深入研究BufferedReader底层源码
1 概述
最近研究JDK IO流这一块源码,发现真的比较简单,而且还有很多意外发现,如果大家对JDK源码感兴趣,不妨从IO流这一块入手,说不定你会爱上JDK源码。今天我所分享的就是BufferedReader
2 BufferedReader源码分析
public class BufferedReader extends Reader {
// 真正干活的流,这里使用到了装饰着模式
private Reader in;
//缓存字符数组
private char cb[];
/*
nchars cb[]数组目前存储的字符总数
nextChar cb[]数组下一个字符
*/
private int nChars, nextChar;
/*
INVALIDATED代表无效 当markedChar=INVALIDATED代表无效时 调用reset()方法会抛出异常
*/
private static final int INVALIDATED = -2;
// 该流中没有任何标记
private static final int UNMARKED = -1;
// mark标记
private int markedChar = UNMARKED;
/*
从markedChar开始可以最多可以读取的字符 如果超过该长度限制 那么markdChar会失效 调用reset()方法会抛异常
*/
private int readAheadLimit = 0; /* Valid only when markedChar > 0 */
/** If the next character is a line feed, skip it */
private boolean skipLF = false;
/** The skipLF flag when the mark was set */
private boolean markedSkipLF = false;
// 默认缓存数组cb[]大小
private static int defaultCharBufferSize = 8192;
// 用在readLine()方法中 默认一行占80个字符
private static int defaultExpectedLineLength = 80;
/**
* Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses an input buffer of
* the specified size.
*
* @param in A Reader
* @param sz Input-buffer size
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException If {@code sz <= 0}
*/
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {
super(in);
if (sz <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
this.in = in;
cb = new char[sz];
nextChar = nChars = 0;
}
/**
* Creates a buffering character-input stream that uses a default-sized
* input buffer.
*
* @param in A Reader
*/
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {
this(in, defaultCharBufferSize);
}
/** Checks to make sure that the stream has not been closed */
private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {
if (in == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
/**
* Fills the input buffer, taking the mark into account if it is valid.
* 该方法的目的就是 填充cb[]缓存数组
* 注意当markedChar有效时[markedChar, nextChar)必须保留,不能覆盖
*/
private void fill() throws IOException {
int dst; // 数据填充的起始位置
if (markedChar <= UNMARKED) { // 说明没有标记 可以从cb[0]开始填充数组
/* No mark */
dst = 0;
} else {
/* Marked */
int delta = nextChar - markedChar;
if (delta >= readAheadLimit) {
/* Gone past read-ahead limit: Invalidate mark */
markedChar = INVALIDATED; // 标记失效 从cb[0]开始填充数组
readAheadLimit = 0;
dst = 0;
} else {
// 说明mark标记有效 且该cb[]数组还有剩余空间
if (readAheadLimit <= cb.length) {
/* Shuffle in the current buffer */
// 将[markedChar, nextChar)保留 其余放弃
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, cb, 0, delta);
markedChar = 0; // markdChar被移至cb[0]
dst = delta;
} else { // 说明 readAheadLimit超过了cb[]长度 需要扩容cb[]数组
/* Reallocate buffer to accommodate read-ahead limit */
char ncb[] = new char[readAheadLimit];
System.arraycopy(cb, markedChar, ncb, 0, delta);
cb = ncb;
markedChar = 0;
dst = delta;
}
nextChar = nChars = delta;
}
}
int n;
do {
n = in.read(cb, dst, cb.length - dst); // 从cb[dst] 开始填充数组
} while (n == 0);
if (n > 0) {
nChars = dst + n;
nextChar = dst;
}
}
/**
* Reads a single character.
