bash启动时加载配置文件过程
bash&shell系列文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/7048359.html
当用户登录系统时,会加载各种bash配置文件,还会设置或清空一系列变量,有时还会执行一些自定义的命令。这些行为都算是启动bash时的过程。
另外,有些时候登录系统是可以交互的(如正常登录系统),有些时候是无交互的(如执行一个脚本),因此总的来说bash启动类型可分为交互式shell和非交互式shell。更细分一层,交互式shell还分为交互式的登录shell和交互式非登录shell,非交互的shell在某些时候可以在bash命令后带上"--login"或短选项"-l",这时也算是登录式,即非交互的登录式shell。
1.1 判断是否交互式、是否登录式
判断是否为交互式shell有两种简单的方法:
方法一:判断变量"-",如果值中含有字母"i",表示交互式。
[root@xuexi ~]# echo $-
himBH [root@xuexi ~]# vim a.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $- [root@xuexi ~]# bash a.sh
hB
方法二:判断变量PS1,如果值非空,则为交互式,否则为非交互式,因为非交互式会清空该变量。
[root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1
[\u@\h \W]\$
判断是否为登录式的方法也很简单,只需执行"shopt login_shell"即可。值为"on"表示为登录式,否则为非登录式。
[root@xuexi ~]# shopt login_shell
login_shell on
[root@xuexi ~]# bash [root@xuexi ~]# shopt login_shell
login_shell off
所以,要判断是交互式以及登录式的情况,可简单使用如下命令:
echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
# 或者
echo $-;shopt login_shell
1.2 几种常见的bash启动方式
(1).正常登录(伪终端登录如ssh登录,或虚拟终端登录)时,为交互式登录shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
[\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell on
(2).su命令,不带"--login"时为交互式、非登录式shell,带有"--login"时,为交互式、登录式shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# su root [root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
[\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell off
[root@xuexi ~]# su -
Last login: Sat Aug :: CST on pts/ [root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
[\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell on
(3).执行不带"--login"选项的bash命令时为交互式、非登录式shell。但指定"--login"时,为交互式、登录式shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# bash [root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
[\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell off
[root@xuexi ~]# bash -l [root@xuexi ~]# echo $PS1;shopt login_shell
[\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell on
(4).使用命令组合(使用括号包围命令列表)以及命令替换进入子shell时,继承父shell的交互和登录属性。
[root@xuexi ~]# (echo $BASH_SUBSHELL;echo $PS1;shopt login_shell) [\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell on
[root@xuexi ~]# su [root@xuexi ~]# (echo $BASH_SUBSHELL;echo $PS1;shopt login_shell) [\u@\h \W]\$
