零基础学习java------day17------缓冲字节流,转换字节流,简化流,缓冲字符流,序列化和对象流
1. 缓冲字节流
缓冲区:缓冲区实质上是一个数组。通常它是一个字节数组,但是也可以使用其他种类的数组。但是一个缓冲区不 仅仅 是一个数组。缓冲区提供了对数据的结构化访问,而且还可以跟踪系统的读/写进程。
缓冲流出现的原因:使用字节流每次从文件中进行读写的时候,都需要和文件进行大量的IO交互,与磁盘交互的效率其实是比较低的,所以为了降低与磁盘的交互次数,可以使用字节缓冲流。字节缓冲流将数据放到缓存区,而缓冲区是一个内存区域的概念,我们直接和缓冲区做交互,可以提升效率。

注意:
(1)什么时候缓冲区的数据写入硬盘中?
当缓冲区被写满时,或是使用flush方法将至写入硬盘(注意关流后,缓存区的内容会被写入硬盘,因为关流内部会调用flush方法)
(2)byte数组的大小要小于缓存区,缓存区的数据是通过数组间接读入的
1.1 缓冲字节输出流
BufferOutputStream(OutputStream);
1.1.1 构造方法:
(1)public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
(2)public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size): 此处参数size表示缓冲区的大小,默认是8kb
1.1.2 成员方法:
(1)public void write(int b)
(2)public void write(byte b[])
(3)public void write(byte b[], int off, int len):off表示偏移量,len表示从偏移量位置开始写入数据的长度
(4)public void flush(): 刷新,将缓存区的内容写到文件中,一般只有带缓冲的输出流才有这样的方法
public class BufferOutputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e:/a.txt"));
){
bos.write("妈妈,他们抛弃了我".getBytes());//妈妈,他们抛弃了我
bos.write(97); //a
bos.write("妈妈,他们抛弃了我".getBytes(),0,6);//妈妈
bos.flush(); //一般使用输出流的时候,尽量把flish写出来
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意,此处若没用自动关流,由于缓存区的内存没被写满,所以内容不会被写进a.txt,
1.2 缓冲字节输入流
BufferedInputStream(InputStream)
BufferedInputStream(InputStream)
BufferedInputStream(InputStream,int size) size: 缓冲区大小,默认8k
其读取数据的方法和FileInputStream是一样的(见上)
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:/b.txt"));// b.txt中的内容为:这个世界会好吗
){
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len ;
while((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) { //判断数据读完的条件
System.out.println(new String(bs,0,len));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
练习:使用BufferedOutputStream/BufferedInputStream拷贝文件,并比较和FileInput的拷贝性能
1 public class CopyFile {
2 public static void fileStream(String srcPath,String destPath) {
3 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
4 try(
5 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcPath);
6 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destPath);
7 ) {
8 byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
9 int len;
10 while((len = fis.read(bs)) != -1) {
11 fos.write(bs,0,len);
12 }
13 long end = new Date().getTime();
14 System.out.println("字节流耗时为:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
15 } catch (Exception e) {
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }
18 }
19 public static void bufferedFileStream(String srcPath,String destPath) {
20 long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
21 try (
22 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
23 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath));
24 ){
25 int len;
26 byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
27 while((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) {
28 bos.write(bs,0,len);
29 }
30 long end = new Date().getTime();
31 System.out.println("缓冲字节流耗时为:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
32 } catch (Exception e) {
33 e.printStackTrace();
34 }
35 }
36 }
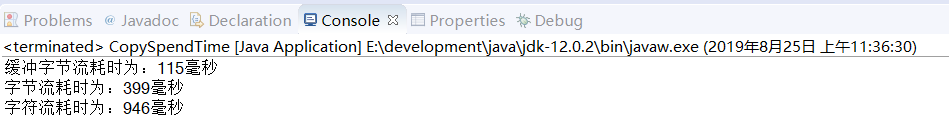
运行结果是:缓冲字节流与字节流拷贝同一个文件,前者花了95毫秒,后者花了405毫秒,可见缓冲字节流效率很高
2.转换字节流
2.1 前提
转换流的本质是一种字符流,为什么叫转换流,因为其构造方法中有个字节流对象参数,相当于将字节流对象转为字符流对象
2.1.1 转换流出现的原因及思想
由于字节流操作中文不是特别的方便,所以,java就提供了转换流,其本质就是带了编码表的字节流,即:字符流=字节流+编码表
2.1.2 字符串中的编码问题
编码:把文字转为二进制
解码:把二进制转成文件
字符流只能处理纯文本文件
2.2 字符输出流
2.2.1 构造方法
(1)public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream)
(2)public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName):此处的charsetName表示设置编码的格式,默认是utf-8
2.2.2 成员方法(用法和字节流差不多,只是这里的参数由byte数组转换为char数组,此外还可以使用String参数):
(1)public void write(int c)
(2)public void write(char[ ] cbuf)
