什么。你还没有搞懂Spring事务增强器 ,一篇文章让你彻底搞懂Spring事务,虽然很长但是干货满满
上一篇文章主要讲解了事务的Advisor是如何注册进Spring容器的,也讲解了Spring是如何将有配置事务的类配置上事务的,也讲解了Advisor,pointcut验证流程;但是还未提到的那个Advisor里面的advice,想要知道这个我们就先来看一下TransactionInterceptor这个类吧:
TransactionInterceptor这个类继承自TransactionAspectSupport并且实现了MethodInterceptor接口。所以调用该类是从invoke方法开始;接下来我们就看一下:
- 看源码(
TransactionInterceptor.java)
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
}
);
}
注意invoke方法里面的invokeWithinTransaction这个方法,我们继续来追踪一下
- 看源码(
TransactionAspectSupport.java)
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 获取对应事务属性
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
// 获取beanFactory中的transactionManager属性
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager) {
Boolean isSuspendingFunction = KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method);
Boolean hasSuspendingFlowReturnType = isSuspendingFunction &&
COROUTINES_FLOW_CLASS_NAME.equals(new MethodParameter(method, -1).getParameterType().getName());
if (isSuspendingFunction && !(invocation instanceof CoroutinesInvocationCallback)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Coroutines invocation not supported: " + method);
}
CoroutinesInvocationCallback corInv = (isSuspendingFunction ? (CoroutinesInvocationCallback) invocation : null);
ReactiveTransactionSupport txSupport = this.transactionSupportCache.computeIfAbsent(method, key -> {
Class<?> reactiveType =
(isSuspendingFunction ? (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? Flux.class : Mono.class) : method.getReturnType());
ReactiveAdapter adapter = this.reactiveAdapterRegistry.getAdapter(reactiveType);
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply reactive transaction to non-reactive return type: " +
method.getReturnType());
}
return new ReactiveTransactionSupport(adapter);
}
);
InvocationCallback callback = invocation;
if (corInv != null) {
callback = () -> CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, corInv.getTarget(), corInv.getArguments());
}
Object result = txSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(method, targetClass, callback, txAttr, (ReactiveTransactionManager) tm);
if (corInv != null) {
Publisher<?> pr = (Publisher<?>) result;
return (hasSuspendingFlowReturnType ? KotlinDelegate.asFlow(pr) :
KotlinDelegate.awaitSingleOrNull(pr, corInv.getContinuation()));
}
return result;
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
// 构造方法唯一标识(类.方法,如:service.UserServiceImpl.save)
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// 声明式事务处理
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 创建 TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 执行原方法
// 继续调用方法拦截器链,这里一般会调用目标类方法;如:AccountByXMLServiceImpl.save方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// 异常回滚
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
// 手动向上抛出异常,则下面的提交事务不会执行
// 如果自事务出现异常,则外层事务代码需catch住子事务的代码,不然外层事务也会回滚
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 消除信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
} else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
try {
// 编程式事务处理
result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) ptm).execute(txAttr, status -> {
TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
try {
Object retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
return retVal;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
// A RuntimeException: will lead to a rollback.
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
} else {
throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
}
} else {
// A normal return value: will lead to a commit.
throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
return null;
}
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
}
);
}
catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
}
throw ex2;
}
// Check result state: It might indicate a Throwable to rethrow.
if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
throw throwableHolder.throwable;
}
return result;
}
}
创建事务Info对象(TransactionInfo)
然后我们继续分析上面代码中的创建事务Info的函数,也就是:TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
- 看源码(
TransactionAspectSupport.java)
protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager tm,
@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
// If no name specified, apply method identification as transaction name.
