(数据科学学习手札119)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——多页面应用
本文示例代码已上传至我的
Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes
1 简介
这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web应用开发的第十六期,在过往所有的教程及案例中,我们所搭建的Dash应用的访问地址都是单一的,是个单页面应用,即我们所有的功能都排布在同一个url之下。
而随着我们所编写的Dash应用功能的日趋健全和复杂,单一url的内容组织方式无法再很好的满足需求,也不利于构建逻辑清晰的web应用。
因此我们需要在Dash应用中引入路由的相关功能,即在当前应用主域名下,根据不同的url来渲染出具有不同内容的页面,就像我们日常使用的绝大多数网站那样。
而今天的教程,我们就将一起学习在Dash中编写多url应用并进行路由控制的常用方法。
 图1
图1
2 编写多页面Dash应用
2.1 Location()的基础使用
要想在Dash中实现url路由功能,首先我们需要捕获到浏览器中地址栏对应的url是什么,这在Dash中可以通过在app.layout中构建一个可以持续监听当前Dash应用url信息的部件来实现。
我们使用官方依赖库dash_core_components中的Location()部件来实现上述功能,它的核心参数或属性有href、pathname、search和hash,让我们通过下面的例子来直观的了解它们各自记录了地址栏url中的哪些信息:
app1.py
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dcc.Location(id='url'),
html.Ul(id='output-url')
],
style={
'paddingTop': '100px'
}
)
@app.callback(
Output('output-url', 'children'),
[Input('url', 'href'),
Input('url', 'pathname'),
Input('url', 'search'),
Input('url', 'hash')]
)
def show_location(href, pathname, search, hash):
return (
html.Li(f'当前href为:{href}'),
html.Li(f'当前pathname为:{pathname}'),
html.Li(f'当前search为:{search}'),
html.Li(f'当前hash为:{hash}'),
)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
