皓远的第二次博客作业(最新pta集,链表练习及期中考试总结)
前言:
- 知识点运用:正则表达式,有关图形设计计算的表达式和算法,链表的相关知识,Java类的基础运用,继承、容器与多态。
- 题量:相较于上次作业,这几周在java方面的练习花了更多的精力和时间,所要完成的任务都变得更新颖复杂,难度也逐渐增加。
设计与分析:
(这里主要挑了一些重点,及对笔者而言难度较大及体会深刻的题目)
PTA题目集题目小结:
①题目集四——7-2(线的计算):
题目:
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与直线有关的计算。选项包括:
1:输入两点坐标,计算斜率,若线条垂直于X轴,输出"Slope does not exist"。
2:输入三个点坐标,输出第一个点与另外两点连线的垂直距离。
3:输入三个点坐标,判断三个点是否在一条线上,输出true或者false。
4:输入四个点坐标,判断前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线是否平行,输出true或者false.
5:输入四个点坐标,计算输出前两个点所构成的直线与后两点构成的直线的交点坐标,x、y坐标之间以英文分隔",",并输出交叉点是否在两条线段之内(不含四个端点)的判断结果(true/false),判断结果与坐标之间以一个英文空格分隔。若两条线平行,没有交叉点,则输出"is parallel lines,have no intersection point"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。
例如:1:0,0 1,1
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
不论哪个选项,如果格式、点数量都符合要求,但构成任一条线的两个点坐标重合,输出"points coincide",
输出格式:
见题目描述。
这里笔者先给出自己的源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class Main {
4
5
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
8 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
9 String s = in.nextLine();
10
11 // 选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y
12 //输入的选项
13 int choice = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0, 1));
14 if(!(choice >= 1 && choice <= 5))
15 {
16 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
17 System.exit(0);
18
19 }
20
21 //判断有无':',并位置有无错误。
22 if(s.charAt(1)!=':')
23 {
24 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
25 System.exit(0);
26 }
27 int bool1 = s.indexOf(':',2);
28 if(bool1 != -1)
29 {
30 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
31 System.exit(0);
32 }
33
34 switch(choice)
35 {
36 case 1://计算斜率
37 {
38 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
39 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
40 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
41 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
42
43 //判断0是否在首位
44 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
45 {
46 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
47 {
48 if(i<s.length()-2)
49 {
50 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
51 {
52 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
53 System.exit(0);
54 }
55
56 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
57 {
58 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
59 System.exit(0);
60 }
61 }
62 }
63 }
64
65 //点的数量
66 if(index_null1 == -1)
67 {
68 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
69 System.exit(0);
70 }
71 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
72 if(index_null2 !=-1)
73 {
74 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
75 System.exit(0);
76 }
77
78 //判断逗号数量是否不对
79 int sum_char = 0;
80 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
81 {
82 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
83 sum_char ++;
84 }
85 if(sum_char != 2 )
86 {
87 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
88 System.exit(0);
89 }
90 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
91 {
92 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
93 System.exit(0);
94 }
95
96
97 double x1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
98 double y1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
99 double x2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
100 double y2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x2+1, s.length()));
101
102 if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
103 {
104 System.out.println("points coincide");
105 System.exit(0);
106 }
107
108 if(x1 == x2)
109 {
110 System.out.println("Slope does not exist");
111 System.exit(0);
112 }
113 double k = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2);
114 System.out.print(k);
115 }break;
116
117 case 2://求一点到一直线的垂直距离
118 {
119 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
120 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
121 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
122 int index_x3 = s.indexOf(',', index_x2+1);
123 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
124 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
125
126 //判断0是否在首位
127 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
128 {
129 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
130 {
131 if(i<s.length()-2)
132 {
133 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
134 {
135 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
136 System.exit(0);
137 }
138
139 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
140 {
141 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
142 System.exit(0);
143 }
144 }
145 }
146 }
147
148 //点的数量
149 if(index_null1 == -1 || index_null2 == -1)
150 {
151 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
152 System.exit(0);
153 }
154 int index_null3 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null2+1);
155 if(index_null3 !=-1)
156 {
157 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
158 System.exit(0);
159 }
160
161 //判断逗号数量是否不对
162 int sum_char = 0;
163 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
164 {
165 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
166 sum_char ++;
167 }
168 if(sum_char != 3 )
169 {
170 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
171 System.exit(0);
172 }
173 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
174 {
175 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
176 System.exit(0);
177 }
178 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null2) == -1)
179 {
180 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
181 System.exit(0);
182 }
183
184
185 double x1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
186 double y1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
187 double x2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
188 double y2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x2+1, index_null2));
189 double x3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null2+1, index_x3));
190 double y3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x3+1, s.length()));
191
192 // if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
193 // {
194 // System.out.println("points coincide");
195 // System.exit(0);
196 // }
197 // if(x1 == x3 && y1 == y3)
198 // {
199 // System.out.println("points coincide");
200 // System.exit(0);
201 // }
202 if(x2 == x3 && y2 == y3)
203 {
204 System.out.println("points coincide");
205 System.exit(0);
206 }
207
208 double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1);
209 double k2 = (y3-y2)/(x3-x2);
210
211 if(k1 == k2)
212 {
213 System.out.print("0.0");
214 System.exit(0);
215 }
216 else
217 {
218 double a = Math.sqrt((Math.pow((x1-x2), 2) + Math.pow((y1-y2), 2)));
219 double b = Math.sqrt((Math.pow((x1-x3), 2) + Math.pow((y1-y3), 2)));
220 double c = Math.sqrt((Math.pow((x2-x3), 2) + Math.pow((y2-y3), 2)));
221 double p = (a+b+c)/2;
222 double area = Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));//海伦公式
223 double distance = 2*area/c;
224 System.out.printf("%.1f",distance);
225 }
226
227 }break;
228
229 case 3://判断三点是否在同一条直线上
230 {
231 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
232 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
233 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
234 int index_x3 = s.indexOf(',', index_x2+1);
235 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
236 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
237
238 //判断0是否在首位
239 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
240 {
