android mvvm实例解析
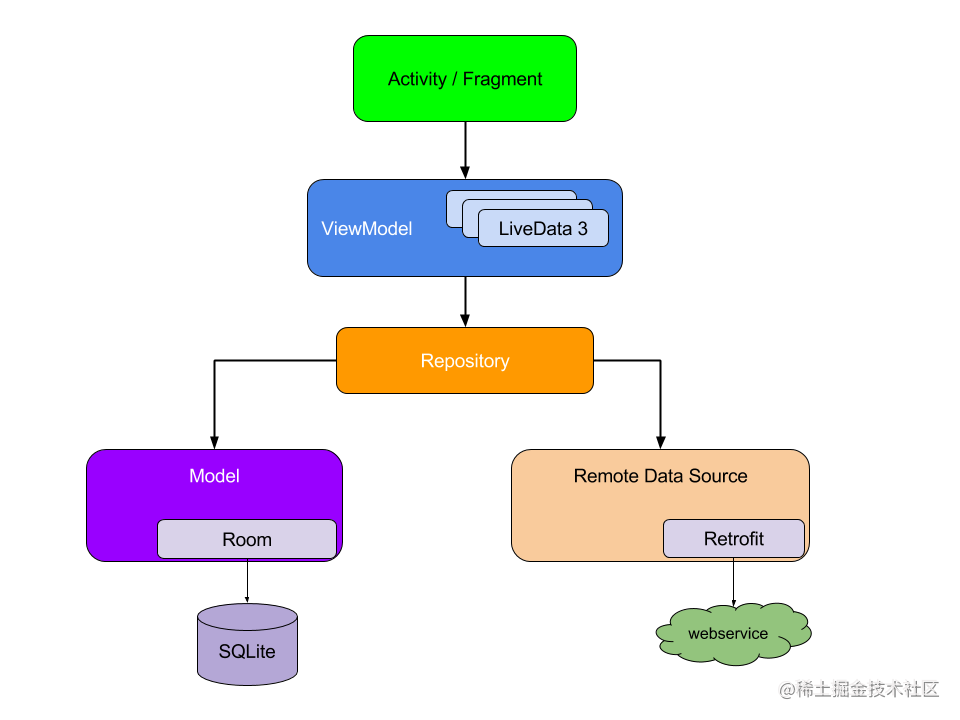
- class ChooseAreaFragment : Fragment() {
- private val viewModel by lazy { ViewModelProviders.of(this, InjectorUtil.getChooseAreaModelFactory()).get(ChooseAreaViewModel::class.java) }
- private var progressDialog: ProgressDialog? = null
- private lateinit var adapter: ArrayAdapter<String>
- override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
- val view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.choose_area, container, false)
- val binding = DataBindingUtil.bind<ChooseAreaBindingImpl>(view)
- binding?.viewModel = viewModel
- return view
- }
- override fun onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
- super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState)
- adapter = ChooseAreaAdapter(context!!, R.layout.simple_item, viewModel.dataList)
- listView.adapter = adapter
- observe()
- }
- private fun observe() {
- viewModel.currentLevel.observe(this, Observer { level ->
- when (level) {
- LEVEL_PROVINCE -> {
- titleText.text = "中国"
- backButton.visibility = View.GONE
- }
- LEVEL_CITY -> {
- titleText.text = viewModel.selectedProvince?.provinceName
- backButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
- }
- LEVEL_COUNTY -> {
- titleText.text = viewModel.selectedCity?.cityName
- backButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
- }
- }
- })
- viewModel.dataChanged.observe(this, Observer {
- adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()
- listView.setSelection(0)
- closeProgressDialog()
- })
- viewModel.isLoading.observe(this, Observer { isLoading ->
- if (isLoading) showProgressDialog()
- else closeProgressDialog()
- })
- viewModel.areaSelected.observe(this, Observer { selected ->
- if (selected && viewModel.selectedCounty != null) {
- if (activity is MainActivity) {
- val intent = Intent(activity, WeatherActivity::class.java)
- intent.putExtra("weather_id", viewModel.selectedCounty!!.weatherId)
- startActivity(intent)
- activity?.finish()
- } else if (activity is WeatherActivity) {
- val weatherActivity = activity as WeatherActivity
- weatherActivity.drawerLayout.closeDrawers()
- weatherActivity.viewModel.weatherId = viewModel.selectedCounty!!.weatherId
- weatherActivity.viewModel.refreshWeather()
- }
- viewModel.areaSelected.value = false
- }
- })
- if (viewModel.dataList.isEmpty()) {
- viewModel.getProvinces()
- }
- }
- /**
- * 显示进度对话框
- */
- private fun showProgressDialog() {
- if (progressDialog == null) {
- progressDialog = ProgressDialog(activity)
- progressDialog?.setMessage("正在加载...")