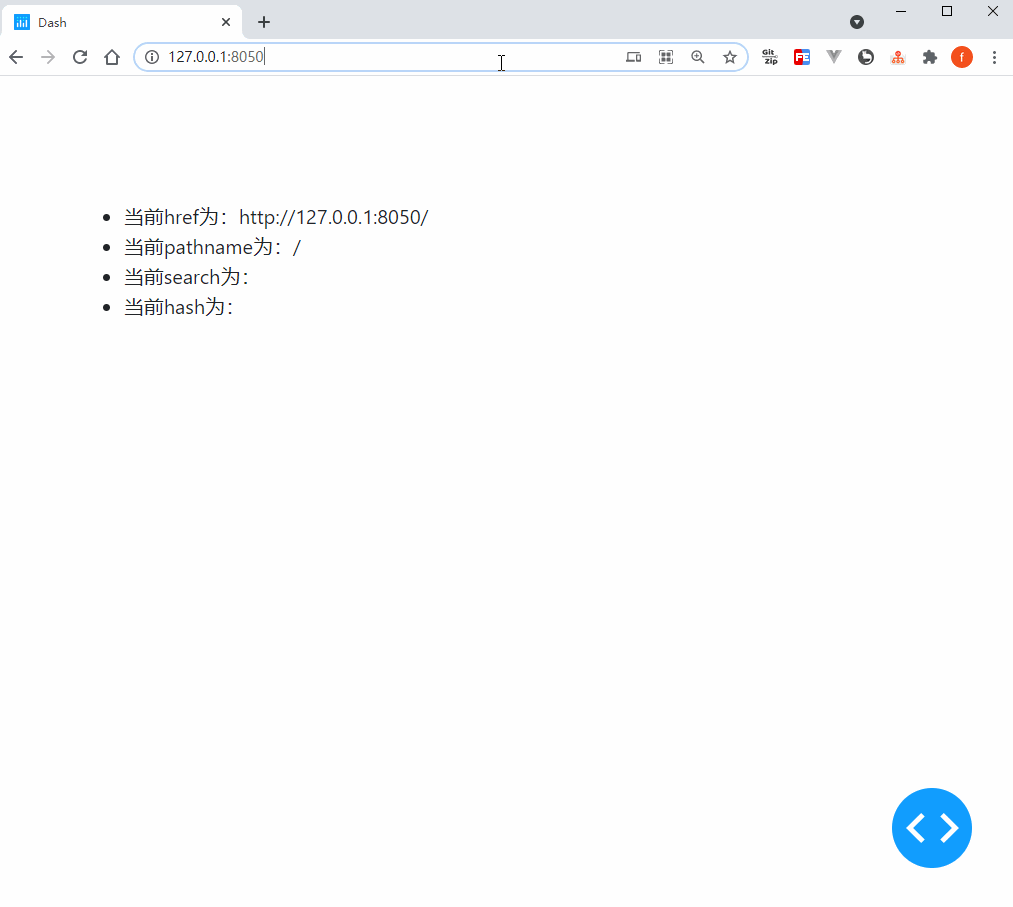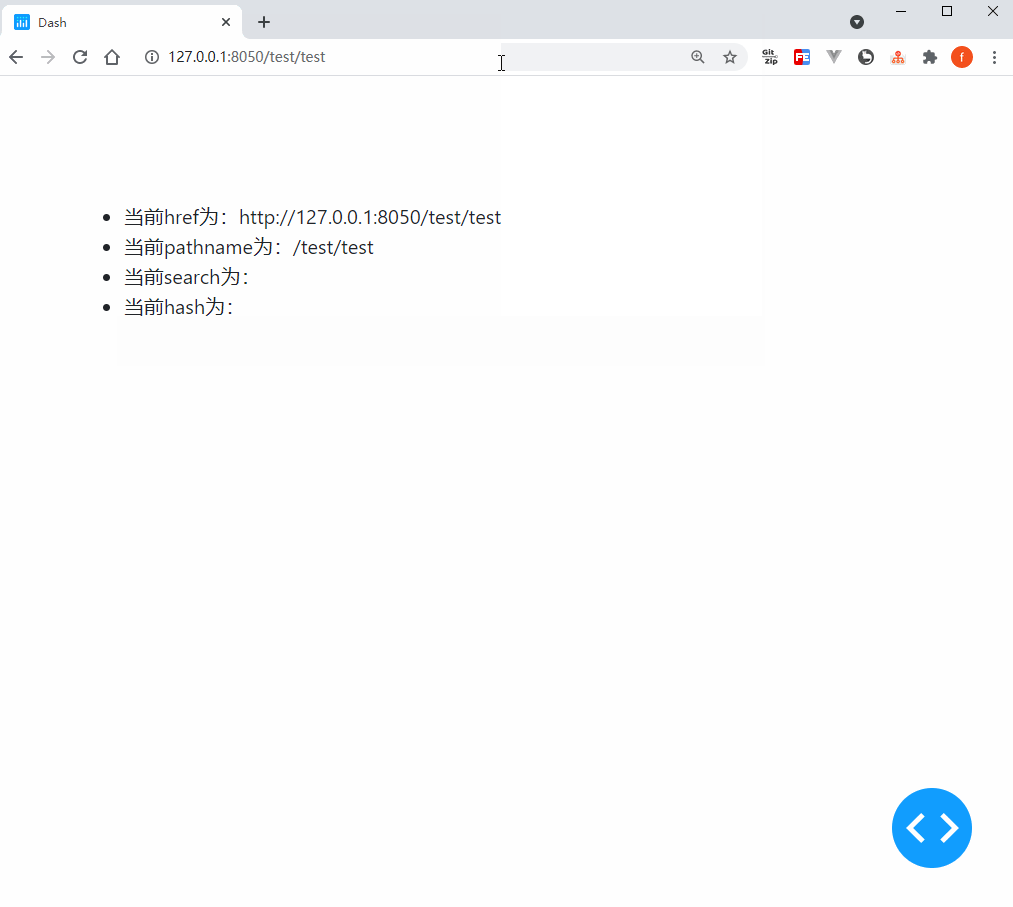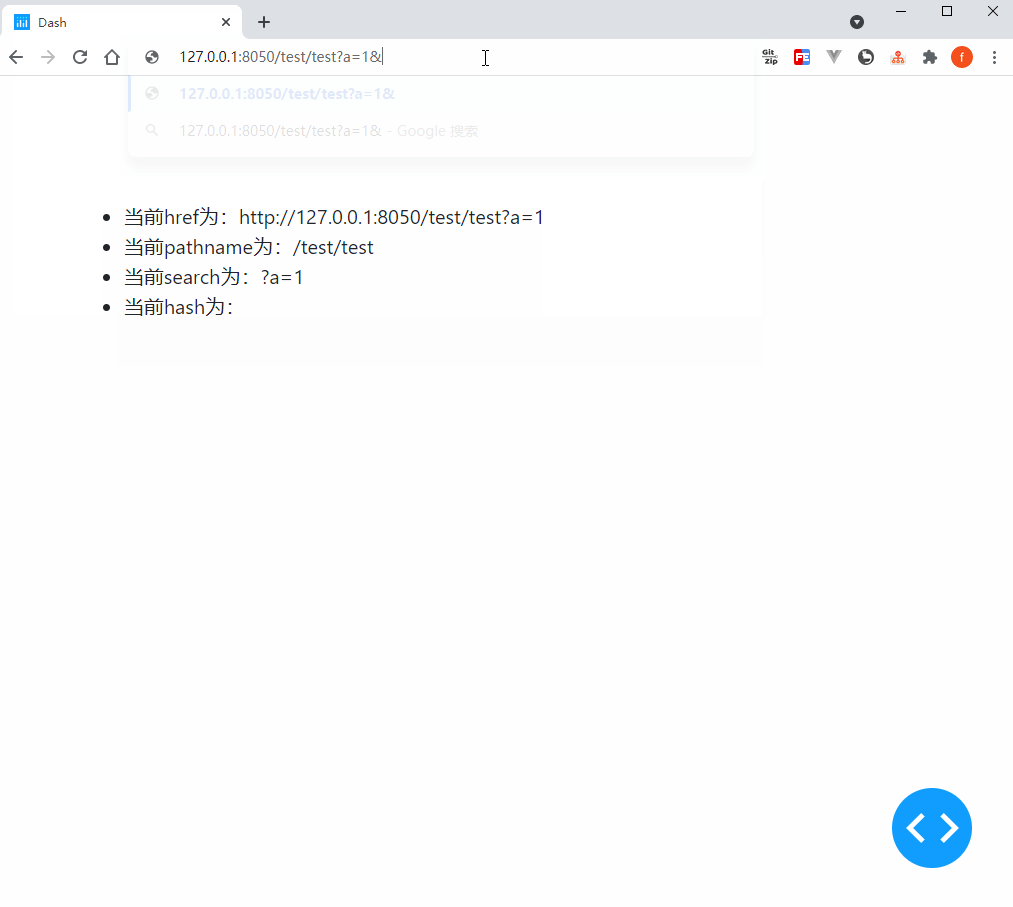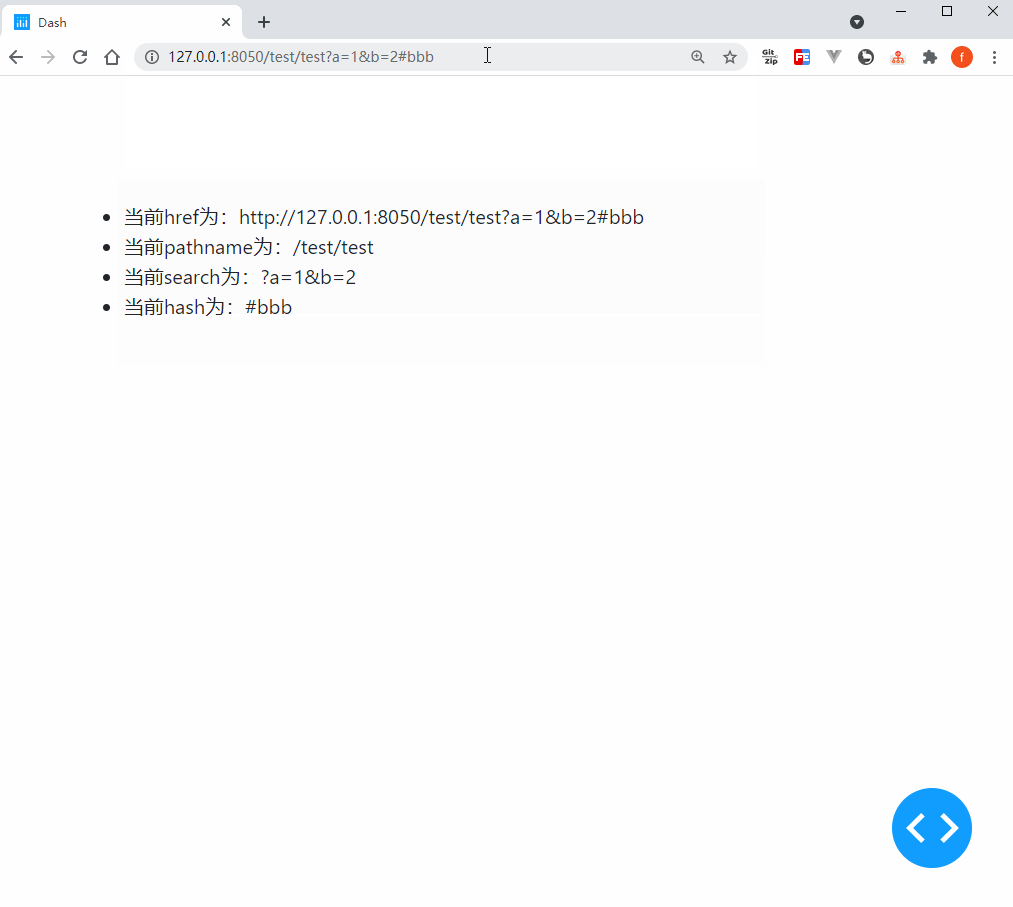 图2
图2
因此在Dash中编写多url应用的核心策略是利用埋点Location()捕获到地址栏对应信息的变化,并以这些信息作为回调函数的输入,来输出相应的页面内容变化,让我们从下面这个简单的例子中get上述这一套流程的运作方式:
app2.py
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dcc.Location(id='url', refresh=False),
dbc.Row(
[
dbc.Col(
[
html.A('页面A', href='/pageA'),
html.Br(),
html.A('页面B', href='/pageB'),
html.Br(),
html.A('页面C', href='/pageC'),
],
width=2,
style={
'backgroundColor': '#eeeeee'
}
),
dbc.Col(
html.H3(id='render-page-content'),
width=10
)
]
)
],
style={
'paddingTop': '20px',
'height': '100vh',
'weight': '100vw'
}
)
@app.callback(
Output('render-page-content', 'children'),
Input('url', 'pathname')
)
def render_page_content(pathname):
if pathname == '/':
return '欢迎来到首页'
elif pathname == '/pageA':
return '欢迎来到页面A'
elif pathname == '/pageB':
return '欢迎来到页面B'
elif pathname == '/pageC':
return '欢迎来到页面C'
else:
return '当前页面不存在!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
 图3
图3
2.2 利用Location()实现页面重定向
在上一小节我们对dcc.Location()的基础用法进行了介绍,而它的功能可不止监听url变化这么简单,我们还可以利用它在Dash中实现重定向,使用方式简单一句话描述就是将Location()作为对应回调的输出(记住一定要定义id属性),这样地址栏url会在回调完成后对应跳转。
让我们通过下面这个简单的例子来get这个技巧:
app3.py
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
html.Div(id='redirect-url-container'),
dbc.Button('跳转到页面A', id='jump-to-pageA', style={'marginRight': '10px'}),
