022.Python模块序列化模块(json,pickle)和math模块
序列化模块
一 序列化模块 pickle
1.1 基本认识
- 序列化:把不能够直接存储的数据变成可存储的过程就是序列化
- 反序列化:把储存的数据拿出来恢复成原来的数据类型就是反序列化
例如,一个文件不可以写的数据
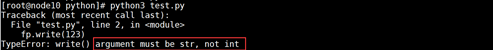
[root@node10 python]# cat test.py
with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(123)
执行
使用列表
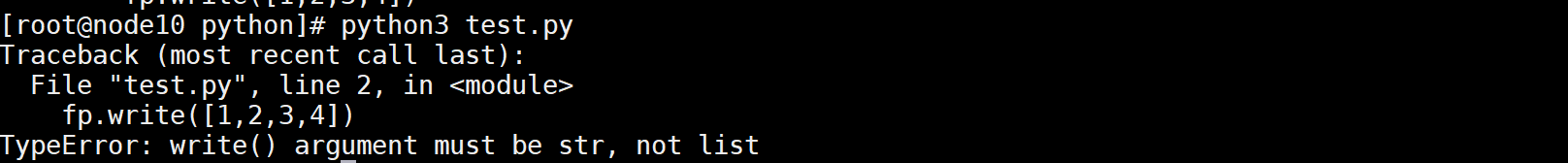
with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write([1,2,3,4])
执行报错
换成字典
with open('0209.txt',mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write({"a":1,"b":2})
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test.py", line 2, in <module>
fp.write({"a":1,"b":2})
TypeError: write() argument must be str, not dict
只能写的只能是字符串或者字节流
对于不能写入文件的数据,只有序列化才能写入php的序列化使用(serialize)反序列化(unserialize)
1.2 使用pickle模块
dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes
import pickle #引入模块 引入pickle模块
#dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes
dic = {"a":1,"b":2}
res = pickle.dumps(dic)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
b'\x80\x03}q\x00(X\x01\x00\x00\x00aq\x01K\x01X\x01\x00\x00\x00bq\x02K\x02u.'
loads 把任意bytes反序列化成原来数据
import pickle
#dumps 把任意对象序列化成一个bytes
dic = {"a":1,"b":2}
res = pickle.dumps(dic)
print(res) res = pickle.loads(res)
print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
b'\x80\x03}q\x00(X\x01\x00\x00\x00aq\x01K\x01X\x01\x00\x00\x00bq\x02K\x02u.'
{'a': 1, 'b': 2} <class 'dict'>
函数序列化
import pickle
def func():
print("我是一个函数")
res = pickle.dumps(func)
print(res)
print("<==>")
res = pickle.loads(res)
res()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
b'\x80\x03c__main__\nfunc\nq\x00.'
<==>
我是一个函数
迭代器序列化
import pickle
from collections import Iterator,Iterable
it = iter(range(10))
print(isinstance(it,Iterator))
res = pickle.dumps(it)
print(res)
res = pickle.loads(res)
print(res)
for i in range(3):
print(next(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
True
b'\x80\x03cbuiltins\niter\nq\x00cbuiltins\nrange\nq\x01K\x00K\nK\x01\x87q\x02Rq\x03\x85q\x04Rq\x05K\x00b.'
<range_iterator object at 0x7f6618065cc0>
0
1
2
所有的数据类型都可以通过pickle进行序列化
dump 把对象序列化后写入到file-like Object(即文件对象)
import pickle
dic = {"a":1,"b":2}
with open("0209_1.txt",mode="wb") as fp:
# pickle.dump(数据类型,文件对象) 先把数据变成二进制字节流 在存储在文件当中
pickle.dump(dic,fp) #load 把file-like Object(即文件对象)中的内容拿出来,反序列化成原来数据
with open("0209_1.txt",mode="rb") as fp:
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'a': 1, 'b': 2}
[root@node10 python]# cat 0209_1.txt
▒}q(XaqKXbqKu.