241 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
242 {
243 if(i<s.length()-2)
244 {
245 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
246 {
247 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
248 System.exit(0);
249 }
250
251 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
252 {
253 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
254 System.exit(0);
255 }
256 }
257 }
258 }
259
260 if(index_null1 == -1 || index_null2 == -1)
261 {
262 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
263 System.exit(0);
264 }
265 int index_null3 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null2+1);
266 if(index_null3 !=-1)
267 {
268 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
269 System.exit(0);
270 }
271
272 //判断逗号数量是否不对
273 int sum_char = 0;
274 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
275 {
276 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
277 sum_char ++;
278 }
279 if(sum_char != 3 )
280 {
281 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
282 System.exit(0);
283 }
284 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
285 {
286 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
287 System.exit(0);
288 }
289 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null2) == -1)
290 {
291 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
292 System.exit(0);
293 }
294
295
296
297 double x1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
298 double y1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
299 double x2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
300 double y2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x2+1, index_null2));
301 double x3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null2+1, index_x3));
302 double y3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x3+1, s.length()));
303
304
305 if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
306 {
307 System.out.println("points coincide");
308 System.exit(0);
309 }
310 if(x1 == x3 && y1 == y3)
311 {
312 System.out.println("points coincide");
313 System.exit(0);
314 }
315 if(x2 == x3 && y2 == y3)
316 {
317 System.out.println("points coincide");
318 System.exit(0);
319 }
320
321 double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1);
322 double k2 = (y3-y2)/(x3-x2);
323
324 if(k1 == k2)
325 {
326 System.out.print("true");
327 System.exit(0);
328 }
329 else
330 {
331 System.out.print("false");
332 System.exit(0);
333 }
334
335 }break;
336
337 case 4://判断两条直线是否平行
338 {
339 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
340 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
341 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
342 int index_x3 = s.indexOf(',', index_x2+1);
343 int index_x4 = s.indexOf(',', index_x3+1);
344 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
345 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
346 int index_null3 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null2+1);
347
348 //判断0是否在首位
349 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
350 {
351 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
352 {
353 if(i<s.length()-2)
354 {
355 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
356 {
357 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
358 System.exit(0);
359 }
360
361 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
362 {
363 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
364 System.exit(0);
365 }
366 }
367 }
368 }
369
370 if(index_null1 == -1 || index_null2 == -1 || index_null3 == -1)
371 {
372 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
373 System.exit(0);
374 }
375
376 //判断逗号数量是否不对
377 int sum_char = 0;
378 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
379 {
380 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
381 sum_char ++;
382 }
383 if(sum_char != 4 )
384 {
385 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
386 System.exit(0);
387 }
388 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
389 {
390 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
391 System.exit(0);
392 }
393 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null2) == -1)
394 {
395 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
396 System.exit(0);
397 }
398 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null3) == -1)
399 {
400 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
401 System.exit(0);
402 }
403
404
405 double x1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
406 double y1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
407 double x2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
408 double y2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x2+1, index_null2));
409 double x3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null2+1, index_x3));
410 double y3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x3+1, index_null3));
411 double x4 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null3+1, index_x4));
412 double y4 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x4+1, s.length()));
413
414 if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
415 {
416 System.out.println("points coincide");
417 System.exit(0);
418 }
419 if(x3 == x4 && y3 == y4)
420 {
421 System.out.println("points coincide");
422 System.exit(0);
423 }
424
425 //斜率不存在
426 if(x1 == x2)
427 {
428 if(x3 == x4)
429 {
430 System.out.print("true");
431 System.exit(0);
432 }
433 else
434 {
435 System.out.print("false");
436 System.exit(0);
437 }
438 }
439 else if(x3 == x4)
440 {
441 if(x1 == x2)
442 {
443 System.out.print("true");
444 System.exit(0);
445 }
446 else
447 {
448 System.out.print("false");
449 System.exit(0);
450 }
451 }
452 else//斜率存在
453 {
454 double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1);
455 double k2 = (y4-y3)/(x4-x3);
456
457 if(k1 == k2)
458 {
459 System.out.print("true");
460 System.exit(0);
461 }
462 else
463 {
464 System.out.print("false");
465 System.exit(0);
466 }
467 }
468
469 }break;
470
471 case 5://求交点坐标
472 {
473 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
474 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
475 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
476 int index_x3 = s.indexOf(',', index_x2+1);
477 int index_x4 = s.indexOf(',', index_x3+1);
478 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
479 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
480 int index_null3 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null2+1);
481
482 //判断0是否在首位
483 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
484 {
485 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
486 {
487 if(i<s.length()-2)
488 {
489 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
490 {
491 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
492 System.exit(0);
493 }
494
495 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
496 {
497 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
498 System.exit(0);
499 }
500 }
501 }
502 }
503
504 if(index_null1 == -1 || index_null2 == -1 || index_null3 == -1)
505 {
506 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
507 System.exit(0);
508 }
509 int index_null4 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null3+1);
510 if(index_null4 !=-1)
511 {
512 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
513 System.exit(0);
514 }
515
516 //判断逗号数量是否不对
517 int sum_char = 0;
518 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
519 {
520 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
521 sum_char ++;
522 }
523 if(sum_char != 4 )