dbc.Button('跳转到页面B', id='jump-to-pageB'),
],
style={
'paddingTop': '100px'
}
)
@app.callback(
Output('redirect-url-container', 'children'),
[Input('jump-to-pageA', 'n_clicks'),
Input('jump-to-pageB', 'n_clicks')],
)
def jump_to_target(a_n_clicks, b_n_clicks):
ctx = dash.callback_context
if ctx.triggered[0]['prop_id'] == 'jump-to-pageA.n_clicks':
return dcc.Location(id='redirect-url', href='/pageA')
elif ctx.triggered[0]['prop_id'] == 'jump-to-pageB.n_clicks':
return dcc.Location(id='redirect-url', href='/pageB')
return dash.no_update
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
 图4
图4
2.3 用Link()实现“无缝”页面切换
你应该注意到了,在Dash中利用Location()和普通的A()部件实现跳转时,页面在跳转后会整体刷新,这会一定程度上破坏整个web应用的整体体验。
而dash_core_components中的Link()部件则是很好的替代,它的基础属性与A()无异,但额外的refresh参数默认为False,会在点击后进行Dash应用内跳转时无缝切换,页面不会整体刷新:
app4.py
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
app = dash.Dash(__name__)
app.layout = dbc.Container(
[
dcc.Location(id='url'),
dcc.Link('页面A', href='/pageA', refresh=True),
html.Br(),
dcc.Link('页面B', href='/pageB'),
html.Hr(),
html.H1(id='render-page-content')
],
style={
'paddingTop': '100px'
}
)
@app.callback(
Output('render-page-content', 'children'),
Input('url', 'pathname')
)
def render_page_content(pathname):
if pathname == '/':
return '欢迎来到首页'
elif pathname == '/pageA':
return '欢迎来到页面A'
