分析AppClassLoader,ExtClassLoader 和URLClassLoader 的关系
测试代码:
class Hello
{
public String str = "Hello World";
public void fun()
{
System.out.println(str);
7 }
} public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Hello hello = new Hello();
hello.fun(); System.out.println("----------------------"); //Hello类的类加载器
ClassLoader classLoaderOfHello = Hello.class.getClassLoader(); System.out.println("Hello is Loaded by : "+classLoaderOfHello); 24 System.out.println("----------------------"); //Hello类的类加载器的Class对象
Class AppClazz = classLoaderOfHello.getClass(); //分析Hello类的类加载器的Class对象的类继承关系
while(AppClazz != null)
31 {
System.out.println(AppClazz); 34 AppClazz = AppClazz.getSuperclass();
35 } System.out.println("----------------------"); //取得扩展器加载器的类对象Class
Class ExtClazz = classLoaderOfHello.getParent().getClass(); while(ExtClazz != null)
{
System.out.println(ExtClazz); ExtClazz = ExtClazz.getSuperclass();
}
}
}
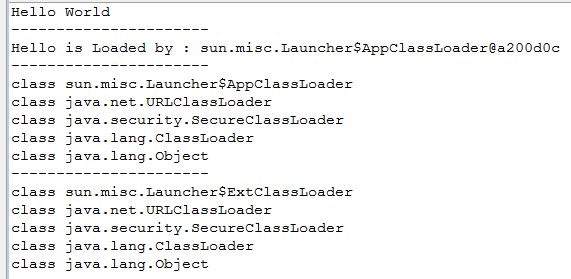
结论:
1. 用户自定义的类是由 应用(系统)类加载器AppClassLoader加载
2. 在”父亲委托机制”中,扩展类加载器ExtClassLoader是AppClassLoader的父亲,并不是继承关系,而是ExtClassLoader加载了AppClassLoader
3. AppClassLoader 和 ExtClassLoader 都扩展于 URLClassLoader加载器.
4. 也同时说明AppClassLoader而非继承ExtClassLoader.
继承关系:
java.lang.Object
--- java.lang.ClassLoader
--- java.security.SecureClassLoader
--- java.net.URLClassLoader
--- sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader
java.lang.Object
--- java.lang.ClassLoader
--- java.security.SecureClassLoader
--- java.net.URLClassLoader
--- sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader
其实很简单嘛,直接看AppClassLoader的源代码就可以了嘛,哈哈,终于找到了好东东,上
JDK7: http://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk7/
JDK6: http://download.java.net/openjdk/jdk6/
下载其源代码就可以了
现在直接来看其源代码:
/**
* The class loader used for loading from java.class.path.
* runs in a restricted security context.
*/
static class AppClassLoader extends URLClassLoader {
static {
ClassLoader.registerAsParallelCapable();
}
public static ClassLoader getAppClassLoader(final ClassLoader extcl)
throws IOException
{
final String s = System.getProperty("java.class.path");
final File[] path = (s == null) ? new File[0] : getClassPath(s);
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<AppClassLoader>() {
public AppClassLoader run() {
URL[] urls =
(s == null) ? new URL[0] : pathToURLs(path);
return new AppClassLoader(urls, extcl);
}
});
}
/*
* Creates a new AppClassLoader
*/
AppClassLoader(URL[] urls, ClassLoader parent) {
super(urls, parent, factory);
}
/**
* Override loadClass so we can checkPackageAccess.
*/
public Class loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
int i = name.lastIndexOf('.');
if (i != -1) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPackageAccess(name.substring(0, i));
}
}
return (super.loadClass(name, resolve));
}
/**
* allow any classes loaded from classpath to exit the VM.
*/
protected PermissionCollection getPermissions(CodeSource codesource)
{
PermissionCollection perms = super.getPermissions(codesource);
perms.add(new RuntimePermission("exitVM"));
return perms;
}
/**
* This class loader supports dynamic additions to the class path
* at runtime.
*
* @see java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation#appendToSystemClassPathSearch
*/
private void appendToClassPathForInstrumentation(String path) {
assert(Thread.holdsLock(this));
// addURL is a no-op if path already contains the URL
super.addURL( getFileURL(new File(path)) );
}
/**
* create a context that can read any directories (recursively)
* mentioned in the class path. In the case of a jar, it has to
* be the directory containing the jar, not just the jar, as jar
* files might refer to other jar files.
