08-----pymysql模块使用
pymysql的下载和使用
exctue() 之sql注入
增、删、改:conn.commit()
查:fetchone、fetchmany、fetchall
一、pytmysql的下载和使用
(1)pymysql 模块安装
- pip3 install pymysql
(2)pymysql的使用
- # 实现:使用Python实现用户登录,如果用户存在则登录成功(假设该用户已在数据库中)
- import pymysql
- user = input('请输入用户名:')
- pwd = input('请输入密码:')
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- #注意%s需要加引号
- sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%s' and pwd='%s'" %(user, pwd)
- print(sql)
- # 3.执行sql语句
- cursor.execute(sql)
- result=cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句,返回sql查询成功的记录数目
- print(result)
- # 关闭连接,游标和连接都要关闭
- cursor.close()
- conn.close()
- if result:
- print('登陆成功')
- else:
- print('登录失败')
二、excute()之sql注入
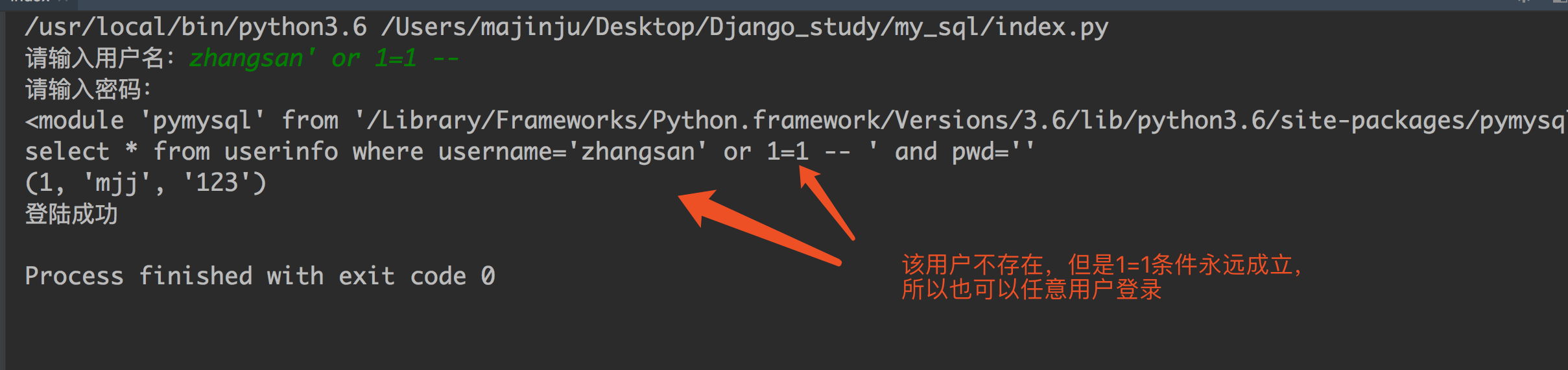
- 最后那一个空格,在一条sql语句中如果遇到select * from userinfo where username='mjj' -- asadasdas' and pwd='' 则--之后的条件被注释掉了(注意--后面还有一个空格)
- #1、sql注入之:用户存在,绕过密码
- mjj' -- 任意字符
- #2、sql注入之:用户不存在,绕过用户与密码
- xxx' or 1=1 -- 任意字符

解决办法:
- # 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接
- # sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(username,pwd)
- # print(sql)
- # result=cursor.execute(sql)
- #改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了)
- sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上
- result=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。
代码:
- #!C:/Python36/python3
- #-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
- import pymysql
- user = input('请输入用户名:')
- pwd = input('请输入密码:')
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',password = '',db='db4',charset='utf8')
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- sql = "select * from userinfo WHERE username=%s and pwd = %s"
- print(sql)
- # cursor.execute(sql)
- result = cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd])
- print(result)
- cursor.close()
- conn.close()
- if result:
- print("登录成功")
- else:
- print("登陆失败")
三、增、删、改:conn。commit()
commit() 方法:在数据库里增、删、改的时候,必须要进行提交,否则插入的数据不生效。
- import pymysql
- username = input('请输入用户名:')
- pwd = input('请输入密码:')
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- # 操作
- # 增
- # sql = "insert into userinfo(username,pwd) values (%s,%s)"
- # effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,(username,pwd))
- # 同时插入多条数据
# cursor.executemany(sql,[('李四','110'),('王五','119')])- # print(effect_row)
- # 改
- # sql = "update userinfo set username = %s where id = 2"
- # effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,username)
- # print(effect_row)
- # 删
- sql = "delete from userinfo where id = 2"
- effect_row = cursor.execute(sql)
- print(effect_row)
- #一定记得commit
- conn.commit()
- # 4.关闭游标
- cursor.close()
- # 5.关闭连接
- conn.close()