elif pathname == '/pageB':
return '欢迎来到页面B'
elif pathname == '/pageC':
return '欢迎来到页面C'
else:
return '当前页面不存在!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
 图5
图5
类似的功能还有dash_bootstrap_components中的NavLink(),用法与Link()相似,这里就不再赘述。
3 动手开发个人博客网站
掌握了今天的知识之后,我们来用Dash开发一个简单的个人博客网站,思路是在Location()监听url变化的前提下,后台利用网络爬虫从我的博客园Dash主题下爬取相应的网页内容,并根据用户访问来渲染出对应的文章:
app5.py
import dash
import dash_core_components as dcc
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_bootstrap_components as dbc
import dash_dangerously_set_inner_html # 用于直接渲染html源码字符串
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
import re
from html import unescape
import requests
from lxml import etree
app = dash.Dash(__name__, suppress_callback_exceptions=True)
app.layout = html.Div(
dbc.Spinner(
dbc.Container(
[
dcc.Location(id='url'),
html.Div(
id='page-content'
)
],
style={
'paddingTop': '30px',
'paddingBottom': '50px',
'borderRadius': '10px',
'boxShadow': 'rgb(0 0 0 / 20%) 0px 13px 30px, rgb(255 255 255 / 80%) 0px -13px 30px'
}
),
fullscreen=True
)
)
@app.callback(
Output('article-links', 'children'),
Input('url', 'pathname')
)
def render_article_links(pathname):
response = requests.get('https://www.cnblogs.com/feffery/tag/Dash/',
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.114 Safari/537.36'
})
tree = etree.HTML(response.text)
