剑指offer刷题
1、面试题43. 1~n整数中1出现的次数
输入一个整数 n ,求1~n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。
例如,输入12,1~12这些整数中包含1 的数字有1、10、11和12,1一共出现了5次。
这个题目的核心思想是考虑:每个位是任意数字时,可以包含多少个这个位为1的数字
分了三种情况



class Solution {
public int countDigitOne(int n) {
//digit表示位因子,就是10、100、1000...
long digit=1;
int count=0;
while(n/digit!=0){
long high=n/(digit*10);
long cur=(n/digit)%10;
long low=n-(n/digit*digit);
if(cur==0){
count+=(high*digit);
}
else if(cur==1){
count+=(high*digit)+low+1;
}
else if(cur>1){
count +=(high+1)*digit;
}
digit*=10;
}
return count;
}
}
class Solution {
public int countDigitOne(int n) {
return f(n);
}
private int f(int n ) {
if (n <= 0)
return 0;
String s = String.valueOf(n);
int high = s.charAt(0) - '0';
int pow = (int) Math.pow(10, s.length()-1);
int last = n - high*pow;
if (high == 1) {
return f(pow-1) + last + 1 + f(last);
} else {
return pow + high*f(pow-1) + f(last);
}
}
}
2、面试题60. n个骰子的点数
动态规划。。
动态规划
使用动态规划解决问题一般分为三步:
- 表示状态
- 找出状态转移方程
- 边界处理



public double[] twoSum(int n) {
int dp[][]=new int[n+1][6*n+1];//表示i个骰子掷出s点的次数
for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) {
dp[1][i]=1;//表示一个骰子掷出i点的次数为1
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) {//表示骰子的个数
for(int s=i;s<=6*i;s++) {//表示可能会出现的点数之和
for(int j=1;j<=6;j++) {//表示当前这个骰子可能掷出的点数
if(s-j<i-1) {//当总数还没有j大时,就不存在这种情况
break;
}
dp[i][s]+=dp[i-1][s-j];//当前n个骰子出现的点数之和等于前一次出现的点数之和加上这一次出现的点数
}
}
}
double total = Math.pow((double)6,(double)n);//掷出n次点数出现的所有情况
double[] ans = new double[5*n+1];//因为最大就只会出现5*n+1中点数
for(int i=n;i<=6*n;i++){
ans[i-n]=((double)dp[n][i])/total;//第i小的点数出现的概率
}
return ans;
}
3、面试题65. 不用加减乘除做加法
位运算
class Solution {
public int add(int a, int b) {
while(b != 0) { // 当进位为 0 时跳出
int c = (a & b) << 1; // c = 进位
a ^= b; // a = 非进位和
b = c; // b = 进位
}
return a;
}
}
4、面试题49. 丑数
我们把只包含因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。求按从小到大的顺序的第 n 个丑数。
又是动态规划,前期刷题遇到很多困难,要善于总结,加油孰能生巧:)