524 {
525 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
526 System.exit(0);
527 }
528 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
529 {
530 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
531 System.exit(0);
532 }
533 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null2) == -1)
534 {
535 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
536 System.exit(0);
537 }
538 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null3) == -1)
539 {
540 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
541 System.exit(0);
542 }
543
544
545
546 float x1 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
547 float y1 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
548 float x2 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
549 float y2 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_x2+1, index_null2));
550 float x3 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_null2+1, index_x3));
551 float y3 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_x3+1, index_null3));
552 float x4 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_null3+1, index_x4));
553 float y4 = Float.parseFloat(s.substring(index_x4+1, s.length()));
554
555 if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
556 {
557 System.out.println("points coincide");
558 System.exit(0);
559 }
560 if(x3 == x4 && y3 == y4)
561 {
562 System.out.println("points coincide");
563 System.exit(0);
564 }
565
566
567 //斜率不存在
568 if(x1 == x2)
569 {
570 if(x3 == x4)
571 {
572 System.out.print("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");
573 System.exit(0);
574 }
575 else
576 {
577 float k2 = (y3-y4)/(x3-x4);
578 float b2 = (x3*y4-x4*y3)/(x3-x4);
579
580 float x = x1;
581 float y = k2*x + b2;
582 float min = x3;
583 if(min > x4)
584 {
585 min = x4;
586 }
587 if(min > x1)
588 {
589 min = x1;
590 }
591
592 float max = x3;
593 if(max < x4)
594 {
595 max = x4;
596 }
597 if(max < x1)
598 {
599 max = x1;
600 }
601
602 if(x>min && x<max)
603 {
604 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"true");
605 System.exit(0);
606 }
607 else
608 {
609 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"false");
610 System.exit(0);
611 }
612
613 }
614 }
615 else if(x3 == x4)
616 {
617 if(x1 == x2)
618 {
619 System.out.print("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");
620 System.exit(0);
621 }
622 else
623 {
624 float k1 = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2);
625 float b1 = (x1*y2-x2*y1)/(x1-x2);
626
627
628 float x = x3;
629 float y = k1*x + b1;
630 float min = x1;
631 if(min > x2)
632 {
633 min = x2;
634 }
635 if(min > x3)
636 {
637 min = x3;
638 }
639
640 float max = x1;
641 if(max < x2)
642 {
643 max = x2;
644 }
645 if(max < x3)
646 {
647 max = x3;
648 }
649
650 if(x>min && x<max)
651 {
652 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"true");
653 System.exit(0);
654 }
655 else
656 {
657 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"false");
658 System.exit(0);
659 }
660
661 }
662 }
663 else//斜率存在
664 {
665 float k1 = (y1-y2)/(x1-x2);
666 float b1 = (x1*y2-x2*y1)/(x1-x2);
667 float k2 = (y3-y4)/(x3-x4);
668 float b2 = (x3*y4-x4*y3)/(x3-x4);
669
670
671 if(k1==k2)
672 {
673 System.out.print("is parallel lines,have no intersection point");
674 System.exit(0);
675 }
676 float x = (b2-b1)/(k1-k2);
677 float y = (b2-b1)/(k1-k2)*k1 + b1;
678 float min1 = x1;
679 float min2 = x3;
680 if(min1 > x2)
681 {
682 min1 = x2;
683 }
684 if(min2 > x4)
685 {
686 min2 = x4;
687 }
688 float min = min1;
689 if(min > min2)
690 {
691 min = min2;
692 }
693
694 float max1 = x1;
695 float max2 = x3;
696 if(max1 < x2)
697 {
698 max1 = x2;
699 }
700 if(max2 < x4)
701 {
702 max2 = x4;
703 }
704 float max = max1;
705 if(max < max2)
706 {
707 max = max2;
708 }
709
710
711 if(x>min && x<max)
712 {
713 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"true");
714 System.exit(0);
715 }
716 else
717 {
718 System.out.print(x+","+y+" "+"false");
719 System.exit(0);
720 }
721
722 }
723
724 }break;
725 default:
726 {
727 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
728 System.exit(0);
729 }
730 }
731
732
733 }
734
735 }
题目分析:题目的要求是比较直接的(只要按照题目的要求写过去,拿个30多分是没有问题的),笔者认为,主要难点有两个:i:信息的输入问题,如何从输入中得到
需要的信息及判断输入格式是否错误(这里笔者了解的有两个方向,正则表达式和字符串操作),这一点大家按照自己第一题的写法去写是没有什么大问题的。 ii:格式输
入错误的测试点,不知道大家是不是和笔者一样,将题目所有要求的代码实现了,题目所给的测试用例都通过了,但就是有一两个格式错误的测试点不能通过。可以这样说,
笔者在这题写代码花了半天,改bug卡了两天。最终,是因为一次偶然的机会,随便输入的一个样例测试(1: -3 ,01 -1,+1)发现结果不是输出wrong format,于是根据这个样例修改代码,
终于拿到了满分。
代码思路分析:这里笔者对正则表达式还不太熟练,因此对像这样类似的输入一整行数据,笔者是通过字符串操作切割提取出需要的的选项及坐标信息,进行一系列
的计算及操作。因此,按这种想法,思路是比较直接的(直接按题目要求一步一步写过去即可),写起来比较简单,但是代码重复很多,很多代码基本上都是复制前面
写好的代码粘贴过来的。也有很大一部分原因是笔者比较懒,不想将专门判断输入格式,及获取坐标信息的代码单独提出来专门做一个类或者方法,这样的话至少能
减少三百行代码。
踩坑心得:由于这题其实题目想法比较简单,只要耐着性子一步一步写过去其实都没有什么大问题的,所以笔者其实没有碰到什么很大的坑,唯一想说的就是,大家
写代码时可以多运用自己曾经学过的知识(尤其是数学),这样可以扩展你的思路。
例如:题目要求的第二点,如何求得点到直线的距离呢?

这里笔者刚开始的想法是用点到直线的距离公式,但再想一下发现不对,这样求直线的公式太麻烦了,再转念一想,求点到直线的距离不就是求这个点到已知线段
组成的三角形的高吗?三角形的高不就是面积的两倍除以这条已知线段的长度吗?已知线段的长度是非常好求的,那三角形的面积呢?笔者刚开始脑海中闪过的就是
初中学过的海伦公式,于是说干就干,这样,第二点就什么障碍都没了。

改进建议:就像笔者前面分析说的,如果将专门判断输入格式,及获取坐标信息的代码单独提出来专门做一个类或者方法,可以大大地减少代码。
1 int index_char = s.indexOf(':');
2 int index_x1 = s.indexOf(',');
3 int index_x2 = s.indexOf(',', index_x1+1);
4 int index_x3 = s.indexOf(',', index_x2+1);
5 int index_null1 = s.indexOf(" ");
6 int index_null2 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null1+1);
7
8 //判断0是否在首位
9 for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++)
10 {
11 if(s.charAt(i) == '0')
12 {
13 if(i<s.length()-2)
14 {
15 if(s.charAt(i+1)=='0')
16 {
17 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
18 System.exit(0);
19 }
20
21 if(s.charAt(i+1)>'0' && s.charAt(i+1)<='9')
22 {
23 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
24 System.exit(0);
25 }
26 }
27 }
28 }
29
30 //点的数量
31 if(index_null1 == -1 || index_null2 == -1)
32 {
33 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
34 System.exit(0);
35 }
36 int index_null3 = s.indexOf(" ", index_null2+1);
37 if(index_null3 !=-1)
38 {
39 System.out.println("wrong number of points");
40 System.exit(0);
41 }
42
43 //判断逗号数量是否不对
44 int sum_char = 0;
45 for(int i = 1; i<s.length(); i++)
46 {
47 if(s.charAt(i) == ',')
48 sum_char ++;
49 }
50 if(sum_char != 3 )
51 {
52 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
53 System.exit(0);
54 }
55 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null1) == -1)
56 {
57 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
58 System.exit(0);
59 }
60 if(s.indexOf(',', index_null2) == -1)
61 {
62 System.out.print("Wrong Format");
63 System.exit(0);
64 }
65
66
67 double x1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_char+1, index_x1));
68 double y1 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x1+1, index_null1));
69 double x2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null1+1, index_x2));
70 double y2 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x2+1, index_null2));
71 double x3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_null2+1, index_x3));
72 double y3 = Double.parseDouble(s.substring(index_x3+1, s.length()));
还有一点,就是判断输入格式是否错误的时候可以用正则表达式,这样可以强制输入必须是正确匹配的,不是直接输出wrong format,这样也可以
节省很多功夫。
②题目集六——7-3(银行类业务设计)
题目:
编写一个银行业务类BankBusiness,具有以下属性和方法:
(1)公有、静态的属性:银行名称bankName,初始值为“中国银行”。
(2)私有属性:账户名name、密码password、账户余额balance。
(3)银行对用户到来的欢迎(welcome)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“中国银行欢迎您的到来!”,其中“中国银行”自动使用bankName的值。
(4)银行对用户离开的提醒(welcomeNext)动作(静态、公有方法),显示“请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!”
