转: OVER() 系列函数介绍
OVER(PARTITION BY)函数介绍
Oracle从8.1.6开始提供分析函数,分析函数用于计算基于组的某种聚合值,它和聚合函数的不同之处是:对于每个组返回多行,而聚合函数对于每个组只返回一行。
开窗函数指定了分析函数工作的数据窗口大小,这个数据窗口大小可能会随着行的变化而变化,举例如下:
1:over后的写法:
over(order by salary) 按照salary排序进行累计,order by是个默认的开窗函数
over(partition by deptno)按照部门分区
2:开窗的窗口范围:
over(order by salary range between 5 preceding and 5 following):窗口范围为当前行数据幅度减5加5后的范围内的。
举例:
--sum(s)over(order by s range between 2 preceding and 2 following) 表示加2或2的范围内的求和
select name,class,s, sum(s)over(order by s range between 2 preceding and 2 following) mm from t2
adf 3 45 45 --45加2减2即43到47,但是s在这个范围内只有45
asdf 3 55 55
cfe 2 74 74
3dd 3 78 158 --78在76到80范围内有78,80,求和得158
fda 1 80 158
gds 2 92 92
ffd 1 95 190
dss 1 95 190
ddd 3 99 198
gf 3 99 198
举例:
select name,class,s, sum(s)over(order by s rows between 2 preceding and 2 following) mm from t2
adf 3 45 174 (45+55+74=174)
asdf 3 55 252 (45+55+74+78=252)
cfe 2 74 332 (74+55+45+78+80=332)
3dd 3 78 379 (78+74+55+80+92=379)
fda 1 80 419
gds 2 92 440
ffd 1 95 461
dss 1 95 480
ddd 3 99 388
gf 3 99 293
3、与over函数结合的几个函数介绍
下面以班级成绩表t2来说明其应用
t2表信息如下:
cfe 2 74
dss 1 95
ffd 1 95
fda 1 80
gds 2 92
gf 3 99
ddd 3 99
adf 3 45
asdf 3 55
3dd 3 78
select * from
(
select name,class,s,rank()over(partition by class order by s desc) mm from t2
)
where mm=1;
得到的结果是:
dss 1 95 1
ffd 1 95 1
gds 2 92 1
gf 3 99 1
ddd 3 99 1
注意:
1.在求第一名成绩的时候,不能用row_number(),因为如果同班有两个并列第一,row_number()只返回一个结果;
select * from
(
select name,class,s,row_number()over(partition by class order by s desc) mm from t2
)
where mm=1;
1 95 1 --95有两名但是只显示一个
2 92 1
3 99 1 --99有两名但也只显示一个
2.rank()和dense_rank()可以将所有的都查找出来:
如上可以看到采用rank可以将并列第一名的都查找出来;
rank()和dense_rank()区别:
--rank()是跳跃排序,有两个第二名时接下来就是第四名;
select name,class,s,rank()over(partition by class order by s desc) mm from t2
dss 1 95 1
ffd 1 95 1
fda 1 80 3 --直接就跳到了第三
gds 2 92 1
cfe 2 74 2
gf 3 99 1
ddd 3 99 1
3dd 3 78 3
asdf 3 55 4
adf 3 45 5
--dense_rank()l是连续排序,有两个第二名时仍然跟着第三名
select name,class,s,dense_rank()over(partition by class order by s desc) mm from t2
dss 1 95 1
ffd 1 95 1
fda 1 80 2 --连续排序(仍为2)
gds 2 92 1
cfe 2 74 2
gf 3 99 1
ddd 3 99 1
3dd 3 78 2
asdf 3 55 3
adf 3 45 4
--sum()over()的使用
select name,class,s, sum(s)over(partition by class order by s desc) mm from t2 --根据班级进行分数求和
dss 1 95 190 --由于两个95都是第一名,所以累加时是两个第一名的相加
ffd 1 95 190
fda 1 80 270 --第一名加上第二名的
gds 2 92 92
cfe 2 74 166
gf 3 99 198
ddd 3 99 198
3dd 3 78 276
asdf 3 55 331
adf 3 45 376
first_value() over()和last_value() over()的使用
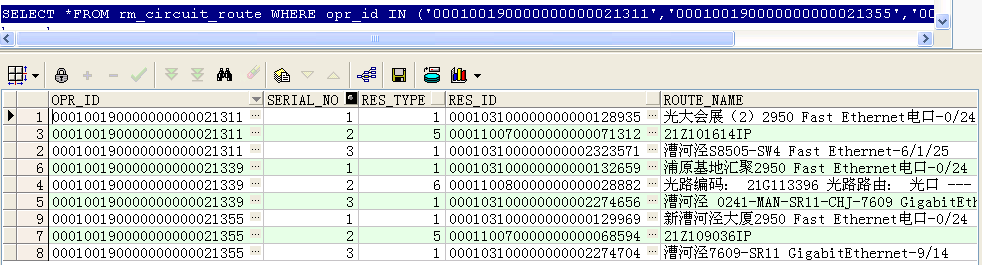
--找出这三条电路每条电路的第一条记录类型和最后一条记录类型
first_value(res_type) over(PARTITION BY opr_id ORDER BY res_type) low,