class Solution {
public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
int a=0,b=0,c=0;
int[] dp=new int[n];
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int n2=dp[a]*2,n3=dp[b]*3,n5=dp[c]*5;
dp[i]=Math.min(Math.min(n2,n3),n5);
if(dp[i]==n2)a++;
if(dp[i]==n3)b++;
if(dp[i]==n5)c++;
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}5、面试题52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。
有个技巧学会了就会
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode cur_headA=headA,cur_headB=headB;
while(cur_headA!=cur_headB){
if(cur_headA==null)cur_headA=headB;
else cur_headA=cur_headA.next;
if(cur_headB==null)cur_headB=headA;
else cur_headB=cur_headB.next;
}
return cur_headA;
}
}6、面试题36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
中序遍历的使用,考虑使用中序遍历访问树的各节点 cur ;并在访问每个节点时构建 cur和前驱节点 pre的引用指向;中序遍历完成后,最后构建头节点和尾节点的引用指向即可。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val,Node _left,Node _right) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
Node head,pre=null;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root==null)return null;
dfs(root);
pre.right=head;
head.left=pre;
return head;
}
public void dfs(Node cur){
if(cur==null)return;
dfs(cur.left);
if(pre==null) head = cur;
else pre.right=cur;
cur.left=pre;
pre=cur;
dfs(cur.right);
}
}
7、面试题33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
后序遍历的递归实现、递归分治法
代码想到了,但是忘了建立函数了。吐了吃一堑长一智
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
return recur(postorder,0,postorder.lenght-1);
}
boolean recur(int[] postorder, int i, int j) {
if(i >= j) return true;
int p = i;
while(postorder[p] < postorder[j]) p++;
int m = p;
while(postorder[p] > postorder[j]) p++;
return p == j && recur(postorder, i, m - 1) && recur(postorder, m, j - 1);
}
8、面试题68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
原题
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null||root==p||root==q)return root;
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null&right!=null)return root;
else if(left!=null&&right==null)return left;
else return right;
}
}9、面试题54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
中序
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
midcur(root);
return list.get(k-1);
}
public void midcur(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return;
midcur(root.right);
list.add(root.val);
midcur(root.left);
}
}10、面试题34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
被容器套容器搞晕了,思路是对的,注意有个回溯
由于path会变,因此每次赋值为一个对象
class Solution {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res=new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path=new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
recur(root,sum);
return res;
}
public void recur(TreeNode root,int tar){
if(root==null)return;
path.add(root.val);
tar-=root.val;
if(tar==0&&root.left==null&root.right==null){
res.add(new LinkedList(path));
}
recur(root.left,tar);
recur(root.right,tar);
path.removeLast();
}
}11、面试题68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null||root==p||root==q)return root;
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null&&right!=null)return root;
if(left!=null&&right==null)return left;
if(right!=null&&left==null)return right;
return null;
}
}12、面试题55 - I. 二叉树的深度
回溯法牛逼
class Solution {
int max=0;
int count=0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(count>max)max=count;
if(root==null)return max;
count++;
maxDepth(root.left);
maxDepth(root.right);
count--;
return max;
}
}13、面试题27. 二叉树的镜像
简单,换个位子就行,树学的很好:)
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return null;
TreeNode cur=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=cur;
mirrorTree(root.left);
mirrorTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}14、面试题04. 二维数组中的查找
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix==null||matrix.length==0||matrix[0].length==0)return false;
int i_length=matrix.length;
int j_length=matrix[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<i_length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<j_length;j++){
if(matrix[i][j]==target)return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}暴力就是爽。。但是不太优雅,线性探查法 。
从二维数组的右上角开始查找。如果当前元素等于目标值,则返回 true。如果当前元素大于目标值,则移到左边一列。如果当前元素小于目标值,则移到下边一行。
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0, column = columns - 1;
while (row < rows && column >= 0) {
int num = matrix[row][column];
if (num == target) {
return true;
} else if (num > target) {
column--;
} else {
row++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
15、面试题15. 二进制中1的个数
位运算一直学的不行,要重视基础
https://www.cnblogs.com/findbetterme/p/10787118.html
代码很容易,注意点就是==的优先级和&的优先级
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int res=0;
while(n!=0){
//注意==的优先级大于&
if((n&1)==1)res++;
n=n>>>1;
}
return res;
}
}16、面试题32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
这个题目很重要,层序遍历有个重要的知识点就是统计一层的长度,对每层长度进行处理
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list=new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode>queue =new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null)queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> tmp=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=queue.size();i>0;i--){
TreeNode node=queue.pollFirst();
tmp.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)queue.add(node.right);
}
list.add(tmp);
}
return list;
}
}17、剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
之字打印,用的是俩个list完成push 和 pop
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue1=new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue2=new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list=new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null)queue1.add(root);
while(!queue1.isEmpty()||!queue2.isEmpty()){
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> tmp=new LinkedList<>();
while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode head=queue1.pop();
tmp.add(head.val);
if(head.left!=null)queue2.push(head.left);
if(head.right!=null)queue2.push(head.right);
}
list.add(tmp);
}
if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> tmp=new LinkedList<>();
while(!queue2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode head=queue2.pop();
tmp.add(head.val);
if(head.right!=null)queue1.push(head.right);
if(head.left!=null)queue1.push(head.left);
}
list.add(tmp);
}
}
return list;
}
}奇数偶数层的判断方法更好

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
LinkedList<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(res.size() % 2 == 0) tmp.addLast(node.val); // 偶数层 -> 队列头部
else tmp.addFirst(node.val); // 奇数层 -> 队列尾部
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
18、剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
这个题目不同之处在于是要求不用一行一行输出的,而是一起输出,注意返回结果,需要用集合

class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{ add(root); }};
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}19、剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
用的递归,其实也可用个stack
class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
reverse(head);
int arr[]=new int[list.size()];
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
arr[i]=list.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
public void reverse(ListNode head){
if(head==null) return;
reverse(head.next);
list.add(head.val);
}
}class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while(head != null) {
stack.addLast(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] res = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = stack.removeLast();
return res;
}
}
20、 剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode cur=head;
if(cur.val==val)return head.next;
ListNode pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
pre.next=cur.next;
}
pre=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}21、剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子
本题就是数学题计算出规律
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n <= 3) return n - 1;
int a = n / 3, b = n % 3;
if(b == 0) return (int)Math.pow(3, a);
if(b == 1) return (int)Math.pow(3, a - 1) * 4;
return (int)Math.pow(3, a) * 2;
}
}
22、剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
俩道剪绳子,人都被秀傻了,这是编程题吗,明明是数学题
此题与 面试题14- I. 剪绳子 主体等价,唯一不同在于本题目涉及 “大数越界情况下的求余问题” 。
建议先做上一道题,在此基础上再研究此题目的大数求余方法。