login_shell off
(5).ssh执行远程命令,但不登录时,为非交互、非登录式。
[root@xuexi ~]# ssh localhost 'echo $PS1;shopt login_shell' login_shell off
(6).执行shell脚本时,为非交互、非登录式shell。但指定了"--login"时,将为非交互、登录式shell。
例如,脚本内容如下:
[root@xuexi ~]# vim b.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $PS1
shopt login_shell
不带"--login"选项时,为非交互、非登录式shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# bash b.sh login_shell off
带"--login"选项时,为非交互、登录式shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# bash -l b.sh login_shell on
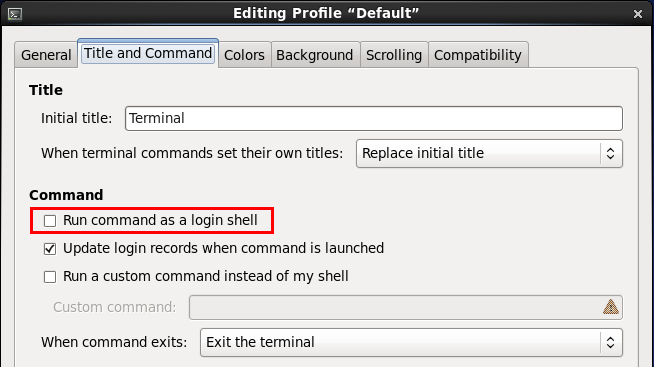
(7).在图形界面下打开终端时,为交互式、非登录式shell。
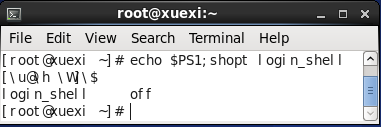
但可以设置为使用交互式、登录式shell。
1.3 加载bash环境配置文件
无论是否交互、是否登录,bash总要配置其运行环境。bash环境配置主要通过加载bash环境配置文件来完成。但是否交互、是否登录将会影响加载哪些配置文件,除了交互、登录属性,有些特殊的属性也会影响读取配置文件的方法。
bash环境配置文件主要有/etc/profile、~/.bash_profile、~/.bashrc、/etc/bashrc和/etc/profile.d/*.sh,为了测试各种情形读取哪些配置文件,先分别向这几个配置文件中写入几个echo语句,用以判断该配置文件是否在启动bash时被读取加载了。
echo "echo '/etc/profile goes'" >>/etc/profile
echo "echo '~/.bash_profile goes'" >>~/.bash_profile
echo "echo '~/.bashrc goes'" >>~/.bashrc
echo "echo '/etc/bashrc goes'" >>/etc/bashrc
echo "echo '/etc/profile.d/test.sh goes'" >>/etc/profile.d/test.sh
chmod +x /etc/profile.d/test.sh
①.交互式登录shell或非交互式但带有"--login"(或短选项"-l",例如在shell脚本中指定"#!/bin/bash -l"时)的bash启动时,将先读取/etc/profile,再依次搜索~/.bash_profile、~/.bash_login和~/.profile,并仅加载第一个搜索到且可读的文件。当退出时,将执行~/.bash_logout中的命令。
但要注意,在/etc/profile中有一条加载 /etc/profile.d/*.sh 的语句,它会使用source加载/etc/profile.d/下所有可执行的sh后缀的脚本。
[root@xuexi ~]# grep -A \*\.sh /etc/profile
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
fi
done
内层if语句中的 "${-#*i}" != "$-" 表示将"$-"从左向右模式匹配"*i"并将匹配到的内容删除(即进行变量切分),如果"$-"切分后的值不等于"$-",则意味着是交互式shell,于是怎样怎样,否则怎样怎样。
同样的,在~/.bash_profile中也一样有加载~/.bashrc的命令。
[root@xuexi ~]# grep -A \~/\.bashrc ~/.bash_profile
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi
而~/.bashrc中又有加载/etc/bashrc的命令。
[root@xuexi ~]# grep -A /etc/bashrc ~/.bashrc
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
其实/etc/bashrc中还有加载 /etc/profile.d/*.sh 的语句,但前提是非登录式shell时才会执行。以下是部分语句:
if ! shopt -q login_shell ; then # We're not a login shell
...
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
fi
done
...
