Java NIO通信的基础,基于TCP C/S例子介绍
为了更好的理解Netty异步事件驱动网络通信框架,有必要先了解一点Java NIO原生的通信理论,下面将结合基于TCP的例子程序,含客户端和服务端的源码,实现了Echo流程。
Java NIO的核心概念有三个:Channel,Selector,ByteBuffer。
而这当中,Channel的比重最大,NIO的功能主要基于Channel来实现,进行业务逻辑操作。Selector主要是IO事件选择器,当一个Channel创建并配置好后,注册到Selector上,与Selector相关的重要概念是SelectionKey,这个上面绑定了IO事件相关的Channel。在获取到Channel后,进行数据的读写操作,Channel的数据读写是不能直接操作数据的,必须基于ByteBuffer进行,然而,Java NIO原生的ByteBuffer操作比较繁琐,要flip和clear操作。
1. 而我们在业务逻辑操作中,用到的channel,主要有ServerSocketChannel,SocketChannel,DataGramChannel。下面,用一个图,来简要的描述下Channel到这三个具体之类之间的继承/实现关系(该图来自网络,若有不妥,请告知,谢谢)。

2. Selector,是事件选择器,创建Selector后,在调用select之前,在注册Channel到这个Selector上时,必须指定关注的事件类型(interestOps)。通过这个类的select函数,可以获取选择上监听到的IO事件。一旦select函数检测到事件,就可以从Selector上获取到具体有哪些IO事件,这些事件通过SelectionKey承载,SelectionKey上标记出该事件的类型,比如是OP_CONNECT,OP_ACCEPT还是OP_READ等。另外,SelectionKey还记录了对应该IO事件发生的Channel,可以通过SelectionKey得到该Channel。
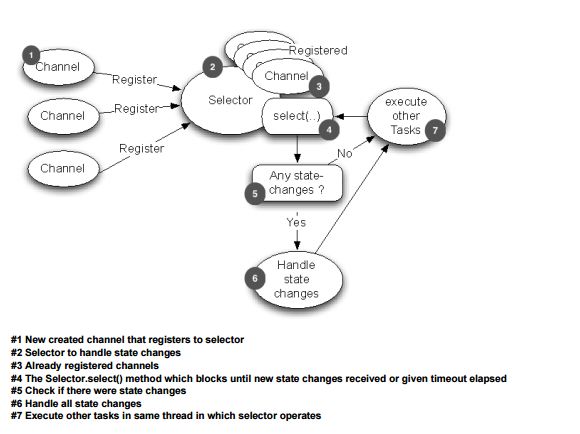
3. ByteBuffer。 因为字节操作,是操作系统与IO设备之间进行通信的基本数据单元,在Java NIO中,各通道Channel之间进行数据通信时,指定必须是基于ByteBuffer的。 ByteBuffer有两个重要的函数,flip和clear。当Channel调用read函数,将数据读到ByteBuffer中后,ByteBuffer的数据长度指针将会移动到数据长度所在的位置,这个位置是小于等于ByteBuffer容量capacity值的。当业务逻辑操作读取到的数据前,需要对ByteBuffer做一下flip操作,就是将limit指针指向当前数据指针position的位置,然后,将position指针指向0的位置。数据逻辑结束后,一般要恢复ByteBuffer,即调用clear函数。

这三个重要的概念,做了一番解释和描述后,就以一个demo程序,基于Java NIO的TCP C/S源码,代码中带有了重要逻辑的注释,后续不再单独解释。
A. TCP Server:
- /**
- * @author "shihuc"
- * @date 2017年3月16日
- */
- package javaSocket.tcp.server;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
- import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
- import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
- import java.nio.channels.Selector;
- import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
- import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
- import java.nio.charset.Charset;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Set;
- import javaSocket.tcp.Constants;
- /**
- * @author chengsh05
- *
- */
- public class TcpServer {
- /**
- * @param args
- */
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try {
- startServer(Constants.SERVER_PORT);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- public static void startServer(int port) throws IOException{
- /*
- *开启一个服务channel,
- *A selectable channel for stream-oriented listening sockets.