(3)public void write(char[ ] cbuf, int len)
(4)public void write(String str)
(5)public void write(String str,int off,int len)
public class OutputStreamWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter((new FileOutputStream("e:/a.txt")),"gbk");
){
osw.write("忽然就流出泪来,忽然间想要听到她的声音,而我却一个人越走越远");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.3 字符输入流
2.3.1 构造方法
(1)public InputStreamReader(InputStream in)
(2)public InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String charsetName)
2.3.2 成员方法
(1)public int read()
(2)public int read(char[] cbuf)
public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("e:/a.txt"),"gbk"); //此处一定要用cbk编码去读取数据,因为.txt是用gbk编码格式写入的
){
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//运行结果:忽然就流出泪来,忽然间想要听到她的声音,而我却一个人越走越远
2.4 字符流拷贝文件
public static void charFileStream(String srcPath,String destPath) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destPath));
){
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(chs)) != -1) {
osw.write(chs,0,len);
}
long end = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("字符流耗时为:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
这里为了比较字符流拷贝文件与字节流以及缓冲字节流拷贝文件的性能,此处同时进行了这三种拷贝文件方法拷贝同一个文件的耗时比较
测试类
public class CopySpendTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyFile.bufferedFileStream("E:\\linked.mkv", "e:/链表1.mkv");
CopyFile.fileStream("E:\\linked.mkv", "e:/链表2.mkv");
CopyFile.charFileStream("E:\\linked.mkv", "E:\\linked1.mkv");
}
}
运行结果:
3 转换流的简化写法,也叫简化流(字符流),其无法指定编码格式
3.1 读写
转换流的名字比较长,而我们常见的操作都是照本地默认编码实现的,所以,为了简化我们的书写,转换流提供了对应的子类,即FileWriter和FileReader
FileWriter:
其构造方法有很多种,这里只列出其可以传什么参数的简单构造方法,至于是否追加或是用什么编码方式的构造方法,可以直接看源码
(1)public FileWriter(String fileName)
(2)public FileWriter(File file)
public class FileWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("e:/a.txt");
){
fw.write("我们生来就是孤独");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileReader:
用法类似FileWrite
public class FileReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileReader fr = new FileReader("e:/a.txt");
){
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在一个程序中先写后读,要注意:写完了以后要关流,否则输出流会继续占用文件,导致读取不回来内容
public class NoticeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("e:/a.txt"); //只要执行这个语句就会创建一个a.txt文件,若加true就不会覆盖a.txt原有的内容(若有带内容的a.txt文件)
FileReader fr = new FileReader("e:/a.txt");
){
fw.write("下起了雨,你觉的冷吗");
fw.close(); //此处一定要关流,否则输出流会继续占用该文件
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.2 简化流拷贝文件
//简化流拷贝文件
public static void SimpleStream(String srcPath, String destPath) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(destPath);
FileReader fr = new FileReader(srcPath);
){
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("简化流耗时为:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
注意srcPath和destPath地址别写反了
4. 缓冲字符流
BufferedReader/bufferedWriter
4.1 缓冲字符输出流
类似缓冲字节流,其构造方法也要传相应流的对象,不能想字符流一样传字符串
特有方法:
new Line:换行
public class BufferedWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("e:/a.txt"));//写法简单,但此种得到缓冲字符流的方法不常用
BufferedWriter bw1 = new BufferedWriter
(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("e:/b.txt")));//很常用,因为我们得到的数据一般都为字节流,所以现将字节流包装成转换流,再讲转换流包装成缓冲字符流
){
bw.write("这被禁忌的游戏");
bw.newLine(); //用于换行
bw.write("一如既往的岁月");
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.2 缓冲字符输入流
特有的方法:readLine 读取一行
注意:尽量不要使用readLine去拷贝文件(有可能会造成空行的丢失)
4.3 缓冲字符流拷贝文件
//缓冲字符流拷贝文件
public static void bufferedCharStream(String srcPath, String destPath) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (
// BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(destPath)));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destPath));