*/
private static AccessControlContext getContext(File[] cp)
throws java.net.MalformedURLException
{
PathPermissions perms =
new PathPermissions(cp);
ProtectionDomain domain =
new ProtectionDomain(new CodeSource(perms.getCodeBase(),
(java.security.cert.Certificate[]) null),
perms);
AccessControlContext acc =
new AccessControlContext(new ProtectionDomain[] { domain });
return acc;
}
}
哈,看了AppClassLoader的源代码后,大家明白了吧,AppClassLoader 继承了URLClassLoader,而且构造函数是直接调用URLClassLoader的构造
函数,loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)方法只是简单做了包的安全检查,然后就调用ClassLoader的 loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)方法了,其它的话,也是差不多..所以其功能和URLClassLoader差不多...
在ExtClassLoader也差不多,大家看看源代码就明了的:
/*
* Creates a new ExtClassLoader for the specified directories.
*/
public ExtClassLoader(File[] dirs) throws IOException {
super(getExtURLs(dirs), null, factory);
}
private static File[] getExtDirs() {
String s = System.getProperty("java.ext.dirs");
File[] dirs;
if (s != null) {
StringTokenizer st =
new StringTokenizer(s, File.pathSeparator);
int count = st.countTokens();
dirs = new File[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dirs[i] = new File(st.nextToken());
}
} else {
dirs = new File[0];
}
return dirs;
}
private static URL[] getExtURLs(File[] dirs) throws IOException {
Vector<URL> urls = new Vector<URL>();
for (int i = 0; i < dirs.length; i++) {
String[] files = dirs[i].list();
if (files != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < files.length; j++) {
if (!files[j].equals("meta-index")) {
File f = new File(dirs[i], files[j]);
urls.add(getFileURL(f));
}
}
}
}
URL[] ua = new URL[urls.size()];
urls.copyInto(ua);
return ua;
}
/*
* Searches the installed extension directories for the specified
* library name. For each extension directory, we first look for
* the native library in the subdirectory whose name is the value
* of the system property <code>os.arch</code>. Failing that, we
* look in the extension directory itself.
*/
public String findLibrary(String name) {
name = System.mapLibraryName(name);
URL[] urls = super.getURLs();
File prevDir = null;
for (int i = 0; i < urls.length; i++) {
// Get the ext directory from the URL
File dir = new File(urls[i].getPath()).getParentFile();
if (dir != null && !dir.equals(prevDir)) {
// Look in architecture-specific subdirectory first
// Read from the saved system properties to avoid deadlock
String arch = VM.getSavedProperty("os.arch");
if (arch != null) {
File file = new File(new File(dir, arch), name);
if (file.exists()) {
return file.getAbsolutePath();
}
}
// Then check the extension directory
File file = new File(dir, name);
if (file.exists()) {
return file.getAbsolutePath();
}
}
prevDir = dir;
}
return null;
}
private static AccessControlContext getContext(File[] dirs)
throws IOException
{
PathPermissions perms =
new PathPermissions(dirs);
ProtectionDomain domain = new ProtectionDomain(
new CodeSource(perms.getCodeBase(),
(java.security.cert.Certificate[]) null),
perms);
AccessControlContext acc =
new AccessControlContext(new ProtectionDomain[] { domain });
return acc;
}
}
---------------------
作者:irelandken
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/irelandken/article/details/7046689
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
分析AppClassLoader,ExtClassLoader 和URLClassLoader 的关系的更多相关文章
- 源码分析:动态分析 Linux 内核函数调用关系
源码分析:动态分析 Linux 内核函数调用关系 时间 2015-04-22 23:56:07 泰晓科技 原文 http://www.tinylab.org/source-code-analysi ...
- <十>面向对象分析之UML核心元素之关系
关系 --->在UML中关系是非常重要的语义,它抽象出对象之间的联系,让对象构成特定的结构. 一,关联关系(association)
- 数据挖掘(data mining),机器学习(machine learning),和人工智能(AI)的区别是什么? 数据科学(data science)和商业分析(business analytics)之间有什么关系?