class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n <= 3) return n - 1;
int b = n % 3, p = 1000000007;
long rem = 1, x = 3;
for(int a = n / 3 - 1; a > 0; a /= 2) {
if(a % 2 == 1) rem = (rem * x) % p;
x = (x * x) % p;
}
if(b == 0) return (int)(rem * 3 % p);
if(b == 1) return (int)(rem * 4 % p);
return (int)(rem * 6 % p);
}
}
贪心思路,也就是先3后2
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2) {
return 1;
}
if(n == 3){
return 2;
}
int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
long res = 1;
while(n > 4) {
res *= 3;
res %= mod;
n -= 3;
}
return (int)(res * n % mod);
}
}
23、剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
使用个minstack辅助栈就可以解决问题
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> stackData=new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stackMin=new Stack<>();
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stackData.push(x);
if(stackMin.isEmpty())stackMin.push(x);
else if(x<=stackMin.peek()){
stackMin.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
int value=stackData.pop();
if(value==stackMin.peek()){
stackMin.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stackData.peek();
}
public int min() {
return stackMin.peek();
}
}
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.min();
*/24、剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
链表经典题,背诵
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode next=null;
while(head!=null){
next=head.next;
head.next=pre;
pre=head;
head=next;
}
return pre;
}
}25、剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
不难主要是思路
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head=new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur=head;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
cur.next=l1;
l1=l1.next;
}
else{
cur.next=l2;
l2=l2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=l1!=null?l1:l2;
return head.next;
}
}26、剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字

这个思路遇到过,主要是利用边界点来进行操作
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i < j) {
int s = nums[i] + nums[j];
if(s < target) i++;
else if(s > target) j--;
else return new int[] { nums[i], nums[j] };
}
return new int[0];
}
}
27、剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
思路很简单,主要是语法
class Solution {
public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {
int i = 1; // 滑动窗口的左边界
int j = 1; // 滑动窗口的右边界
int sum = 0; // 滑动窗口中数字的和
List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
while (i <= target / 2) {
if (sum < target) {
// 右边界向右移动
sum += j;
j++;
} else if (sum > target) {
// 左边界向右移动
sum -= i;
i++;
} else {
// 记录结果
int[] arr = new int[j-i];
for (int k = i; k < j; k++) {
arr[k-i] = k;
}
res.add(arr);
// 左边界向右移动
sum -= i;
i++;
}
}
return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]);
}
}28、剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字

class Solution {
public int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>(n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
list.add(i);
}
int idx=0;
while(n>1){
idx=(idx+m-1)%n;
list.remove(idx);
n--;
}
return list.get(0);
}
}还有数学推导法
class Solution {
public int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
int ans = 0;
// 最后一轮剩下2个人,所以从2开始反推
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
ans = (ans + m) % i;
}
return ans;
}
}
29、剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
好像太简单了吧
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]==target)count++;
if(nums[i]>target)break;
}
return count;
}
}想简单了,这题是二分法
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 搜索右边界 right
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] <= target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int right = i;
// 若数组中无 target ,则提前返回
if(j >= 0 && nums[j] != target) return 0;
// 搜索左边界 right
i = 0; j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] < target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int left = j;
return right - left - 1;
}
}
30、剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
class Solution { //HashMap实现
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>(); //创建HashMap集合
Node cur=head;
//复制结点值
while(cur!=null){
//存储put:<key,value1>
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val)); //顺序遍历,存储老结点和新结点(先存储新创建的结点值)
cur=cur.next;
}
//复制结点指向
cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
//得到get:<key>.value2,3
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); //新结点next指向同旧结点的next指向
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random); //新结点random指向同旧结点的random指向
cur = cur.next;
}
//返回复制的链表
return map.get(head);
}
}
31、剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
本题非常的重要,知识点很多,最重要的是全排列用的是回溯法的思想好好看看。
class Solution {
Set<String> result =new HashSet<>();
public String[] permutation(String s) {
if(s==null)return new String[0];
boolean[] visited=new boolean[s.length()];
process(s,"",visited);
return result.toArray(new String[result.size()]);
}
private void process(String s, String letter, boolean[] visted){
if(s.length() == letter.length()){
result.add(letter);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
char temp = s.charAt(i);
if(visted[i]) continue;
visted[i] = true;
process(s, letter +temp, visted);
visted[i] = false;
}
}
}32、剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
这个题目是递归的很好的使用,考虑好递归边界

class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? true : recur(root.left, root.right);
}
boolean recur(TreeNode L, TreeNode R) {
if(L == null && R == null) return true;
if(L == null || R == null || L.val != R.val) return false;
return recur(L.left, R.right) && recur(L.right, R.left);
}
}33、剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
正常人写法
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
return s.substring(n) + s.substring(0, n);
}
}面试官一般要求不正常人写法
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = n; i < s.length(); i++)
res.append(s.charAt(i));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
res.append(s.charAt(i));
return res.toString();
}
}
34、剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
先序遍历加深度递归
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return true;
if(Math.abs(depth(root.left)-depth(root.right)) > 1)return false;
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right) ;
}
public int depth(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)return 0;
return Math.max(depth(root.left),depth(root.right))+1;
}
}35、剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
背诵,只有多写多背才能会
public class Codec {
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return "[]";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }};
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node != null) {
res.append(node.val + ",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
else res.append("null,");
}
res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1);
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data.equals("[]")) return null;
String[] vals = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>() {{ add(root); }};
int i = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
queue.add(node.left);
}
i++;
if(!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
queue.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
36、剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
解题思路:
根据题意,此 55 张牌是顺子的 充分条件 如下:
- 除大小王外,所有牌 无重复 ;
- 设此 55 张牌中最大的牌为 maxmax ,最小的牌为 minmin (大小王除外),则需满足:
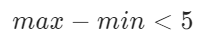
class Solution {
public boolean isStraight(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> repeat = new HashSet<>();
int max = 0, min = 14;
for(int num : nums) {
if(num == 0) continue; // 跳过大小王
max = Math.max(max, num); // 最大牌
min = Math.min(min, num); // 最小牌
if(repeat.contains(num)) return false; // 若有重复,提前返回 false
repeat.add(num); // 添加此牌至 Set
}
return max - min < 5; // 最大牌 - 最小牌 < 5 则可构成顺子
}
}
37、剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
class Solution {
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
int size=(int)Math.pow(10,n)-1;
int[] arr=new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
arr[i]=i+1;
}
return arr;
}
}本题要考虑大数越界的问题,有点难