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(srcPath)));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcPath));
){
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = br.read(chs)) != -1) {
bw.write(chs,0,len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("缓冲字符流耗时为:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
练习
1. 把ArrayList集合中的字符串数据存储到文本文件,要求每个元素占一行,然后从文本文件中读取数据(每一行为一个字符串数据 )到集合中,并遍历集合
public class Exer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("热河");
arrayList.add("下雨");
arrayList.add("梵高先生");
arrayList.add("山荫路上的夏天");
ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<>();
try (
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("e:/a.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("e:/a.txt"));
){
//将集合总的内容写入文件a.txt
for (String str : arrayList) {
// char[] chs = str.toCharArray();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
// 将文件a.txt中的内容写入集合array
String str = null;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
array.add(str);
}
//遍历集合元素
for (String arr : array) {
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. 复制单级文件夹,复制单级文件夹中指定文件并
(1) 和原来名字保持一致
(2)修改新的名字(使用纳秒值命名)
5. 序列化和对象流
5.1 概述
java序列化是指把java对象转换为字节序列(二进制)的过程,java反序列化是指把字节序列恢复为java对象的过程,当两个java进程进行通信时,发送方需要把这个java对象转换为字节序列,然后在网络上传送;另一方面,接收方需要从字节序列中恢复java的对象
持久化:把内存数据存储到磁盘上(一般数据库)
5.2 java序列化API
(1)ObjectOutputStream:表示对象输出流
writeObject(Object obj)方法可以对参数指定的obj对象进行序列化,把得到的字节序列写到一个目标输出流中
(2)ObjectInputStream:表示对象输入流
readObject()方法从输入流中读取字节序列,再把它们反序列化成为一个对象,并将其返回
5.3 java对象序列化要求
(1)假定一个Person类,它的对象需要序列化
只有实现了Serializable或Externalizable接口的类的对象才能序列化,否则抛出异常
(2)构造方法
ObjectOutputStream:
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
ObjectInputStream:
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
(3)注意事项
若Person类仅仅实现了Serializable接口,则可以按照以下方式进行序列化和反序列化
ObjectOutputStream采用默认的序列化方式,对Person对象的非transient的实例变量进行序列化
ObjectInputStream采用默认的反序列化方式,对Person对象的非transient的实例变量进行反序列化
(4)实现序列化步骤
1. 让类实现Serializable接口
2. 使用ObjectOutputStream写数据:调用writeObject
3. 使用ObjectInputStream读数据:调用readObject
如果报错:NotSerializable,检查是否实现了Serializable接口
如果报错:java.io.InvalidClassException: com._51doit.javase.day17.Person; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = 7515133156099803333, local class serialVersionUID = 4493040116463270318
是由模板(如Person类中重写了toString方法)改变导致的:
解决方法:
1. 重写一遍,然后再进行读操作
2. 生成序列化id(此ID只是改变前的id)
光标放到类名的黄线上,选择两个中的任意一种(这个时候再该模板后,进行读操作就不会报错)
案例
定义Person类(一定要实现Serializable接口)
public class Person implements Serializable{
String name;
int age;
char gender;
public Person(String name,int age,char gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", gender=" + gender + "]";
}
}
写
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("老王",38,'男');
try (
ObjectOutputStream oot = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e:/a.txt"));
){
oot.writeObject(p);
oot.writeInt(100); //此处要注意写入的顺序,这里是先写p,再写的100,读的时候也要按照这个顺序读
oot.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
将内容读出来
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:/a.txt"));
){
Object o = ois.readObject();
ois.readIn(); // 此处若将这一行和上一行换个顺序,将会出现java.io.EOFException错误,因为写入文件的内容是先p,再100
Person p = (Person)o;
System.out.println(p.name+p.age+p.gender);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:老王38男
练习:使用对象流写一个person对象,再写一个Map<Integer,Person>
零基础学习java------day17------缓冲字节流,转换字节流,简化流,缓冲字符流,序列化和对象流的更多相关文章
- 音乐出身的妹纸,零基础学习JAVA靠谱么
问:表示音乐出身的妹纸一枚 某一天突然觉得身边认识的是一群程序员 突然想 要不要也去试试... 众好友都觉得我该去做个老师,可是我怕我会误人子弟,祸害祖国下一代..... 要不要 要不要 学Ja ...
- 总结了零基础学习Java编程语言的几个基础知识要点
很多Java编程初学者在刚接触Java语言程序的时候,不知道该学习掌握哪些必要的基础知识.本文总结了零基础学习Java编程语言的几个基础知识要点. 1先了解什么是Java的四个方面 初学者先弄清这 ...