四、查:fetchone、fetchmany、fetchall
- fetchone():获取下一行数据,第一次为首行;
- fetchall():获取所有行数据源
- fetchmany():获取4行数据
使用 fetchone():
- import pymysql
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- sql = 'select * from userinfo'
- cursor.execute(sql)
- # 查询第一行的数据
- row = cursor.fetchone()
- print(row) # (1, 'mjj', '')
- # 查询第二行数据
- row = cursor.fetchone()
- print(row) # (3, '张三', '')
- # 4.关闭游标
- cursor.close()
- # 5.关闭连接
- conn.close()
使用 fetchall():
- import pymysql
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- sql = 'select * from userinfo'
- cursor.execute(sql)
- # 获取所有的数据
- rows = cursor.fetchall()
- print(rows)
- # 4.关闭游标
- cursor.close()
- # 5.关闭连接
- conn.close()
- #运行结果
- ((1, 'mjj', ''), (3, '张三', ''), (4, '李四', ''))
默认情况下,我们获取到的返回值是元组,只能看到每行的数据,却不知道每一列代表的是什么,这个时候可以使用以下方式来返回字典,每一行的数据都会生成一个字典:
- cursor = conn.cursor() #换成以下
- cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) #在实例化的时候,将属性cursor设置为
在 fetchone 示例中,在获取行数据的时候,可以理解开始的时候,有一个行指针指着第一行的上方,获取一行,它就向下移动一行,所以当行指针到最后一行的时候,就不能再获取到行的内容,所以我们可以使用如下方法来移动行指针:
- # 1.Python实现用户登录
- # 2.Mysql保存数据
- import pymysql
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
- sql = 'select * from userinfo'
- cursor.execute(sql)
- # 查询第一行的数据
- row = cursor.fetchone()
- print(row) # (1, 'mjj', '')
- # 查询第二行数据
- row = cursor.fetchone() # (3, '张三', '')
- print(row)
- cursor.scroll(-1,mode='relative') #设置之后,光标相对于当前位置往前移动了一行,所以打印的结果为第二行的数据
- row = cursor.fetchone()
- print(row)
- cursor.scroll(0,mode='absolute') #设置之后,光标相对于首行没有任何变化,所以打印的结果为第一行数据
- row = cursor.fetchone()
- print(row)
- # 4.关闭游标
- cursor.close()
- # 5.关闭连接
- conn.close()
- #结果如下
- {'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': ''}
- {'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': ''}
- {'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': ''}
- {'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': ''}
fetchmany():
- import pymysql
- # 1.连接
- conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
- # 2.创建游标
- cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
- sql = 'select * from userinfo'
- cursor.execute(sql)
- # 获取2条数据
- rows = cursor.fetchmany(2)
- print(rows)
- # 4.关闭游标
- # rows = cursor.fetchall()
- # print(rows)
- cursor.close()
- # 5.关闭连接
- conn.close()
- #结果如下:
- [{'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': '123'}, {'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': '110'}]
08-----pymysql模块使用的更多相关文章
- Python中操作mysql的pymysql模块详解
Python中操作mysql的pymysql模块详解 前言 pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同.但目前pymysql支持python3.x而后者不支持 ...
- python实战第一天-pymysql模块并练习
操作系统 Ubuntu 15.10 IDE & editor JetBrains PyCharm 5.0.2 ipython3 Python版本 python-3.4.3 安装pymysql模 ...