last_value(res_type) over(PARTITION BY opr_id ORDER BY res_type rows BETWEEN unbounded preceding AND unbounded following) high
FROM rm_circuit_route
WHERE opr_id IN ('000100190000000000021311','000100190000000000021355','000100190000000000021339')
ORDER BY opr_id;
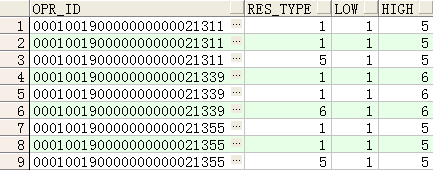
注:rows BETWEEN unbounded preceding AND unbounded following 的使用
--取last_value时不使用rows BETWEEN unbounded preceding AND unbounded following的结果
first_value(res_type) over(PARTITION BY opr_id ORDER BY res_type) low,
last_value(res_type) over(PARTITION BY opr_id ORDER BY res_type) high
FROM rm_circuit_route
WHERE opr_id IN ('000100190000000000021311','000100190000000000021355','000100190000000000021339')
ORDER BY opr_id;
如下图可以看到,如果不使用

数据如下:
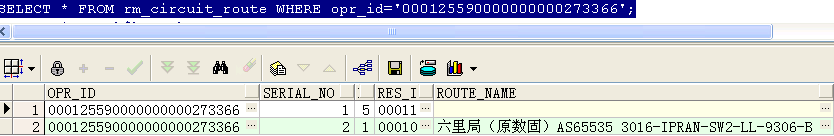
取出该电路的第一条记录,加上ignore nulls后,如果第一条是判断的那个字段是空的,则默认取下一条,结果如下所示:

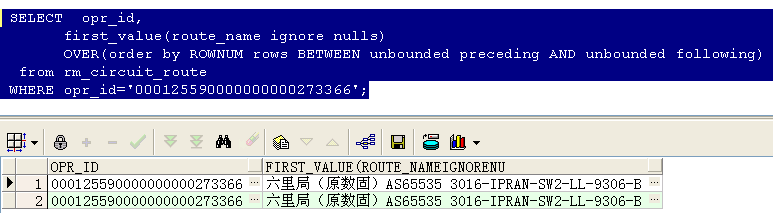
lag(expresstion,<offset>,<default>)
with a as
(select 1 id,'a' name from dual
union
select 2 id,'b' name from dual
union
select 3 id,'c' name from dual
union
select 4 id,'d' name from dual
union
select 5 id,'e' name from dual
)
select id,name,lag(id,1,'')over(order by name) from a;
--lead() over()函数用法(取出后N行数据)
lead(expresstion,<offset>,<default>)
with a as
(select 1 id,'a' name from dual
union
select 2 id,'b' name from dual
union
select 3 id,'c' name from dual
union
select 4 id,'d' name from dual
union
select 5 id,'e' name from dual
)
select id,name,lead(id,1,'')over(order by name) from a;
--ratio_to_report(a)函数用法 Ratio_to_report() 括号中就是分子,over() 括号中就是分母
with a as (select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 2 a from dual
union all
select 3 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 5 a from dual
)
select a, ratio_to_report(a)over(partition by a) b from a
order by a;
with a as (select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 2 a from dual
union all
select 3 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 5 a from dual
)
select a, ratio_to_report(a)over() b from a --分母缺省就是整个占比
order by a;
with a as (select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 1 a from dual
union all
select 2 a from dual
union all
select 3 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 4 a from dual
union all
select 5 a from dual
)
select a, ratio_to_report(a)over() b from a
group by a order by a;--分组后的占比
--转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/yyhxqx/p/4795296.html
转: OVER() 系列函数介绍的更多相关文章
- openssl之EVP系列之13---EVP_Open系列函数介绍
openssl之EVP系列之13---EVP_Open系列函数介绍 ---依据openssl doc/crypto/EVP_OpenInit.pod翻译和自己的理解写成 (作者:Dra ...
