DevExpress MVVM<1>
DevExpress MVVM
概念
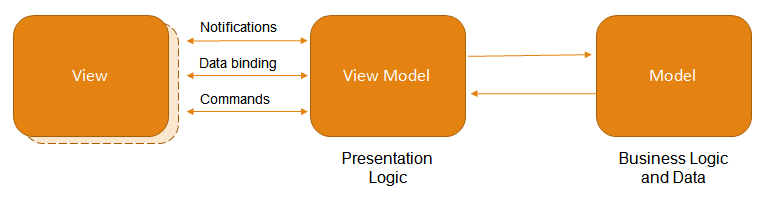
- 模型 -定义数据和您的业务逻辑。
- 视图 -指定UI,包括绑定到ViewModel中的属性和命令的所有可视元素(按钮,标签,编辑器等)。
- ViewModel-连接模型和视图。该层是View的抽象,它公开了用于将数据绑定到GUI元素并管理此数据的公共属性和命令。
约定和属性Conventions and Attributes
属性的语法正确,则可以将其视为可绑定的,这些语法规则称为约定。
约定:约定熟成的语法
可绑定属性
所有公共实现的虚拟属性都是可绑定的
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
也可以禁止
[Bindable(false)]
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
带有字段的属性默认不可进行数据绑定,可以使用BindableProperty属性显式标记此类属性,以仍然能够将其用于数据绑定。
using DevExpress.Mvvm.DataAnnotations;
//. . .
string test;
[BindableProperty]
public virtual string Test
{
get { return test; }
set { test = value; }
}
属性依赖
属性依赖项是一种方法,当其相关属性更改或将要更改时,该方法将自动执行。
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
protected void OnTestChanged() {
//do something
}
为了实现属性依赖,属性依赖的方法必须要命名为On<Related_Property_Name>Changing 或On<Related_Property_Name>Changed.
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
protected void OnTestChanged() {
//do something
}
On<Related_Property_Name>Changing 和On<Related_Property_Name>Changed方法有一个参数时有一些区别
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
protected void OnTestChanging(string newValue) {
//do something
}
protected void OnTestChanged(string oldValue) {
//do something
}
自定义change方法
[BindableProperty(OnPropertyChangingMethodName = "BeforeChange", OnPropertyChangedMethodName = "AfterChange")]
public virtual string Test { get; set; }
protected void BeforeChange() {
//. . .
}
protected void AfterChange() {
//. . .
}
命令Commands
事件处理程序转移到命令-封装特定操作的对象
在POCO ViewModels中void methods带有0或1个参数的都被视为命令
public void DoSomething(object p) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("The parameter passed to command is {0}.", p));
}
以 ...Command命名的方法会引发异常,需要在上面添加特定的特性,并通过设定Name来命名
using DevExpress.Mvvm.DataAnnotations;
[Command(Name="DoSomething")]
public void DoSomethingCommand(object p) {
//do something
}
对于每一个命令方法,框架都会生成相应的备用属性,这个属性会被默认命名为方法名Command通过Command特性的name可以为这个备用属性重命名。
[Command(Name = "MyMvvmCommand")]
public void DoSomething(object p) {
//do something
}
命令可以带有一个CanExecute的返回bool方法,用来指示方法是否可以被执行,同时该方法必须命名为Can<Related_Command_Name>.
//this command will be executed only if "p" equals 4
public void DoSomething(int p) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("The parameter passed to command is {0}.", p));
}
public bool CanDoSomething(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p;
}
可以通过Command特性的CanExecuteMethodName参数修改可以执行方法的名字
[Command(CanExecuteMethodName = "DoSomethingCriteria")]
public void DoSomething(int p) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("The parameter passed to command is {0}.", p));
}
public bool DoSomethingCriteria(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p;
}
当命令刚刚绑定到目标时,首先检查CanExecute子句(以获取目标的初始状态)。以后每次CanExecuteChanged事件通知命令目标有关命令状态更改时,都会重新计算此标准。在基础命令对象级别声明此事件。要从ViewModel级别发送此类通知,请按如下所示调用RaiseCanExecuteChanged扩展方法。
//a bindable property
public virtual bool IsModified { get; protected set; }
//a command
public void Save() {
//. . .
}
//a CanExecute condition
public bool CanSave() {
return IsModified;
}
//the OnChanged method calls the RaiseCanExecuteChanged method for the "Save" command
//this forces the command to update its CanExecute condition
public void OnIsModifiedChanged() {
this.RaiseCanExecuteChanged(x=>x.Save());
}
服务Service
用于为MVVM应用程序中的视图提供特定的UI感知功能的界面
为了解析服务,框架需要重写接口类型的虚拟属性,而且这些属性的名字都必须以Service结尾。
public virtual IMyNotificationService MyService {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
public virtual IMyNotificationService AnotherService {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
可以使用ServiceProperty特性来显示标注其他服务属性
using DevExpress.Mvvm.DataAnnotations;
//. . .
[ServiceProperty]
public virtual IMyNotificationService MyProvider {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
当框架覆盖服务属性时,它将生成相应的GetService <>扩展方法调用。该ServiceProperty特性可以为这个方法传递一个特殊的参数(例如,业务密钥)。
[ServiceProperty(Key="Service1")]
public virtual IMyNotificationService Service {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
[ServiceProperty(Key = "Service2")]
public virtual IMyNotificationService AnotherService {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
数据绑定 Data binding和通知Notifications
概念
若要将控件绑定到所需的数据,需要将相关的绑定添加到Control.DataBindings集合。例如有一个编辑器(textbox,editor)和viewmodel中的title属性进行绑定
editor.DataBindings.Add("EditValue", viewModel, "Title", true, DataSourceUpdateMode.OnPropertyChanged)
在运行时,必须可以更新UI元素的属性值,所以Viewmodel必须实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口.
public class LoginViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged {
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
string userNameCore;
public string UserName {
get { return userNameCore; }
set {
if(userNameCore == value) return;
this.userNameCore = value;
PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = PropertyChanged;
if(handler != null)
handler(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("UserName"));
}
}
}
基类
从DevExpress提供的BindableBase 和 ViewModelBase类中派生ViewModels,这两个类已经实现了INotifyPropertyChanged 接口。
public class SampleViewModel : BindableBase {
string titleValue;
public string Title {
get { return titleValue; }
set { SetProperty(ref titleValue, value, "Title");}
}
}
绑定属性是使用的字符串名字,这样会有一个问题就是如果重新命名了但是编译器不会报错,最好是使用POCO属性
POCO属性
DevExpress MVVM Framework可以将上述代码简化
public class SampleViewModel {
public virtual string Title { get; set; }
}
这个简化的属性称为POCO(Plain Old CLR Objects)属性,该类称为POCO类,DevExpress MVVM Framework可以识别此类自动将该属性扩展,在上面代码里,POCO类包含一个string Title可绑定属性属性。绑定:
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, "Title");
使用Fluent API实现相同的功能
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluentAPI.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, x => x.Title);
使用 POCO ViewModels时,不需要隐式创建实例,有两种方法,
- 使用DevExpress.Mvvm.POCO.ViewModelSource类的Create方法
//SampleViewModel.cs
public static SampleViewModel Create() {
return ViewModelSource.Create<SampleViewModel>();
}
//MainViewModel.cs
var sampleViewModel = SampleViewModel.Create();
- 使用MvvmContext的ViewModelType 属性,MvvmContext 组件创建POCO ViewModel,同时要确保ViewModel 引用了相关的接口
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(WindowsFormsApplication1.ViewModels.SampleViewModel);
POCO依赖
实例:实例化viewmodel,将两个文本编辑器绑定到Operand1和Operand2,并将一个结果label绑定到ResultText,并使其具有关联的On ... Changed方法。两个文本编辑器的MaskProperties.MaskType 属性必须设置成 MaskType.Numeric.