*
* @return The character read, as an integer in the range
* 0 to 65535 (<tt>0x00-0xffff</tt>), or -1 if the
* end of the stream has been reached
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
for (;;) {
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars)
// 说明没有数据了
return -1;
}
/*
skipLF默认是false 全局搜索skipLF = ture 会发现只有readLine()会使用它
只要不混用read()和readLine()就不会跳过换行
*/
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
continue;
}
}
return cb[nextChar++];
}
}
}
/**
* Reads characters into a portion of an array, reading from the underlying
* stream if necessary.
*/
private int read1(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (nextChar >= nChars) {
/* If the requested length is at least as large as the buffer, and
if there is no mark/reset activity, and if line feeds are not
being skipped, do not bother to copy the characters into the
local buffer. In this way buffered streams will cascade
harmlessly.
如果len长度大于缓存数组长度 并且没有标记 并且 skipLF为false
那么就直接从底层流中读取数据*/
if (len >= cb.length && markedChar <= UNMARKED && !skipLF) {
return in.read(cbuf, off, len);
}
fill();
}
if (nextChar >= nChars) return -1;
/*
skipLF默认是false 全局搜索skipLF = ture 会发现只有readLine()会使用它
只要不混用read1()和readLine()就不会跳过换行
*/
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars)
return -1;
}
}
// 读取的个数 不能超过缓存数组cb[]有效字符个数
int n = Math.min(len, nChars - nextChar);
System.arraycopy(cb, nextChar, cbuf, off, n);
nextChar += n;
return n;
}
/**
* Reads characters into a portion of an array.
*
* <p> This method implements the general contract of the corresponding
* <code>{@link Reader#read(char[], int, int) read}</code> method of the
* <code>{@link Reader}</code> class. As an additional convenience, it
* attempts to read as many characters as possible by repeatedly invoking
* the <code>read</code> method of the underlying stream. This iterated
* <code>read</code> continues until one of the following conditions becomes
* true: <ul>
*
* <li> The specified number of characters have been read,
*
* <li> The <code>read</code> method of the underlying stream returns
* <code>-1</code>, indicating end-of-file, or
*
* <li> The <code>ready</code> method of the underlying stream
* returns <code>false</code>, indicating that further input requests
* would block.
*
* </ul> If the first <code>read</code> on the underlying stream returns
* <code>-1</code> to indicate end-of-file then this method returns
* <code>-1</code>. Otherwise this method returns the number of characters
* actually read.
*
* <p> Subclasses of this class are encouraged, but not required, to
* attempt to read as many characters as possible in the same fashion.
*
* <p> Ordinarily this method takes characters from this stream's character
* buffer, filling it from the underlying stream as necessary. If,
* however, the buffer is empty, the mark is not valid, and the requested
* length is at least as large as the buffer, then this method will read
* characters directly from the underlying stream into the given array.
* Thus redundant <code>BufferedReader</code>s will not copy data
* unnecessarily.
*
* @param cbuf Destination buffer
* @param off Offset at which to start storing characters
* @param len Maximum number of characters to read
*
* @return The number of characters read, or -1 if the end of the
* stream has been reached
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
/*
此方法判断数组越界情况 并调用read1(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
*/
public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if ((off < 0) || (off > cbuf.length) || (len < 0) ||
((off + len) > cbuf.length) || ((off + len) < 0)) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = read1(cbuf, off, len);
if (n <= 0) return n;
// 当读取的n小于期望的len时并底层流没有被阻塞 会尝试继续读取数据
while ((n < len) && in.ready()) {
int n1 = read1(cbuf, off + n, len - n);
if (n1 <= 0) break;
n += n1;
}
return n;
}
}
/**
* Reads a line of text. A line is considered to be terminated by any one
* of a line feed ('\n'), a carriage return ('\r'), or a carriage return
* followed immediately by a linefeed.