- progressDialog?.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(false)
- }
- progressDialog?.show()
- }
- /**
- * 关闭进度对话框
- */
- private fun closeProgressDialog() {
- progressDialog?.dismiss()
- }
- companion object {
- const val LEVEL_PROVINCE = 0
- const val LEVEL_CITY = 1
- const val LEVEL_COUNTY = 2
- }
- }
- class ChooseAreaViewModel(private val repository: PlaceRepository) : ViewModel() {
- var currentLevel = MutableLiveData<Int>()
- var dataChanged = MutableLiveData<Int>()
- var isLoading = MutableLiveData<Boolean>()
- var areaSelected = MutableLiveData<Boolean>()
- var selectedProvince: Province? = null
- var selectedCity: City? = null
- var selectedCounty: County? = null
- lateinit var provinces: MutableList<Province>
- lateinit var cities: MutableList<City>
- lateinit var counties: MutableList<County>
- val dataList = ArrayList<String>()
- fun getProvinces() {
- currentLevel.value = LEVEL_PROVINCE
- launch {
- provinces = repository.getProvinceList()
- dataList.addAll(provinces.map { it.provinceName })
- }
- }
- private fun getCities() = selectedProvince?.let {
- currentLevel.value = LEVEL_CITY
- launch {
- cities = repository.getCityList(it.provinceCode)
- dataList.addAll(cities.map { it.cityName })
- }
- }
- private fun getCounties() = selectedCity?.let {
- currentLevel.value = LEVEL_COUNTY
- launch {
- counties = repository.getCountyList(it.provinceId, it.cityCode)
- dataList.addAll(counties.map { it.countyName })
- }
- }
- fun onListViewItemClick(parent: AdapterView<*>, view: View, position: Int, id: Long) {
- when {
- currentLevel.value == LEVEL_PROVINCE -> {
- selectedProvince = provinces[position]
- getCities()
- }
- currentLevel.value == LEVEL_CITY -> {
- selectedCity = cities[position]
- getCounties()
- }
- currentLevel.value == LEVEL_COUNTY -> {
- selectedCounty = counties[position]
- areaSelected.value = true
- }
- }
- }
- fun onBack() {
- if (currentLevel.value == LEVEL_COUNTY) {
- getCities()
- } else if (currentLevel.value == LEVEL_CITY) {
- getProvinces()
- }
- }
- private fun launch(block: suspend () -> Unit) = viewModelScope.launch {
- try {
- isLoading.value = true
- dataList.clear()
- block()
- dataChanged.value = dataChanged.value?.plus(1)
- isLoading.value = false
- } catch (t: Throwable) {
- t.printStackTrace()
- Toast.makeText(CoolWeatherApplication.context, t.message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
- dataChanged.value = dataChanged.value?.plus(1)
- isLoading.value = false
- }
- }
- }
- class PlaceRepository private constructor(private val placeDao: PlaceDao, private val network: CoolWeatherNetwork) {
- suspend fun getProvinceList() = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
- var list = placeDao.getProvinceList()
- if (list.isEmpty()) {
- list = network.fetchProvinceList()
- placeDao.saveProvinceList(list)
- }
- list
- }
- suspend fun getCityList(provinceId: Int) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
- var list = placeDao.getCityList(provinceId)
- if (list.isEmpty()) {
- list = network.fetchCityList(provinceId)
- list.forEach { it.provinceId = provinceId }
- placeDao.saveCityList(list)
- }
- list
- }
- suspend fun getCountyList(provinceId: Int, cityId: Int) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
- var list = placeDao.getCountyList(cityId)
- if (list.isEmpty()) {
- list = network.fetchCountyList(provinceId, cityId)
- list.forEach { it.cityId = cityId }
- placeDao.saveCountyList(list)
- }
- list
- }
- companion object {
- private var instance: PlaceRepository? = null
- fun getInstance(placeDao: PlaceDao, network: CoolWeatherNetwork): PlaceRepository {
- if (instance == null) {
- synchronized(PlaceRepository::class.java) {
- if (instance == null) {
- instance = PlaceRepository(placeDao, network)
- }
- }
- }
- return instance!!