class Solution {
char[] num;
int[] ans;
int count = 0,n;
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
this.n = n;
num = new char[n];
ans = new int[(int) (Math.pow(10, n) - 1)];
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int n) {
if (n == this.n) {
String tmp = String.valueOf(num);
int curNum = Integer.parseInt(tmp);
if (curNum!=0) ans[count++] = curNum;
return;
}
for (char i = '0'; i <= '9'; i++) {
num[n] = i;
dfs(n + 1);
}
}
}public class solution {
public void printNumbers(int n) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
// 将str初始化为n个'0'字符组成的字符串
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
str.append('0');
}
while(!increment(str)){
// 去掉左侧的0
int index = 0;
while (index < str.length() && str.charAt(index) == '0'){
index++;
}
System.out.println(str.toString().substring(index));
}
}
public boolean increment(StringBuilder str) {
boolean isOverflow = false;
for (int i = str.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
char s = (char)(str.charAt(i) + 1);
// 如果s大于'9'则发生进位
if (s > '9') {
str.replace(i, i + 1, "0");
if (i == 0) {
isOverflow = true;
}
}
// 没发生进位则跳出for循环
else {
str.replace(i, i + 1, String.valueOf(s));
break;
}
}
return isOverflow;
}
}
38、剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数
大数的规律注意,第二段代码更容易理解
class Solution {
public int strToInt(String str) {
char[] c = str.trim().toCharArray();
if(c.length == 0) return 0;
int res = 0, bndry = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10;
int i = 1, sign = 1;
if(c[0] == '-') sign = -1;
else if(c[0] != '+') i = 0;
for(int j = i; j < c.length; j++) {
if(c[j] < '0' || c[j] > '9') break;
if(res > bndry || res == bndry && c[j] > '7') return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
res = res * 10 + (c[j] - '0');
}
return sign * res;
}
}
public int strToInt(String str) {
char[] cs = str.trim().toCharArray();//这个必须在前,否则" "输入在第二个if处会报错
if(cs.length==0) return 0;//字符串为空或字符串仅包含空白字符时,返回0;
int i = 0;
int flag = 1;//默认输出的数为正数
//确定是否存在符号位
if(cs[i]=='+') i++;
else if(cs[i]=='-') {//这里else不能少,否则"+"或者"+-"输入会报错
i++;
flag=-1;
}
long res= 0;//这里必须是long,否则后面的判断临界值时计算会越界,无法判断出正确的结果,如输入"-91283472332"时
while(i<cs.length){//尽量取更多的数字
if(cs[i]>'9'||cs[i]<'0') break;
if(flag==1&&res*10+flag*(cs[i]-'0')>Integer.MAX_VALUE) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(flag==-1&&res*10+flag*(cs[i]-'0')<Integer.MIN_VALUE) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
res = res*10+flag*(cs[i]-'0');
i++;
}
return (int)res;//这里强转不能省略;
}39、剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
没有思路,字符的排列匹配
动态规划
这题真的很典型的动态规划值得好好学学,不用追求速度,需要追求质量
解题思路:
根据题意,可按照下图的思路,总结出 “递推公式” (即转移方程)。
因此,此题可用动态规划解决,以下按照流程解题。
动态规划解析:

class Solution {
public int translateNum(int num) {
String s = String.valueOf(num);
int[] dp = new int[s.length()+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= s.length(); i ++){
String temp = s.substring(i-2, i);
if(temp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && temp.compareTo("25") <= 0)
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
else
dp[i] = dp[i-1];
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
}40、剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
通过在排序时传入一个自定义的 Comparator 实现,重新定义 String 列表内的排序方法,若拼接 s1 + s2 > s2 + s1,那么显然应该把 s2 在拼接时放在前面,以此类推,将整个 String 列表排序后再拼接起来。
class Solution {
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
List<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
strList.add(String.valueOf(num));
}
strList.sort((s1, s2) -> (s1 + s2).compareTo(s2 + s1));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String str : strList) {
sb.append(str);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}41、剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
递归会出现栈溢出