// 如果没有指定名称,则使用方法唯一标识,并使用 DelegatingTransactionAttribute 封装 txAttr
if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
@Override
public String getName() {
return joinpointIdentification;
}
}
;
}
TransactionStatus status = null;
if (txAttr != null) {
if (tm != null) {
// 获取Transaction
status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
"] because no transaction manager has been configured");
}
}
}
// 根据指定的属性 与 status准备一个TransactionInfo
return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
}
- 源码分析
针对createTransactionIfNecessary这个函数,主要做了以下几个事情:
使用DelegatingTransactionAttribute封装传入TransactionAttribute实例
对于TransactionAttribute类型的参数txAttr,当前的实际类型是
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute,是由获取事务属性时生成,主要用于数据承载,而这里之所以使用DelegatingTransactionAttribute进行封装,当然是提供了更多功能。获取事务
事务处理当然是以事务为核心,那么获取事务就是最重要的事
构建事务信息
根据之前几个步骤获取的信息构建TransactionInfo并返回
获取事务
其主要核心就是在createTransactionIfNecessary函数中的getTransaction方法中:
- 看源码(
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java)
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取一个transaction
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
Boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 如果在这之前已经存在事务,就进入存在事务的方法中
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// 事务超时验证
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
}
// 走到这里说明此时没有存在事务,如果事务的传播特性是 MANDATORY 则抛出异常
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// 如果此时不存在事务,当传播特性是 REQUIRED REQUIRES_NEW NESTED 都会进入if语句块 else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
// PROPAGATION_REQUIRED PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW PROPAGATION_NESTED 都需要新建事务,、
// 因为此时不存在事务,将null 挂起
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
}
try {
// 注意这个方法
// new 一个status,存放刚刚创建的transaction,然后将其标记为新事务
// 新开一个连接的地方,非常重要
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
} else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
}
// 其它的事务传播特性一律返回一个空事务,transaction=null
// 当前不存在事务,且传播机制=PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS/PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED/PROPAGATION_NEVER,这三种情况,创建“空”事务
Boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
简单说一下上面函数中的startTransaction方法:
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
Boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources) {
Boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// new 一个status,存放刚刚创建的transaction,然后将其标记为新事务
// 这里的 transaction 后面的一个参数决定是否是新事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 新开一个连接的地方,非常重要
doBegin(transaction, definition);
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
接下来继续查看getTransaction这个函数,看看是如何将transaction创建出来的;看方法doGetTransaction:(这里这里看的是实现类DataSourceTransactionManager的)
- 看源码(
DataSourceTransactionManager.java)
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction() {
// 这里的 DataSourceTransactionObject 是一个事务管理器的一个内部类
// DataSourceTransactionObject 就是一个transaction 这里直接new 了一个
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
// 解绑与绑定的作用在此时体现,如果当前线程有绑定的话,将会取出holder
// 第一次 conHolder 指定是null
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 此时的 holder被标记成一个旧holder
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
return txObject;
}
- 源码解析
看到上面的源码后我们不难发现其实创建事务的过程其实很简单,接下来我们继续分析创建完事务它又做了什么?回到getTransaction这个方法,发现它接着就会判断当前是否存在事务(也就是isExistingTransaction(transaction)):
- 看源码(
DataSourceTransactionManager.java)
@Override
protected Boolean isExistingTransaction(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
return (txObject.hasConnectionHolder() && txObject.getConnectionHolder().isTransactionActive());
}
接着看一下这个函数中的hasConnectionHolder方法
public boolean hasConnectionHolder() {