posts = [
(href, title.strip())
for href, title in zip(
tree.xpath("//div[@class='postTitl2']/a/@href"),
tree.xpath("//div[@class='postTitl2']/a/span/text()")
)
]
return [
html.Li(
dcc.Link(title, href=f'/article-{href.split("/")[-1]}', target='_blank')
)
for href, title in posts
]
@app.callback(
Output('page-content', 'children'),
Input('url', 'pathname')
)
def render_article_content(pathname):
if pathname == '/':
return [
html.H2('博客列表:'),
html.Div(
id='article-links',
style={
'width': '100%'
}
)
]
elif pathname.startswith('/article-'):
response = requests.get('https://www.cnblogs.com/feffery/p/%s.html' % re.findall('\d+', pathname)[0])
tree = etree.HTML(response.text)
return (
html.H3(tree.xpath("//title/text()")[0].split(' - ')[0]),
html.Em('作者:费弗里'),
dash_dangerously_set_inner_html.DangerouslySetInnerHTML(
unescape(etree.tostring(tree.xpath('//div[@id="cnblogs_post_body"]')[0]).decode())
)
)
return dash.no_update
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run_server(debug=True)
 图6
图6
按照类似的思路,你可以随心所欲地开发自己的多页面应用,进一步丰富完善你的Dash应用功能。
以上就是本文的全部内容,欢迎在评论区发表你的意见和想法。
(数据科学学习手札119)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——多页面应用的更多相关文章
- (数据科学学习手札102)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——基础概念篇
本文示例代码与数据已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的新系列教程Python+Dash快 ...