- pymysql 模块介绍
pymysql模块是python与mysql进行交互的一个模块. pymysql模块的安装: pymysql模块的用法: import pymysql user=input('user>> ...
- Mysql(六):数据备份、pymysql模块
一 IDE工具介绍 生产环境还是推荐使用mysql命令行,但为了方便我们测试,可以使用IDE工具 下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bpo5mqj 掌握: #1. 测试+链接 ...
- python如何使用pymysql模块
Python 3.x 操作MySQL的pymysql模块详解 前言pymysql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同.但目前pymysql支持python3.x而M ...
- MySQL之pymysql模块
MySQL之pymysql模块 import pymysql #s链接数据库 conn = pymysql.connect( host = '127.0.0.1', #被连接数据库的ip地址 po ...
- PyMySQL模块的使用
PyMySQL介绍 PyMySQL是在Python3.x版本中用于连接MySQL服务器的一个库,Python2系列中则使用mysqldb.Django中也可以使用PyMySQL连接MySQL数据库. ...
- MySQL学习12 - pymysql模块的使用
一.pymysql的下载和使用 1.pymysql模块的下载 2.pymysql的使用 二.execute()之sql注入 三.增.删.改:conn.commit() 四.查:fetchone.fet ...
- 数据库入门-pymysql模块的使用
一.pymysql模块安装 由于本人的Python版本为python3.7,所以用pymysql来连接数据库(mysqldb不支持python3.x) 方法一: #在cmd输入 pip3 instal ...
- Python连接MySQL数据库之pymysql模块使用
安装PyMySQL pip install pymysql PyMySQL介绍 PyMySQL是在python3.x版本中用于连接MySQL服务器的一个库,2中则使用mysqldb. Django中也 ...
随机推荐
- 【摘自张宴的"实战:Nginx"】http auth baseic模块(打开页面需要密码验证)
location /admin { auth_basic "kingsoft"; auth_basic_user_file httppasswd; #密码文件的路径 默 ...
- python3-while与if
# Auther: Aaron Fan age_of_oldboy = 56 #定义一个while循环的起始判断值countcount = 0#当count小于3的情况下一直执行while循环whil ...
- win7 64位 [Microsoft][ODBC 驱动程序管理器] 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认
问题描述: VBA程序连接Access数据库,Excel中执行相关宏,提示[Microsoft][ODBC 驱动程序管理器] 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认 解决方案: 1.重新安装 AccessDa ...
- Windows下启动redis错误1067:进程意外中止
已解决: 在redis-64.3.0.503文件夹下新建一个空文件夹,命名为logs,如下图所示: 最后成功了 开启服务:redis-server --service-start
- Jquery 插件开发——citylinkage(省、市、县城市联动选择)
第一部分:背景 开发源于需求,本次城市联动选择插件算是我写插件的一个特例吧,不是我目前工作需要些的,算是兴趣驱使吧.之前呢,一直想写这个插件,然后错过了一个写这个插件的机会(这个得回顾到很久以前了. ...
- C#用GDI+解析Json文件绘制Chart
using System.Collections.Generic; namespace Chart { public class Program { static void Main(string[] ...
- Oracle SQL判断字符串是否在目标字符串中的函数
转自:http://dacoolbaby.iteye.com/blog/1772156 根据需求,写了一段方法. 用于识别以下的情况: 判断 字符串A 在用逗号分隔的字符串B中是否存在 如: v_s ...
- vue框架搭建的详细步骤(一)
在这里我们先快速的搭建一个vue的脚手架: (1).在安装vue的环境之前,安装NodeJS环境是必须的.可以使用node -v指令检查,需要保证安装了4.0版本以上的nodeJS环境. 没有安装的话 ...
- UVa_Live 3664(精度坑)
题意很好理解的贪心题,然而却卡疯了的精度坑. 再次理解一下double小数运算时可能导致的精度问题,本题为避免该问题可以将小数乘以100化为整数进行比较,输出的时候再除以100就ok: 思路也很好想, ...
- python安装出现的证书问题
1. pip install pyenv 安装时出现下图错误 Could not install packages due to an EnvironmentError: HTTPSConnectio ...