本来我以为不需要解释这个问题的,到底数据挖掘(data mining),机器学习(machine learning),和人工智能(AI)有什么区别,但是前几天因为有个学弟问我,我想了想发现我竟然也回答 ...
- 使用UML工具分析类图与类的关系-bouml(java和C++)
在分析类之间的关系时可以借助工具来实现. bouml是一个UML分析工具,最新的版本是收费的,但是之前的版本是免费的. 这里使用的是4.23版. Bouml安装: 安装软件就按照流程走就行了.但是第一 ...
- 通过分析iframe和无阻塞脚本关系能让我们更懂iframe
在我上篇文章里,我提到一种使用iframe完成无阻塞脚本加载的方式,因为我对iframe的偏见很大,所以上篇文章里我没有展开讨论这个问题. 文章发表后有位网友问了我这样一个问题,下面是他问题的原文,如 ...
- spring源码分析系列2:Bean与BeanDefinition关系
接口表示一种能力,实现了一个接口,即拥有一种能力. BeanDefinition与Bean的关系, 就好比类与对象的关系. 类在spring的数据结构就是BeanDefinition.根据BeanDe ...
- MyBatis源码分析(1)——整体依赖关系图
后续补充更新
- 源码分析:静态分析 C 程序函数调用关系图
http://www.tinylab.org/callgraph-draw-the-calltree-of-c-functions/
- 0032 Java学习笔记-类加载机制-初步
JVM虚拟机 Java虚拟机有自己完善的硬件架构(处理器.堆栈.寄存器等)和指令系统 Java虚拟机是一种能运行Java bytecode的虚拟机 JVM并非专属于Java语言,只要生成的编译文件能匹 ...
随机推荐
- eclipse 项目的创建 编写 'Hello World'
写项目之前确保 eclipse 安装完成 以及JDK 环境配置 成功 开始: 打开eclipse 右键file ->new->java project 如图: 然后输入项目名 点击Fin ...
- 记录 Docker 的学习过程 (安装基础篇)
docker 通过内核来实现 特点是效率高 1. centos7 三台(推荐2c 4g 最低 1c1g)2. 关闭防火墙 selinux3. 做好主机名解析,三台能互相ping通主机名host参考文件 ...
- Selenium3+python自动化009-iframe定位
iframe 一.frame:HTML页面中的一种框架,主要作用是在当前页面中指定区域显示另一页面元素: 二.操作Frame中的页面元素 定位元素: 1.id定位driver.switch_to.fr ...
- SAM的应用及例题
专门开一个帖子记录一下自己在学习SAM时做的题,并总结一下做法 1.LCS https://www.cnblogs.com/wenci/p/10432932.html 这道题是要求对两个字符串查找最长 ...
- sencha Architect 3.2及以下版本都适用的 破解方法
找到 没有的话 打开隐藏文件夹 C:\Users\ll\AppData\Local\Sencha\Sencha Architect 3.2 用编辑器 打开user.license 把 Print 修改 ...
- 共享v2射线局域网http代理方法
问题描述 默认v节点大部分是socks代理,实际使用过程中存在以下问题: 部分浏览器无法支持socks需要走http代理. 局域网内其他设备(手机.PS4等)需要配置代理. 解决方法 1.在PC托盘图 ...
- openstack入门及应用
一.OpenStack云计算的介绍 (一)云计算的服务类型 IAAS:基础设施即服务,如:云主机 PAAS:平台即服务,如:docker SAAS:软件即服务,如:购买企业邮箱,CDN 传统IT IA ...
- AdaBoost级联分类器
Haar分类器使用AdaBoost算法,但是把它组织为筛选式的级联分类器,每个节点是多个树构成的分类器,且每个节点的正确识别率很高.在任一级计算中,一旦获得“不在类别中”的结论,则计算终止.只有通过分 ...
- SQL Server 检查和处理死锁问题
SELECT spid, blocked, DB_NAME(sp.dbid) AS DBName, program_name, waitresource, lastwaittype, sp.login ...
- 使用acme.sh签发Let's Encrypt的免费数字证书
--------------安装----------------curl https://get.acme.sh | sh#让alias生效source ~/.bashrc ------------- ...
