Iris_data_analysis
SVM调用实例——鸢尾花
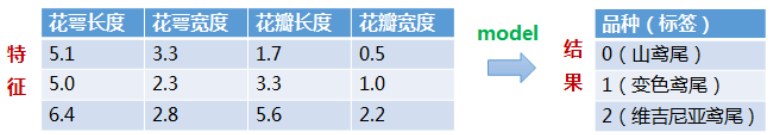
任务描述:
构建一个模型,根据鸢尾花的花萼和花瓣大小将其分为三种不同的品种。
数据集:
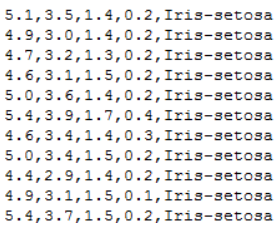
每一行数据由4个特征值及1个目标值组成,4个特征值分别为:萼片长度、萼片宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,目标值为三种不同类别的鸢尾花。
代码实现:
# ! /usr/bin/env python37
# ! -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ====#====#====#====
# HomePage:https://www.cnblogs.com/Qzzz/
# FileName: Iris.py
# Version:1.0.5
# ====#====#====#====
#*************导入必要的包***********************
# numpy:用于科学计算
# matplotlib:用于进行可视化
# sklearn:机器学习算法
import numpy as np
from sklearn import model_selection as mo
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import colors
#*************将字符串转为整型,便于数据加载***********************
#在函数中建立了一个对应字典,输入字符串,输出字符串对应的数字
def iris_type(s):
# print(type(s))
it = {b'Iris-setosa':0, b'Iris-versicolor':1, b'Iris-virginica':2}
return it[s]
#加载数据
data_path='./iris.data'
data = np.loadtxt(data_path, #数据文件的路径
dtype = float, #数据类型
delimiter=',', #数据分隔符
converters={4:iris_type}) #将第五列使用函数iris_type进行转换
# print(data)
# print(data.shape)
#数据分割
x,y = np.split(data, #要切分的数组
(4,), #沿轴切分的位置,第5列开始往后为y
axis=1) #1代表纵向分割,按列分割
x = x[:,0:2]
#第一个逗号之前表示行,只有冒号表示所有行,第二个冒号0:2表示0,1两列
#在X中我们取前两列作为特征,为了后面的可视化,原始的四维不好画图,x[:,0:4]代表第一为全取,第二维取0~2
#????剩下两列的数据不做处理????
# print(x)
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=mo.train_test_split(x, #所要划分的样本特征集
y, #所要划分的样本结果
random_state=1, #随机数种子确保产生的随机数组相同
test_size=0.3) #测试样本占比
#**********************SVM分类器构建*************************
def classifier():
#clf = svm.SVC(C=0.8, kernel='rbf', gamma=50, decision_function_shape='ovr)
clf = svm.SVC(C=0.5, #误差项惩罚系数,默认值是1
kernel = 'linear', #线性核 kernel='rbf':高斯核
decision_function_shape = 'ovr') #决策函数
return clf
clf = classifier()