class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n == 1) return x;
if (n == -1) return 1 / x;
if (n % 2 == 0) {
double t = myPow(x, n / 2);
return t * t;
} else {
double t = myPow(x, n / 2);
if (n < 0) x = (1 / x);
return t * t * x;
}
}
}
42、剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
找规律
class Solution {
public int findNthDigit(int n) {
int digit = 1;
long start = 1;
long count = 9;
while (n > count) { // 1.
n -= count;
digit += 1;
start *= 10;
count = digit * start * 9;
}
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit; // 2.
return Long.toString(num).charAt((n - 1) % digit) - '0'; // 3.
}
}
43、剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数
先贴上自己的hanbi方法
class MedianFinder {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MedianFinder() {
}
public void addNum(int num) {
list.add(num);
}
public double findMedian() {
Collections.sort(list);
if(list.size()==1)return list.get(0);
else if(list.size()%2==1)return list.get(list.size()/2);
else return (list.get(list.size()/2)+list.get(list.size()/2-1))/2.0;
}
}然后再看大佬的正确思路

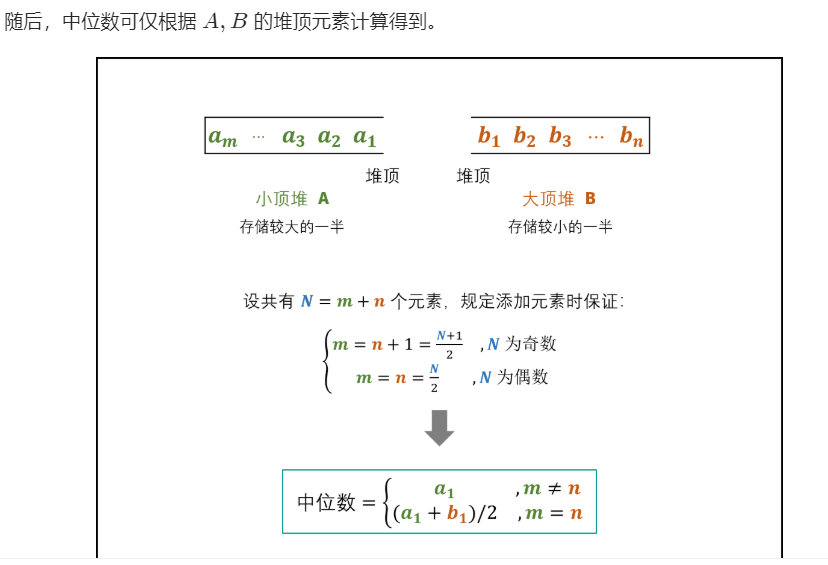


学习一下优先队列和堆排序的使用
使用PriorityQueue来实现最大堆
PriorityQueue是java中数据结构Queue的实现子类
按照源码中标注的原意:PriorityQueue是一个有着默认容量大小(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11)并且内部元素是按照指定的比较器方式所排列的。
(1)min-heap:
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.val - y.val);
(2)max-heap:
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> y.val - x.val);
默认最小堆,最大堆后面减前面
常用方法
①boolean add(E o):将指定的元素插入优先队列中
②void clear():清理队列元素
③boolean contains(object o):查看是否元素包含在队列中
④boolean offer(E o):将指定的元素插入优先队列中
⑤E peek():返回队列头部元素
⑥E poll():弹出队列头部元素
⑦boolean remove(object o):删除某个元素(如果存在的话)
class MedianFinder {
Queue<Integer> A, B;
public MedianFinder() {
A = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 小顶堆,保存较大的一半
B = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (y - x)); // 大顶堆,保存较小的一半
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if(A.size() != B.size()) {
A.add(num);
B.add(A.poll());
} else {
B.add(num);
A.add(B.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
return A.size() != B.size() ? A.peek() : (A.peek() + B.peek()) / 2.0;
}
}
44、剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
HashMap来记数的方法,虽然垃圾但是实用。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
int i=0;
for(;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.get(nums[i])==null)map.put(nums[i],1);
else map.put(nums[i],map.get(nums[i])+1);
if(map.get(nums[i])>nums.length/2)break;
}
return nums[i];
}
}