二 json模块
2.1 基本认识
json 的功能也是序列化,不过他序列化的最终结果是一个字符串
不同的语言之间,进行数据交流都使用json数据格式
所有语言都能够识别的数据格式叫做json ,json数据格式
python 中能够使用json格式的数据类型 只有如下:int float bool str list tuple dict None [不包含complex set]
语言和语言之间的交流用json(字符串)
数据之间的传输和存储用pickle(二进制字节流)
2.2 序列话字符串
第一对 dumps 和 loads 把数据序列化或者反序列化成字符串
import json
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
res = json.dumps(dic)
print(res,type(res))
执行
{
"name": "\u5218\u94c1\u86cb",
"age": 18,
"sex": "\u5973\u6027",
"family": ["father", "\u5988\u5988"],
"agz": 1
}
<class 'str'>
识别中文编码
- ensure_ascii=True (默认值) 如果想要显示中文 如下:ensure_ascii = False
- sort_keys=False 对字典的键进行排序 (会按照ascii 字符的从小到大进行排序)
import json
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
res = json.dumps(dic,ensure_ascii=False,sort_keys=True)
print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{
"age": 18,
"agz": 1,
"family": ["father", "妈妈"],
"name": "刘铁蛋",
"sex": "女性"
}
<class 'str'>
2.3 数据存储转化
第二对 dump 和 load 应用在数据的存储的转化上
import json
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
with open("0209_2.txt",mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
json.dump(dic,fp,ensure_ascii=False) with open("0209_2.txt",mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
res = json.load(fp)
print(res,type(res))
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'>
[root@node10 python]# cat 0209_2.txt
{"name": "刘铁蛋", "age": 18, "sex": "女性", "family": ["father", "妈妈"], "agz": 1}
2.4 pickle 和 json 之间的用法区别
- json 可以连续dump , 但是不能连续load , load是一次性拿出所有数据而不能识别.
- 可以使用loads ,一行一行的读取,一行一行的通过loads来转化成原有数据类型
json
import json
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
with open("0209_3.txt" , mode="w",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
json.dump(dic,fp)
fp.write('\n')
json.dump(dic,fp)
fp.write('\n') print("<===>")
with open("0209_3.txt" ,mode="r",encoding="utf-8") as fp:
# load 是一次性把所有的数据拿出来,进行识别
# load 不能识别多个数据混在一起的情况
# 用loads 来解决load 不能识别多个数据的情况
# res = json.load(fp)
for i in fp:
print(i,type(i))
res = json.loads(i)
print(res,type(res)) # print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
<===>
{"name": "\u5218\u94c1\u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "\u5973\u6027", "family": ["father", "\u5988\u5988"], "agz": 1}
<class 'str'>
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'>
{"name": "\u5218\u94c1\u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "\u5973\u6027", "family": ["father", "\u5988\u5988"], "agz": 1}
<class 'str'>
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1} <class 'dict'>
[root@node10 python]# cat 0209_3.txt
{"name": "\u5218\u94c1\u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "\u5973\u6027", "family": ["father", "\u5988\u5988"], "agz": 1}
{"name": "\u5218\u94c1\u86cb", "age": 18, "sex": "\u5973\u6027", "family": ["father", "\u5988\u5988"], "agz": 1}
pickle
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
import pickle
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="wb") as fp:
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="rb") as fp:
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
[root@node10 python]# cat 0209_4.txt
▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
使用try
dic = {"name":"刘铁蛋","age":18,"sex":"女性","family":["father","妈妈"],"agz":1}
import pickle
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="wb") as fp:
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
pickle.dump(dic,fp)
with open("0209_4.txt",mode="rb") as fp:
try:
while True:
res = pickle.load(fp)
print(res)
except:
pass
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
{'name': '刘铁蛋', 'age': 18, 'sex': '女性', 'family': ['father', '妈妈'], 'agz': 1}
[root@node10 python]# cat 0209_4.txt
▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
Ku.▒}q(XnameqX 刘铁蛋qXageqKXsexqX女性qXfamilyq]q(XfatherX妈妈q eXagzq
2.5 try的异常处理
try:
...