return (this.connectionHolder != null);
}
- 源码解析
这里判断是否存在事务的依据主要是获取holder中的transactionActive变量是否为true,holder直接为null判断不存在了,如果是第二此进入事务transactionActive变量是为true的(后面会提到在哪里把它变为true的),由此来判断当前是否已经存在事务了。
到这里源码分成了2条处理线
- 当前已经存在事务isExistingTransaction()判断是否存在事务,存在事务handlerExistingTransaction()根据不同传播机制不同处理;
- 当前不存在事务:不同传播机制不同处理
当前不存在事务
如果当前不存在事务,传播特性又是REQUIRED 、 REQUIRES_NEW 、 NESTED,将会先挂起null,这个挂起方法后面再说;然后创建一个DefaultTransactionStatus,并将其标记为新事务,然后执行doBegin(transaction, definition);这个方法也是一个比较关键的方法;
这里我们提到了DefaultTransactionStatus 一个status对象,这是一个十分重要的对象我们记下来来简单看一下TransactionStatus接口
- 看源码(
TransactionStatus.java)
public interface TransactionStatus extends TransactionExecution, SavepointManager, Flushable {
/**
* 返回该事务是否在内部携带保存点,也就是说,已经创建为基于保存点的嵌套事务。
* @return
*/
Boolean hasSavepoint();
/**
* 将会话刷新到数据存储区
*/
@Override
void flush();
}
我们再来看一下TransactionStatus层次结构发现这个类继承了TransactionExecution接口,进去查看一下
- 看源码(
TransactionExecution.java)
package org.springframework.transaction;
public interface TransactionExecution {
/**
* 返回当前事务是否为新事务(否则将参与到现有事务中,或者可能一开始就不在实际事务中运行)
* @return
*/
Boolean isNewTransaction();
/**
* 设置事务仅回滚。
*/
void setRollbackOnly();
/**
* 返回事务是否已标记为仅回滚
* @return
*/
Boolean isRollbackOnly();
/**
* 返回事物是否已经完成,无论提交或者回滚。
* @return
*/
Boolean isCompleted();
}
接下来我们再查看一下实现类DefaultTransactionStatus
- 看源码(
DefaultTransactionStatus.java)
package org.springframework.transaction.support;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.transaction.NestedTransactionNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.transaction.SavepointManager;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class DefaultTransactionStatus extends AbstractTransactionStatus {
// 事务对象
@Nullable
private final Object transaction;
// 事务对象
private final Boolean newTransaction;
private final Boolean newSynchronization;
private final Boolean readOnly;
private final Boolean debug;
// 事务对象
@Nullable
private final Object suspendedResources;
public DefaultTransactionStatus(
@Nullable Object transaction, Boolean newTransaction, Boolean newSynchronization,
Boolean readOnly, Boolean debug, @Nullable Object suspendedResources) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.newTransaction = newTransaction;
this.newSynchronization = newSynchronization;
this.readOnly = readOnly;
this.debug = debug;
this.suspendedResources = suspendedResources;
}
/**
* Return the underlying transaction object.
* @throws IllegalStateException if no transaction is active
*/
public Object getTransaction() {
Assert.state(this.transaction != null, "No transaction active");
return this.transaction;
}
/**
* Return whether there is an actual transaction active.
*/
public Boolean hasTransaction() {
return (this.transaction != null);
}
@Override
public Boolean isNewTransaction() {
return (hasTransaction() && this.newTransaction);
}
/**
* Return if a new transaction synchronization has been opened
* for this transaction.
*/
public Boolean isNewSynchronization() {
return this.newSynchronization;
}
/**
* Return if this transaction is defined as read-only transaction.
*/
public Boolean isReadOnly() {
return this.readOnly;
}
/**
* Return whether the progress of this transaction is debugged. This is used by
* {@link AbstractPlatformTransactionManager} as an optimization, to prevent repeated
* calls to {@code logger.isDebugEnabled()}. Not really intended for client code.
*/
public Boolean isDebug() {
return this.debug;
}
/**
* Return the holder for resources that have been suspended for this transaction,
* if any.
*/
@Nullable
public Object getSuspendedResources() {
return this.suspendedResources;
}
@Override
public Boolean isGlobalRollbackOnly() {