*
* @param ignoreLF If true, the next '\n' will be skipped
*
* @return A String containing the contents of the line, not including
* any line-termination characters, or null if the end of the
* stream has been reached
*
* @see java.io.LineNumberReader#readLine()
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
String readLine(boolean ignoreLF) throws IOException {
StringBuffer s = null;
int startChar;
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
boolean omitLF = ignoreLF || skipLF;
bufferLoop:
for (;;) {
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars) { /* EOF */
if (s != null && s.length() > 0)
return s.toString();
else
return null;
}
// eol 表示是否遇到 换行符
boolean eol = false;
char c = 0;
int i;
/* Skip a leftover '\n', if necessary */
if (omitLF && (cb[nextChar] == '\n'))
nextChar++;
skipLF = false;
omitLF = false;
charLoop: // 这里有两种情况跳出循环 1 缓存数组cb[]有效字符被读完 2 遇到 \n or \r
for (i = nextChar; i < nChars; i++) {
c = cb[i];
if ((c == '\n') || (c == '\r')) {
eol = true;
break charLoop;
}
}
startChar = nextChar;
nextChar = i;
// 遇到换行符了 需要返回该行的内容了
if (eol) {
String str;
if (s == null) {
str = new String(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
} else { // 执行else 必须先执行 341行的逻辑
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
str = s.toString();
}
nextChar++;
if (c == '\r') {
skipLF = true;
}
return str;
}
// 说明没有遇到换行符 但是缓存数组cb[]已经被读完 需要再次fill()
if (s == null)
s = new StringBuffer(defaultExpectedLineLength);
s.append(cb, startChar, i - startChar);
}
}
}
/**
* Reads a line of text. A line is considered to be terminated by any one
* of a line feed ('\n'), a carriage return ('\r'), or a carriage return
* followed immediately by a linefeed.
*
* @return A String containing the contents of the line, not including
* any line-termination characters, or null if the end of the
* stream has been reached
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*
* @see java.nio.file.Files#readAllLines
*/
public String readLine() throws IOException {
return readLine(false);
}
/**
* Skips characters.
*
* @param n The number of characters to skip
*
* @return The number of characters actually skipped
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException If <code>n</code> is negative.
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
if (n < 0L) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("skip value is negative");
}
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
long r = n;
while (r > 0) {
if (nextChar >= nChars)
fill();
if (nextChar >= nChars) /* EOF */
break;
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n') {
nextChar++;
}
}
long d = nChars - nextChar;
// 说明cb[]有效字符个数 大于skip(long n) 跳过的字符个数
if (r <= d) {
nextChar += r;
r = 0;
break;
}
// cb[]有效字符个数不够 需要再次fill()
else {
r -= d;
nextChar = nChars;
}
}
return n - r;
}
}
/**
* Tells whether this stream is ready to be read. A buffered character
* stream is ready if the buffer is not empty, or if the underlying
* character stream is ready.
*
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
public boolean ready() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
/*
* If newline needs to be skipped and the next char to be read
* is a newline character, then just skip it right away.
*/
if (skipLF) {
/* Note that in.ready() will return true if and only if the next
* read on the stream will not block.
*/
if (nextChar >= nChars && in.ready()) {
fill();
}
if (nextChar < nChars) {
if (cb[nextChar] == '\n')
nextChar++;
skipLF = false;
}
}
return (nextChar < nChars) || in.ready();
}
}
/**
* Tells whether this stream supports the mark() operation, which it does.
*/
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
/**
* Marks the present position in the stream. Subsequent calls to reset()
* will attempt to reposition the stream to this point.
*
* @param readAheadLimit Limit on the number of characters that may be
* read while still preserving the mark. An attempt
* to reset the stream after reading characters
* up to this limit or beyond may fail.
* A limit value larger than the size of the input
* buffer will cause a new buffer to be allocated
* whose size is no smaller than limit.
* Therefore large values should be used with care.