except:
把有问题的代码赛到try 代码块当中
如果发生异常报错,直接执行except其中的代码块
优点:不会因为报错终止程序运行
示例:
listvar = [1,15,2]
print(listvar[15])
执行

使用try函数
try :
listvar = [1,15,2]
print(listvar[15])
except:
pass
再次执行不会报错
json 和 pickle 两个模块的区别:
- json序列化之后的数据类型是str,所有编程语言都识别,但是仅限于(int float bool)(str list tuple dict None),json不能连续load,只能一次性拿出所有数据
- pickle序列化之后的数据类型是bytes,所有数据类型都可转化,但仅限于python之间的存储传输.pickle可以连续load,多套数据放到同一个文件中
三 math数学模块
ceil() 向上取整操作 (对比内置round)
import math
res = math.ceil(4.01)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
5
floor() 向下取整操作 (对比内置round)
import math
res = math.floor(3.99)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
3
pow() 计算一个数值的N次方(结果为浮点数) (对比内置pow)
import math
res = math.pow(2,3)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
8.0
math模块中的pow没有第三个参数
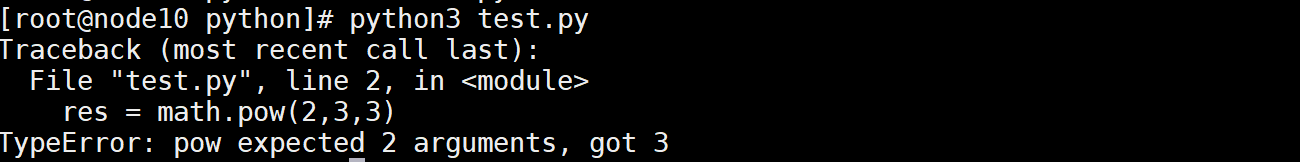
import math
res = math.pow(2,3,3)
print(res)
执行报错
sqrt() 开平方运算(结果浮点数)
import math
res = math.sqrt(10)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
3.1622776601683795
fabs() 计算一个数值的绝对值 (结果浮点数) (对比内置abs)
import math
res = math.fabs(-56)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
56.0
modf() 将一个数值拆分为整数和小数两部分组成元组
import math
res = math.modf(14.677)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
(0.6769999999999996, 14.0)
copysign() 将参数第二个数值的正负号拷贝给第一个
import math
res = math.copysign(-1,-5)
print(res) # 得到浮点数结果 , 它的正负号取决于第二个值
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
-1.0
fsum() 将一个容器数据中的数据进行求和运算 (结果浮点数)(对比内置sum)
import math
listvar = [1,2,3,4,5,99,6]
res = math.fsum(listvar)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
120.0
圆周率常数 pi
import math
print(math.pi)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
3.141592653589793
022.Python模块序列化模块(json,pickle)和math模块的更多相关文章
- Python全栈之路----常用模块----序列化(json&pickle&shelve)模块详解
把内存数据转成字符,叫序列化:把字符转成内存数据类型,叫反序列化. Json模块 Json模块提供了四个功能:序列化:dumps.dump:反序列化:loads.load. import json d ...
- Python模块:shutil、序列化(json&pickle&shelve)、xml
shutil模块: 高级的 文件.文件夹.压缩包 处理模块 shutil.copyfileobj(fscr,fdst [, length]) # 将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中 import shu ...
- Python序列化,json&pickle&shelve模块
1. 序列化说明 序列化可将非字符串的数据类型的数据进行存档,如字典.列表甚至是函数等等 反序列化,将通过序列化保存的文件内容反序列化即可得到数据原本的样子,可直接使用 2. Python中常用的序列 ...
- 常用模块(random,os,json,pickle,shelve)
常用模块(random,os,json,pickle,shelve) random import random print(random.random()) # 0-1之间的小数 print(rand ...
- python序列化: json & pickle & shelve 模块
一.json & pickle & shelve 模块 json,用于字符串 和 python数据类型间进行转换pickle,用于python特有的类型 和 python的数据类型间进 ...
