ThreadPoolExecutor线程池
为什么使用线程池:
1、创建/销毁线程伴随着系统开销,过于频繁的创建/销毁线程,会很大程度上影响处理效率。
2、线程并发数量过多,抢占系统资源从而导致阻塞。
3、对线程进行一些简单的管理。
在java中,线程池的类为ThreadPoolExecutor,首先来看一下该类的继承关系
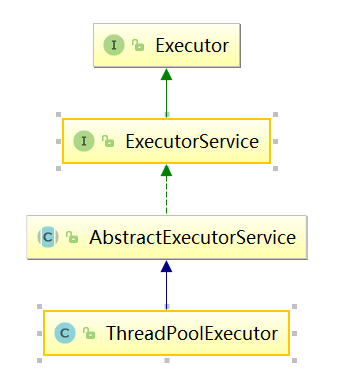
大抵所有的线程池都是来自于Executor接口,这个接口里面定义了线程池的抽象方法:
void execute(Runnable command);
在Executor接口之后的是ExecutorServer接口,里面定义了一些submit()、shutdown()方法。
然后我们来看一下ThreadPoolExecutor类提供的四种构造方法:
//五个参数的构造函数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) //六个参数的构造函数-1
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) //六个参数的构造函数-2
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) //七个参数的构造函数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
方法中的参数:
int corePoolSize 线程池中核心线程大小
在线程池中的线程小于核心线程数时,则新建的线程属于核心线程,否则属于非核心线程。默认情况下,核心线程会一直存货于线程池,即使什么也不做。但如果指定类中的allowCoreThreadTimeOut为true,则核心线程闲置一定时间后也会被销毁,具体时间,由参数指定。
int maximumPoolSize 线程池中最大线程数
线程池中存在的线程数量不会超过最大线程数,如果在达到最大线程数后仍有新的任务需要执行,则会进行排队。
long keepAliveTime 非核心线程的最大存活时间
线程池中的非核心线程处于闲置状态时,则会开始计时,达到指定时间后将被销毁。如果指定参数allowCoreThreadTimeOut为true,则核心线程同样适用。
TimeUnit unit keepAliveTime的单位
类型TimeUnit是枚举类型,包括
NANOSECONDS : 1微毫秒 = 1微秒 / 1000
MICROSECONDS : 1微秒 = 1毫秒 / 1000
MILLISECONDS : 1毫秒 = 1秒 /1000
SECONDS : 秒
MINUTES : 分
HOURS : 小时
DAYS : 天
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue 任务队列
等待执行的Runnable对象所组成的队列。如果所有核心线程都正在执行,则任务会进行队列。如果队列满了,则新建非核心线程。
常用的workQueue类型:
SynchronousQueue:这个队列接收任务后直接提交给线程处理而不会保留它。为了避免线程数量达到maximumPoolSize而无法新建新的线程,通常将maximumPoolSize设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE,即无限大。
LinkedBlockingQueue:这个队列接收任务后,将任务交给核心线程处理,如果没有空闲的核心线程,则会保留在队列中。由于该队列没有数量限制,因此线程数永远不会超过核心线程数,即maximumPoolSize无效。
ArrayBlockingQueue:这个队列与LinkedBlockingQueue的区别在于有数量限制,当队列已满后将新建非核心线程,如果总线程数达到maximumPoolSize,则发生错误。
DelayQueue:队列内元素必须实现delayed接口,即传进去的任务必须先实现delayed接口。接收到的任务会先进入队列,达到了指定的延时时间,才会执行任务。
ThreadFactory threadFactory 创建线程的方式。
这是一个接口,new的时候需要实现Thread newThread(Runnable r)方法。
RejectedExecutionHandler handler 异常
用来抛出异常,如发生异常,则由该异常对象抛出信息,即使不指定也会有个默认值。
向线程池添加任务
ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(Runnable command) //这个方法是在ThreadPoolExcutor中重写,没有返回结果的添加线程任务
// 这个方法也可以被用来往线程池中添加线程任务。不同处在于它是定义在AbstractExecutorServer中,在ThreadPoolExecutor中没有再重写它。
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);
execute(ftask); //内部仍是调用了execute()方法。
return ftask;
}
ThreadPoolExecutor的策略
当一个任务被添加进线程池后:
1、线程数未达到核心线程数,新建一个核心线程数。
2、线程数已达到核心线程数,任务保留进队列。
3、线程数已达到核心线程数,任务队列已满,新建一个非核心线程数。
4、线程数已达到最大线程数,任务队列已满,抛出异常。
常见的四种线程池
(在阿里巴巴JAVA开发手册中是不建议通过Executors来创建这些配置好的线程池)
java对线程池类ThreadPoolExecutor进行了封装,提供了常用的四种线程池。这四种线程池都是或直接或间接配置ThreadPoolExecutor的参数实现。
1、CachedThreadPool() 可缓存线程池
- 线程数无限
- 有空闲线程则使用空闲线程,否则创建新线程
- 一定程度上减少创建/销毁线程的开销
创建方法
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
源码
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
2、FixedThreadPool() 定长线程池
- 可控制线程最大并发数
- 超出的线程会在队列中等待
创建方法
//nThreads => 最大线程数即maximumPoolSize
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads); //threadFactory => 创建线程的方法
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory);
源码
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
3、ScheduledTheadPool() 定长线程池
- 支持定时周期性的执行任务
创建方法
//nThreads => 最大线程数即maximumPoolSize
ExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize);
源码
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
//ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor():
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
4、SingleThreadExecutor() 单线程线程池
有且仅有一个工作线程执行任务
所有任务按照指定顺序执行,即遵循队列的出队入队规则。
创建方法
ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadPool();
源码
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
ThreadPoolExecutor任务拒绝策略
ThreadPoolExecutor里面定义了4个静态内部类,用来标识不同的异常类型:
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy //拒绝接收任务并抛出rejectedExecuption
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy //拒绝接收任务,但不抛出任何异常
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy //将等待队列中的第一个任务抛弃,接收新的线程任务。
ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy //由调用线程处理该任务。
下面我们来分别用代码测试一下这几种任务拒绝策略
public void testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