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException If {@code readAheadLimit < 0}
* @exception IOException If an I/O error occurs
*/
/*
IO流中的mark(int readAheadLimit)一定要注意 该readAheadLimit表示
mark方法调用过后,最多能读取的字符个数
比如执行mark(10),如果你读取了11字符,那么mark标记就无效了 但是不会报错
但是当你执行reset()方法时 会抛出异常
*/
public void mark(int readAheadLimit) throws IOException {
if (readAheadLimit < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Read-ahead limit < 0");
}
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
this.readAheadLimit = readAheadLimit;
markedChar = nextChar;
markedSkipLF = skipLF;
}
}
/**
* Resets the stream to the most recent mark.
*
* @exception IOException If the stream has never been marked,
* or if the mark has been invalidated
*/
public void reset() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
ensureOpen();
if (markedChar < 0)
throw new IOException((markedChar == INVALIDATED)
? "Mark invalid"
: "Stream not marked");
nextChar = markedChar;
skipLF = markedSkipLF;
}
}
public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (in == null)
return;
try {
in.close();
} finally {
in = null;
cb = null;
}
}
}
/**
* Returns a {@code Stream}, the elements of which are lines read from
* this {@code BufferedReader}. The {@link Stream} is lazily populated,
* i.e., read only occurs during the
* <a href="../util/stream/package-summary.html#StreamOps">terminal
* stream operation</a>.
*
* <p> The reader must not be operated on during the execution of the
* terminal stream operation. Otherwise, the result of the terminal stream
* operation is undefined.
*
* <p> After execution of the terminal stream operation there are no
* guarantees that the reader will be at a specific position from which to
* read the next character or line.
*
* <p> If an {@link IOException} is thrown when accessing the underlying
* {@code BufferedReader}, it is wrapped in an {@link
* UncheckedIOException} which will be thrown from the {@code Stream}
* method that caused the read to take place. This method will return a
* Stream if invoked on a BufferedReader that is closed. Any operation on
* that stream that requires reading from the BufferedReader after it is
* closed, will cause an UncheckedIOException to be thrown.