//View
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(MultViewModel);
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor1, e => e.EditValue, "Operand1");
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor2, e => e.EditValue, "Operand2");
mvvmContext.SetBinding(resultLabel, l => l.Text, "ResultText");
//ViewModel
public class MultViewModel {
public MultViewModel() {
UpdateResultText();
}
public virtual int Operand1 { get; set; }
public virtual int Operand2 { get; set; }
public virtual int Result { get; set; }
public virtual string ResultText { get; set; }
// OnChanged callback is created for the Operand1 property from this method.
protected void OnOperand1Changed() {
UpdateResult();
}
// OnChanged callback is created for the Operand2 property from this method.
protected void OnOperand2Changed() {
UpdateResult();
}
// OnChanged callback is created for the Result property from this method.
protected void OnResultChanged() {
UpdateResultText();
}
void UpdateResult() {
Result = Operand1 * Operand2;
}
void UpdateResultText() {
ResultText = string.Format("The result of operands multiplication is: {0:n0}", Result);
}
}
另一个相同实现使用BindableProperty特性来指向NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged方法
//View
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(SumViewModel);
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor1, e => e.EditValue, "Operand1");
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor2, e => e.EditValue, "Operand2");
mvvmContext.SetBinding(resultLabel, l => l.Text, "ResultText");
//ViewModel
public class SumViewModel {
[BindableProperty(OnPropertyChangedMethodName = "NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged")]
public virtual int Operand1 { get; set; }
[BindableProperty(OnPropertyChangedMethodName = "NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged")]
public virtual int Operand2 { get; set; }
// We raise change notifications for the Result and ResultText properties manually
public int Result {
get { return Operand1 + Operand2; }
}
public string ResultText {
get { return string.Format("The result of operands summarization is: {0:n0}", Result); }
}
protected void NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged() {
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.Result); // change-notification for the Result
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.ResultText); // change-notification for the ResultText
}
}
Meta-POCO绑定
POCO减轻了很多代码量,但重命名后会导致相关绑定失败。
使用Meta-POCO可以解决这个问题,
public virtual int Result { get; set; }
public virtual int Operand1 { get; set; }
public virtual int Operand2 { get; set; }
public string ResultText {
get { return string.Format("The result of operands summarization is: {0:n0}", Result); }
}
Meta-POCO声明:创建一个包含元数据的嵌套类,该嵌套类明确指定将哪些方法用作属性OnPropertyChanged回调的表达式。元数据类还可以使特定的POCO属性不可绑定。该嵌套类必须实现IMetadataProvider接口。下面的代码说明了ViewModel及其元数据声明。
[System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.MetadataType(typeof(Metadata))]
//ViewModel
public class SumViewModel_MetaPOCO {
public SumViewModel_MetaPOCO() {
}
protected void NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged() {
Result = Operand1 + Operand2;
}
// Metadata class for the SumViewModel_MetaPOCO
public class Metadata : IMetadataProvider<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO> {
void IMetadataProvider<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO>.BuildMetadata(MetadataBuilder<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO> builder) {
//Metadata
}
}
}
使用BuildMetadata方法,您可以遍历所有ViewModel属性并提供每个属性的行为。例如,在下面的代码中,Operand1和Operand2属性被视为引发OnPropertyChanged回调的可绑定属性。
public class Metadata : IMetadataProvider<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO> {
void IMetadataProvider<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO>.BuildMetadata(MetadataBuilder<SumViewModel_MetaPOCO> builder) {
builder.Property(x => x.Result)
.DoNotMakeBindable();
builder.Property(x => x.Operand1).
OnPropertyChangedCall(x => x.NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged());
builder.Property(x => x.Operand2).
OnPropertyChangedCall(x => x.NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged());
}
}
可以手动引发更改通知
protected void NotifyResultAndResultTextChanged() {
Result = Operand1 + Operand2;
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.Result); // change-notification for the Result
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.ResultText); // change-notification for the ResultText
}
集合绑定
需多数据类型的绑定是集合,ObservableCollection集合对象存储Test实例。该例子公开两个属性ID和Text,添加记录和删除记录两个公共方法。
public class Test {
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Text { get; set; }
}
public class TestViewModel {
public TestViewModel() {
Entities = new ObservableCollection<Test>();
}
public virtual Test SelectedEntity { get; set; }
public virtual ObservableCollection<Test> Entities { get; set; }
public void Add() {
Entities.Add(new Test() { ID = Entities.Count, Text = string.Format("Test {0}", Entities.Count) });
}
public void Remove(string title) {
Test element = Entities.Single<Test>(x => x.Text == title);
if (element != null) Entities.Remove(element);
}
}
利用MvvmContext组件的API,SetItemsSourceBinding 方法 可以绑定集合的每一个实例,并用实例填充tileControl的每一小块
mvvmContext1.ViewModelType = typeof(TestViewModel);
var fluentApi = mvvmContext1.OfType<TestViewModel>();
TileGroup group = tileControl1.Groups[0];
fluentApi.SetItemsSourceBinding(
group, //Target
g => g.Items, //Items Selector
x => x.Entities, //Source Selector
(tile, entity) => object.Equals(tile.Tag, entity), //Match Expression
entity => new TileItem() { Tag = entity }, //Create Expression
null, //Dispose Expression
(tile, entity) => ((TileItem)tile).Text = entity.Text); //Change Expression
此方法的参数说明
- Target - 应该填充的目标. A TileGroup in this example.
- Items Selector - 一个表达式负责在目标中找到项目集合. For this example, you need the TileGroup.Items collection.
- Source Selector - 一个表达式查找应用于填充目标的项目集合.
- Match Expression - 确定数据源项与源元素是否相同的表达式
- Create Expression - 当出现新的原纪录时,该表达式将创建一个新的目标元素。
- Dispose Expression - 除去目标元素的相关源集合记录后,处置目标元素的表达式
- Change Expression - 添加新的源集合记录或修改现有记录时,匹配表达式将查找与此记录相关的目标元素
var fluentApi = mvvmContext1.OfType<TestViewModel>();
fluentApi.ViewModel.Add();
fluentApi.ViewModel.Remove("Test 3");
UI触发器Trigger
有一个复选框和标签,当选中复选框的时候,复选框值绑定到IsChecked属性,然后触发OnIsCheckedChanged方法来更新绑定到Labeltext属性。这样的程序太复杂,触发器简化这一开发流程,当一个属性更改的时候触发器直接更新某个UI.