#************************模型训练*****************************
# y_train.ravel() #扁平化操作,将原来的二维数组转换为一维数组
# array([2., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 2., 2., 2., 2., 2., 1., 2., 1., 0., 2.,
# 2., 0., 0., 2., 0., 2., 2., 1., 1., 2., 2., 0., 1., 1., 2., 1., 2.,
# 1., 0., 0., 0., 2., 0., 1., 2., 2., 0., 0., 1., 0., 2., 1., 2., 2.,
# 1., 2., 2., 1., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0., 1., 0., 0., 2., 2., 2., 0.,
# 0., 1., 0., 2., 0., 2., 2., 0., 2., 0., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 1.,
# 0., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 2., 0., 0., 2., 1., 2., 1., 2., 2.,
# 1., 2., 0.])
def train(clf, x_train, y_train):
clf.fit(x_train, #训练及特征向量,fit表示输入数据开始拟合
y_train.ravel()) #训练集目标值扁平化,将原来的二维数组转换为一维数组
train(clf, x_train, y_train)
#**************模型评估并判断ab是否相等,计算acc的均值*************
def show_accuracy(a, b, tip):
acc = a.ravel() == b.ravel()
print('%s Accuracy:%.3f' %(tip, np.mean(acc)))
def print_accuracy(clf, x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test):
#分别打印训练集和测试集的准确率
print('training prediction:%.3f' %(clf.score(x_train, y_train)))
print('test data prediction:%.3f' %(clf.score(x_test, y_test)))
#原始结果与预测结果进行比对
show_accuracy(clf.predict(x_train), y_train, 'training data')
show_accuracy(clf.predict(x_test), y_test, 'testing data')
#计算决策函数的值,表示x到各分割平面的距离
print('decision_function:\n', clf.decision_function(x_train))
print_accuracy(clf, x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test)
#************************模型使用*************************
def draw(clf, x):
iris_feature = 'sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal lenght', 'petal width'
# 开始画图
x1_min, x1_max = x[:, 0].min(), x[:, 0].max() #第0列的范围
x2_min, x2_max = x[:, 1].min(), x[:, 1].max() #第1列的范围
x1, x2 = np.mgrid[x1_min:x1_max:200j, x2_min:x2_max:200j] #生成网格采样点 开始坐标:结束坐标(不包括):步长
#flat将二维数组转换成1个1维的迭代器,然后把x1和x2的所有可能值给匹配成为样本点
grid_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) #stack():沿着新的轴加入一系列数组,竖着(按列)增加两个数组,grid_test的shape:(40000, 2)
print('grid_test:\n', grid_test)
# 输出样本到决策面的距离
z = clf.decision_function(grid_test)
print('the distance to decision plane:\n', z)
grid_hat = clf.predict(grid_test) # 预测分类值 得到【0,0.。。。2,2,2】
print('grid_hat:\n', grid_hat)
grid_hat = grid_hat.reshape(x1.shape) # reshape grid_hat和x1形状一致
#若3*3矩阵e,则e.shape()为3*3,表示3行3列
#light是网格测试点的配色,相当于背景
#dark是样本点的配色
cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0', '#FFA0A0', '#A0A0FF'])
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'b', 'r'])
#画出所有网格样本点被判断为的分类,作为背景
plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, grid_hat, cmap=cm_light) # pcolormesh(x,y,z,cmap)这里参数代入
# x1,x2,grid_hat,cmap=cm_light绘制的是背景。
#squeeze()把y的个数为1的维度去掉,也就是变成一维。
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=np.squeeze(y), edgecolor='k', s=50, cmap=cm_dark) # 样本点
plt.scatter(x_test[:, 0], x_test[:, 1], s=200, facecolor='yellow', zorder=10, marker='+') # 测试点
plt.xlabel(iris_feature[0], fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel(iris_feature[1], fontsize=20)
plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max)
plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.title('svm in iris data classification', fontsize=30)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Iris_data_analysis的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- Windows 客户端802.1x的一些设置
802.1x作为网络准入的验证,自然有很多好处.但是在实施过程中也遇到了些小问题.我在这里记录下来,希望对大家有帮助,遇到问题的时候能有个参考. 基于用户验证的方式,当用户修改了密码后,验证失败.此时 ...
- python基础__十大经典排序算法
用Python实现十大经典排序算法! 排序算法是<数据结构与算法>中最基本的算法之一.排序算法可以分为内部排序和外部排序,内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,而外部排序是因排序的数据很大, ...
- Elasticsearch:Smart Chinese Analysis plugin
Smart Chinese Analysis插件将Lucene的Smart Chinese分析模块集成到Elasticsearch中,用于分析中文或中英文混合文本. 支持的分析器在大型训练语料库上使用 ...
- ERP是什么呢?
ERP(Enterprise Resource Planning,企业资源计划)系统,是进行物质资源.资金资源和信息资源集成一体化管理的企业信息管理系统,ERP统领企业全局,为管理层服务,重心在于企业 ...
- C#-8 数组
一 关于数组 数组是由一个变量名称表示的一组同类型的数据元素.数组中的元素通过变量名和方括号索引来访问. int[] intArray = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; //声明了一个 ...
- 微信小程序实现与登录
一.小程序的实现原理 在小程序中,渲染层和逻辑层是分开的,双线程同时运行,渲染层和逻辑层这两个通信主体之间的通讯以及通讯主体与第三方服务器之间的通信,都是通过微信客户端进行转发.小程序启动运行两种情况 ...
- 11.MongoDB系列之连接副本集
1. Python连接副本集 from pymongo import MongoClient from bson.codec_options import CodecOptions from retr ...
- Vue中使用Switch开关用来控制商品的上架与下架情况、同时根据数据库商品的状态反应到前台、前台修改商品状态保存到数据库
一般后台对商品的信息管理.包含商品的上架与下架.为了提高用户的体验.将商品上下架的操作做成开关的形式.同时后台数据库中保存的商品状态能够根据开关状态改变. 1.效果展示 这种效果:== 当开关是开启状 ...
- IDEA& Android Studio 配置
1.配置环境 首先要安装好JDK,但不需要单独下载SDK,只需在IDEA或AS的"设置->外观与行为->->系统设置->Android SDK"中下载相应版 ...
- vue2和vue3组合使用教程地址
https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/essentials/watchers.html#eager-watchers