(5)带参数的构造方法,完成开户操作。需要账户名name、密码password信息,同时让账户余额为0。
(6)用户的存款(deposit)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息),密码不对时无法存款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确、完成用户存款操作后,要提示用户的账户余额,例如“您的余额有1000.0元。”。
(7)用户的取款(withdraw)操作(公有方法,需要密码和交易额信息)。密码不对时无法取款且提示“您的密码错误!”;密码正确但余额不足时提示“您的余额不足!”;密码正确且余额充足时扣除交易额并提示用户的账户余额,例如“请取走钞票,您的余额还有500.0元。”。
编写一个测试类Main,在main方法中,先后执行以下操作:
(1)调用BankBusiness类的welcome()方法。
(2)接收键盘输入的用户名、密码信息作为参数,调用BankBusiness类带参数的构造方法,从而创建一个BankBusiness类的对象account。
(3)调用account的存款方法,输入正确的密码,存入若干元。密码及存款金额从键盘输入。
(4)调用account的取款方法,输入错误的密码,试图取款若干元。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(5)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额大于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(6)调用account的取款方法,输入正确的密码,试图取款若干元(取款金额小于余额)。密码及取款金额从键盘输入。
(7)调用BankBusiness类的welcomeNext()方法。
输入格式:
输入开户需要的姓名、密码
输入正确密码、存款金额
输入错误密码、取款金额
输入正确密码、大于余额的取款金额
输入正确密码、小于余额的取款金额
输出格式:
中国银行(银行名称)欢迎您的到来!
您的余额有多少元。
您的密码错误!
您的余额不足!
请取走钞票,您的余额还有多少元。
请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!
这里笔者先给出自己的源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 class BankBusiness{
4 public static String bankname = "中国银行";
5 private String name;
6 private int password;
7 private double balance = 0;
8
9
10 public BankBusiness() {
11 super();
12 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
13 }
14
15 public void welcome() {//欢迎
16 System.out.println(bankname + "欢迎您的到来!");
17 }
18
19 public void welcomeNext() {//送客
20 System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
21 }
22
23 public BankBusiness(String name, int password) {
24 super();
25 this.name = name;
26 this.password = password;
27 }
28
29 public void deposit(int password,int sum_money) {//存款
30 if(password != this.password) {
31 System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
32 }
33 else
34 {
35 this.balance += sum_money;
36 System.out.println("您的余额有" + this.balance + "元。");
37 }
38 }
39
40 public void withdraw(int password,int sum_money) {//取款
41 if(password != this.password) {
42 System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
43 }
44 else {
45 if(sum_money > this.balance) {
46 System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
47 }
48 else {
49 this.balance -= sum_money;
50 System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有" + this.balance + "元。");
51 }
52 }
53 }
54
55
56
57 }
58 public class Main {
59
60 public static void main(String[] args) {
61 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
62 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
63 BankBusiness account = new BankBusiness();
64 account.welcome();
65 String name_input = in.next();
66 int password_input = in.nextInt();
67 account = new BankBusiness(name_input, password_input);
68
69 account.deposit(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
70 account.withdraw(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
71 account.withdraw(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
72 account.withdraw(in.nextInt(), in.nextInt());
73 account.welcomeNext();
74
75 }
76
77 }
代码设计:
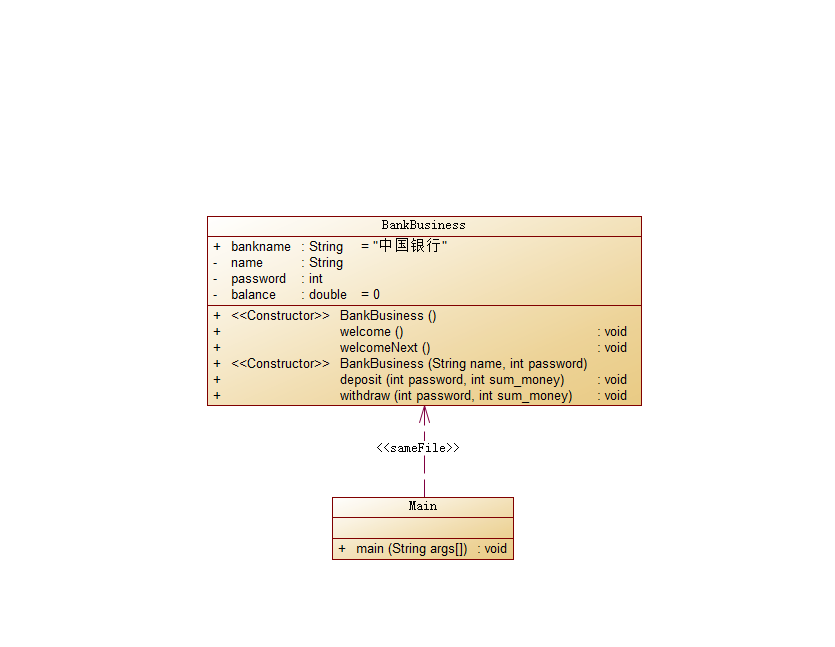
题目分析:相较于上次做的ATM类模拟系统,这一题,就显得简单多了,不过这里是通过类的设计实现的,也算是贴近我们
这门课程的学习内容吧。题目给的信息和提示很多,甚至连main方法的步骤都写出来了,所以这题难度不大,也是按照题目
提示一步一步写即可。