// 先定义一个线程池,核心线程数2,最大线程数4,非核心线程过期时间10分钟,队列最大任务数2.
ThreadPoolExecutor te =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(,,,
TimeUnit.MINUTES, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(), handler);
// 一次性添加20个任务进入线程池,由于我们配置的线程池最大只能接收6个任务,因此一旦超过6个就会触发拒绝策略
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
final int j = i;
te.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread() + "正在执行" + j + "!" + new Date());
Thread.sleep( * );
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
测试第一个任务拒绝策略
AbortPolicy :
testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
返回结果:线程池中添加的任务超出了6个,抛出异常,并拒绝接收,可以看到打印出来的i是从0到5。
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException: Task Main5$@681a9515 rejected from java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor@3af49f1c[Running, pool size = , active threads = , queued tasks = , completed tasks = ]
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$AbortPolicy.rejectedExecution(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.reject(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.execute(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:)
at Main5.testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(Main5.java:)
at Main5.main(Main5.java:)
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行5!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行0!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行1!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行4!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行2!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行3!Thu May :: CST
测试第二个任务拒绝策略
DiscardPolicy :
testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy ());
返回结果:和AbortPolicy区别只在于没有抛出异常。
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行1!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行4!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行5!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行0!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行3!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行2!Thu May :: CST
测试第三个任务拒绝策略
DiscardOldestPolicy :
testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
返回结果:在这里,首先执行前4个线程任务,同时还会有2两个线程任务存放在队列中等待竞争。此时第7个任务进来,将队列中的第一个任务丢弃,将第7个任务添加进队列,第8个,第9个一直如此,直到第19个任务被添加进来,此时队列中的两个任务只剩下了18和19。其余的任务已经都被丢弃。因此等到前面4个任务执行完成后,第18和19个任务开始执行。
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行4!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行0!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行1!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行5!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行18!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行19!Thu May :: CST
测试第四个任务拒绝策略:
CallerRunsPolicy :
testThreadPoolRejectedPoicy(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
返回结果:任务比较多就只取了前面部分。可以看到线程池中一直有4个线程在执行任务,并且队列中也保持了两个任务等待。此时添加了新的任务进来,会交由当前线程(我是在main方法中执行,因此是main线程)执行任务。当main线程执行任务的时候,会与往线程池中添加新任务处于竞争状态。在这种情况下,20个线程任务会被一直执行到全部完成。
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行4!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行1!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行5!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行0!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[main,,main]正在执行6!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行3!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行2!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行7!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[pool--thread-,,main]正在执行8!Thu May :: CST
当前线程Thread[main,,main]正在执行9!Thu May :: CST 2019
……
……
原文链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/210eab345423
ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的更多相关文章
- 13.ThreadPoolExecutor线程池之submit方法
jdk1.7.0_79 在上一篇<ThreadPoolExecutor线程池原理及其execute方法>中提到了线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的原理以及它的execute方法 ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的源码解析
1.背景介绍 上一篇从整体上介绍了Executor接口,从上一篇我们知道了Executor框架的最顶层实现是ThreadPoolExecutor类,Executors工厂类中提供的newSchedul ...