- */
- ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
- serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
- /*
- * 创建一个selector
- */
- Selector selector = Selector.open();
- /*
- * 将创建的serverChannel注册到selector选择器上,指定这个channel只关心OP_ACCEPT事件
- */
- serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
- while (true) {
- /*
- * select()操作,默认是阻塞模式的,即,当没有accept或者read时间到来时,将一直阻塞不往下面继续执行。
- */
- int readyChannels = selector.select();
- if (readyChannels <= ) {
- continue;
- }
- /*
- * 从selector上获取到了IO事件,可能是accept,也有可能是read
- */
- Set<SelectionKey> SelectonKeySet = selector.selectedKeys();
- Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = SelectonKeySet.iterator();
- /*
- * 循环遍历SelectionKeySet中的所有的SelectionKey
- */
- while (iterator.hasNext()) {
- SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
- if (key.isAcceptable()) { //处理OP_ACCEPT事件
- SocketChannel socketChannel = serverChannel.accept();
- socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
- } else if (key.isReadable()) { //处理OP_READ事件
- SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate();
- int readBytes = ;
- int ret = ;
- /*
- * 注意读数据的时候,ByteBuffer的操作,需要flip,clear进行指针位置的调整
- */
- while ((ret = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)) > ) {
- readBytes += ret;
- byteBuffer.flip();
- sb.append(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer).toString());
- byteBuffer.clear();
- }
- if (readBytes == ) {
- System.err.println("handle opposite close Exception");
- socketChannel.close();
- }
- String message = sb.toString();
- System.out.println("Message from client: " + message);
- if (Constants.CLIENT_CLOSE.equalsIgnoreCase(message.toString().trim())) {
- System.out.println("Client is going to shutdown!");
- socketChannel.close();
- } else if (Constants.SERVER_CLOSE.equalsIgnoreCase(message.trim())) {
- System.out.println("Server is going to shutdown!");
- socketChannel.close();
- serverChannel.close();
- selector.close();
- System.exit();
- } else {
- String outMessage = "Server response:" + message;
- socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(outMessage));
- }
- }
- /*
- * 将selector上当前已经监听到的且已经处理了的事件标记清除掉。
- */
- iterator.remove();
- }
- }
- }
- }
B. TCP Client
- /**
- * @author "shihuc"
- * @date 2017年3月16日
- */
- package javaSocket.tcp.client;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
- import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
- import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
- import java.nio.channels.Selector;
- import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
- import java.nio.charset.Charset;
- import java.util.Scanner;
- import javaSocket.tcp.Constants;
- /**
- * @author chengsh05
- *
- */
- public class TcpClient {
- /**
- * @param args
- */
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- try {