return ((this.transaction instanceof SmartTransactionObject) &&
((SmartTransactionObject) this.transaction).isRollbackOnly());
}
@Override
protected SavepointManager getSavepointManager() {
Object transaction = this.transaction;
if (!(transaction instanceof SavepointManager)) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction object [" + this.transaction + "] does not support savepoints");
}
return (SavepointManager) transaction;
}
public Boolean isTransactionSavepointManager() {
return (this.transaction instanceof SavepointManager);
}
@Override
public void flush() {
if (this.transaction instanceof SmartTransactionObject) {
((SmartTransactionObject) this.transaction).flush();
}
}
}
看完这里我们接下来继续回到AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中的getTransaction函数里面的
startTransaction函数。这里有这里有这么一句话。
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
我们来查看一下newTransactionStatus函数:
- 看源码(
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java)
// 这里是构造一个status对象的方法
protected DefaultTransactionStatus newTransactionStatus(
TransactionDefinition definition, @Nullable Object transaction, Boolean newTransaction,
Boolean newSynchronization, Boolean debug, @Nullable Object suspendedResources) {
Boolean actualNewSynchronization = newSynchronization &&
!TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive();
return new DefaultTransactionStatus(
transaction, newTransaction, actualNewSynchronization,
definition.isReadOnly(), debug, suspendedResources);
}
- 源码解析
实际上就是封装了事务属性definition新建的transaction,并且将事务状态属性设置为新事物,最后一个参数为被挂起的事务。
简单了解一下关键参数:
第二个参数transaction:事务对象,在一开头就有创建,其就是事务管理器的一个内部类
第三个参数newTransaction:布尔值,一个标识,用于判断是否是新的事务,用于提交或者回滚方法用。是新的才会提交或者回滚
最后一个参数suspendedResources:被挂起的对象资源,挂起操作会返回旧的holder,将其与一些事务属性一起封装成一个对象,就是这个suspendedResources对象了,它会放再status中,在最后的清理工作方法中判断status中是否有这个挂起对象,如果有会恢复它
接下来我们再回到startTransaction方法中的doBegin(transaction, definition);具体实现还是看DataSourceTransactionManager。
- 看源码(
DataSourceTransactionManager.java)
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try {
// 判断如果transaction 没有holder的话,才去dataSource中获取一个新的连接
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
// 通过 dataSource获取
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
}
// 所以只有transaction的holder为空时,才会设置新的holder
// 将获取的连接封装进 ConnectionHolder 然后封装进 transaction 的 connectionholder 属性
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
}
// 设置新的连接为事务同步中
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
// con设置事务隔离级别为 只读
con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
// /DataSourceTransactionObject设置事务隔离级别
txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);
txObject.setReadOnly(definition.isReadOnly());
// Switch to manual commit if necessary. This is very expensive in some JDBC drivers,
// so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
// configured the connection pool to set it already).
// 如果是自动提交切换到手动提交
if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
}
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
// 如果只读,执行sql设置事务只读
prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
//设置connection 持有者的事务开启状态
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);
int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
// 设置超时秒数
txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);
}
// Bind the connection holder to the thread.
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
// 将当前获取到的连接绑定到当前线程
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, obtainDataSource());
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
}
throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
}
}
接下来我们看一下doBegin方法中的con设置事务隔离级别的方法(Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition)
- 看源码(