MvvmContext组件的SetTrigger设置触发器
//View
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(UIViewModel);
// Data binding for the IsActive property
mvvmContext.SetBinding<CheckEdit, UIViewModel, bool>(checkEdit, c => c.Checked, x => x.IsActive);
// Property-change Trigger for the IsActive property
mvvmContext.SetTrigger<UIViewModel, bool>(x => x.IsActive, (active) =>
{
label.Text = active ? "Active" : "Inactive";
});
//ViewModel
public class UIViewModel {
public virtual bool IsActive { get; set; }
}
这边的SetBinding方法的语法有所变化,是定义了ViewModel,并使用Lambda来获得此属性,可以避免重命名的错误。
使用Fluent API可以实现相同的效果
// Set type of POCO-ViewModel
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(UIViewModel);
// Data binding for the IsActive property
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<UIViewModel>();
fluentAPI.SetBinding(checkEdit, c => c.Checked, x => x.IsActive);
// Property-change Trigger for the IsActive property
fluentAPI.SetTrigger(x => x.IsActive, (active) =>
{
label.Text = active ? "Active" : "Inactive";
});
自定义ViewModel
自定义的ViewModel怎么兼容DevExpress MVVM框架
MvvmContext设置为此特定的ViewModel类型,以与旧版ViewModel一起使用。
var legacyViewModel = new LegacyViewModel("Legacy ViewModel");
// initialize the MVVMContext with the specific ViewModel's instance
mvvmContext.SetViewModel(typeof(LegacyViewModel), legacyViewModel);
完成后数据绑定语法兼容
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, "Title");
另一种方法
可以绑定控件到子ViewModels,怎么做呢
首先,定义一个嵌套的ViewModel和一个获得该ViewModel属性。
public ViewModel() {
// Create Nested ViewModel as POCO-ViewModel
Child = ViewModelSource.Create<NestedViewModel>();
}
public NestedViewModel Child { get; private set; }
然后就可以使用数据绑定,绑定的属性是嵌套ViewModel的一部分。
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, "Child.Title");
也可以使用fluent API实现绑定
var fluent = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluent.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, x => x.Child.Title)
值转换Value Converters
在介绍POCO的时候了解了编辑器Editor绑定Title属性
mvvmContext.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, "Title");
EditValue 属性类型和绑定的string属性类型是一致的,但是有些时候可能是不同类型,在下面的例子中,整形Progress属性修改TrackBarControl 和TextEdit控件的可视状态,Value是int类型,Text是string类型
var fluent = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluent.SetBinding(trackBar, e => e.Value, x => x.Progress);
fluent.SetBinding(editor, e => e.Text, x => x.Progress);
第二个绑定是正常的,当绑定的类型不一样时,转换器会尝试查找源类型的适当替代并将其强制转换为该类型。
当转换显而易见且简单时,例如上面示例中的Int32-String转换,默认转换器就可以处理大多数任务。对于更复杂的任务,请使用SetBinding方法重载手动转换值,该重载将自定义和反向转换器作为最后两个参数。
fluent.SetBinding(check, e => e.CheckState, x => x.ModelState,
modelState =>
{
// Convert the ViewModel.State to the editor's CheckState
switch(modelState) {
case ViewModel.State.Active:
return CheckState.Checked;
case ViewModel.State.Inactive:
return CheckState.Unchecked;
default:
return CheckState.Indeterminate;
}
},
checkState =>
{
// Convert back from editor's CheckState to the ViewModel.State
switch(checkState) {
case CheckState.Checked:
return ViewModel.State.Active;
case CheckState.Unchecked:
return ViewModel.State.Inactive;
default:
return ViewModel.State.Suspended;
}
});
自定义值转换器将自定义状态类型的'ModelState'属性转换为CheckState类型,由检查编辑器识别。反向转换器将编辑器的检查状态转换回State枚举器值。
只需要单向值转换,则可以跳过设置反向转换器的步骤。
fluent.SetBinding(check, e => e.Text, x => x.ModelState, modelState =>
string.Format("Click to change the current ViewModel state from {0} to {1}", modelState, (ViewModel.State)((1 + (int)modelState) % 3)));
格式化绑定
mvvmContext.SetBinding(label, l => l.Text, "Price");
public class ViewModel {
public virtual int Price { get; set; }
}
mvvmContext.SetBinding(label, l => l.Text, "Price", "Price: {0:C}");
多个属性绑定
绑定多个值
mvvmContext.SetMultiBinding(editForFullName, e => e.Text, new string[] { "FirstName", "LastName" });
必须使用转换器来进行双向绑定,以便将在编辑器中进行的更改传递回可绑定属性。下面的代码将单独的可绑定属性值转换为联合字符串,反之亦然。
mvvmContext.SetMultiBinding(editForFullName, e => e.EditValue, new string[] { "FirstName", "LastName" },
jointString => string.Join(", ", jointString), singleString => ((string)singleString).Split(','));
命令Commands
在WinForms平台上执行某些动作的常用方法是处理特定事件并在事件处理程序中执行所需的方法。例如,如果您需要在单击按钮时显示消息框,则处理ButtonClick事件并调用MessageBox.Show方法。
但是,此模式打破了在MVVM中分离Views和ViewModels的想法,因为您的View获得的代码应放置在ViewModel或Presenter中。MVVM模式提出了一种不同的方法:您的操作应封装到其他位置定义的特定对象中。该对象绑定到特定的UI元素,单击(检查,修改等)此UI元素将触发该对象,该对象将执行所需的功能。这使您的视图不受业务逻辑代码的影响。这样的对象称为Commands。
委托命令Delegate Commands
委托命令是简单的命令,设计用于同步执行的动作。在一个简单的场景中,仅通过Execute函数将命令定义为DelegateCommand对象。
DelegateCommand command = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
MessageBox.Show("Hello! I'm running!");
});
要绑定命令,您可以使用BindCommand方法,该方法可用于大多数DevExpress UI控件(按钮,复选框,栏项目等)。
commandButton.BindCommand(command);
BindCommand方法的其他构造
包含一个CanExecute 方法,指示命令和相关UI的可用性
//If this function returns false, the command is disabled
Func<bool> canExecute = () => (2 + 2 == 4);
DelegateCommand command = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
MessageBox.Show("Hello! I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True`. Try to change this condition!");
}, canExecute);
给命令方法传递参数
DelegateCommand<object> command = new DelegateCommand<object>((v) =>
{
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}. Try to change this parameter!", v));
});
object parameter = 5;
commandButton.BindCommand(command, () => parameter);
一个参数和一个可执行方法
Func<int, bool> canExecute = (p) => (2 + 2 == p);
// This command is created parameterized and with 'canExecute' parameter.