- openssl之EVP系列之12---EVP_Seal系列函数介绍
openssl之EVP系列之12---EVP_Seal系列函数介绍 ---依据openssl doc/crypto/EVP_SealInit.pod翻译和自己的理解写成 (作者:Dra ...
- openssl之EVP系列之11---EVP_Verify系列函数介绍
openssl之EVP系列之11---EVP_Verify系列函数介绍 ---依据openssl doc/crypto/EVP_VerifyInit.pod翻译和自己的理解写成 (作者 ...
- openssl之EVP系列之10---EVP_Sign系列函数介绍
openssl之EVP系列之10---EVP_Sign系列函数介绍 ---依据openssl doc/crypto/EVP_SignInit.pod翻译 (作者:DragonKing, ...
- Mem系列函数介绍及案例实现
昨天导师甩给我们一个项目案例,让我们自己去看一看熟悉一下项目内容,我看到了这个项目里面大量使用memset(sBuf,0,sizeof(sBuf));这一块内存填充的代码,于是回想起以前查过Mem ...
- Python开发【第三章】:Python函数介绍
一. 函数介绍 1.函数是什么? 在学习函数之前,一直遵循面向过程编程,即根据业务逻辑从上到下实现功能,其往往用一长段代码来实现指定功能,开发过程中最常见的操作就是粘贴复制,也就是将之前实现的代码块复 ...
- 从简单需求到OLAP的RANK系列函数
同事问了一个非常简单的问题,怎么取出每个partition里面另外一个列的最小值? create table t1 (int c1, int c2); 假如按照c2分区,0-10,10-20,20 ...
- linux tricks 之VA系列函数.
VA函数(variable argument function),参数个数可变函数,又称可变参数函数.C/C++编程中,系统提供给编程人员的va函数很少.*printf()/*scanf()系列函数, ...
- 原子操作 Interlocked系列函数
上一篇<多线程第一次亲密接触 CreateThread与_beginthreadex本质区别>中讲到一个多线程报数功能.为了描述方便和代码简洁起见,我们可以只输出最后的报数结果来观察程序是 ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode算法扫题系列19
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/9104677.html LeetCode算法第19题(难度:中等) 题目:给定一个链表,删 ...
- MVC 视图助手书写规范及注意点
@Html.TextBoxFor() 讲解(其他类似的 @Html.LabelFor 等)同理 @Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.SearchParams.Name ...
- webapi接口发布出错 OwinStartupAttribute
解决办法:在 webconfig 中 <appSettings> <add key="owin:AutomaticAppStartup" value=" ...
- Python网络编程Socket之协程
一.服务端 __author__ = "Jent Zhang" import socket import gevent from gevent import monkey monk ...
- sql server 行转列存储过程
if object_id('[P_GetPriceTableBuy]','P') is not null drop procedure P_GetPriceTableBuy SET ANSI_NULL ...
- SQL Server远程连接 provider: Named Pipes Provider, error: 40 解决方法
置SQLServer,允许远程连接 按照上面的文章一步步配置后,远程连接出现下面所示的报错(Navicat 和 SQL Server Management Studio) SQL Server Man ...
- Oracle高效分页查询(转)
page --没有order by的查询 -- 嵌套子查询,两次筛选(推荐使用) --SELECT * -- FROM (SELECT ROWNUM AS rowno, t.* -- FROM DON ...
- Retrofit2 原理解析
Retrofit是什么 官网介绍是A type-safe HTTP client for Android and Java,是一个 RESTful 的 HTTP 网络请求框架的封装,但网络请求不是Re ...
- Java io 入门
目录 前言 代码演练 字符流 FileReader,FileWriter: BufferedReader,BufferedWriter: InputStreamReader,OutputStreamW ...
- CDRAF之Service mesh
最近翻看一些网上的文章,偶然发现我们的CDRAF其实就是Service mesh的C++版本.不管从架构的理念上,或者功能的支持上面,基本完全符合.发几个简单的文章链接,等有时间的时候,再来详细描述. ...