fi
从内层if语句和/etc/profile中对应的判断语句的作用是一致的,只不过判断方式不同,写法不同。
因此,交互式的登录shell加载bash环境配置文件的实际过程如下图:

以下结果验证了结论:
Last login: Mon Aug 14 04:49:29 2017 # 新开终端登录时
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/profile goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
~/.bash_profile goes
[root@xuexi ~]# ssh localhost # ssh远程登录时
root@localhost's password:
Last login: Mon Aug 14 05:05:50 2017 from 172.16.10.1
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/profile goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
~/.bash_profile goes
[root@xuexi ~]# bash -l # 执行带有"--login"选项的login时
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/profile goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
~/.bash_profile goes
[root@xuexi ~]# su - # su带上"--login"时
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/profile goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
~/.bash_profile goes
[root@xuexi ~]# vim a.sh # 执行shell脚本时带有"--login"时
#!/bin/bash -l
echo haha [root@xuexi ~]# ./a.sh
/etc/profile goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
~/.bash_profile goes
haha
之所以执行shell脚本时没有显示执行 /etc/profile.d/*.sh ,是因为它是非交互式的,根据/etc/profile中的 if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ] 判断,它将会把 /etc/profile.d/*.sh 的执行结果重定向到/dev/null中。也就是说,即使是shell脚本(带"--login "选项),它也加载了所有bash环境配置文件。
②.交互式非登录shell的bash启动时,将读取~/.bashrc,不会读取/etc/profile和~/.bash_profile、~/.bash_login和~/.profile。
因此,交互式非登录shell加载bash环境配置文件的实际过程为下图内方框中所示:
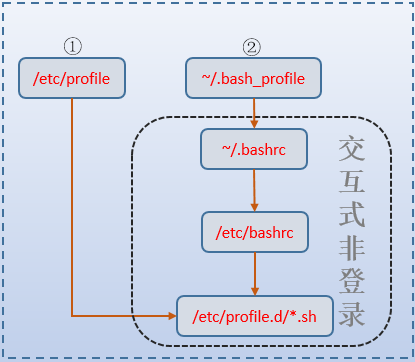
例如,执行不带"--login"的bash命令或su命令时。
[root@xuexi ~]# bash
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
[root@xuexi ~]# su
/etc/profile.d/*.sh goes
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
③.非交互式、非登录式shell启动bash时,不会加载前面所说的任何bash环境配置文件,但会搜索变量BASH_ENV,如果搜索到了,则加载其所指定的文件。但并非所有非交互式、非登录式shell启动时都会如此,见情况④。
它就像是这样的语句:
if [ -n "$BASH_ENV" ];then
. "$BASH_ENV"
fi
几乎执行所有的shell脚本都不会特意带上"--login"选项,因此shell脚本不会加载任何bash环境配置文件,除非手动配置了变量BASH_ENV。
④.远程shell方式启动的bash,它虽然属于非交互、非登录式,但会加载~/.bashrc,所以还会加载/etc/bashrc,由于是非登录式,所以最终还会加载/etc/profile.d/*.sh,只不过因为是非交互式而使得执行的结果全部重定向到了/dev/null中。
如果了解rsync,就知道它有一种远程shell连接方式。所谓的远程shell方式,是指通过网络的方式启动bash并将bash的标准输出关联起来,就像它连接了一个远程的shell守护进程一样。一般由sshd实现这样的连接方式,老版的rshd也一样支持。
事实也确实如此,使用ssh连接但不登录远程主机时(例如只为了执行远程命令),就是远程shell的方式,但它却是非交互、非登录式的shell。
[root@xuexi ~]# ssh localhost echo haha
root@localhost's password:
/etc/bashrc goes
~/.bashrc goes
haha
正如上文所说,它同样加载了 /etc/profile.d/*.sh ,只不过/etc/bashrc中的if判断语句 if [ "$PS1" ]; then 使得非交互式的shell要将执行结果重定向到/dev/null中。
bash启动时加载配置文件过程的更多相关文章
- tomcat启动时加载配置文件 报错
原因: @serice("customerService") 和@Repository(value="customerDao") 解决: 直接@ ...
- 微服务架构 | *2.3 Spring Cloud 启动及加载配置文件源码分析(以 Nacos 为例)
目录 前言 1. Spring Cloud 什么时候加载配置文件 2. 准备 Environment 配置环境 2.1 配置 Environment 环境 SpringApplication.prep ...
- Servlet在启动时加载的tomcat源码(原创)
tomcat 8.0.36 知识点: 通过配置loadOnStartup可以设置Servlet是否在Tomcat启动时加载,以及按值大小进行有序加载,其最小有效值为0,最大有效值为Integer.MA ...
- ElasticSearch 启动时加载 Analyzer 源码分析
ElasticSearch 启动时加载 Analyzer 源码分析 本文介绍 ElasticSearch启动时如何创建.加载Analyzer,主要的参考资料是Lucene中关于Analyzer官方文档 ...