class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int x = 0, votes = 0;
for(int num : nums){
if(votes == 0) x = num;
votes += num == x ? 1 : -1;
}
return x;
}
}
45、剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
无脑hashmap,但是没这么简单
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.get(nums[i])==null)map.put(nums[i],1);
else map.put(nums[i],map.get(nums[i])+1);
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.get(nums[i])==1)return nums[i];
}
return 0;
}
}以下解题思路来自剑指Offer,侵删。
解题思路:如果数组中的数字除一个只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了两次。我们可以如Solution56_1一样用异或位运算(^)解决这个问题。
上述思路不能解决这里的问题,因为三个相同的数字的异或结果还是该数字。尽管我们这里不能应用异或运算,我们还是可以沿用位运算的思路。
如果一个数字出现三次,那么它的二进制表示的每一位(0或者1)也出现三次。如果把所有出现三次的数字的二进制表示的每一位都分别加起来,那么每一位的和都能被3整除。如果某一位的和能被3整除,那么那个只出现一次的数字二进制表示中对应的那一位是0;否则就是1;
上述思路同样适用于数组中一个数字出现一次,其他数字出现奇数次问题(如果是偶数次,直接用异或就可)。
这种解法的时间效率是O(n)。我们需要一个长度为32的辅助数组存储二进制表示的每一位的和。由于数组的长度是固定的,因此空间效率是O(1)。
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null||nums.length==0)return 0;
int result=0;
for(int i=0;i<32;i++){
int count=0;
int index=1<<i;
for(int j:nums){
if((index&j)!=0){
count++;
}
}
if(count%3==1){
result|=index;
}
}
return result;
}
}46、剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
看到题目第一眼就觉得应该是需要用到异或来做的。
题目又要求了:时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
因此不能用 map空间复杂度为 O(n)与双重循环嵌套空间复杂度为 O(n^2)
由于数组中存在着两个数字不重复的情况,我们将所有的数字异或操作起来,最终得到的结果是这两个数字的异或结果:(相同的两个数字相互异或,值为0)) 最后结果一定不为0,因为有两个数字不重复。
此时我们无法通过 111(二进制),去获得 110 和 001。
那么当我们可以把数组分为两组进行异或,那么就可以知道是哪两个数字不同了。
我们可以想一下如何分组:
重复的数字进行分组,很简单,只需要有一个统一的规则,就可以把相同的数字分到同一组了。例如:奇偶分组。因为重复的数字,数值都是一样的,所以一定会分到同一组!
此时的难点在于,对两个不同数字的分组。
此时我们要找到一个操作,让两个数字进行这个操作后,分为两组。
我们最容易想到的就是 & 1 操作, 当我们对奇偶分组时,容易地想到 & 1,即用于判断最后一位二进制是否为 1。来辨别奇偶。
你看,通过 & 运算来判断一位数字不同即可分为两组,那么我们随便两个不同的数字至少也有一位不同吧!
我们只需要找出那位不同的数字mask,即可完成分组( & mask )操作。
由于两个数异或的结果就是两个数数位不同结果的直观表现,所以我们可以通过异或后的结果去找 mask!
所有的可行 mask 个数,都与异或后1的位数有关。
class Solution {
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {
//用于将所有的数异或起来
int k = 0;
for(int num: nums) {
k ^= num;
}
//获得k中最低位的1
int mask = 1;
//mask = k & (-k) 这种方法也可以得到mask,具体原因百度 哈哈哈哈哈
while((k & mask) == 0) {
mask <<= 1;
}
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
for(int num: nums) {
if((num & mask) == 0) {
a ^= num;
} else {
b ^= num;
}
}
return new int[]{a, b};
}
}
47、剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
归并排序,刷题就是为了弥补不会的知识,本题就归并排序的具体实现。
public class Solution {
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if (len < 2) {
return 0;
}
int[] copy = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
copy[i] = nums[i];
}
int[] temp = new int[len];
return reversePairs(copy, 0, len - 1, temp);
}
/**
* nums[left..right] 计算逆序对个数并且排序
*
* @param nums
* @param left
* @param right
* @param temp
* @return
*/
private int reversePairs(int[] nums, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left == right) {
return 0;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
int leftPairs = reversePairs(nums, left, mid, temp);
int rightPairs = reversePairs(nums, mid + 1, right, temp);
if (nums[mid] <= nums[mid + 1]) {
return leftPairs + rightPairs;
}
int crossPairs = mergeAndCount(nums, left, mid, right, temp);
return leftPairs + rightPairs + crossPairs;
}
/**
* nums[left..mid] 有序,nums[mid + 1..right] 有序
*
* @param nums
* @param left
* @param mid
* @param right
* @param temp
* @return
*/
private int mergeAndCount(int[] nums, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
temp[i] = nums[i];
}
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int count = 0;
for (int k = left; k <= right; k++) {
if (i == mid + 1) {
nums[k] = temp[j];
j++;
} else if (j == right + 1) {
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
} else if (temp[i] <= temp[j]) {
nums[k] = temp[i];
i++;
} else {
nums[k] = temp[j];
j++;
count += (mid - i + 1);
}
}
return count;
}
}
48、剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] num=new int[nums.length];
int i=0;
for(;i<nums.length;i++){
num[nums[i]]++;
if(num[nums[i]]==2)break;
}
return nums[i];
}
}如果没有重复数字,那么正常排序后,数字i应该在下标为i的位置,所以思路是重头扫描数组,遇到下标为i的数字如果不是i的话,(假设为m),那么我们就拿与下标m的数字交换。在交换过程中,如果有重复的数字发生,那么终止返回ture
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
while (nums[i]!=i){
if(nums[i]==nums[nums[i]]){
return nums[i];
}
temp=nums[i];
nums[i]=nums[temp];
nums[temp]=temp;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