DataSourceUtils.java)
@Nullable
public static Integer prepareConnectionForTransaction(Connection con, @Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws SQLException {
Assert.notNull(con, "No Connection specified");
Boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// Set read-only flag.
// 设置数据连接的只读标识
if (definition != null && definition.isReadOnly()) {
try {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Setting JDBC Connection [" + con + "] read-only");
}
con.setReadOnly(true);
}
catch (SQLException | RuntimeException ex) {
Throwable exToCheck = ex;
while (exToCheck != null) {
if (exToCheck.getClass().getSimpleName().contains("Timeout")) {
// Assume it's a connection timeout that would otherwise get lost: e.g. from JDBC 4.0
throw ex;
}
exToCheck = exToCheck.getCause();
}
// "read-only not supported" SQLException -> ignore, it's just a hint anyway
logger.debug("Could not set JDBC Connection read-only", ex);
}
}
// Apply specific isolation level, if any.
// 设置数据库连接的隔离级别
Integer previousIsolationLevel = null;
if (definition != null && definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Changing isolation level of JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to " +
definition.getIsolationLevel());
}
int currentIsolation = con.getTransactionIsolation();
if (currentIsolation != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
previousIsolationLevel = currentIsolation;
con.setTransactionIsolation(definition.getIsolationLevel());
}
}
return previousIsolationLevel;
}
从上面我们可以看到都是通过Connection去设置的。
接下来我们再回到doBegin方法看这一行
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(obtainDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
这行代码是将当前获取到的连接绑定到当前线程,绑定解绑围绕一个线程变量,这个变量就在TransactionSynchronizationManager中,如下:
private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transactional resources");
这是一个static final修饰的线程变量,存储的是一个Map,我们再看一下doBegin的静态方法,也就是上面提到的:bindResource方法:
- 看源码(
TransactionSynchronizationManager.java)
public static void bindResource(Object key, Object value) throws IllegalStateException {
// 从上面可以知道,线程变量是一个 map ,而这个key就是dataSource,这个value 就是 holder
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
Assert.notNull(value, "Value must not be null");
// 获取这个线程变量的 map
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
// set ThreadLocal Map if none found
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap<>();
resources.set(map);
}
// 将新的 holder 作为 value ,dataSource作为 key 放入到当前线程 map 中
Object oldValue = map.put(actualKey, value);
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (oldValue instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) oldValue).isVoid()) {
oldValue = null;
}
if (oldValue != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Already value [" + oldValue + "] for key [" + actualKey + "] bound to thread");
}
}
扩充知识点
这里提一下,mybatis中获取的数据库连接,就是dataSource从ThreadLocal中获取的,以查询举例,会调用Executor#doQuery方法
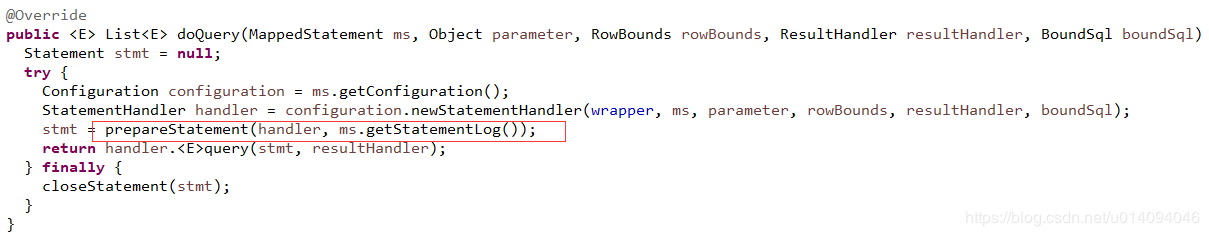
最终会调用DataSourceUtils#doGetConnection方法获取,真正的数据库连接,其中的TransactionSynchronization中保存的就是方法调用前,spring增强方法中绑定到线程的connection,从而保证整个事务过程中connection的一致性
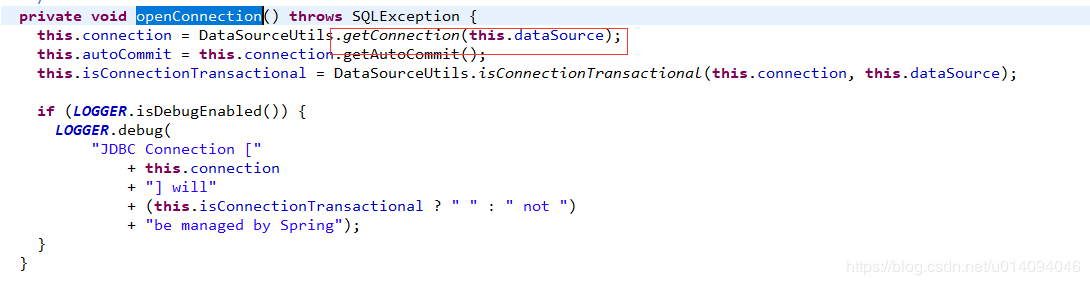
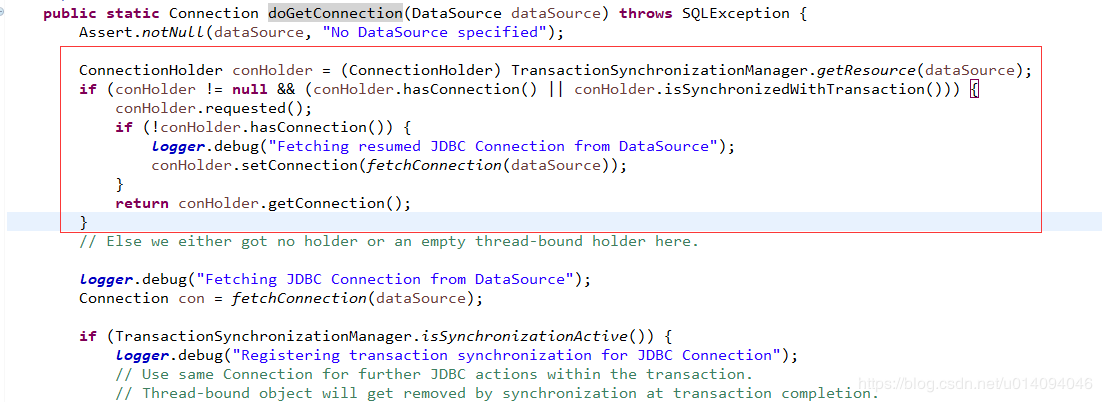
我们继续来看看TransactionSynchronizationManager的getResource(Object key)这个方法
- 看源码(
TransactionSynchronizationManager.java)
@Nullable
public static Object getResource(Object key) {
Object actualKey = TransactionSynchronizationUtils.unwrapResourceIfNecessary(key);
return doGetResource(actualKey);
}
继续追踪一下里面的doGetResource方法
- 看源码(
TransactionSynchronizationManager.java)
@Nullable
private static Object doGetResource(Object actualKey) {
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = map.get(actualKey);