DelegateCommand<int> command = new DelegateCommand<int>((v) =>
{
MessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"And I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", v));
}, canExecute);
int parameter = 4;
commandButton.BindCommand(command, () => parameter);
如果在ViewModel中定义DelegateCommands,则必须将它们用作特定属性的返回值,并通过指定Execute和CanExecute方法的委托来构造它们。然后,使用只读属性将该命令公开给视图,该属性返回对ICommand的引用
using System.Windows.Input;
public class QuestionnaireViewModel
{
public QuestionnaireViewModel()
{
this.SubmitCommand = new DelegateCommand<object>(
this.OnSubmit, this.CanSubmit );
}
//add the PresentationCore assembly to the project to use the ICommand interface
public ICommand SubmitCommand { get; private set; }
private void OnSubmit(object arg) {...}
private bool CanSubmit(object arg) { return true; }
}
POCO命令
DevExpress MVVM框架中,定义为此类中没有参数或只有一个参数的void方法
public class ViewModelWithParametrizedCommand {
public void DoSomething(object p) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format("Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}. Try to change this parameter!", p));
}
}
绑定命令需要MvvmContext的API
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithSimpleCommand);
mvvmContext.BindCommand<ViewModelWithSimpleCommand>(commandButton, x => x.DoSomething());
POCO也支持CanExecute
//View
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand);
int parameter = 4;
mvvmContext.BindCommand<ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand, int>(commandButton, (x, p) => x.DoSomething(p), x => parameter);
//ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand
public class ViewModelWithParametrizedConditionalCommand {
// Parameterized POCO-command will be created from this method.
public void DoSomething(int p) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! The parameter passed to command is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"And I'm running, because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", p));
}
// Parameterized `CanExecute` method for the `DoSomething` command.
public bool CanDoSomething(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p;
}
}
POCO工作流,(1)是一个POCO命令执行关于收集实体(例如,选择的网格控制行)某些动作。当前选择的实体将保留为可绑定的SelectedEntity(2)属性的值,每当此属性更改其值时,都会自动触发其OnSelectedEntityChanged回调(3)此回调触发DoSomething命令的标准DevExpress POCO RaiseCanExecuteChanged方法(4)调用此方法时,将重新检查CanDoSomething方法的返回值(5)并更新DoSomething 命令的可用性。
//2 - Bindable Property
public virtual MyEntity SelectedEntity{ get; set; }
//3 - Changed callback
protected void OnSelectedEntityChanged(){
//4 - Checks the CanExecute return value
this.RaiseCanExecuteChanged(x=>x.DoSomething());
}
//1 - POCO Command
public void DoSomething() {
// command body
}
//5 - CanExecute function for the POCO Command
public bool CanDoSomething() {
//CanExecute condition (Amount>500$)
return (SelectedEntity != null) && (SelectedEntity.Amount > 500);
}
异步命令
异步命令需要用到System.Threading.Tasks.Task类型方法
public class ViewModelWithAsyncCommand {
// Asynchronous POCO-command will be created from this method.
public Task DoSomethingAsynchronously() {
return Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000); // do some work here
});
}
}
绑定异步命令和之前没有区别,BindCommand
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithAsyncCommand);
mvvmContext.BindCommand<ViewModelWithAsyncCommand>(commandButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
该异步方法可以取消
public class ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation {
// An asynchronous POCO-command will be created from this method.
public Task DoSomethingAsynchronously() {
var dispatcher = this.GetService<IDispatcherService>();
return Task.Factory.StartNew(() => {
var asyncCommand = this.GetAsyncCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
if(asyncCommand.IsCancellationRequested) // cancellation check
break;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(25); // do some work here
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(dispatcher, i);
}
UpdateProgressOnUIThread(dispatcher, 0);
});
}
// Property for progress
public int Progress { get; private set; }
void UpdateProgressOnUIThread(IDispatcherService dispatcher, int progress) {
dispatcher.BeginInvoke(() => {
Progress = progress;
this.RaisePropertyChanged(x => x.Progress);
});
}
}
绑定UI,支持取消操作,MvvmContext组件的BindCancelCommand
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation);
// Binding the async command
mvvmContext.BindCommand<ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation>(commandButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
// Binding the cancellation for the previous command
mvvmContext.BindCancelCommand<ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation>(cancelButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
没有为async命令手动定义CanExecute方法。框架自动完成所有工作,并锁定调用async命令的UI元素,直到该命令完成(或取消)。取消异步命令的UI元素也将自动禁用,直到启动目标命令为止。
兼容已有命令
和数据绑定相同,
//ViewModel
public class LegacyCommandWithParameter {
public void Execute(object parameter) {
MessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"Hello! I'm a Legacy command and the parameter passed to me is {0}." + Environment.NewLine +
"I'm running because the `canExecute` condition is `True` for this parameter." + Environment.NewLine +
"Try to change this parameter!", parameter));
}
public bool CanExecute(object parameter) {
return object.Equals(2 + 2, parameter);
}
}
//View
// This is parameterized legacy-command with both the Execute (object) and the CanExecute (object) methods.
LegacyCommandWithParameter command = new LegacyCommandWithParameter();
int parameter = 4;
// UI binding for button with `queryParameter` function
commandButton.BindCommand(command, () => parameter);
服务Services
显示ViewModel通知,消息框,是View的一部分,如果直接从ViewModel中显示消息框(MessageBox.Show()方法),这样会破坏MVVM框架原则,为了解决这个问题DevExpress MVVM Framework实现了Services。
服务是一种IOC模式,它删除了ViewModel和View层之间的所有引用。在代码中,服务是ViewModel代码中使用的接口,无需假设实现此接口的“何时”和“方式”。
无论是自定义服务还是使用DevExpress服务,都要符合一下工作流。
- 用代码定义服务(如果您使用的是DevExpress已实现的服务,则跳过);
- 在特定的视图中注册;
- 在ViewModel中检索服务并使用其方法。
DevExpress MVVM框架已经为大多数常见任务提供了即用型服务-显示消息,弹出窗口,对话框,添加Application UI Manager文档等。
ViewModel代码定义了IMessageBoxService类型的属性来检索XtraMessageBoxService
//ViewModel
public class MyViewModel {
protected IMessageBoxService MessageBoxService {
get { return this.GetService<IMessageBoxService>(); }