49、剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
最基础的动态规划
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n==0)return 0;
if(n==1)return 1;
int[] arr=new int[n+1];
arr[0]=0;
arr[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=(arr[i-1]+arr[i-2])%1000000007;
}
return arr[n];
}
}50、剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
for(int i=1;i<numbers.length;i++){
if(numbers[i]<numbers[i-1])return numbers[i];
}
return numbers[0];
}
}二分查找
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if (numbers[m] > numbers[j]) i = m + 1;
else if (numbers[m] < numbers[j]) j = m;
else j--;
}
return numbers[i];
}
}
51、剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(Character c : s.toCharArray())
{
if(c == ' ') res.append("%20");
else res.append(c);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
52、剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
int[] num =new int[k];
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
num[i]=arr[i];
}
return num;
}
}快速排序
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
// 最后一个参数表示我们要找的是下标为k-1的数
return quickSearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k - 1);
}
private int[] quickSearch(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int k) {
// 每快排切分1次,找到排序后下标为j的元素,如果j恰好等于k就返回j以及j左边所有的数;
int j = partition(nums, lo, hi);
if (j == k) {
return Arrays.copyOf(nums, j + 1);
}
// 否则根据下标j与k的大小关系来决定继续切分左段还是右段。
return j > k? quickSearch(nums, lo, j - 1, k): quickSearch(nums, j + 1, hi, k);
}
// 快排切分,返回下标j,使得比nums[j]小的数都在j的左边,比nums[j]大的数都在j的右边。
private int partition(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
int v = nums[lo];
int i = lo, j = hi + 1;
while (true) {
while (++i <= hi && nums[i] < v);
while (--j >= lo && nums[j] > v);
if (i >= j) {
break;
}
int t = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = t;
}
nums[lo] = nums[j];
nums[j] = v;
return j;
}
}
堆排序
// 保持堆的大小为K,然后遍历数组中的数字,遍历的时候做如下判断:
// 1. 若目前堆的大小小于K,将当前数字放入堆中。
// 2. 否则判断当前数字与大根堆堆顶元素的大小关系,如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶还大,这个数就直接跳过;
// 反之如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶小,先poll掉堆顶,再将该数字放入堆中。
class Solution {
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
// 默认是小根堆,实现大根堆需要重写一下比较器。
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v2 - v1);
for (int num: arr) {
if (pq.size() < k) {
pq.offer(num);
} else if (num < pq.peek()) {
pq.poll();
pq.offer(num);
}
}
// 返回堆中的元素
int[] res = new int[pq.size()];
int idx = 0;
for(int num: pq) {
res[idx++] = num;
}
return res;
}
}
53、剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if(s.length()==0)return 0;
char[] num=s.toCharArray();
int length=0;
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++){
HashSet set=new HashSet();
for(int j=i;j<num.length;j++){
if(!set.add(num[j]))break;
}
if (set.size()>length)length=set.size();
}
return length;
}
}滑动窗口
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
//这里 是不包含start的
int ans = 0, start = -1;
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length() ; i++){
char k = s.charAt(i);
if(map.containsKey(k)){
// 如果遇到重复字符,就要更新了!
int index = map.get(k);
if(index > start) start = index;
}
map.put(k, i);
ans = Math.max(ans, i - start);
}
return ans;
}
}
54、剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
class Solution {
int m,n,k;
boolean[][] visited;
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
this.m=m;
this.n=n;
this.k=k;
visited=new boolean[m][n];
return dfs(0,0);
}
public int dfs(int i, int j){
if(i>=m||j>=n||visited[i][j]||count(i,j)>k){
return 0;
}
visited[i][j]=true;
return 1+dfs(i+1,j)+dfs(i,j+1);
}
public int count(int i,int j){
int sum=0;
while(i!=0){
sum+=i%10;
i/=10;
}
while(j!=0){
sum+=j%10;
j/=10;
}
return sum;
}
}55、剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组
class Solution {
public int[] constructArr(int[] a) {
if(a.length == 0) return new int[0];
int[] b = new int[a.length];
b[0] = 1;
int tmp = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
b[i] = b[i - 1] * a[i - 1];
}
for(int i = a.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
tmp *= a[i + 1];
b[i] *= tmp;
}
return b;
}
}
56、剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer>stack =new Stack<>();
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<pushed.length;i++){
stack.push(pushed[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()==popped[j]){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}57、剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
