Java自定义线程池-记录每个线程执行耗时
ThreadPoolExecutor是可扩展的,其提供了几个可在子类化中改写的方法,如下:
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) { }
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) { }
protected void terminated() { }
现基于此,完成一个统计每个线程执行耗时,并计算平均耗时的 自定义线程池样例。通过 beforeExecute、afterExecute、terminated 方法来添加日志记录和统计信息收集。为了测量任务的运行时间,beforeExecute必须记录开始时间并把它保存到一个ThreadLocal变量中,然后由afterExecute来读取。同时,使用两个 AtomicLong变量,分别用以记录已处理的任务数和总的处理时间,并通过terminated来输出包含平均任务时间的日志消息。
自定义线程池代码如下:
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.logging.Logger; /**
* 自定义线程池
*/
public class TimingThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor { private final ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>();
private final Logger log = Logger.getLogger("TimingThreadPool");
private final AtomicLong numTasks = new AtomicLong();
private final AtomicLong totalTime = new AtomicLong(); public TimingThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
} @Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
log.info(String.format("Thread %s: start %s",t,r));
startTime.set(System.nanoTime());
} @Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
try {
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long taskTime = endTime - startTime.get();
numTasks.incrementAndGet();
totalTime.addAndGet(taskTime);
log.info(String.format("Thread %s: end %s, time=%dns",t,r,taskTime)); } finally {
super.afterExecute(r,t);
}
} @Override
protected void terminated() {
try {
log.info(String.format("Terminated: avg time=%dns",totalTime.get() / numTasks.get()));
} finally {
super.terminated();
}
}
}
测试执行效果代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /**
* 测试自定义线程池
*/
public class TestCustomThreadPool { public static void main(String[] args) { try {
TimingThreadPool threadPool = new TimingThreadPool(,,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); List<TestCallable> tasks = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
tasks.add(new TestCallable());
} List<Future<Long>> futures = threadPool.invokeAll(tasks);
for (Future<Long> future :
futures) {
System.out.print(" - "+future.get());
}
threadPool.shutdown(); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} } static class TestCallable implements Callable<java.lang.Long> { @Override
public Long call() throws Exception {
long total = ;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++) {
long now = getRandom();
total += now;
}
Thread.sleep(total);
return total;
} public long getRandom () {
return Math.round(Math.random() * );
}
} }
执行结果:
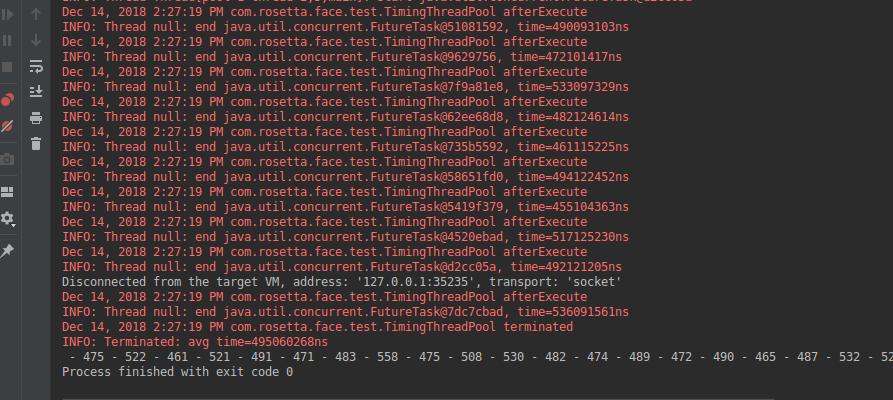
Java自定义线程池-记录每个线程执行耗时的更多相关文章
- Java如何判断线程池所有任务是否执行完毕
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class Tes ...
- Java 线程池记录
Java通过Executors提供四种线程池,分别为:newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程.newFixe ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”03之 线程池原理(二)
概要 在前面一章"Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”02之 线程池原理(一)"中介绍了线程池的数据结构,本章会通过分析线程池的源码,对线程池进行说明.内容包括:线程池示例参考代 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”04之 线程池原理(三)
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3509960.html 本章介绍线程池的生命周期.在"Java多线程系列--“基础篇”01之 基 ...
- Java线程池二:线程池原理
最近精读Netty源码,读到NioEventLoop部分的时候,发现对Java线程&线程池有些概念还有困惑, 所以深入总结一下 Java线程池一:线程基础 为什么需要使用线程池 Java线程映 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”01之 线程池架构
概要 前面分别介绍了"Java多线程基础"."JUC原子类"和"JUC锁".本章介绍JUC的最后一部分的内容——线程池.内容包括:线程池架构 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”02之 线程池原理(一)
概要 在上一章"Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”01之 线程池架构"中,我们了解了线程池的架构.线程池的实现类是ThreadPoolExecutor类.本章,我们通过分析Th ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”05之 线程池原理(四)
概要 本章介绍线程池的拒绝策略.内容包括:拒绝策略介绍拒绝策略对比和示例 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3512947.html 拒绝策略 ...
- 深入浅出 Java Concurrency (34): 线程池 part 7 线程池的实现及原理 (2)[转]
线程池任务执行流程 我们从一个API开始接触Executor是如何处理任务队列的. java.util.concurrent.Executor.execute(Runnable) Executes t ...
随机推荐
- 几种事务的隔离级别,InnoDB如何实现?
事务ACID特性,其中I代表隔离性(Isolation). 什么是事务的隔离性? 隔离性是指,多个用户的并发事务访问同一个数据库时,一个用户的事务不应该被其他用户的事务干扰,多个并发事务之间要相互隔离 ...
- .net core实践系列之SSO-同域实现
前言 SSO的系列还是以.Net Core作为实践例子与大家分享,SSO在Web方面复杂度分同域与跨域.本篇先分享同域的设计与实现,跨域将在下篇与大家分享. 如有需要调试demo的,可把SSO项目部署 ...
- OSGI嵌入jetty应用服务器
1.搭建osgi基础环境,参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/dyh004/p/10642383.html 2.引入jetty相关的依赖包 修改jetty启动端口 3.com.ksz ...
- 六、input框中的数字(金额)只能输入正整数
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入整数" onkeyup="this.value=this.value.re ...
- stl stack用法
栈后进先出 #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> #include<stack> ...
- C. Prefixes and Suffixes
链接 [https://codeforces.com/contest/1092/problem/C] 题意 给你某个字符串的长度n,再给你2*n-2个前缀或者后缀 让你判断那些是前缀那些是后缀 关键是 ...
- Telnet服务器和客户端请求处理
Telnet服务器和客户端请求处理 本文的控制台项目是根据SuperSocket官方Telnet示例代码进行调试的,官方示例代码:Telnet示例. 开始我的第一个Telnet控制台项目之旅: 创建控 ...
- semantic-ui 容器与栅格
semantic中可以指定one-sixteen这16个单词来指定网格column所占的长度.也就是说,在网页中,一行最多只有16个column,超过16个之后,自动移到下一行. 栅格可以使用i,di ...
- mysql 5.7:show_compatibility_56
show_compatibility_56 - rudy gao - CSDN博客 https://blog.csdn.net/rudygao/article/details/50403107 [SO ...
- npm5踩过的坑!
1. 版本问题导致环境问题 我们第一次npm install时是根据package.json来安装相关依赖的,但是它里面的版本不固定,因此默认会根据最高的版本来安装相关依赖,但是在npm5是根据pac ...