- startClient(Constants.SERVER_IP, Constants.SERVER_PORT);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- public static void startClient(String serverIp, int serverPort) throws IOException{
- /*
- * 创建一个SocketChannel,指定为非阻塞模式
- * A selectable channel for stream-oriented connecting sockets.
- */
- SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
- socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- /*
- * 连接到指定的服务地址
- */
- socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(serverIp, serverPort));
- /*
- * 创建一个事件选择器Selector
- */
- Selector selector = Selector.open();
- /*
- * 将创建的SocketChannel注册到指定的Selector上,并指定关注的事件类型为OP_CONNECT
- */
- socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
- /*
- * 从系统输入终端读取数据,作为客户端信息输入源
- */
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- String cont = null;
- while(true){
- if(socketChannel.isConnected()){
- cont = sc.nextLine();
- socketChannel.write(Charset.forName("UTF-8").encode(cont));
- if(cont == null || cont.equalsIgnoreCase(Constants.CLIENT_CLOSE)){
- socketChannel.close();
- selector.close();
- sc.close();
- System.out.println("See you, 客户端退出系统了");
- System.exit();
- }
- }
- /*
- * 设置1sec的超时时间,进行IO事件选择操作
- */
- int nSelectedKeys = selector.select();
- if(nSelectedKeys > ){
- for(SelectionKey skey: selector.selectedKeys()){
- /*
- * 判断检测到的channel是不是可连接的,将对应的channel注册到选择器上,指定关心的事件类型为OP_READ
- */
- if(skey.isConnectable()){
- SocketChannel connChannel = (SocketChannel) skey.channel();
- connChannel.configureBlocking(false);
- connChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
- connChannel.finishConnect();
- }
- /*
- * 若检测到的IO事件是读事件,则处理相关数据的读相关的业务逻辑
- */
- else if(skey.isReadable()){
- SocketChannel readChannel = (SocketChannel) skey.channel();
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- /*
- * 定义一个ByteBuffer的容器,容量为1k
- */
- ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate();
- int readBytes = ;
- int ret = ;
- /*
- * 注意,对ByteBuffer的操作,需要关心的是flip,clear等。
- */
- while ((ret = readChannel.read(byteBuffer)) > ) {
- readBytes += ret;
- byteBuffer.flip();
- sb.append(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(byteBuffer).toString());
- byteBuffer.clear();
- }
- if (readBytes == ) {
- System.err.println("handle opposite close Exception");
- readChannel.close();
- }
- }
- }
- /*
- * 一次监听的事件处理完毕后,需要将已经记录的事件清除掉,准备下一轮的事件标记
- */
- selector.selectedKeys().clear();
- }else{
- System.err.println("handle select timeout Exception");
- socketChannel.close();
- }
- }
- }
- }
阅读上述代码时,请注意,server和client的实现风格不太一样,主要是针对SelectionKeySet的遍历,一次select操作获取到的所有的SelectionKey处理完后的扫尾工作,体现出Selector的工作逻辑,若写过C程序实现过TCP server/client程序,对事件选择的过程应该就更清楚了。
最后,总结一下Java NIO TCP协议下的C/S结构程序流程图,为彻底理解Java NIO服务。
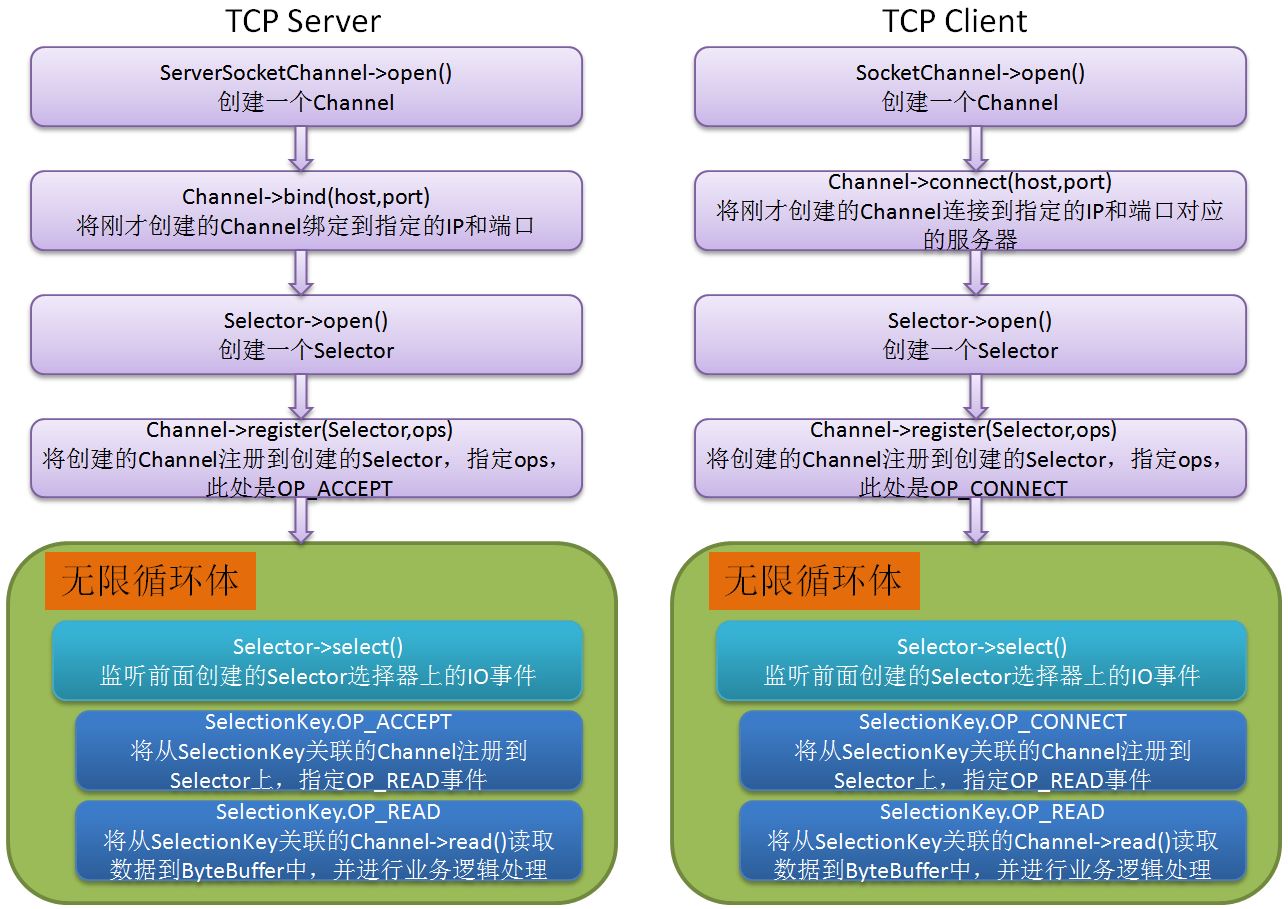
基于这个例子引出的Java NIO的逻辑过程和思想,再去研读Netty的代码,相信会容易理解Netty的核心reactor模型工作原理。
Java NIO通信的基础,基于TCP C/S例子介绍的更多相关文章
- Java NIO通信框架在电信领域的实践
[http://www.codeceo.com/article/java-nio-communication.html] 华为电信软件技术架构演进 Java NIO框架在技术变迁中起到的关键作用 ...