踩坑心得:
①:注意区分中英文,保险起见最好直接复制题目要的输出粘贴到代码上:

这里题目要求输出的感叹号其实都是中文的,可笔者想当然的认为都是英文的,所以后面改的时候出现了很多不必要的麻烦,
因此,为了减去不必要的麻烦,建议大家写输出结果的时候直接将题目给的粘贴过去即可。
②:没有必要的方法不要创建,培养良好的习惯。
这个在后面的期中考试分析部分会深刻的体现出来。
2、链表练习:
(很惭愧,笔者的双向链表其实是不符合老师要求的,为避免误人子弟,这里就给出笔者单向链表的内容)
题目:
使用Java实现链表功能,具体功能如下(参考):
public interface LinearListInterface <E>{
public boolean isEmpty();
public int getSize();
public E get(int index);
public void remove(int index);
public void add(int index, E theElement);
public void add(E element);
public void printList();
}
结构如下:
//LinkedList class
public class LList<E>{
private Node<E> head,curr,tail;//头结点(非第一个节点),当前节点,尾节点
private int size = 0;
}
//Node
public class Node<E>{
private E data;
private Node<E> next;
}
提交物:工程文件夹压缩文件,保证解压后可以直接import运行
笔者源码如下:
1 //单向链表
2 import java.util.Scanner;
3
4 //泛型接口(E)
5 interface LinearListInterface<E> {
6
7 //判断链表数据是否为空
8 public boolean isEmpty();
9
10 //返回链表大小
11 public int size();
12
13 //返回链表指定下标的数据
14 public E get(int index);
15
16 //删除指定下标的信息
17 public void remove(int index);
18
19 //在指定下标处添加元素
20 public void add(int index, E theElement);
21
22 //在节点尾部添加元素
23 public void add(E element);
24
25 //输出链表中的所有信息
26 public void printList();
27 }
28
29 //LinkedList class(链表类)
30 class LList<E> implements LinearListInterface<E>{
31 private Node<E> head;
32 private Node<E> tail;
33 private Node<E> curr;
34 private int size;
35
36 public boolean isEmpty() {//判断链表数据是否为空
37 if(this.tail == null)
38 {
39 return false;
40 }
41 else
42 {
43 return true;
44 }
45 }
46
47 public int size() { //返回链表大小
48 return this.size;
49 }
50
51 public E get(int index) { //返回链表指定下标的数据
52 int sign = 0;//sign:对照(指针):确定index对应链表的地址
53 if(index>=0 && index<=size)
54 {
55 this.curr = head;
56 while(sign < index) {
57 this.curr = this.curr.next;
58 sign++;
59 }
60 return this.curr.o;//返回当前节点(sign = index)
61 }
62 else
63 {
64 return null;//输入下标超出链表可选范围
65 }
66 }
67
68 public void remove(int index) {//删除指定下标的信息
69 int sign = 0;
70 if(index>=0 && index<=size) {
71 if(sign == 0) {//目标为头部
72 this.head = this.head.next;//头节点指向下一个
73 this.size--;
74 }
75 else
76 {
77 this.curr = this.head;
78 while(sign < index-1) {
79 this.curr = this.curr.next;
80 sign++;
81 }
82 this.curr.next = this.curr.next.next;
83 }
84 this.size--;
85 }
86 }
87
88 public void add(int index, E theElement) { //在指定下标处添加元素
89 int count = 0;
90 if(index>=0&&index<=this.size)
91 {
92 if(index==0)
93 {
94 this.head = new Node<E>(theElement,this.head);//如果添加在头部,theElement成为新头节点
95 }
96 else
97 {
98 this.curr = head;
99 while(count<index-1)
100 {//找到要添加信息的节点的位置
101 this.curr = this.curr.next;
102 count++;
103 }
104 this.curr.next = new Node<E>(theElement,this.curr.next);
105 }
106 this.size++;
107 }
108
109 }
110
111
112 public void add(E element) {//在节点尾部添加元素
113 Node<E> node =new Node<E>(element,null);//新节点
114 this.curr = this.tail;
115 this.tail = node;
116 if(curr==null) {
117 head = node;
118 }else{
119 curr.next = node;
120 }
121 this.size++;
122 }
123
124 public void printList() {//输出链表中的所有信息
125 for(int i = 0;i<this.size;i++) {
126 System.out.print(get(i).toString()+" ");
127 }
128 }
129
130 }
131
132 //Node(节点类)
133 class Node<E>{
134 public E o;//数据域
135 public Node<E> next;//指针域
136 public Node(E o,Node<E> next) {
137 this.o = o;