- }
- }
- }
android mvvm实例解析的更多相关文章
- 【转】Android HAL实例解析
原文网址:http://www.embedu.org/Column/Column339.htm 作者:刘老师,华清远见嵌入式学院讲师. 一.概述 本文希望通过分析台湾的Jollen的mokoid 工程 ...
- Android HAL实例解析
一.概述 本文希望通过分析台湾的Jollen的mokoid 工程代码,和在s5pc100平台上实现过程种遇到的问题,解析Andorid HAL的开发方法. 二.HAL介绍 现有HAL架构由Patric ...
- Android AIDL实例解析
AIDL这项技术在我们的开发中一般来说并不是很常用,虽然自己也使用新浪微博的SSO登录,其原理就是使用AIDL,但是自己一直没有动手完整的写过AIDL的例子,所以就有了这篇简单的文章. AIDL(An ...
- Android实例-Delphi开发蓝牙官方实例解析(XE10+小米2+小米5)
相关资料:1.http://blog.csdn.net/laorenshen/article/details/411498032.http://www.cnblogs.com/findumars/p/ ...
- Android开发之IPC进程间通信-AIDL介绍及实例解析
一.IPC进程间通信 IPC是进程间通信方法的统称,Linux IPC包括以下方法,Android的进程间通信主要采用是哪些方法呢? 1. 管道(Pipe)及有名管道(named pipe):管道可用 ...
- Android Service完全解析,关于服务你所需知道的一切(上)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/11952435 相信大多数朋友对Service这个名词都不会陌生,没错,一个老练的A ...
- [转] Android Volley完全解析(一),初识Volley的基本用法
版权声明:本文出自郭霖的博客,转载必须注明出处. 目录(?)[-] Volley简介 下载Volley StringRequest的用法 JsonRequest的用法 转载请注明出处:http ...
- Android IntentService完全解析 当Service遇到Handler
一 概述 大家都清楚,在Android的开发中,凡是遇到耗时的操作尽可能的会交给Service去做,比如我们上传多张图,上传的过程用户可能将应用置于后台,然后干别的去了,我们的Activity就很可能 ...
- Android Volley完全解析
1. Volley简介 我们平时在开发Android应用的时候不可避免地都需要用到网络技术,而多数情况下应用程序都会使用HTTP协议来发送和接收网络数据.Android系统中主要提供了两种方式来进行H ...
- Android Bitmap 全面解析(四)图片处理效果对比 ...
对比对象: UIL Volley 官方教程中的方法(此系列教程一里介绍的,ImageLoader的处理方法和官方的差不多) -------------------------------------- ...
随机推荐
- linux 开机默认进入命令行模式
.markdown-body { line-height: 1.75; font-weight: 400; font-size: 16px; overflow-x: hidden; color: rg ...
- 问题--链表指针传参,修改next指针只传值
1.问题--链表指针传参,修改next指针只传值 Link_creat_head(&head, p_new);//将新节点加入链表 在这当中head头指针传的是地址,而p_new传的是值,这二 ...
- MyBatis03——ResultMap和分页相关
ResultMap和分页相关 当属性名和字段名不一致的时候 解决方法 1.数据库中创建user表 字段 id.name.pwd 2.Java中的实体类 @Data public class User ...
- Linux-文件权限-rwx-chmod
- 【Kafka系列】(一)Kafka入门
有的时候博客内容会有变动,首发博客是最新的,其他博客地址可能会未同步,认准https://blog.zysicyj.top 首发博客地址 系列文章地址 Kafka是什么? 一句话概括:Apache K ...
- [转帖]oracle rac后台进程和LMS说明
本文摘抄录oracle官方文档,oracle rac使用的后台进程,用以备忘,记录之. About Oracle RAC Background Processes The GCS and GES pr ...
- [转帖]设置kafka 数据保留时间
https://www.cnblogs.com/gao88/p/12539112.html kafka 单独设置某个topic的数据过期时间kafka 默认存放7天的临时数据,如果遇到磁盘空间小,存放 ...
- [转帖]Linux—微服务启停shell脚本编写模板
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1e1080a39dc5 run.sh #!/bin/bash if [ -s java.pid ] then echo "重复启动,退出 ...
- [转帖]Nginx性能优化详解
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/886146?spm=a2c6h.24874632.expert-profile.256.7c46cfe9h5DxWK 感觉文 ...
- vue/cli中css.sourceMap-open-inline-host-port-https-openPage-compress -devServer.proxy的简单介绍
Vue/cli4.0 配置属性--css.sourceMap 设置是否开启 css 的 sourse map功能. css 的 sourse map作用类似与 js 的 sourse map. 注意: ...