*
* @return a {@code Stream<String>} providing the lines of text
* described by this {@code BufferedReader}
*
* @since 1.8
*/
/*
流操作
*/
public Stream<String> lines() {
Iterator<String> iter = new Iterator<String>() {
String nextLine = null;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (nextLine != null) {
return true;
} else {
try {
nextLine = readLine();
return (nextLine != null);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new UncheckedIOException(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public String next() {
if (nextLine != null || hasNext()) {
String line = nextLine;
nextLine = null;
return line;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
};
return StreamSupport.stream(Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(
iter, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL), false);
}
}
3 意外发现
我在debugBufferedReader代码的时候,发现JVM在启动的时候,会调用BufferedReader的相关方法。
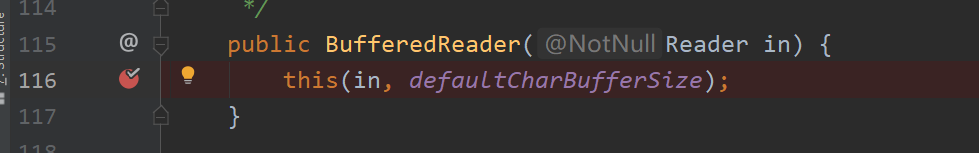
整个Java项目,仅仅在BufferedReader 第116行打上断点,然后debug运行Demo程序
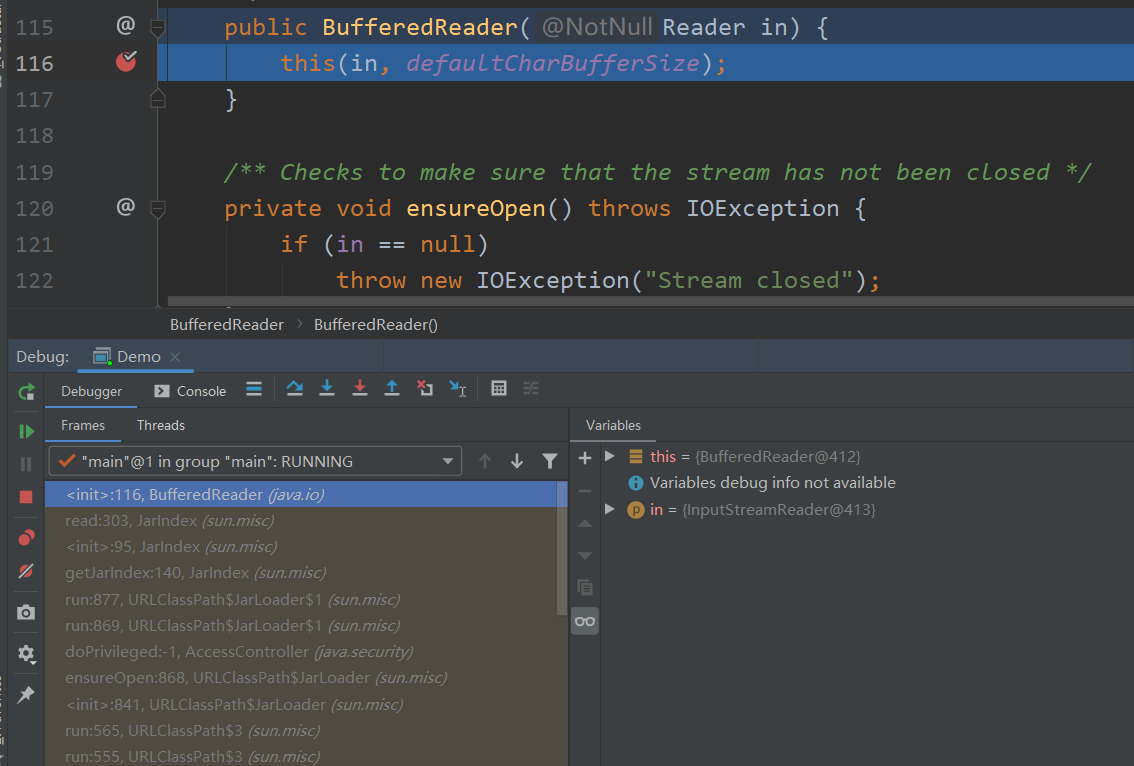
直接debug Demo程序,我们会发现,程序会自动进入BufferedReader这个断点下,说明JVM启动的时候,初始化了这个类,并用到了该类的某些方法。
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/AdaiCoffee/
本文以学习、研究和分享为主,欢迎转载。如果文中有不妥或者错误的地方还望指出,以免误人子弟。如果你有更好的想法和意见,可以留言讨论,谢谢!
深入研究BufferedReader底层源码的更多相关文章
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅵ——图解Android事件分发机制(深入底层源码)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- 为什么很多类甚者底层源码要implements Serializable ?
为什么很多类甚者底层源码要implements Serializable ? 在碰到异常类RuntimeException时,发现Throwable实现了 Serializable,还有我们平进的ja ...
- List-LinkedList、set集合基础增强底层源码分析
List-LinkedList 作者 : Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 继上一章继续讲解,上章内容: List-ArreyLlist集合基础增强底层源码分析:https:// ...
- List-ArrayList集合基础增强底层源码分析
List集合基础增强底层源码分析 作者:Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 集合分为三个系列,分别为:List.set.map List系列 特点:元素有序可重复 有序指的是元素的 ...
- 从底层源码浅析Mybatis的SqlSessionFactory初始化过程
目录 搭建源码环境 POM依赖 测试SQL Mybatis全局配置文件 UserMapper接口 UserMapper配置 User实体 Main方法 快速进入Debug跟踪 源码分析准备 源码分析 ...
- Java泛型底层源码解析-ArrayList,LinkedList,HashSet和HashMap
声明:以下源代码使用的都是基于JDK1.8_112版本 1. ArrayList源码解析 <1. 集合中存放的依然是对象的引用而不是对象本身,且无法放置原生数据类型,我们需要使用原生数据类型的包 ...