return (A != null && B != null) && (recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
boolean recur(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if(B == null) return true;
if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return recur(A.left, B.left) && recur(A.right, B.right);
}
}
58、剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配
妙啊
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int n=s.length();
int m=p.length();
boolean[][] f = new boolean[n+1][m+1];
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<=m;j++){
//分为空正则表达式和非空正则表达式俩种
if(j==0){
f[i][j]=i==0;
}
else {
//非空正则分为两种情况*和非*
if(p.charAt(j-1)!='*'){
if(i > 0 && (s.charAt(i-1) == p.charAt(j-1) || p.charAt(j-1) =='.')){
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-1];
}
}
else{
//碰到*,分为看和不看两种情况
//不看
if(j>=2){
f[i][j] |= f[i][j-2];
//看
if( i>=1 && (s.charAt(i-1) == p.charAt(j-2) || p.charAt(j-2)=='.')){
f[i][j] |= f[i-1][j];
}
}
}
}
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
}59、剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
class Solution {
public int sumNums(int n) {
boolean flag = n > 0 && (n += sumNums(n - 1)) > 0;
return n;
}
}
class Solution {
public int sumNums(int n) {
return (int) (Math.pow(n, 2) + n) >> 1;
}
}60、剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if (nums == null || k < 1 || nums.length < k) {
return new int[0];
}
int index=0;
int[] res=new int[nums.length-k+1];
LinkedList<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
while(!queue.isEmpty()&&nums[queue.peekLast()]<=nums[i]){
queue.pollLast();
}
queue.add(i);
if(queue.peekFirst()==(i-k)){
queue.pollFirst();
}
if(i>=(k-1)){
res[index++]=nums[queue.peekFirst()];
}
}
return res;
}
}剑指offer刷题的更多相关文章
- 剑指offer刷题(Tree)
开篇 二刷剑指offer了,本来用Tyora记的笔记,发现字数到四万了就变得好卡o(╥﹏╥)o,刚好开始写博客,就转过来吧,记下来子自己看.不废话,开刷... JZ26. 树的子结构 输入两棵二叉树A ...
- 牛客网剑指offer刷题总结
二维数组中的查找: 题目描述:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. 两 ...
- LeetCode剑指Offer刷题总结(一)
LeetCode过程中值得反思的细节 以下题号均指LeetCode剑指offer题库中的题号 本文章将每周定期更新,当内容达到10题左右时将会开下一节. 二维数组越界问题04 public stati ...
- 剑指offer ------ 刷题总结
面试题3 -- 搜索二维矩阵 写出一个高效的算法来搜索 m × n矩阵中的值. 这个矩阵具有以下特性: 1. 每行中的整数从左到右是排序的. 2. 每行的第一个数大于上一行的最后一个整数. publi ...
- 剑指offer刷题记录
目录 二维数组中的查找 替换空格 从尾到头打印链表 反转链表 重建二叉树 用两个栈实现队列 旋转数组的最小数字 斐波拉切数列 跳台阶 变态跳台阶 矩形覆盖 二进制中1的个数 数值的整次方 链表中倒数第 ...
- 剑指offer刷题笔记
删除链表中重复的结点:较难 在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针. 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4- ...
- 剑指offer刷题总结
★ 二维数组的查找 在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否 ...
- 剑指offer刷题(算法类_2)
排序 035-数组中的逆序对(归并排序) 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 029-最小的K个数(堆排序) 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 029-最小的K个数(快速排序) 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 位 ...
- 剑指offer刷题(算法类_1)
斐波那契数列 007-斐波拉契数列 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 008-跳台阶 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 009-变态跳台阶 题目描述 题解 代码 复杂度 010-矩形覆盖 题目描述 题解 代码 ...
随机推荐
- 调整是为了更好的上涨,牛市下的SPC空投来了!
2021年刚过没几天,比特币就开启了牛市的旅程,BTC涨到4万美元,ETH涨到1300多美元,BGV也涨到了621.05美元,牛市已然来袭. 虽然从近两日,比特币带领着主流币进行了一波调整,但是只涨不 ...
- spring boot用ModelAndView向Thymeleaf模板传参数
最近在调试一个Spring Boot向Thymeleaf模板传参数的例子,但踩了很多坑,这里就把详细过程记录下来,以供大家参考. 先说下,这里遇到哪些坑呢? 1 我用的是IDEA社区版,这不支持JSP ...
- Elasticsearch 及其套件的安装上手
前言 本文主要讲解Elasticsearch及其套件Kibana.Logstash的安装及启动,还讲解如何导入数据用于后续的实验. 说明:Elasticsearch是基于Java开发的,所以如果是下载 ...
- 从微信小程序到鸿蒙js开发【12】——storage缓存&自动登录
鸿蒙入门指南,小白速来!从萌新到高手,怎样快速掌握鸿蒙开发?[课程入口] 正文: 在应用开发时,我们常需要将一些数据缓存到本地,以提升用户体验.比如在一个电商的app中,如果希望用户登录成功后,下次打 ...
- js实现复制粘贴
项目中经常会遇到点击按钮复制订单号.订单id等内容到粘贴板中的需求.可是通常我们都是用Ctrl + c或右击复制的,别操心,js也是有复制命令的,那就是document.execCommand('co ...
- JUnit5学习之四:按条件执行
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- java与freemarker遍历map
一.java遍历MAP /** * 1.把key放到一个集合里,遍历key值同时根据key得到值 (推荐) */ Set set =map.keySet(); Iterator it=set.iter ...
- SpringMVC异步处理的 5 种方式
作者:丁仪 来源:https://chengxuzhixin.com/blog/post/SpringMVC-yi-bu-chu-li-de-5-zhong-fang-shi.html 前段时间研究了 ...
- springboot源码解析-管中窥豹系列之自动装配(九)
一.前言 Springboot源码解析是一件大工程,逐行逐句的去研究代码,会很枯燥,也不容易坚持下去. 我们不追求大而全,而是试着每次去研究一个小知识点,最终聚沙成塔,这就是我们的springboot ...
- 企业安全_检测SQL注入的一些方式探讨
目录 寻找SQL注入点的 way MySQL Inject 入门案例 自动化审计的尝试之旅 人工审计才能保证精度 寻找SQL注入点的 way 在企业中有如下几种方式可以选择: 自动化 - 白盒基于源码 ...

