POJ - 3984 迷宫问题 (搜索)
Problem Description
int maze[5][5] = {
0, 1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
};
它表示一个迷宫,其中的1表示墙壁,0表示可以走的路,只能横着走或竖着走,不能斜着走,要求编程序找出从左上角到右下角的最短路线。
Input
Output
Sample Input
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
Sample Output
(0, 0)
(1, 0)
(2, 0)
(2, 1)
(2, 2)
(2, 3)
(2, 4)
(3, 4)
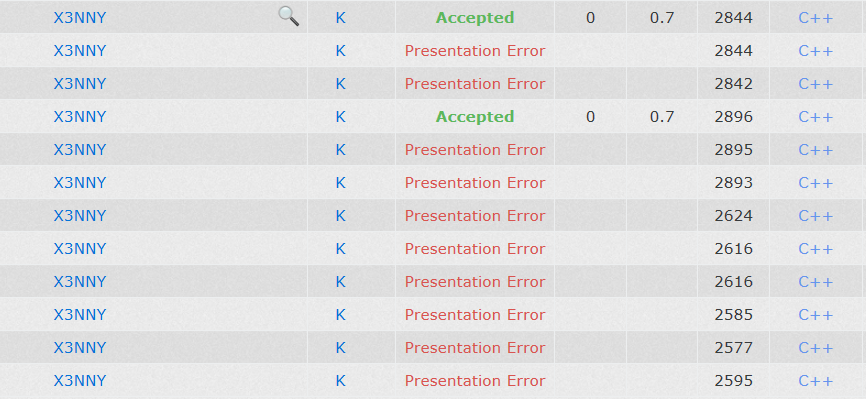
(4, 4) 也是kuangbin搜索专题里面的,说起这道题,也是满满的恶意,先看图吧
整整花了一个小时去找到底哪里PE了。
题目思路很明确,BFS或者DFS都可以,但其实这个题目没必要DFS,简单BFS标记一下前驱就行了,何为前驱,就是说你走到了下一步你上一步 是从哪里走来的,然后用优先队列保证每次优先走距离右下角最近的路。那么问题来了,如何输出,因为我们存的是前驱,所以可以先把所有前驱 入栈,再依次出栈输出就行了,但最开始我想到了另一种更好的方法,因为我发现
ostringstream outt;
outt << << << ; string s = outt.str();
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << s << endl;
利用ostringstream流,最后倒过来就可以实现直接顺序输出了,提交PE。找了半天发现是<<endl;倒序后变成先输出了,那么我第一个不加endl,再次提交PE、PE、PE、PE。到这里我觉得可能是ostringstream影响缓冲区,不能这样,改成栈模拟,还是PE =7=,直到最后我发现,(a, b)中间 逗号后面 有个空格 /微笑/微笑。然后改了两种方法都AC了;
AC代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <deque>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <cmath>
#include <bitset>
#include <ctime>
#include <fstream>
#include <limits.h>
#include <numeric> using namespace std; #define F first
#define S second
#define mian main
#define ture true #define MAXN 1000000+5
#define MOD 1000000007
#define PI (acos(-1.0))
#define EPS 1e-6
#define MMT(s) memset(s, 0, sizeof s)
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
typedef long double ldb;
typedef stringstream sstm;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; int mp[][],vis[][];
int fx[][] = {,,-,,,-,,};
vector< pair< int, pair<int,int> > >bj(); //记录前驱和位置
ostringstream outt;
class cmp{ //优先队列使得曼哈顿距离小的优先出队
public:
bool operator() (const pair<int,int>a,const pair<int,int>b) const{
int ax = - a.F + - a.S;
int bx = - b.F + - b.S;
return ax > bx;
}
}; void bfs(){
priority_queue< pair<int,int>,vector< pair<int,int> >, cmp >q;
//queue< pair<int,int> >q;
q.push(make_pair(,));
vis[][] = ;
while(!q.empty()){
pair<int,int>nx = q.top();
q.pop();
//cout << nx.F << " " << nx.S << endl;
if( - (nx.F + nx.S) == ){
bj[].F = nx.F*+nx.S;
bj[].S.F = , bj[].S.S = ;
break;
} for(int i = ; i < ; i++){
int nxx = nx.F + fx[i][];
int nxy = nx.S + fx[i][];
if(nxx < || nxx > || nxy < || nxy > || mp[nxx][nxy] == || vis[nxx][nxy])
continue;
vis[nxx][nxy] = ;
q.push(make_pair(nxx,nxy));
bj[nxx*+nxy].F = nx.F*+nx.S;
bj[nxx*+nxy].S.F = nxx, bj[nxx*+nxy].S.S = nxy;
}
}
int nex = ;
/* //这是用栈模拟的方式
stack<int>p;
while(nex){
p.push(nex);
nex = bj[nex].F;
}
p.push(0);
while(!p.empty()){
nex = p.top();
p.pop();
cout << "(" << bj[nex].S.F << ", " << bj[nex].S.S << ")"<< endl;
}
*/
while(){ //反向输出到ostringstream中
//cout << nex << endl;
if(nex == ){
outt << ")" << bj[nex].S.S << " ," << bj[nex].S.F << "(";
break;
}
outt << ")" << bj[nex].S.S << " ," << bj[nex].S.F << "(" << "\n";
nex = bj[nex].F;
} } int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cout.tie();
cin.tie();
fill(vis[],vis[]+*,);
for(int i = ; i < ; i++){
for(int j = ; j < ; j++){
cin>>mp[i][j];
}
}
bfs();
string s = outt.str();
reverse(s.begin(),s.end()); //再次逆序
cout << s << endl; return ;
}
其他就是一个简单的BFS,值得注意就是优先队列的使用,当然用DFS也行 ,而且DFS就不需要这么多繁杂的逆序了,直接记录从起点到终点的路径输出就好了。
POJ - 3984 迷宫问题 (搜索)的更多相关文章
- BFS(最短路+路径打印) POJ 3984 迷宫问题
题目传送门 /* BFS:额,这题的数据范围太小了.但是重点是最短路的求法和输出路径的写法. dir数组记录是当前点的上一个点是从哪个方向过来的,搜索+,那么回溯- */ /************* ...