// Transparently remove ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
value = null;
}
return value;
}
到这里我们就知道了getResource这个方法就说明了就是从线程变量的Map中根据DataSource获取的ConnectionHolder
已经存在的事务
前面我们提到过,第一次事务开始时必会新创建一个holder然后做绑定操作,此时线程变量是有holder的且active为true,如果第二个事务进来,去new一个transaction之后去线程变量中去holder,holder是不为空的且active是为true的;所以会进入handleExistingTransaction方法;回到AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的getTransaction函数:查看handleExistingTransaction方法:
- 看源码(
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java)
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, Boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException {
// 1. PROPAGATION_NEVER(不支持当前事务,如果当前事务存在,则抛出异常) 报错
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
}
// PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED (不支持当前事务,现有同步将挂起),挂起当前事务,返回一个空事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
}
// 这里会将原来的事务挂起,并返回被挂起的对象。
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
Boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
// 这里可以看到,第二个参数transaction传了一个空事务,第三个参数false为旧标记
// 最后一个参数就是将前面的挂起的对象封装进了一个新的Status中,当前事务执行完成后,就恢复suspendedResources
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
// 挂起当前事务,创建新事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 将原事务挂起,此时新建事务,不与原事务有关系。
// 会将transaction 中的holder 设置为 null ,然后解绑
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try {
// 注意这个函数。
// new一个status出来,传入transaction,并且为新事务标记,然后传入挂起事务
// 这里也做了一次doBegin,此时的transaction中holer是为空的,因为之前的事务被挂起了
// 所以这里会取一次新的连接,并且绑定!
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx) {
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
}
}
// 如果此时的传播特性是 PROPAGATION_NESTED,不会挂起事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
// 这里如果是JTA事务管理器,就不可以用savePoint了,将不会进入此方法
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
// 这里不会挂起事务,说明NESTED的特性是原事务的子事务而已
// new一个status,传入transaction,传入旧事务标记,传入挂起对象=null
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
// 这里是NESTED特性特殊的地方,在先前存在事务的情况下会建立一个savePoint
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
} else {
// JTA事务走这个分支,创建新事务
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
// JTA事务走这个分支,创建新事务
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
}
if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
}
}
if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
}
}
}
// 到这里PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 或 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED或PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,存在事务加入事务即可,标记为旧事务,空挂起
Boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
- 源码解析
从上述源码中,对于已经存在事务的处理过程中,我们看到很多熟悉的操作,但是也有些不同的地方,函数中对已经存在的事务处理考虑分两种情况:
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW表示当前方法必须在它自己的事务里运行,一个新的事务将被启动,而如果有一个事务正在运行的话,则在这个方法运行期间被挂起。而Spring中对于此种传播方式的处理和新建事务建立的最大的不同点就是使用suspend方法将原事务挂起。将信息挂起的目的当然是为了在当前事务执行完毕后再将原事务还原。
PROPAGATION_NESTED表示如果当前有一个事务正在运行中,则该方法应该运行在一个嵌套的事务中,被嵌套的事务可以独立于封装事务进行提交或者回滚,如果封装事务不存在,行为就像PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW。对于嵌入式事务的处理,Spring中主要考虑了两种处理方式:
- Spring中允许嵌入事务的时候,则首选设置保存点的方式作为异常处理的回滚
- 对于其他方式,比如JTA无法使用保存点的方式,那么处理方式PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW相同,而一旦出现异常,则由Spring的事务异常处理机制去完成后续操作
对于挂起操作的主要目的是记录原有事务的状态,以便于后续操作对事务的恢复。
总结:
到这里我们可以知道,在当前存在事务的情况下,根据传播特性去决定是否为新事务,是否挂起当前事务。
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED:会挂起事务,不运行doBegin方法传空transaction,标记为旧事务。封装status对象。
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW:将会挂起事务且运行doBegin方法,标记为新事务。封装status对象:
// 注意这个函数。
// new一个status出来,传入transaction,并且为新事务标记,然后传入挂起事务
// 这里也做了一次doBegin,此时的transaction中holer是为空的,因为之前的事务被挂起了
// 所以这里会取一次新的连接,并且绑定!