- python 全栈开发,Day25(复习,序列化模块json,pickle,shelve,hashlib模块)
一.复习 反射 必须会 必须能看懂 必须知道在哪儿用 hasattr getattr setattr delattr内置方法 必须能看懂 能用尽量用__len__ len(obj)的结果依赖于obj. ...
- 模块(序列化(json&pickle)+XML+requests)
一.序列化模块 Python中用于序列化的两个模块: json 跨平台跨语言的数据传输格式,用于[字符串]和 [python基本数据类型] 间进行转换 pickle python内置的数据 ...
- python模块概况,json/pickle,time/datetime,logging
参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/5501365.html http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/51 ...
- Python全栈开发记录_第八篇(模块收尾工作 json & pickle & shelve & xml)
由于上一篇篇幅较大,留下的这一点内容就想在这里说一下,顺便有个小练习给大家一起玩玩,首先来学习json 和 pickle. 之前我们学习过用eval内置方法可以将一个字符串转成python对象,不过, ...
- python 模块二(os,json,pickle)
#################################总结##################### os常用 os.makedirs('baby/安哥拉/特斯拉/黄晓明') os.mkd ...
随机推荐
- Dynamics CRM报表点击自动运行方法
当我们点击了报表后一般会进入到条件筛选界面,再点击运行报表才可以直接运行报表.有一个方法可以点击报表后直接运行报表. 文本编辑器打开报表的rdl文件 找到如下位置的代码: 把Value部分改为: &l ...
- PAT A1032 Sharing
题意:给出两条链表的首地址以及若干节点的地址,数据,下一个节点的地址,求两条链表的首个共用节点的地址.如果两条链表没有共用节点,则输出-1.思路步骤1:由于地址的范围很小,因此可以直接用静态链表,但是 ...
- Spring Boot 快速迁移至 Quarkus
Quarkus 是一个目前非常火的 Java 应用开发框架,定位是轻量级的微服务框架.,Quarkus 提供了优秀的容器化整合能力,相较于传统开发框架(Spring Boot)有着更快的启动速度.更小 ...
- 【笔记】《Redis设计与实现》chapter11 AOF持久化
11.1 AOF持久化的实现 命令追加 当AOF持久化处于开启状态时,服务器执行完一个写命令之后,会以协议格式将被执行的写明了追加到服务器状态的aof_buf缓冲区 struct redisServe ...
- 详细Tomcat安装及问题排查
一.安装 1.下载官网:https://tomcat.apache.org/ 2.将下载后的包解压到目录中会出现以下页面 3.设置环境变量,向path中添加tomcat的bin目录地址 4.cmd进入 ...
- shell脚本 5 sed和awk
文本处理三剑客 在 Shell 下使用这些正则表达式处理文本最多的命令有下面几个工具: 命令 描述 grep 默认不支持扩展表达式,加-E 选项开启 ERE.如果不加-E 使用花括号要加转义符\{\} ...
- 如何查看显著性SNP在数据中的频率?
我们做完GWAS的关联分析后需要查看显著性SNP在我们数据中的频率分布情况.这时候我们需要用到plink和我们做关系分析所用的二进制文件datas. 第一步,我们用R语言读取分析结果,即*.assoc ...
- Day14_77_反射( newInstance() 方法)
newInstance() 方法 * 通过反射获取class类型的对象之后,可以通过该对象创建所对应的class类型的对象 * newInstance() 用来创建Class获取的类所表示的一个新实例 ...
- python进阶(17)协程
协程 协程(Coroutine),又称微线程,纤程.(协程是一种用户态的轻量级线程) 作用:在执行 A 函数的时候,可以随时中断,去执行 B 函数,然后中断B函数,继续执行 A 函数 (可以自动切 ...
- Python 3.10 中新的功能和变化
随着最后一个alpha版发布,Python 3.10 的功能更改全面敲定! 现在,正是体验Python 3.10 新功能的理想时间!正如标题所言,本文将给大家分享Python 3.10中所有重要的功能 ...