- web.xml中配置启动时加载的servlet,load-on-starup
web.xml中配置启动时加载的servlet,load-on-starup 使用servlet来初始化配置文件数据: 在servlet的配置当中,<load-on-startup>1&l ...
- spring项目中监听器作用-ContextLoaderListener(项目启动时,加载一些东西到缓存中)
作用:在启动Web容器时,自动装配Spring applicationContext.xml的配置信息. 因为它实现了ServletContextListener这个接口,在web.xml配置这个监听 ...
- 设置程序启动时加载的storyboard
这个设置表明:程序启动时会加载Main.storyboard
- Tomcat启动时加载数据到缓存---web.xml中listener加载顺序(例如顺序:1、初始化spring容器,2、初始化线程池,3、加载业务代码,将数据库中数据加载到内存中)
最近公司要做功能迁移,原来的后台使用的Netty,现在要迁移到在uap上,也就是说所有后台的代码不能通过netty写的加载顺序加载了. 问题就来了,怎样让迁移到tomcat的代码按照原来的加载顺序进行 ...
- Tomcat启动时加载数据到缓存---web.xml中listener加载顺序(优先初始化Spring IOC容器)
JavaWebSpringTomcatCache 最近用到在Tomcat服务器启动时自动加载数据到缓存,这就需要创建一个自定义的缓存监听器并实现ServletContextListener接口,并且 ...
随机推荐
- 100+个MySQL调试和优化技巧
MySQL是一个功能强大的开源数据库.随着越来越多的数据库驱动的应用程序,人们一直在推动MySQL发展到它的极限.这里是101条调节和优化MySQL安装的技巧.一些技巧是针对特定的安装环境的,但这些思 ...
- Oracle,Mysql ,SQL Server 三大数据库带参数的模糊查询, 拼接查询条件问题
最近项目开发一直在不断切换数据库,有时候一条sql 要同时考虑多种数据库中的兼容问题 , 先总结一条模糊查询拼接查询条件的问题,后续追加总结. 目前使用 mybatis: 1. Oracle 中使 ...
- (转)ManyToMany注解
@ManyToMany 注释:表示此类是多对多关系的一边,mappedBy 属性定义了此类为双向关系的维护端,注意:mappedBy 属性的值为此关系的另一端的属性名. 例如,在Student类中有 ...
- BootLoader--改进(基于2440)
BootLoader--改进 之前编写的Bootloader启动内核时间使用差不多7秒钟的时间,大多都是用在CPU将内核从Nandflash读取到SDRam中,故首先想到的方法是改变CPU时钟频率. ...
- Django学习(八)---修改文章和添加文章
博客页面的修改文章和添加新文章 从主页点击不同文章的超链接进入文章页面,就是传递了一个id作为参数,然后后台代码根据这个参数从数据库中取出来对应的文章,并把它传递到前端页面 修改文章和添加新文章,是要 ...
- java基础07 多线程
在学习操作系统时,我们会学习进程和线程,那么进程和线程又是什么东西呢? 进程是具有一定独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合上的一次运行活动,进程是系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位. 线程(thread) ...
- java用户界面——加载图片 jpg GIF
java用户界面--加载图片 jpg GIF 代码如下: package day08; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.Icon;impo ...
- 有关Android插件化思考
最近几年移动开发业界兴起了「 插件化技术 」的旋风,各个大厂都推出了自己的插件化框架,各种开源框架都评价自身功能优越性,令人目不暇接.随着公司业务快速发展,项目增多,开发资源却有限,如何能在有限资源内 ...
- 文本处理常用命令--sort,uniq,cut,wc
#文本处理命令--sort,cut,wc及其他 文本处理命令还有其他常用的,比如:sort,cut,wc 1.cut命令的用法 cut命令: cut - remove sections from ea ...
- 天地图使用过程中由于display:none导致加载部分地图瓦片失败
在为按钮添加点击事件让地图显示的时候,初始加载未加载到当前页面尺寸的所有地图瓦片,在display:none之后停止加载地图,所以display:none属性去掉,改为dom解析完成之后$('#map ...