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// startTransaction函数
...
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
...
PROPAGATION_NESTED:不会挂起事务且不会运行doBegin方法,标记为旧事务,但会创建savePoint。封装status对象:
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
其他事务例如:PROPAGATION_REQUIRED:不会挂起事务,封装原有的transaction不会运行doBegin方法,标记旧事务,封装status对象:
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
挂起:
对于挂起操作的主要目的是记录原有事务的状态,以便后续操作对事务的恢复:
- 看源码(
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java)
@Nullable
protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(@Nullable Object transaction) throws TransactionException {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization();
try {
Object suspendedResources = null;
if (transaction != null) {
// 这里是真正做挂起的方法,这里返回的是一个holder
suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
}
// 这里将名称、隔离级别等信息从线程变量中取出并设置对应属性为null到线程变量
String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null);
Boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null);
Boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false);
// 将事务各个属性与挂起的holder一并封装进SuspendedResourcesHolder对象中
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(
suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive);
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
// doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
throw ex;
}
} else if (transaction != null) {
// Transaction active but no synchronization active.
Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources);
} else {
// Neither transaction nor synchronization active.
return null;
}
}
我们看一下doSuspend方法,在实现类DataSourceTransactionManager中
- 看源码(
DataSourceTransactionManager.java)
@Override
protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
// 将transaction中的holder属性设置为空
txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
// ConnnectionHolder从线程变量中解绑!
return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainDataSource());
}
我们紧接着继续追unbindResource函数里面的doUnbindResource:
- 看源码(
TransactionSynchronizationManager.java)
@Nullable
private static Object doUnbindResource(Object actualKey) {
// 取得当前线程的线程变量Map
Map<Object, Object> map = resources.get();
if (map == null) {
return null;
}
// 将key为dataSourece的value移除出Map,然后将旧的Holder返回
Object value = map.remove(actualKey);
// Remove entire ThreadLocal if empty...
// 如果此时map为空,直接清除线程变量
if (map.isEmpty()) {
resources.remove();
}
// Transparently suppress a ResourceHolder that was marked as void...
if (value instanceof ResourceHolder && ((ResourceHolder) value).isVoid()) {
value = null;
}
// 将旧Holder返回
return value;
}
回顾:
简单回顾一下解绑的操作。其实主要做了三件事:
- 将transaction中的holder属性设置为空
- 解绑(会返回线程中的那个旧的holder出来,从而封装到SuspendedResourcesHolder对象中)
- 将SuspendedResourcesHolder放入到status中,方便后期子事务完成后,恢复外层事务。
好了本次文章到这里就告一段落了,希望对你能有所帮助。
欢迎微信搜索【码上遇见你】获取更多精彩内容
什么。你还没有搞懂Spring事务增强器 ,一篇文章让你彻底搞懂Spring事务,虽然很长但是干货满满的更多相关文章
- MySQL命令,一篇文章替你全部搞定
MySQL命令,一篇文章替你全部搞定 MySQL的基本操作可以包括两个方面:MySQL常用语句如高频率使用的增删改查(CRUD)语句和MySQL高级功能,如存储过程,触发器,事务处理等.而这两个方面又 ...
- Spring实战第四章学习笔记————面向切面的Spring
Spring实战第四章学习笔记----面向切面的Spring 什么是面向切面的编程 我们把影响应用多处的功能描述为横切关注点.比如安全就是一个横切关注点,应用中许多方法都会涉及安全规则.而切面可以帮我 ...
- 一篇文章让你彻底弄懂SSL/TLS协议
目录 SSL/TLS的应用 TLS协议的架构 握手协议 主密码和预备主密码 TLS记录协议 一篇文章让你彻底弄懂SSL/TLS协议 SSL/TLS是一种密码通信框架,他是世界上使用最广泛的密码通信方法 ...
- 【面试】一篇文章帮你彻底搞清楚“I/O多路复用”和“异步I/O”的前世今生
曾经的VIP服务 在网络的初期,网民很少,服务器完全无压力,那时的技术也没有现在先进,通常用一个线程来全程跟踪处理一个请求.因为这样最简单. 其实代码实现大家都知道,就是服务器上有个ServerSoc ...