- 2018.11.20 Struts2中对结果处理方式分析&struts2内置的方式底层源码剖析
介绍一下struts2内置帮我们封装好的处理结果方式也就是底层源码分析 这是我们的jar包里面找的位置目录 打开往下拉看到result-type节点 name那一列就是我们的type类型取值 上一篇博 ...
- 全方位深度剖析PHP7底层源码(已完结)
第1章 课程介绍本章主要介绍课程要讲的知识点,以及课程要求等. 第2章 PHP7的新特性本章主要介绍PHP7的新特性,做基准测试,与PHP5对比验证PHP7的性能提升程度,引出对PHP7源码学习的必要 ...
- BAT资深工程师 由浅入深分析 Tp5&Tp6底层源码 - 分享
BAT资深工程师由浅入深分析Tp5&Tp6底层源码 第1章 课程简介 本章主要让大家知道本套课程的主线, 导学内容,如何学习源码等,看完本章要让小伙伴觉得这个是必须要掌握的,并且对加薪有很大的 ...
随机推荐
- 机器学习——支持向量机(SVM)
支持向量机原理 支持向量机要解决的问题其实就是寻求最优分类边界.且最大化支持向量间距,用直线或者平面,分隔分隔超平面. 基于核函数的升维变换 通过名为核函数的特征变换,增加新的特征,使得低维度空间中的 ...
- css绝对定位
绝对定位是我们在使用css时经常使用到的一种布局方式,下面说一下什么是绝对定位. 绝对定位使用position:absolute来定义,首先,要理解的是使用了绝对定位的元素它会脱离文档流,所谓脱离文档 ...
- Java机械分词
这是我们做的一个小作业,不多说 直接附上我写的代码: public void Zheng() { try { BufferedReader bre = null; //String file = &q ...
- java多线程之Executor 与 ExecutorService两个基本接口
一.Executor 接口简介 Executor接口是Executor框架的一个最基本的接口,Executor框架的大部分类都直接或间接地实现了此接口. 只有一个方法 void execute(Run ...
- springcloud(五):Spring Cloud 配置中心的基本用法
Spring Cloud 配置中心的基本用法 1. 概述 本文介绍了Spring Cloud的配置中心,介绍配置中心的如何配置服务端及配置参数,也介绍客户端如何和配置中心交互和配置参数说明. 配置中心 ...
- Intellij IDEA使用restclient测试
Intellij IDEA内置了restclient来帮忙我们测试我们的后台代码,让我们可以脱离第三方工具测试,也更不需要我们编写前端代码,直接让我们能想网站发送get,post,put,delet ...
- 实验吧CTF练习题---WEB---因缺思汀的绕过解析
实验吧web之因缺思汀的绕过 地址:http://www.shiyanbar.com/ctf/1940 flag值: 解题步骤: 1.点开题目,观察题意 2.通过观察题目要求,判断此道题还有代码审 ...
- 8 分钟了解 Kubernetes
Kubernetes 脱胎于 Google 的 Borg 系统,是一个功能强大的容器编排系统.Kubernetes 及其整个生态系统(工具.模块.插件等)均使用 Go 语言编写,从而构成一套面向 AP ...
- 多场景抢红包业务引发.NETCore下使用适配器模式实现业务接口分离
事情的起因 我们公司现有一块业务叫做抢红包,最初的想法只是实现了一个初代版本,就是给指定的好友单发红包,随着业务的发展,发红包和抢红包的场景也越来越多,目前主要应用的场景有:单聊发红包.群聊发红包.名 ...
- 将dos格式文件转换为unix格式
在windows下换行符是\r\n,表示回到行首并换到下一行 而unix系统中换行符是\n 这样就存在一个问题,在windows上的文档到了unix上可能就无法使用了 针对这个情况有几种解决办法: 1 ...