138 this.next = next;
139 }
140 }
141
142
143 public class link {
144 //主方法
145 public static void main(String[] args) {
146 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
147
148 LList<Integer> list = new LList<Integer>();//接口
149 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
150
151 System.out.println(" < 简单示例 > -->输入五个数据 ");
152 for(int i = 0;i<5;i++) {
153 list.add(in.nextInt());
154 }
155 System.out.println("所输入链表信息为:");
156 list.printList();//输出输入的数据
157
158 System.out.println("");
159 System.out.println("选择你要执行的链表操作:");
160 System.out.println("1.在指定下标添加节点信息");
161 System.out.println("2.在尾部添加节点信息");
162 System.out.println("3.退出");
163
164 int choice = in.nextInt();
165 while(true)
166 {
167 switch(choice)
168 {
169 case 1:
170 {
171 System.out.println("请输入指定下标:");
172 int index = in.nextInt();
173 System.out.println("请输入需添加的整型数据:");
174 int element = in.nextInt();
175 list.add(index, element);
176 System.out.println("\n增加第"+index+"节点后的链表:");
177 list.printList();//输出链表
178
179 System.out.println("");
180 System.out.println("选择你要执行的链表操作:");
181 System.out.println("1.在指定下标添加节点信息");
182 System.out.println("2.在尾部添加节点信息");
183 System.out.println("3.退出");
184 choice = in.nextInt();
185 }break;
186 case 2:
187 {
188 System.out.println("请输入需添加的信息:");
189 int index = in.nextInt();
190 list.add(index);
191 System.out.println("添加节点后的链表信息:");
192 list.printList();//输出链表
193
194 System.out.println("");
195 System.out.println("选择你要执行的链表操作:");
196 System.out.println("1.在指定下标添加节点信息");
197 System.out.println("2.在尾部添加节点信息");
198 System.out.println("3.退出");
199 choice = in.nextInt();
200 }break;
201 case 3:
202 {
203 System.exit(0);
204 }break;
205 default: System.exit(0);
206 }
207
208 }
209 }
分析:笔者认为,相对于双向链表,单向链表比较直接,因为就像上学期c语言那样,只需关注一个next指针即可
,这样设计功能接口时思路也会比较清新,所以笔者比较适应单向链表。对于双向链表,笔者就会比较晕,不知道
怎么协调两个指针pre和next,当然,最后做是做出来的,但功能实现方面,肯定是没有完全符合老师给的要求的。
运行示例:
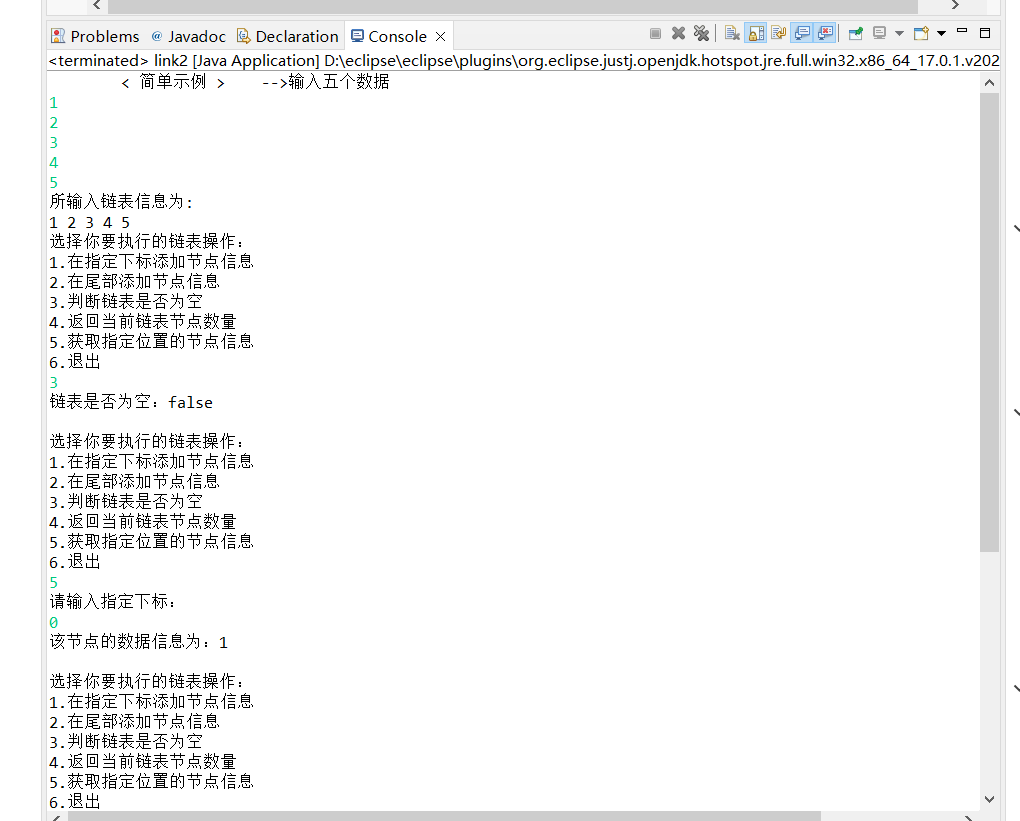
心得:说到运行,笔者就想说一下main方法的事情,因为在双向链表互评的时候,笔者改的三人,有两个是没有写main函数的
可老师要求的是要可以运行调试,可你没main方法,你是怎么运行的呢,就确定写完之后就一定是对的吗?因此,建议大家做事一定
要做到尽善尽美,这样你开心,别人也舒服。
3、期中考试小结:
前言分析:这次期中考试题目不难,三题呈迭代进行,正如老师所说,上一题的源码可以直接复制到下一题使用,再进行修改即可。
第一题非常直接,笔者就不在这赘述了。
第二、三题:
源码:
1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 import javax.lang.model.element.Element;
4
5 public class Main {
6
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
9 Point point1 = new Point();
10 Point point2 = new Point();
11 Plane plane = new Plane();
12 double x1 = in.nextDouble();
13 double y1 = in.nextDouble();
14 double x2 = in.nextDouble();
15 double y2 = in.nextDouble();
16
17 if (x1 > 0 && x1 <= 200 && y1 > 0 && y1 <= 200 && x2 > 0 && x2 <= 200 && y2 > 0 && y2 <= 200) {
18 point1.setX(x1);
19 point1.setY(y1);
20 point2.setX(x2);
21 point2.setY(y2);
22 } else {
23 System.out.println("Wrong Format");
24 System.exit(0);
25 }
26 String color = in.next();
27 Line line = new Line(point1, point2, color);
28 plane.setColor(color);
29
30 // point1.display();
31 // System.out.println("");
32 // point2.display();
33 // System.out.println("");
34 // line.display();
35 // System.out.println("");
36 // plane.display();
37
38 // Element element;
39 // element = (Element) point1;// 起点Point
40 // ((Point) element).display();
41 //