- 一篇文章帮你彻底搞清楚“I/O多路复用”和“异步I/O”的前世今生
在网络的初期,网民很少,服务器完全无压力,那时的技术也没有现在先进,通常用一个线程来全程跟踪处理一个请求.因为这样最简单. 其实代码实现大家都知道,就是服务器上有个ServerSocket在某个端口监 ...
- 一篇文章让你彻底搞清楚Python中self的含义
刚开始学习Python的类写法的时候觉得很是麻烦,为什么定义时需要而调用时又不需要,为什么不能内部简化从而减少我们敲击键盘的次数? 你看完这篇文章后就会明白所有的疑问. self代表类的实例,而非类. ...
- 一篇文章让你彻底弄懂WinForm GDI 编程基本原理
一 GDI编程原理 GDI(Graphics Device Interface,图形设备接口),主要负责Windows系统与绘图程序之间的信息交换,处理所有Windows程序的图形输出. GDI的常用 ...
- 五分钟学Java:一篇文章搞懂spring和springMVC
原创声明 本文作者:黄小斜 转载请务必在文章开头注明出处和作者. 本文思维导图 什么是Spring,为什么你要学习spring? 你第一次接触spring框架是在什么时候?相信很多人和我一样,第一次了 ...
- 五分钟学Java:一篇文章带你搞懂spring全家桶套餐
原创声明 本文首发于微信公众号[程序员黄小斜] 本文作者:黄小斜 转载请务必在文章开头注明出处和作者. 本文思维导图 什么是Spring,为什么你要学习spring? 你第一次接触spring框架是在 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL MHA 运行状态监控
一 项目描述 1.1 背景 MHA(Master HA)是一款开源的 MySQL 的高可用程序,它为 MySQL 主从复制架构提供了 automating master failover 功能.MHA ...
- List接口常用实现类对比
相同点 都实现了List接口 储存了有序 可重复的数据 不同点 ArrayList 线程不安全 但是效率高 底层使用 Object[] elementData 实现 LinkedList 底层使用双向 ...
- Setoolkit部署
禁止使用本文的知识进行违法犯罪活动!!学习这些内容是为了更好的防范钓鱼网站 详见我的github仓库 Setoolkit : Social-Engineer Toolkit(社会工程学工具包) 其作为 ...
- C#开发BIMFACE系列53 WinForm程序中使用CefSharp加载模型图纸1 简单应用
BIMFACE二次开发系列目录 [已更新最新开发文章,点击查看详细] 在我的博客<C#开发BIMFACE系列52 CS客户端集成BIMFACE应用的技术方案>中介绍了多种集成BIM ...
- 初始HTML05
HTML 表单控件属性 表单控件可设置以下标签属性 属性名 取值 type 设置控件类型 name 设置控件名称,最终与值一并发送给服务器 value 设置控件的值 placeholder 设置输入框 ...
- filebeat收集日志到elsticsearch中并使用ingest node的pipeline处理
filebeat收集日志到elsticsearch中 一.需求 二.实现 1.filebeat.yml 配置文件的编写 2.创建自定义的索引模板 3.加密连接到es用户的密码 1.创建keystore ...
- 「笔记」$Min\_25$筛
总之我也不知道这个奇怪的名字是怎么来的. \(Min\_25\)筛用来计算一类积性函数前缀和. 如果一个积性函数\(F(x)\)在质数单点是一个可以快速计算的关于此质数的多项式. 那么可以用\(Min ...
- 单片机stm32零基础入门之--初识STM32 标准库
CMSIS 标准及库层次关系 因为基于Cortex 系列芯片采用的内核都是相同的,区别主要为核外的片上外设的差异,这些差异却导致软件在同内核,不同外设的芯片上移植困难.为了解决不同的芯片厂商生产的Co ...
- Linux线程互斥学习笔记--详细分析
一.互斥锁 为啥要有互斥? 多个进程/线程执行的先后顺序不确定,何时切出CPU也不确定. 多个进程/线程访问变量的动作往往不是原子的. 1. 操作步骤 (1)创建锁 // 创建互斥锁mutex pth ...
- 实验7:基于REST API的SDN北向应用实践
一.实验目的 1.能够编写程序调用OpenDaylight REST API实现特定网络功能: 2.能够编写程序调用Ryu REST API实现特定网络功能. 二.实验环境 下载虚拟机软件Oracle ...