}
}
注意:GetService方法不是线程安全的,不应从后台线程中调用。
对于POCO ViewModels可以使用一下语法,会自动调用this.GetService如果发现有错误的话会自动引发一个异常
//POCO ViewModel
protected virtual IMessageBoxService MessageBoxService {
get { throw new System.NotImplementedException(); }
}
获得服务后就可以使用方法
public void SayHello() {
MessageBoxService.Show("Hello!");
}
最后需要注册服务,服务可以本地注册也可以全局注册。
//Global service
DevExpress.Mvvm.ServiceContainer.Default.RegisterService(new SomeService());
//Local service
serviceContainer.RegisterService(new SomeFilterService(ModuleType.MyCustomFilter));
在viewmodel创建的时候,在运行时,注册服务
this.ServiceContainer.RegisterService(new Services.AnotherService());
自定义服务实现,可以覆盖ViewModel层次结构中任何级别的父级服务实现
serviceContainer.RegisterService(new NotImplementedCustomService(ModuleType.MyMainView));
使用MvvmContext组件,您无需记住此基础服务容器机制。该组件的API提供了易于使用的方法来在全局和本地级别上注册服务。
//Static method that registers the global DevExpress XtraDialogService
MVVMContext.RegisterXtraDialogService();
//Registers the Service1 service in the default service container (global service)
mvvmContext1.RegisterDefaultService(new Service1());
//Registers the local Service1 for use within the current View only
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(new Service2());
全局静态容器中已经注册了许多现成的服务,因此您甚至不需要手动注册它们。
如果需要,您可以重新定义这些服务注册。为此,请使用MVVMContext类的相应静态Register ...方法。例如,XtraMessageBoxService和FlyoutMessageBoxService示例的ViewModel与第一个示例的ViewModel相同。这三个ViewModel均检索实现IMessageBoxService的服务。但是,使用不同的静态Register ...方法会强制使用不同的服务。
尽管ViewModel代码是相同的,但是相同的方法允许Dialog Services组中的示例显示不同的对话框。
protected IDialogService DialogService {
get { return this.GetService<IDialogService>(); }
}
由于注册了不同服务的View代码,因此调用了不同的对话框。
// XtraDialog服务
MVVMContext.RegisterXtraDialogService();
// FlyoutDialog服务
MVVMContext.RegisterFlyoutDialogService();
自定义服务
对于自定义服务,您首先需要在单独的类中的某个地方实现此服务。例如,应用程序具有带有Notify方法的自定义接口IMyNotificationService。
//View
public interface IMyNotificationService {
void Notify(string message);
}
然后,实现此接口的自定义服务CustomService1将如下所示。
//Service1.cs
class CustomService1 : IMyNotificationService {
void IMyNotificationService.Notify(string message) {
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(message, "Service1");
}
}
作为一种变体,创建另一个实现相同接口但使用不同方法重载的服务。
//Service2.cs
class CustomService2 : IMyNotificationService {
void IMyNotificationService.Notify(string message) {
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(message, "Service2");
}
}
在ViewModel代码中检索自定义服务的属性如下所示。
//ViewModel
public virtual IMyNotificationService Service {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
public virtual IMyNotificationService AnotherService {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
这是可以绑定到UI元素(例如,按钮)的DoSomething方法。它将显示两条带有相同文本的消息。
//ViewModel
public void DoSomething() {
Service.Notify("Hello");
AnotherService.Notify("Hello");
}
最后,在视图中注册您的自定义服务。由于这些是您自己的定制服务,因此不存在用于注册这些服务的预定义静态MVVMContext方法。而是,调用本地MvvmContext实例的RegisterService方法。
//View
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(new CustomService1());
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(new CustomService2());
所有必要的步骤:实现自定义服务,使用ViewModel检索它们,使用它们的方法并在View中注册它们。但是,如果您在运行时尝试应用程序,则两个消息框都将带有“ Service2”标题。这意味着两个被调用的Notify方法都是CustomService2类的方法。
检索服务问题
注册后,服务将在分层树中占据特定位置。每当框架需要服务时,它就会从树的底部开始寻找,然后向上移动直至找到合适的服务。前面提到,许多现成的服务已经在静态容器中注册。这些服务位于层次结构的最顶层,如果框架未在较低级别找到任何自定义服务,则使用这些服务。如果这两个默认服务都不存在,则会发生异常。在此示例中,两个定制服务都在同一层次结构级别上注册。由于两个服务都实现相同的IMyNotificationService服务,因此当Service或Notify方法的Notify方法都将它们都视为适当的服务。调用AnotherService对象。但是CustomService2是最后一个被注册的,因此它位于层次结构底部附近,并且始终是框架首先“发现”的地方。您可以使用此机制,并使用RegisterDefaultService方法注册CustomService2。这会将您的CustomService2注册到层次结构顶部的静态容器中,并使CustomSerive1成为最低的服务。之后,框架将始终选择CustomService1。
为解决这个问题,定义服务密钥。密钥是标记特定服务的字符串标识符。对于POCO ViewModel,可以将服务密钥设置为[ServiceProperty]属性的参数。
[ServiceProperty(Key="Service1")]
public virtual IMyNotificationService Service {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
[ServiceProperty(Key = "Service2")]
public virtual IMyNotificationService AnotherService {
get { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
对于非POCO ViewModel,可以将服务密钥设置为GetService扩展方法的参数。
public IServiceInterface MyService {
get { return this.GetService<IServiceInterface >("MyServiceKey"); }
}
现在,您必须使用这些唯一的密钥注册自定义服务。
mvvmContext1.RegisterService("Service1", new CustomService1());
mvvmContext1.RegisterService("Service2", new CustomService2());
如此一来,当您调用Notify方法时,该框架不会混淆应该使用哪个IMyNotificationService服务实现。相反,它将采用标有您的自定义密钥的确切服务。例如,AnotherService属性将寻找标有“ Service2”键的服务,并找到已注册的CustomService2服务。与Service属性相同,它将使用CustomService1服务,因为该服务已标记有“ Service1”键。
行为Behavoirs
行为无需修改即可为对象添加额外的功能。例如,关闭按钮关闭选项卡或表单,并另外显示一个确认对话框。您可以使用MVVM应用程序中的行为来完成此操作。
确认行为
简单的确认行为只能附加到可取消的事件(例如,表单关闭或编辑值更改)。要实现自定义行为,请定义一个从ConfirmationBehavior类派生的类。它包含两个虚拟字符串属性,用于确认消息框的标题和文本。覆盖这些属性以分配您的文本字符串。类构造函数应继承具有等于触发此行为的事件名称的参数的基类构造函数。
public class FormCloseBehavior : ConfirmationBehavior<FormClosingEventArgs> {
public FormCloseBehavior() : base("FormClosing") { }
protected override string GetConfirmationCaption() {
return "Confirm exit";
}
protected override string GetConfirmationText() {
return "Do you really want to exit the application?";
}
}
这个ConfirmationBehavior 的虚拟属性值是bool属性,可以覆盖它用来指示相关事件的取消条件
//Inverted confirmation logic
protected override bool Confirm() {
if(MessageBox.Show(GetConfirmationText(), GetConfirmationCaption(), MessageBoxButtons.YesNo) == DialogResult.Yes) return false;
else return true;
}
使用MvvmContext组件的API将此行为附加到目标UI元素。
//View
mvvmContext.AttachBehavior<FormCloseBehavior>(this);
您可以通过将行为声明从单独的类移到通用类来简化此过程。
mvvmContext1.AttachBehavior<ConfirmationBehavior<ChangingEventArgs>>(checkEdit1, behavior => {
behavior.Caption = "CheckEdit State Changing";
behavior.Text = "This checkEdit's checked-state is about to be changed. Are you sure?";
behavior.Buttons = ConfirmationButtons.YesNo;
behavior.ShowQuestionIcon = true;
}, "EditValueChanging");
Fluent API
mvvmContext1.WithEvent<ChangingEventArgs>(checkEdit1, "EditValueChanging").Confirmation(behavior => {
behavior.Caption = "CheckEdit State changing";
behavior.Text = "This checkEdit's checked-state is about to be changed. Are you sure?";
});
Event-To-Command Behaviors
如果确认行为需要接收一个带CancelEventArgs参数类型的事件(某个事件发生时需要执行某个命令),事件到命令行为正好满足这一功能,此行为可以将命令绑定到UI元素,并且该元素某个事件触发可以执行命令。