- JAVA Socket 底层是怎样基于TCP/IP 实现的???
首先必须明确:TCP/IP模型中有四层结构: 应用层(Application Layer).传输层(Transport Layer).网络层(Internet Layer ).链路层( ...
- Java NIO 网络编程基础
Java NIO提供了一套网络api,可以用来处理连接数很多的情况.他的基本思想就是用一个线程来处理多个channel. 123456789101112131415161718192021222324 ...
- java NIO socket 通信实例
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/zhuyijian135757/article/details/37672151 java Nio 通 ...
- python中基于tcp协议的通信(数据传输)
tcp协议:流式协议(以数据流的形式通信传输).安全协议(收发信息都需收到确认信息才能完成收发,是一种双向通道的通信) tcp协议在OSI七层协议中属于传输层,它上承用户层的数据收发,下启网络层.数据 ...
- 海纳百川而来的一篇相当全面的Java NIO教程
目录 零.NIO包 一.Java NIO Channel通道 Channel的实现(Channel Implementations) Channel的基础示例(Basic Channel Exampl ...
- Java NIO的理解和应用
Java NIO是一种基于通道和缓冲区的I/O方式,已经被广泛的应用,成为解决高并发与大量连接和I/O处理问题的有效方式. Java NIO相关组件 Java NIO主要有三个核心部分组成,分别是:C ...
- Java NIO (转)
Java NIO提供了与标准IO不同的IO工作方式: Channels and Buffers(通道和缓冲区):标准的IO基于字节流和字符流进行操作的,而NIO是基于通道(Channel)和缓冲区(B ...
- 【转】java NIO 相关知识
原文地址:http://www.iteye.com/magazines/132-Java-NIO Java NIO(New IO)是从Java 1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO API,可以替代标准的 ...
随机推荐
- binarysearchtree
public class binarytree<Value> { private Node root = null; private class Node{ private Value v ...
- HDU2717-Catch That Cow (BFS入门)
题目传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2717 Catch That Cow Time Limit: 5000/2000 MS (Java/O ...
- 2019 flag
学习 1.学会一种新的编程语言或脚本语言,并编写不少于十个应用 2.读5-8本其他学科书籍,(经济,心里学等) 3.坚持每个月最少更新8-10篇博客(技术,学习) 4.阅读并理解和应用两个开源lib ...
- 2.21 JS处理滚动条
2.21 JS处理滚动条 前言 selenium并不是万能的,有时候页面上操作无法实现的,这时候就需要借助JS来完成了.常见场景:当页面上的元素超过一屏后,想操作屏幕下方的元素,是不能直接定位到 ...
- 又一个opengl教程,多多益善
http://ogldev.atspace.co.uk/index.html http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/modern-opengl-tutorial/tu ...
- VMware网络连接IP设置
网络配置(仅主机模式) 一.改变虚拟机IP地址达到联网目的 仅主机模式,第一步,打开我的电脑属性,查看VMt1网卡IP设置,设置一个区段:192.168.xx.aa xx.aa自由设置,简 ...
- 举例说明MySQL中的事务
一.场景导入 现在有一张仓库表,仓库表中记录了每一个物品的数量,还有一张用户表,用户购买产品,仓库表的产品数量减少,而用户拥有产品的数量增加. 但是如果仓库中的产品数量不足时怎么处理? 例子: #仓库 ...
- MySQL最基本的DML语句
一.什么叫DML? DML(Data Manipulation Language):数据操作语言.主要操作数据表中的数据,使用DML可以完成以后三件事: 插入数据 修改数据 查询数据 二.具体的语句操 ...
- js知识点: 数组
1.行内元素 margin padding 左右值都有效,上下值都无效 2.var ev = ev || window.event document.documentElement.clientW ...
- 20155219 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第7周学习总结
20155219 2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第7周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 认识时间与日期 时间的度量 1.格林威治时间(GMT):通过观察太阳而得,因为地球公转轨道为 ...