42 // element = (Element) point2;// 终点Point
43 // ((Point) element).display();
44 //
45 // element = (Element) line;// 线段
46 // ((Line) element).display();
47 //
48 // element = (Element) plane;// 面
49 // ((Plane) element).display();
50 point1.display();
51 System.out.println("");
52 point2.display();
53 System.out.println("");
54 line.display();
55 System.out.println("");
56 plane.display();
57
58 }
59
60 }
61
62 class Point extends Elememt {
63 private double x;
64 private double y;
65
66 public Point() {
67 super();
68 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
69 }
70
71 public Point(double x, double y) {
72 super();
73 this.x = x;
74 this.y = y;
75 }
76
77 public double getX() {
78 return x;
79 }
80
81 public void setX(double x) {
82 this.x = x;
83 }
84
85 public double getY() {
86 return y;
87 }
88
89 public void setY(double y) {
90 this.y = y;
91 }
92
93 public void display() {
94 System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)", this.x, this.y);
95 }
96
97 }
98
99 class Line extends Elememt {
100 private Point point1 = new Point();
101 private Point point2 = new Point();
102 private String color;
103
104 public Line() {
105 super();
106 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
107 }
108
109 public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) {
110 super();
111 this.point1 = point1;
112 this.point2 = point2;
113 this.color = color;
114 }
115
116 public Point getPoint1() {
117 return point1;
118 }
119
120 public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
121 this.point1 = point1;
122 }
123
124 public Point getPoint2() {
125 return point2;
126 }
127
128 public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
129 this.point2 = point2;
130 }
131
132 public String getColor() {
133 return color;
134 }
135
136 public void setColor(String color) {
137 this.color = color;
138 }
139
140 public double getDistance() {
141 double x = Math.pow((point1.getX() - point2.getX()), 2);
142 double y = Math.pow((point1.getY() - point2.getY()), 2);
143 return Math.sqrt(x + y);
144 }
145
146 public void display() {
147
148 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + this.color);
149 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
150 point1.display();
151 System.out.println("");
152 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
153 point2.display();
154 System.out.println("");
155 System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f", this.getDistance());
156
157 }
158 }
159
160 abstract class Elememt {
161 public abstract void display();
162 }
163
164 class Plane extends Elememt {
165 private String color;
166
167 public Plane() {
168 super();
169 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
170 }
171
172 public Plane(String color) {
173 super();
174 this.color = color;
175 }
176
177 public String getColor() {
178 return color;
179 }
180
181 public void setColor(String color) {
182 this.color = color;
183 }
184
185 public void display() {
186 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + this.color);
187 }
188
189 }
首先,先给大家看个东西:
这是笔者写的代码的类图:
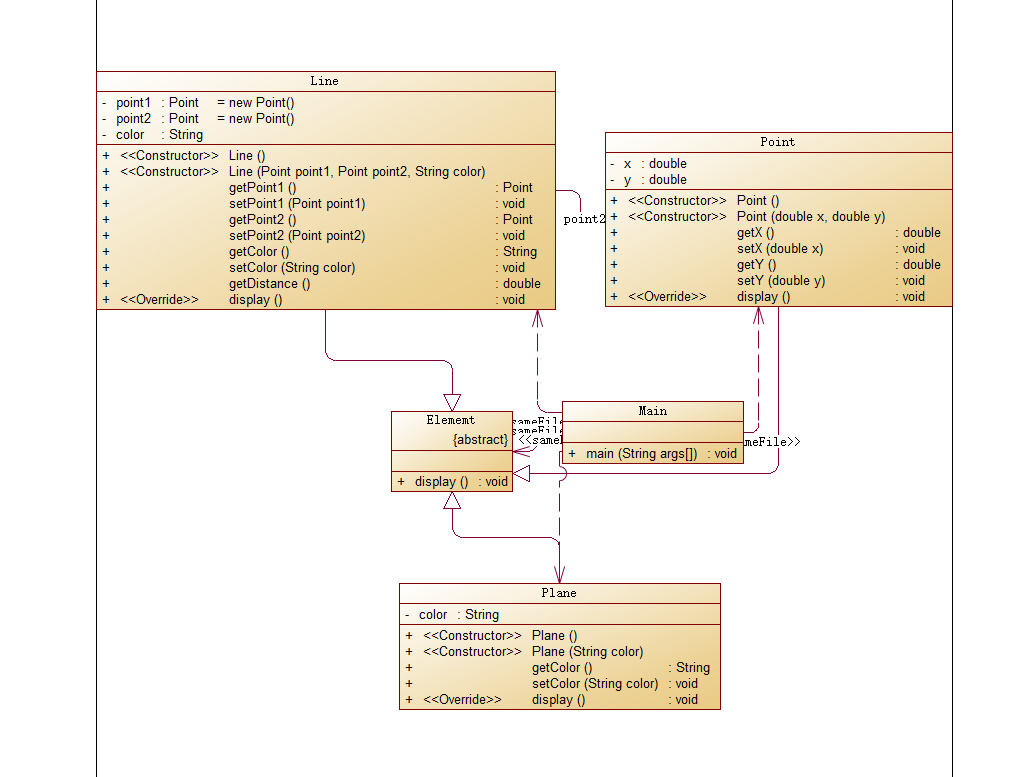
这是题目要求的类图:
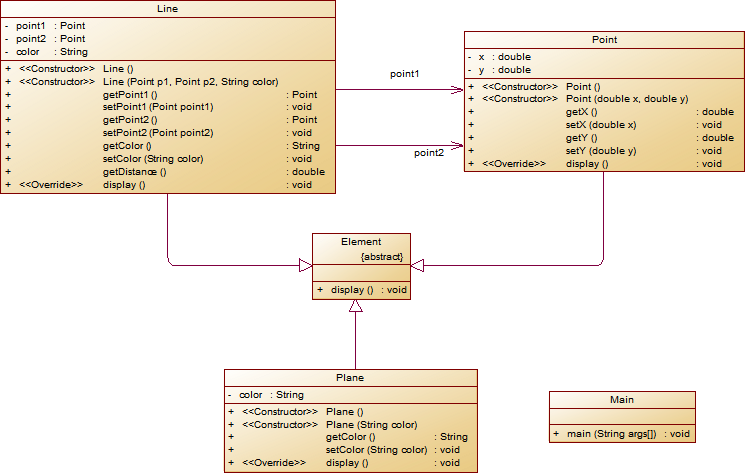
怎么样,是不是没有对比没有伤害,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~。