public class ClickToSayHello : DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.EventToCommandBehavior<ViewModel, EventArgs> {
public ClickToSayHello()
: base("Click", x => x.SayHello()) {
}
}
使用场景:
- 没有实现ISupportCommandBinding接口的第三方UI元素,不能用MvvmContext API进行绑定。
- 需要额外功能的DevExpress控件。
该行为与其他行为的绑定方式相同。
mvvmContext.AttachBehavior<ClickToSayHello>(thirdPartyButton);
使用Fluent API可以实现该行为,不用单独创建类
mvvmContext.WithEvent<ViewModel, EventArgs>(thirdPartyButton, "Click").EventToCommand(x => x.SayHello());mvvmContext.WithEvent<ViewModel, EventArgs>(thirdPartyButton, "Click").EventToCommand(x => x.SayHello());
Key-Command Behaviors
当按键发生时执行某个命令行为
绑定单个按键,ViewModel定义了“ OnAKey”和“ OnAltKey”命令,该命令是基于服务的
public class KeyAwareViewModel {
protected IMessageBoxService MessageBoxService {
get { return this.GetService<IMessageBoxService>(); }
}
public void OnAKey() {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command: A");
}
public void OnAltAKey() {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command: Alt+A");
}
}
使用MvvmContext组件的 fluent API法将这些命令绑定到相关的键:
| WithKey | 第一个方法参数是一个UI元素,当最终用户按下某些键时,必须将其聚焦。第二个参数是按键组合。 |
|---|---|
| KeyToCommand | 指应执行的命令。 |
下面的代码分别将“ OnAKey”和“ OnAltKey”命令绑定到“ A”和“ Alt + A”键。仅当备忘录编辑控件当前具有焦点时,才能同时按下两个键组合以触发相关命令。
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(KeyAwareViewModel);
// Binding the "A" key
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKey(memo, Keys.A)
.KeyToCommand(x => x.OnAKey());
// Binding the "Alt+A" shortcut
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKey(memo, Keys.A | Keys.Alt)
.KeyToCommand(x => x.OnAltAKey());
将多个按键绑定到相同的命令
您要将多个键绑定到同一命令,并将这些键作为参数传递,请使用WithKeys和KeysToCommands方法。下面是示例KeyAwareViewModel视图模型,其中包含参数化的“ OnKey”和“ OnKeyArgs”命令。这些命令通知用户已按下了哪些键。
public class KeyAwareViewModel {
protected IMessageBoxService MessageBoxService {
get { return this.GetService<IMessageBoxService>(); }
public void OnKey(Keys keys) {
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Key Command:" + keys.ToString());
}
public void OnKeyArgs(KeyEventArgs args) {
string message = string.Join(", ",
"KeyValue: " + args.KeyValue.ToString(),
"KeyData: " + args.KeyData.ToString(),
"KeyCode: " + args.KeyCode.ToString(),
"Modifiers: " + args.Modifiers.ToString());
MessageBoxService.ShowMessage("Args = {" + message + "}");
}
}
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(KeyAwareViewModel);
// Binding to the OnKey command
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKeys(memo, new Keys[] { Keys.A, Keys.B, Keys.C })
.KeysToCommand(x => x.OnKey(Keys.None), args => args.KeyCode);
// Binding to the OnKeyArgs command
mvvmContext.OfType<KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKeys(memo, new Keys[] { Keys.Shift | Keys.A, Keys.Shift | Keys.B, Keys.Shift | Keys.C})
.KeysToCommand(x => x.OnKeyArgs((KeyEventArgs)null), args => (KeyEventArgs)args);
自定义行为
例如,Ctrl + C键盘组合默认情况下会复制整个GridView行。如果仅需要复制所选行单元格的值,则可以附加自己的行为。
public class ControlCBehavior : EventTriggerBase<System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventArgs> {
public ControlCBehavior()
: base("KeyDown") {
}
protected override void OnEvent() {
if (Args.Control && Args.KeyCode == System.Windows.Forms.Keys.C) {
var cbService = this.GetService<Services.IClipboardService>();
GridView View = Source as GridView;
if (View.GetRowCellValue(View.FocusedRowHandle, View.FocusedColumn) != null && View.GetRowCellValue(View.FocusedRowHandle, View.FocusedColumn).ToString() != String.Empty)
cbService.SetText(View.GetRowCellValue(View.FocusedRowHandle, View.FocusedColumn).ToString());
else
XtraMessageBox.Show("The value in the selected cell is null or empty!");
Args.Handled = true;
}
}
}
此行为使用将文本复制到剪贴板的自定义IClipboardService服务。
public class ClipboardService : IClipboardService {
public void SetText(string text) {
Clipboard.SetText(text);
}
}
public interface IClipboardService {
void SetText(string text);
}
准备好自定义行为后,注册服务并调用AttachBehavior方法将行为附加到网格视图。
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(new Services.ClipboardService());
mvvmContext1.AttachBehavior<Behaviors.ControlCBehavior>(gridView1);
现在,自定义行为将取消默认的快捷方式处理程序,并仅复制选定的单元格值。
通信Messenger
应用程序有多个View和ViewModel,之间的通讯和数据共享使用DevExpress MVVM Messenger实现。
这种消息机制的思想非常简单:在发送者ViewModel中,您调用Send方法将所需的数据作为消息进行传输。在收件人ViewModel中,调用Register方法以捕获所有消息。
//sender
public void SendCustomMessage() {
Messenger.Default.Send("A message");
}
//receiver
public void RegisterAsStringMessageRecepient() {
Messenger.Default.Register<string>(this, OnStringMessage);
}
void OnStringMessage(string message){
//custom action
}
该注册方法建立你的ViewModels之间的永久连接。这意味着一旦调用,就无需再次调用Register方法-发送的所有后续消息将被自动接收。要断开此连接,请使用Unregister方法。
Messenger.Default.Unregister<string>(this, OnStringMessage);
如果存在多个发送相同类型消息的发件人,则可以使用令牌标记从不同发件人发送的消息。令牌可以是任何类型的对象,下面的代码使用简单的字符串令牌。
public void TransmitMessage1() {
Messenger.Default.Send<string>("This message is sent from Sender 1", "sender1");
}
public void TransmitMessage2() {
Messenger.Default.Send<string>("This message is sent from Sender 2", "sender2");
}
Messenger.Default.Register<string>(this, "sender1", OnStringMessage);
Messenger.Default.Unregister<string>(this, "sender2", OnStringMessage);
Fluent API
Fluent API利用级联的方法来中继后续调用的指令上下文。
属性
属性绑定
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluentAPI.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, x => x.Title);
//ViewModel
public virtual string Title { get; set; }
绑定嵌套属性
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
var fluent = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluent.SetBinding(editor, e => e.EditValue, x => x.Child.Title);
//ViewModel
public NestedViewModel Child { get; private set; }
//NestedViewModel
public virtual string Title { get; set; }
UI触发器
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(UIViewModel);
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<UIViewModel>();
fluentAPI.SetTrigger(x => x.IsActive, (active) =>
{
label.Text = active ? "Active" : "Inactive";
});
//UIViewModel
public virtual bool IsActive { get; set; }
命令
参数命令和CanExecute
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
int parameter = 4;
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluentAPI.BindCommand(commandButton, (x, p) => x.DoSomething(p), x => parameter);
//ViewModel
public class ViewModel {
public void DoSomething(int p) {
//. . .