- j.u.c系列(01) ---初探ThreadPoolExecutor线程池
写在前面 之前探索tomcat7启动的过程中,使用了线程池(ThreadPoolExecutor)的技术 public void createExecutor() { internalExecutor ...
- Java并发——ThreadPoolExecutor线程池解析及Executor创建线程常见四种方式
前言: 在刚学Java并发的时候基本上第一个demo都会写new Thread来创建线程.但是随着学的深入之后发现基本上都是使用线程池来直接获取线程.那么为什么会有这样的情况发生呢? new Thre ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池
TestThreadPoolExecutorMain package core.test.threadpool; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQu ...
- 十、自定义ThreadPoolExecutor线程池
自定义ThreadPoolExecutor线程池 自定义线程池需要遵循的规则 [1]线程池大小的设置 1.计算密集型: 顾名思义就是应用需要非常多的CPU计算资源,在多核CPU时代,我们要让每一个CP ...
- Executors、ThreadPoolExecutor线程池讲解
官方+白话讲解Executors.ThreadPoolExecutor线程池使用 Executors:JDK给提供的线程工具类,静态方法构建线程池服务ExecutorService,也就是Thread ...
- SpringBoot项目框架下ThreadPoolExecutor线程池+Queue缓冲队列实现高并发中进行下单业务
主要是自己在项目中(中小型项目) 有支付下单业务(只是办理VIP,没有涉及到商品库存),目前用户量还没有上来,目前没有出现问题,但是想到如果用户量变大,下单并发量变大,可能会出现一系列的问题,趁着空闲 ...
- 手写线程池,对照学习ThreadPoolExecutor线程池实现原理!
作者:小傅哥 博客:https://bugstack.cn Github:https://github.com/fuzhengwei/CodeGuide/wiki 沉淀.分享.成长,让自己和他人都能有 ...
- 源码剖析ThreadPoolExecutor线程池及阻塞队列
本文章对ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的底层源码进行分析,线程池如何起到了线程复用.又是如何进行维护我们的线程任务的呢?我们直接进入正题: 首先我们看一下ThreadPoolExecuto ...
随机推荐
- MyBatis基础入门《十六》缓存
MyBatis基础入门<十六>缓存 >> 一级缓存 >> 二级缓存 >> MyBatis的全局cache配置 >> 在Mapper XML文 ...
- 从0开始搭建vue+webpack脚手架(二)
接着从0开始搭建vue+webpack脚手架(一) 三.配置webpack-dev-server 1. webpack-dev-server自带一个node的服务器, 项目在服务端运行的同时可以实现热 ...
- jQuery-手风琴效果-2
动画 高级函数:基于底层函数又进行了封装 两大块:简化版的动画函数和万能动画函数 简化版动画函数 显示/隐藏$().show; $(...).hide(); 强调:无参数的show()/hide()使 ...
- beego 初体验 - 环境搭建
首先,安装go运行时和beego beego,在git bash 运行命令: go get github.com/beego/bee go get github.com/astaxie/beego g ...
- qq浏览器默认字体设置
- django 设置不带后缀的访问路径
在urls.py 设置空路径,并指向对应的html文件 url(r'^$', views.index),
- 数据集成工具Kettle、Sqoop、DataX的比较
数据集成工具很多,下面是几个使用比较多的开源工具. 1.阿里开源软件:DataX DataX 是一个异构数据源离线同步工具,致力于实现包括关系型数据库(MySQL.Oracle等).H ...
- loadRunner手动关联, web_reg_save_param_regexp()函数正则匹配字符,赋值给变量
loadRunner写脚本实现登录机票网站,手动关联,获取页面源码中特定字符 手动关联,就是通过函数获取某个步骤生成的字符,赋值给一个变量,这个变量可以作为接下来某个步骤的输入, 以便这个脚本能够在存 ...
- MySQL 0Day漏洞出现 该漏洞可以拿到本地Root权限
2016年9月12日, legalhackers.com网站发布了编号为CVE-2016-6662的0day漏洞公告 .由于该漏洞可以获得MySQL服务器的Root权限,且影响MySql5.5.5.6 ...
- git log的常见用法
git log 使用git log命令,什么参数都没有的话,会以下面的格式输出所有的日志(我当前的git仓库只有三个提交).如果日志特别多的话,在git bash中,按向下键来查看更多,按q键退出查看 ...