这也是笔者的心得之一:
一定一定要按要求写代码。
也许现在有很多像笔者一样,对java还不太熟悉,上学期c语言也没学太好的人,认为这样很难,直接一点不行吗?但我们必须要按原则做事,
正如老师所说,我们是做工程的,做事一定要严谨,这是对我们自己的将来负责。
在期中考试之后,笔者又根据老师给的代码对自己的代码进行改进,功夫不负有心人,笔者终于成功了,为了不再赘述,这里笔者就只给出改进完之后的类图:
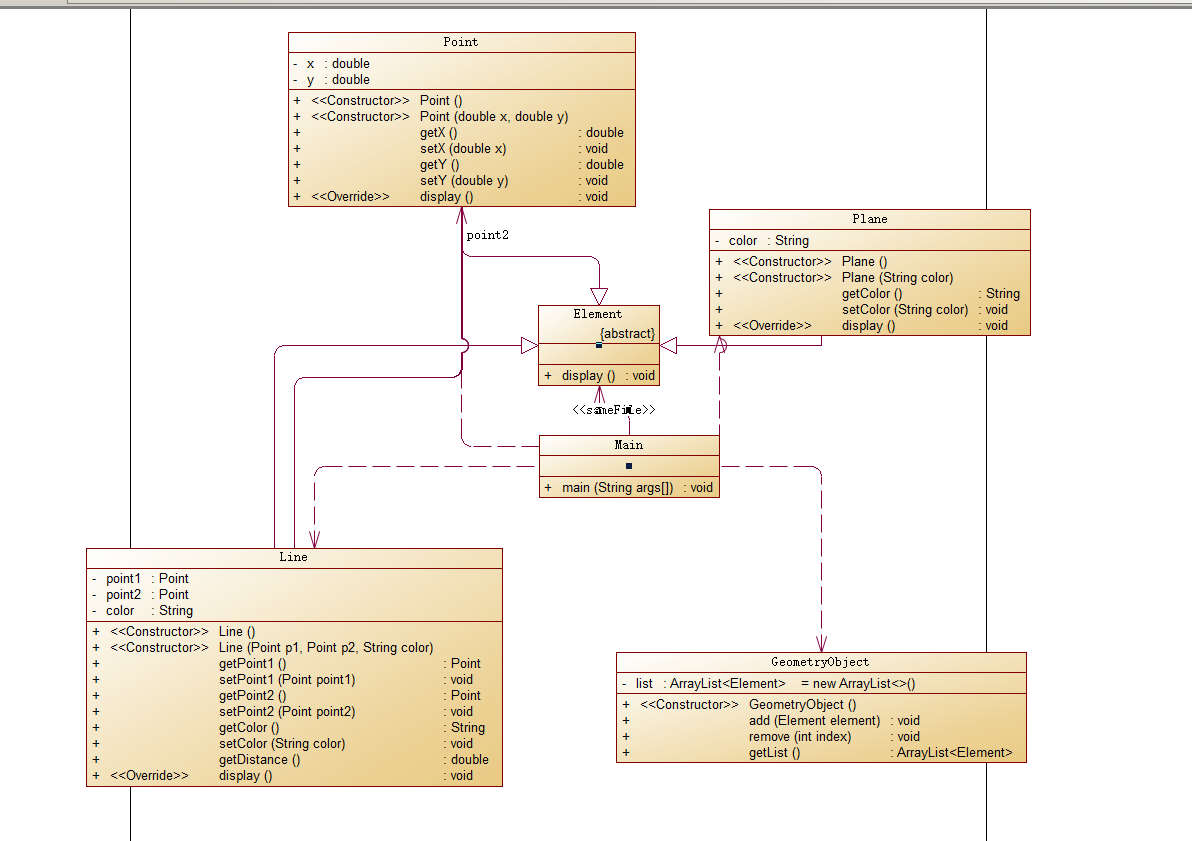
看到是自己写的代码结构这么清晰(虽然借助了外力),笔者感到十分愉悦。
总结:
笔者认为,这几周最大的收获就是可以完全靠自己(不问同学,不网上参考)写题目,并且可以拿到不错的成绩,
这是我自进这个专业以来第一次有这样的感觉,就是好像可以自己做点事情,因为笔者其实对编程这方面没有很大的
兴趣,因此并没有在这方面花太多时间,直到这学期,我才顿悟,这是我的专业啊,所以我一定要认真学,把前面落下
的都补上来,尤其是期中考试的时候,我切实的感受到那种快感,在一个安静的环境下,独自一人完成这些题目,并拿到
属于自己能力应该拿到的分数,这种感觉让我非常愉悦。
但是,笔者也看到了自己还有很多不足之处,就比如说上面提到的类图的事,这让我明白我还有很多知识(如多态、
容器的常用类、面向对象的设计原则等)没有掌握,还有很多坏习惯还有待改正,这些也就是我下半段学期要做到事,
对此,我会不断努力,改进。
在这里笔者以自己的体悟建议大家,不要轻言放弃,现在还不会就加紧学,只要肯下功夫,一定可以突破自己的瓶颈。
对教学方面的改进建议:
没什么特别想说的,就是希望可以早点转换成线下教学,o(* ̄▽ ̄*)ブ。
皓远的第二次博客作业(最新pta集,链表练习及期中考试总结)的更多相关文章
- OO第二次博客作业——电梯调度
OO第二次博客作业——电梯调度 前言 最近三周,OO课程进入多线程学习阶段,主要通过三次电梯调度作业来学习.从单部电梯的傻瓜式调度到有性能要求的调度到多部电梯的调度,难度逐渐提升,对同学们的要求逐渐变 ...
- OO第二次博客作业—17373247
OO第二次博客作业 零.写在前面 OO第二单元宣告结束,在这个单元里自己算是真正对面向对象编程产生了比较深刻的理解,也认识到了一个合理的架构为编程带来的极大的便利. (挂三次评测分数 看出得分接近等差 ...
- Java第二次博客作业
Java第二次博客作业 时间过的很快啊,在不知不觉中这门课程的学习也就快要过去一半了,现在就来总结一下在这个第二个月的学习当中存在的问题以及得到的心得. 1.前言 第四次题目集和第五次题目集给我的感觉 ...
- OO第二次博客作业(第二单元总结)
在我开始写这次博客作业的时候,窗外响起了希望之花,由此联想到乘坐自己写的电梯FROM-3-TO--1下楼洗澡,然后······ 开个玩笑,这么辣鸡的电梯肯定不会投入实际使用的,何况只是一次作业.还是从 ...
- 第二周博客作业 <西北师范大学| 周安伟>
一,本周助教小结 逐步开始适应助教工作,对学生发布的博客进行点评,查看学生对软件工程前期的准备情况. 二,助教本人博客 https://home.cnblogs.com/u/zaw-315/ 三,学生 ...
- C语言第二次博客作业——分支结构
一.PTA实验作业 题目1:计算分段函数 1.实验代码 #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> int main(void) { double x ...
- C语言第二次博客作业---分支结构
一,PTA实验作业 题目1.计算分段函数 本题目要求计算下列分段函数f(x)的值: 1.实验代码 double x,result; scanf("%lf",&x); if( ...
- 第二周博客作业<西北师范大学|李晓婷>
1.助教博客链接:https://home.cnblogs.com/u/lxt-/ 2.点评作业内容: https://www.cnblogs.com/dxd123/p/10494907.html#4 ...
- [2017BUAA软工]第二次博客作业:代码复审
〇.comment链接 https://github.com/hanayashiki/Sudoku/issues/1 一.代码复审 1.概要部分 (1)代码能符合需求和规格说明么? 经测试,对于合法输 ...
随机推荐
- c++对c的拓展_常量引用
常量引用:不能通过引用去修改引用所指向的内容 const int &ref =val; // const int *const ref =&val; 注意:可引用常量 (普通引用无法 ...
- numpy教程01---ndarray的创建
欢迎关注公众号[Python开发实战], 获取更多内容! 工具-numpy numpy是使用Python进行数据科学的基础库.numpy以一个强大的N维数组对象为中心,它还包含有用的线性代数,傅里叶变 ...
- Spring-注入方式(基于xml方式)
1.基于xml方式创建对象 <!--配置User类对象的创建 --> <bean id="user" class="com.at.spring5.Use ...
- spring配置数据源(交给spring容器完成)
##将DataSource的创建权交给spring容器去完成 1.导入spring依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework< ...
- [已解决] error: cannot convert `int*' to `int**' for argument `2' to `void print_f(int, int**)'
#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" #include "time.h" void print_f( ...
- JavaScript学习总结5-作用域
由于所有的全局变量都会绑定到window上,如果不同的JS文件,使用了相同的全局变量,会造成冲突,可以把自己的代码全部放入及定义的唯一空间中,减少全局命名冲突问题
- 深度学习教程 | Seq2Seq序列模型和注意力机制
作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI 教程地址:http://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/35 本文地址:http://www.showmeai.tech/article-det ...
- Divan and bitwise operations
这是一道比较综合的数学题目,光是吧题目看懂就花了我好一会儿时间,先看看题目吧: 题目分析:对于m段给定连续段的或值,要求出n个数的序列子序列的异或值之和: 题解: 这道题,我们先不要把它当作一个数一个 ...
- Java Windows下读取注册表的工具类
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import ...
- 读完学会shell语法,shell脚本80%已经学会
第3章 shell语法讲解 3.1 shell运算讲解 3.1.1 运算符的讲解 3.1.2 shell运算方式的讲解 3.1.2.1 $(())运算 [root@m01 test_init] # a ...