}
public bool CanDoSomething(int p) {
return (2 + 2) == p;
}
}
异步命令
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
var fluentAPI = mvvmContext.OfType<ViewModel>();
fluentAPI.BindCommand(commandButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
fluentAPI.BindCancelCommand(cancelButton, x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
//ViewModel
public class ViewModelWithAsyncCommandAndCancellation
public Task DoSomethingAsynchronously() {
return Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
var asyncCommand = this.GetAsyncCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously());
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
if(asyncCommand.IsCancellationRequested) // cancellation check
break;
//. . .
}
});
}
}
WithCommand一个命令绑定多个UI元素
//binding to one UI element
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())
.Bind(btnDoSomething);
//binding to multiple UI elements
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())
.Bind(btn1DoSomething)
.Bind(btn2DoSomething);
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomethingAsynchronously())
.Bind(btnDo)
.BindCancel(btnCancel);
命令触发器允许您在执行目标命令之前,之后或此命令的CanExecute条件更改时自动调用特定方法。
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())
.After(() => AfterDoSomethingExecuted());
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())
.Before(() => BeforeDoSomethingExecuted());
fluent.WithCommand(x => x.DoSomething())
.OnCanExecuteChanged(() => WhenCanDoSomethingChanged());
行为
确认行为
mvvmContext.WithEvent<ChangingEventArgs>(editor, "EditValueChanging")
.Confirmation(behavior =>
{
behavior.Caption = "CheckEdit State changing";
behavior.Text = "This checkEdit's checked-state is about to be changed. Are you sure?";
});
事件命令行为
mvvmContext.ViewModelType = typeof(ViewModel);
mvvmContext.WithEvent <ViewModel,EventArgs>(thirdPartyButton,“ Click”)
.EventToCommand(x => x.DoSomething());
// ViewModel
public void DoSomething(){
//。。。
}
键命令行为
mvvmContext.OfType <KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKey(备忘录,Keys.A)
.KeyToCommand(x => x.OnAKey());
mvvmContext.OfType <KeyAwareViewModel>()
.WithKeys(备注,新的 Keys [] {Keys.A,Keys.B,Keys.C})
.KeysToCommand(x => x.OnKey(Keys.None),args => args.KeyCode);
视图管理VieManagement
应用程序具有多个单独的View和ViewModel,有时来自不同的程序集。当您需要导航到单独的应用程序模块时,MVVM框架需要知道它应显示的特定视图。几种管理器:
最快,最通用和有效的方法是使用ViewType特性,该特性告诉框架哪个View与目标ViewModel相关。不适用场景:当视图位于单独的程序集中或具有自定义构造函数时,您需要对导航机制进行完全控制
所有DevExpress导航服务都使用DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.UI.IViewLocator服务查找和管理所需的视图。您可以创建此服务的自定义实现并注册(本地或全局)以更改其与应用程序视图一起使用的方式。
如果不想实现自定义服务实现,则将导航服务的实例强制转换为DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.UI.IViewService接口
var service = DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.Services.DocumentManagerService.Create(tabbedView1);
var viewService = service as DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.UI.IViewService;
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(service);之后,处理QueryView事件,该事件使您可以根据所需的视图类型动态分配视图。
viewService.QueryView += (s, e) =>
{
if(e.ViewType == "View1")
e.Result = new Views.View1();
//...
};所需的视图类型是手动指定的。例如,您可以使用以下导航ViewModel,将所有可用View枚举为Modules集合中的项
public class MyNavigationViewModel {
protected IDocumentManagerService DocumentManagerService {
get { return this.GetService<IDocumentManagerService>(); }
}
//Lists all available view types
public string[] Modules {
get { return new string[] { "View1", "View2", "View3" }; }
}
//Bind this command to required UI elements to create and display a document
public void Show(string moduleName) {
var document = DocumentManagerService.CreateDocument(moduleName, null, this);
if(document != null) {
document.Title = moduleName;
document.Show();}
}
}之前的方法是所需任务的全局解决方案- 整个IViewService都会触发QueryView事件。您还可以使用DocumentManagerService所基于的各个View控件提供的API 。
如果将视图作为DocumentManager的选项卡打开,则可以处理BaseView.QueryControl事件以填充这些文档。在这种情况下,视图类型存储为文档的BaseDocument.ControlName属性值。
var service = DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.Services.DocumentManagerService.Create(tabbedView1);
mvvmContext1.RegisterService(service); tabbedView1.QueryControl += (s, e) =>
{
if(e.Document.ControlName == "View 2")
e.Control = new Views.View2();
//...
};
ViewModel管理
在设计时利用MvvmContext组件来构建MVVM应用程序,则该组件将自动管理ViewModel。
如果ViewModel遵循POCO概念,则MVVM框架会将该ViewModel动态转换为包含必要基础结构(以支持例如简化的数据绑定)的新类。该框架可与动态创建的类实例一起使用,这意味着您最初无法在运行时访问这些实例,因为尚未确定其类型。
使用以下选项检索有效的ViewMode:
ViewModelSource.Create方法
在这种方法中,您首先创建一个ViewModel实例,然后调用SetViewModel方法将此实例与特定的ViewModel类型关联。
var mainViewModel = ViewModelSource.Create<MainViewModel>();
mvvmContext1.SetViewModel(typeof(MainViewModel), mainViewModel);
ViewModelBase类
从实现MVVM Framework功能的ViewModelBase类继承ViewModels 。在这种情况下,您可以直接创建ViewModel实例。请注意,还需要调用SetViewModel方法,以指定需要ViewModel时,框架应使用此实例。
public class ViewModel : ViewModelBase {
//. . .