- POJ 3984 迷宫问题
K - 迷宫问题 Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Submit Sta ...
- [POJ 3984] 迷宫问题(BFS最短路径的记录和打印问题)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 宽度优先搜索最短路径的记录和打印问题 #include<iostream> #include<queue> ...
- POJ 3984 迷宫问题(简单bfs+路径打印)
传送门: http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 迷宫问题 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions ...
- poj 3984 迷宫问题(dfs)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 思路:经典型的DFS题目.搜索时注意剪枝:越界处理,不能访问处理. 代码: #include <iostream> ...
- POJ - 3984迷宫问题(最短路径输出)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 题目: 迷宫问题 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submiss ...
- POJ 3984 - 迷宫问题 - [BFS水题]
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 Description 定义一个二维数组: int maze[5][5] = { 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, ...
- POJ 3984 迷宫问题 bfs 难度:0
http://poj.org/problem?id=3984 典型的迷宫问题,记录最快到达某个点的是哪个点即可 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring ...
- POJ 3984 迷宫问题(BFS)
迷宫问题 Description 定义一个二维数组: int maze[5][5] = { 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷 P3648 [APIO2014]序列分割
题意简述 有一个长度为n的序列,分成k + 1非空的块, 选择两个相邻元素把这个块从中间分开,得到两个非空的块. 每次操作后你将获得那两个新产生的块的元素和的乘积的分数.求总得分最大值. 题解思路 f ...
- hadoop2.7作业提交详解之文件分片
在前面一篇文章中(hadoop2.7之作业提交详解(上))中涉及到文件的分片. JobSubmitter.submitJobInternal方法中调用了int maps = writeSplits(j ...
- C#.Net实现AutoCAD块属性提取
https://blog.csdn.net/dengyiyu/article/details/2201175 本文主要给大家介绍一下SmartSoft中用C#.Net实现AutoCAD块属性提取的方法 ...
- C#自动计算字符串公式的四种方法
原地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ifu25/article/details/53292134 四种方式 简单粗暴:利用SQL数据库计算 功能强大:利用JavaScript计算 看不 ...
- 性能测试学习第三天-----loadrunner接口测试&中文乱码处理
loadrunner 接口测试: get.post(3种参数格式).cookie及token处理.加密接口.webservice.socket.文件上传接口.文件下载接口 & 中 ...
- [ZJOI2011]看电影(组合数学,高精度)
[ZJOI2011]看电影 这题模型转化很巧妙.(神仙题) 对于这种题首先肯定知道答案就是合法方案除以总方案. 总方案显然是\(k^n\). 那么考虑怎么算合法方案. 当\(n>k\)的时候显然 ...
- Okhttp3源码解析(4)-拦截器与设计模式
### 前言 回顾: [Okhttp的基本用法](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8e404d9c160f) [Okhttp3源码解析(1)-OkHttpClient分析](htt ...
- Python: 转换文本编码
最近在做周报的时候,需要把csv文本中的数据提取出来制作表格后生产图表. 在获取csv文本内容的时候,基本上都是用with open(filename, encoding ='UTF-8') as f ...
- Mac迅雷瘦身精简教程
迅雷是个大家很熟悉的工具了,尽管吐槽的人不少,但相信大家也都是口嫌体直,边骂边用. 其实 macOS 版迅雷在界面上,相比于 Windows 的客户端来说,已经很克制了,但有些功能仍然对用户造成了干扰 ...
- cogs1709. [SPOJ 705] 不同的子串(后缀数组
http://cogs.pro:8080/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=vyziQkWaP 题意:给定一个字符串,计算其不同的子串个数. 思路:ans=总共子串个数-相同的 ...