- (数据科学学习手札108)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——静态部件篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札109)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——静态部件篇(中)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札112)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——表单控件篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札115)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——交互表格篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札116)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——交互表格篇(中)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札117)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——交互表格篇(下)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札118)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——特殊部件篇
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- (数据科学学习手札120)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——整合数据库
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
随机推荐
- Python网络编程相关的库与爬虫基础
PythonWeb编程 ①相关的库:urlib.urlib2.requests python中自带urlib和urlib2,他们主要使用函数如下: urllib: urlib.urlopen() ur ...
- Go的包
目录 go的包 一.包的创建规则 二.包的导入规则 三.包的函数调用 go的包 一.包的创建规则 一个包就是一个文件夹. 同一个包(文件夹)下,所有go文件都只能用同一个package,也就是每个文件 ...
- ubuntu系统共享桌面的使用和配置
内容转载自我的博客 目录 1. ubuntu共享桌面 2. 局域网登录远程桌面 2.1 ubuntu使用remmina登录远程桌面 2.2 在windows登录远程桌面 2.3 Android使用RD ...
- 【转+】以C++为核心语言的高频交易系统的讨论
[前言]高频交易是量化交易的核心.主要分两个方向:计算机技术和交易策略.策略各有不同,一般都是数据分析的专家或者金融,机器学习从业者.在计算机技术方面,一个是交易平台的性能,二者是硬件的性能,延时的多 ...
- Wayland architecture
Introduction Motivation Most Linux and Unix-based systems rely on the X Window System (or simply X) ...
- Kubernetes Container lifecycle hooks
简介 在kubernetes中,容器hooks旨在解决服务进程启动与停止时的一些优雅操作需求.比如说进程停止时要给进程一个清理数据的时间,保证服务的请求正常结束,而不是强行中断服务的运行,这样在生产环 ...
- 剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表 + 中序遍历 + 二叉排序树
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表 Offer_36 题目描述 题解分析 本题考查的是二叉树的中序遍历以及二叉排序树的特征(二叉排序树的中序遍历序列是升序序列) 利用排序二叉树中序遍历的性 ...
- 非对称加密--密钥交换算法DHCoder
/* * 密钥交换算法,即非对称加密算法 * */ public class DHCoder { //非对称加密算法 public static final Str ...
- java 面试经典题
面向对象编程(OOP) Java是一个支持并发.基于类和面向对象的计算机编程语言.下面列出了面向对象软件开发的优点: 代码开发模块化,更易维护和修改. 代码复用. 增强代码的可靠性和灵活性. 增加代码 ...
- 爬虫-使用BeautifulSoup4(bs4)解析html数据
Beautiful Soup 是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是如何解析和提取 HTML/XML 数据. 一.安装 sudo pip3 install beautifulsoup4 二.使 ...