}
var myViewModel = new ViewModel();
mvvmContext1.SetViewModel(typeof(ViewModel), myViewModel);
不建议使用此方法,会失去POCO模型提供的所有功能。
ViewModelCreate事件
该方法旨在与依赖项注入框架(例如Ninject)一起使用。
public class SamuraiViewModel {
public IWeapon Weapon { get; private set; }
public SamuraiViewModel(IWeapon weapon) {
this.Weapon = weapon;
}
public void Attack() {
Weapon.Hit();
}
}
// Bind a dependency for IWeapon
kernel.Bind<IWeapon>().To<Sword>();
// Set up MVVMContext
var fluent = mvvmContext1.OfType<SamuraiViewModel>();
fluent.BindCommand(simpleButton1, x => x.Attack());
在这种情况下,您需要动态生成的ViewModel并将它们绑定到接口(将接口直接绑定到POCO时,MVVM框架功能会丢失)。要获取所需的实例,请按以下方式处理常规(本地)或静态(全局)ViewModelCreate事件:
// Retrieve the live POCO ViewModel instance with the Ninject kernel
//regular event
mvvmContext1.ViewModelCreate += MVVMContext_ViewModelCreate;
void MVVMContext_ViewModelCreate(object sender, DevExpress.Utils.MVVM.ViewModelCreateEventArgs e) {
// kernel.Bind<SamuraiViewModel>().To(e.RuntimeViewModelType);
// e.ViewModel = kernel.Get<SamuraiViewModel>();
e.ViewModel = kernel.Get(e.RuntimeViewModelType);
}
//static event
MVVMContextCompositionRoot.ViewModelCreate += (s,e)=> {
e.ViewModel = kernel.Get(e.RuntimeViewModelType);
};
静态ViewModelCreate事件是一个弱事件。如果它的寿命短于父容器的寿命,则包含变量的闭包(上例中的“内核”或下面的Autofac示例中的“ rootContainer”作用域),则VS垃圾收集器可以过早地收集此变量和事件。处理程序可能永远不会被调用。
[STAThread]
static void Main() {
//rootContainer is declared at the Main method level
IContainer rootContainer;
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
builder.RegisterType<TestViewModel>();
builder.RegisterType<MyClass>().As<IService>();
rootContainer = builder.Build();
MVVMContextCompositionRoot.ViewModelCreate += (s, e) => {
using (var scope = rootContainer.BeginLifetimeScope(
b => b.RegisterType(e.RuntimeViewModelType).As(e.ViewModelType))) {
e.ViewModel = scope.Resolve(e.ViewModelType);
}
};
}
若要解决潜在的问题,请在执行预订的对象级别将变量声明为属性/字段。
//rootContainer is declared at the root level
private static IContainer rootContainer { get; set; }
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
builder.RegisterType<TestViewModel>();
builder.RegisterType<MyClass>().As<IService>();
rootContainer = builder.Build();
MVVMContextCompositionRoot.ViewModelCreate += (s, e) =>
{
using (var scope = rootContainer.BeginLifetimeScope(
b => b.RegisterType(e.RuntimeViewModelType).As(e.ViewModelType))) {
e.ViewModel = scope.Resolve(e.ViewModelType);
}
};
}
DevExpress MVVM<1>的更多相关文章
- DevExpress.Mvvm.Free
DevExpress MVVM Framework is a set of components helping to work in the Model-View-ViewModel pattern ...
- devexpress WinForms MVVM
WinForms MVVM This section is dedicated to the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architectural pattern. Yo ...
- 【MVVM DEV】DataColumn中的TextBox与ComboBox的并存
一.前言 在WPF编程中,有时候我们使用DataGrid会需要在一个DataColumn中既有TextBox,也要有ComboBox或者TextBlock等其他数据显示样式. 这个时候我们 ...
- DevExpress v18.1新版亮点——WinForms篇(八)
用户界面套包DevExpress v18.1日前终于正式发布,本站将以连载的形式为大家介绍各版本新增内容.本文将介绍了DevExpress WinForms v18.1 的新功能,快来下载试用新版本! ...
- DevExpress 编译成功的 dll
DevExpress 编译成功的 dll 附注册方法 其它的有些文件没有,如: DevExpress.EasyTest 这个程序集找不到 希望有的朋友可以分享一下, 安装程序集 通常,将程序集安装到G ...
- DevExpress 项目目录列表参考(收集的 350个cs project)
DevExpress.ExpressApp.Tools\DBUpdater\DBUpdater.csproj DevExpress.BonusSkins\DevExpress.BonusSkins.c ...
- DevExpress 15.1.sln
Microsoft Visual Studio Solution File, Format Version 12.00 # Visual Studio VisualStudioVersion = 14 ...
- WPF DevExpress Chart控件 需要引用的类库
DevExpress.Charts.v16.1.Core.dll DevExpress.Data.v16.1.dll DevExpress.Mvvm.v16.1.dll DevExpress.Xpf. ...
- PropertyGrid自定义控件
PropertyGrid是一个很强大的控件,使用该控件做属性设置面板的一个好处就是你只需要专注于代码而无需关注UI的呈现,PropertyGrid会默认根据变量类型选择合适的控件显示.但是这也带来了一 ...
随机推荐
- 带着canvas去流浪系列之七 绘制水球图
[摘要] 用原生canvasAPI实现百度echarts 示例代码托管在:http://www.github.com/dashnowords/blogs 一. 任务说明 使用原生canvasAPI绘制 ...
- Java并发编程学习随笔 (一) 使用run() 和 start()的差别
java多线程run()和start()的区别 当你启动线程,使用start(),系统会把run()方法当成线程执行体来处理,这是正常的,也是正确的情况.但是,当你启动线程时,调用run()方法,系统 ...
- git 使用详解(5)—— get log 查看提交历史
git log 查看 提交历史 在提交了若干更新之后,又或者克隆了某个项目,想回顾下提交历史,可以使用 git log 命令查看. 接下来的例子会用我专门用于演示的 simplegit 项目,运行下面 ...
- CoderForces999B- Reversing Encryption
time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output standar ...
- 从零开始openGL——三、模型加载及鼠标交互实现
前言 在上篇文章中,介绍了基本图形的绘制.这篇博客中将介绍模型的加载.绘制以及鼠标交互的实现. 模型加载 模型存储 要实现模型的读取.绘制,我们首先需要知道模型是如何存储在文件中的. 通常模型是由网格 ...
- BX谷 2019年最新所有人都能学会的数据分析课视频教程
第一章 数据分析师职业概览 1-1 数据分析师的职业概览免费试学 数据分析师的"钱"景如何 什么人适合学数据分析 数据分析师的临界知识 数据分析师的主要职责 第二章 数据分析和数据 ...
- [从今天开始修炼数据结构]图的最小生成树 —— 最清楚易懂的Prim算法和kruskal算法讲解和实现
接上文,研究了一下算法之后,发现大话数据结构的代码风格更适合与前文中邻接矩阵的定义相关联,所以硬着头皮把大话中的最小生成树用自己的话整理了一下,希望大家能够看懂. 一.最小生成树 1,问题 最小生成树 ...
- WMB Commands
Check ports: mqsiprofile //Run this first mqsireportproperties MB8BROKER -e AddressSampleProvider -o ...
- 学习Python第一天 ---Hello World
引言 人生苦短,请用 Python(3.+) 越来越多的情况下使用Python语言进行"代码粘合"和"数据分析"变得非常方便,而且Python 在"爬 ...
- zabbix主动模式无法获取网卡和文件系统数据
zabbix版本为4.2,根据网上教程将zabbixagent设置成主动模式后,将templates中各Items的type改为Zabbix agent (active),同时将Discovery r ...
