if(du[sum[x]]==)
q.push(sum[x]);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans/);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int t=;t<v[i].size();t++)
printf("%d %d\n",i,v[i][t]);
}
return ;
}
/*
4
1 1
1 0
1 3
1 2
*/
Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A, B , C 水, map ,拓扑的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A B C 模拟 stl 拓扑排序
A. Contest time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2)C. Misha and Forest(拓扑排序)
传送门 Description Let's define a forest as a non-directed acyclic graph (also without loops and parall ...
- 图论/位运算 Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) C. Misha and Forest
题目传送门 /* 题意:给出无向无环图,每一个点的度数和相邻点的异或和(a^b^c^....) 图论/位运算:其实这题很简单.类似拓扑排序,先把度数为1的先入对,每一次少一个度数 关键在于更新异或和, ...
- 字符串处理 Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) B. Misha and Changing Handles
题目传送门 /* 题意:给出一系列名字变化,问最后初始的名字变成了什么 字符串处理:每一次输入到之前的找相印的名字,若没有,则是初始的,pos[m] 数组记录初始位置 在每一次更新时都把初始pos加上 ...
- 水题 Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) C. Misha and Forest
题目传送门 /* 题意:给出无向无环图,每一个点的度数和相邻点的异或和(a^b^c^....) 图论/位运算:其实这题很简单.类似拓扑排序,先把度数为1的先入对,每一次少一个度数 关键在于更新异或和, ...
- Codeforces Round #367 (Div. 2) A. Beru-taxi (水题)
Beru-taxi 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/706/problem/A Description Vasiliy lives at point (a, b ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem(水.......没做出来)+C题
Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) A. Sweet Problem A. Sweet Problem time limit per test 1 second memory ...
- Codeforces Round #334 (Div. 2) A. Uncowed Forces 水题
A. Uncowed Forces Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/604/pro ...
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div.1 B & Div.2 D) Misha and Permutations Summation --二分+树状数组
题意:给出两个排列,求出每个排列在全排列的排行,相加,模上n!(全排列个数)得出一个数k,求出排行为k的排列. 解法:首先要得出定位方法,即知道某个排列是第几个排列.比如 (0, 1, 2), (0, ...
随机推荐
- mac安装以及删除mysql5.7
关于msyql5.7,安装时最大的改变就是有了一个默认密码 我安装的是mysql-5.7.17-macos10.12-x86_64.dmg 和mysql-workbench-community-6.3 ...
- java 对list 排序
Comparable用Collections.sort方法对list排序有两种方法第一种是list中的对象实现Comparable接口,如下: /*** 根据order对User排序*/public ...
- linux磁盘清理
一.背景: 1.由于linux系统空间是由挂载磁盘得来的,但有时装系统时挂载/根目录空间不大,现仅清除用户下载的大文件 二.方法: 1.输入命令df -h显示当前磁盘挂载(包含剩余空间)情况这里写图片 ...
- php自定义函数: 文件大小转换成智能形式
function format_byte($filesize) { if($filesize >= 1073741824) { $filesize = round($filesize / 107 ...
- Python数据分析与挖掘所需的Pandas常用知识
Python数据分析与挖掘所需的Pandas常用知识 前言Pandas基于两种数据类型:series与dataframe.一个series是一个一维的数据类型,其中每一个元素都有一个标签.series ...
- 从1到N中1的个数
示例1,2...9,10,11中有四个1 int getNumber(int n) { int count = 0; int factor = 1; int low = 0; int cur = 0; ...
- gearman background后台job状态获取
GearmanClient background job有一个方法叫: public array GearmanClient::jobStatus ( string $job_handle ) Get ...
- loadrunner之脚本篇——代理录制
版本:Loadruner 11.0 A.PC端录制Web应用程序 步骤1:根据实际情况,选择对应的协议 本例中选择Web(HTTP/HTML),如下 步骤2:找到代理设置界面 点击 Start Rec ...
- iOS 9 的新功能 universal links
什么是 universal links: (通用链接) 一种能够方便的通过传统 HTTP 链接来启动 APP, 使用相同的网址打开web page和 APP的方式. 第一点,链接打开网址 顾名思义 第 ...
- 架构在APP和前端里的应用和演进
架构设计相关的理念.技术.实践,比如存储高可用.微服务.异地多活等,都是后端系统才会涉及.事实上确实也是如此,通常情况下我们讲架构设计,主要聚焦在后端系统,但这并不意味着 App.前端就没有架构设计了 ...