- 零基础学Java第三节(基本输入输出)
本篇文章是<零基础学Java>专栏的第三篇文章,文章采用通俗易懂的文字.图示及代码实战,从零基础开始带大家走上高薪之路! 本文章首发于公众号[编程攻略] Java程序的命令行参数 我们可以 ...
- 零基础学习hadoop到上手工作线路指导(编程篇)
问题导读: 1.hadoop编程需要哪些基础? 2.hadoop编程需要注意哪些问题? 3.如何创建mapreduce程序及其包含几部分? 4.如何远程连接eclipse,可能会遇到什么问题? 5.如 ...
- 零基础学Java第四节(字符串相关类)
本篇文章是<零基础学Java>专栏的第四篇文章,文章采用通俗易懂的文字.图示及代码实战,从零基础开始带大家走上高薪之路! String 本文章首发于公众号[编程攻略] 在Java中,我们经 ...
- 零基础学Java第一节(语法格式、数据类型)
本篇文章是<零基础学Java>专栏的第一篇文章,从本篇文章开始,将会连更本专栏,带领大家将Java基础知识彻底学懂,文章采用通俗易懂的文字.图示及代码实战,从零基础开始带大家走上高薪之路! ...
- 如何从零基础学习VR
转载请声明转载地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Rodolfo/,违者必究. 近期很多搞技术的朋友问我,如何步入VR的圈子?如何从零基础系统性的学习VR技术? 本人将于2017年1月 ...
- CSS零基础学习笔记.
酸菜记 之 CSS的零基础. 这篇是我自己从零基础学习CSS的笔记加理解总结归纳的,如有不对的地方,请留言指教, 学前了解: CSS中字母是不分大小写的; CSS文件可以使用在各种程序文件中(如:PH ...
- 【零基础学习iOS开发】【转载】
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mjios/archive/2013/04/24/3039357.html 本文目录 一.什么是iOS 二.主流手机操作系统 三.什么是iOS开 ...
随机推荐
- Spring Cloud 微服务实战——nacos 服务注册中心搭建(附源码)
作为微服务的基础功能之一的注册中心担任重要的角色.微服务将单体的服务拆分成不同的模块下的服务,而不同的模块的服务如果进行通信调用呢?这就需要服务注册与发现.本文将使用阿里开源项目 nacos 搭建服务 ...
- vue.js+elementUI文件上传、文件导入、文件下载
1.文件下载 <el-button plain @click ="exportVmExcel()" size='mini' icon="el-icon-downlo ...
- (1)Zookeeper在linux环境中搭建集群
1.简介 ZooKeeper是Apache软件基金会的一个软件项目,它为大型分布式计算提供开源的分布式配置服务.同步服务和命名注册.ZooKeeper的架构通过冗余服务实现高可用性.Zookeeper ...
- 字符串可以这样加索引,你知吗?《死磕MySQL系列 七》
系列文章 三.MySQL强人"锁"难<死磕MySQL系列 三> 四.S 锁与 X 锁的爱恨情仇<死磕MySQL系列 四> 五.如何选择普通索引和唯一索引&l ...
- PTA 哈利·波特的考试 (25分)
PTA 哈利·波特的考试 (25分) 哈利·波特要考试了,他需要你的帮助.这门课学的是用魔咒将一种动物变成另一种动物的本事.例如将猫变成老鼠的魔咒是haha,将老鼠变成鱼的魔咒是hehe等等.反方向变 ...
- 计算机网络-3-5-以太网MAC层及交换机
MAC层的硬件地址 在局域网中,硬件地址又称为物理地址或者MAC地址(因为这种地址用在MAC帧中) IEEE 802标准为局域网规定了一种48位(6字节)的全球地址,固化在适配器的ROM中. 如果计算 ...
- 如何系统学习C 语言(中)之 联合体、枚举篇
在C语言中有一个和结构体非常像的数据类型,它的名字叫做联合体,也被称为共用体或公用体. 1,联合体 1,联合体的定义 定义联合体需要使用"union" 关键字,格式如下: unio ...
- Part 20 Create custom service in AngularJS
Whenever the case changes from lower to upper, a single space character should be inserted. This mea ...
- oracle 与 前台 md5
创建函数: CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION MD5( passwd IN VARCHAR2) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS retval varchar2(32); BE ...
- python实现图像加载与保存,窗口创建与销毁,图片常用属性,ROI,通道的分离与合并,对比度和亮度
目录: (一)图像加载与保存 (二)图像显示窗口创建与销毁 (三)图片的常用属性的获取 (四)生成指定大小的矩形区域(ROI) (五)图片颜色通道的分离与合并 (六)两张图片相加,改变对比度和亮度 ( ...
