SpringCloud学习笔记(三、SpringCloud Netflix Eureka)
目录:
- 服务发现简介
- SpringCloud Netflix Eureka应用
- Eureka高可用
- Eureka源码分析 >>> Eureka Client初始化(客户端定时获取服务列表、客户端定时发送心跳续约、客户端定时注册)源码分析、服务下线源码分析
服务发现简介:
1、什么是服务发现
程序通过一个标识来获取服务列表,且这个服务列表能够跟随服务的状态而动态变更。
2、服务发现的两种模式
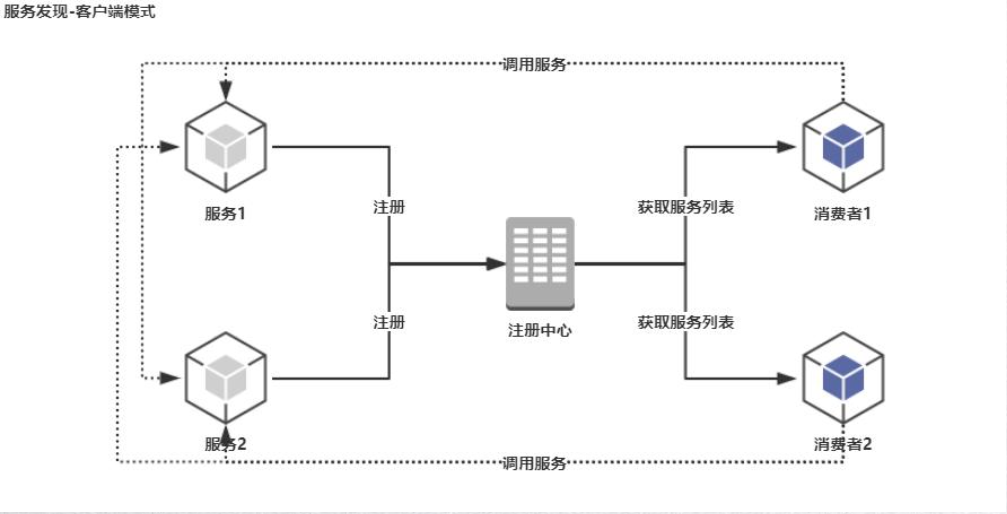
)客户端模式:调用微服务时,首先到注册中心获取服务列表,然后再根据调用本地的负载均衡策略进行服务调用,并且本地会缓存一份服务列表
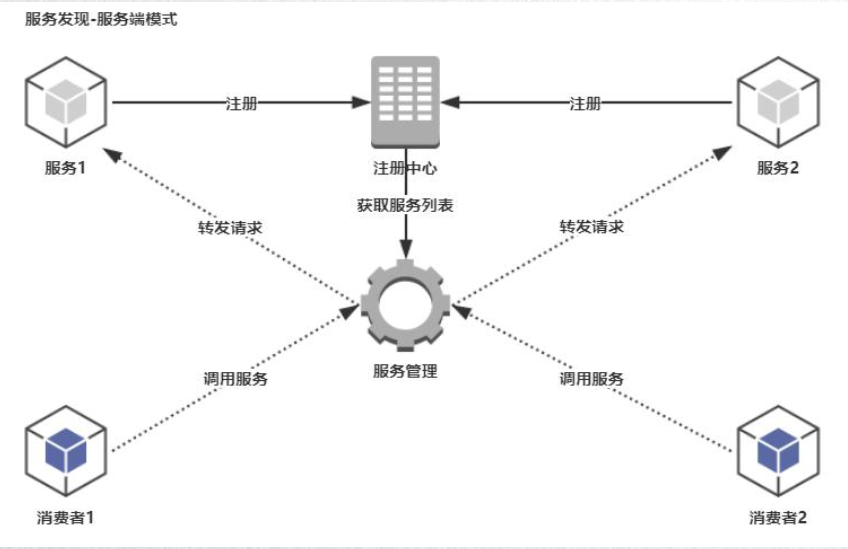
)服务端模式:调用端直接向注册中心发起请求,注册中心再通过自身的负载均衡策略进行服务调用,调用端自身是不需要维护服务发现逻辑。
3、客户端、服务端两种模式的比较
)客户端
a、获取列表为周期性,在调用上减少了一次链路,但每个客户端都需要维护获取服务列表的逻辑
b、可用性高,因为本地缓存了一份服务列表的原因,所以即使注册中心出现故障了也不会影响客户端的正常使用
c、服务端上下线先会对客户端有一定的影响,会出现短暂的调用失败
)服务端
a、简单,客户端不需要维护获取服务列表的逻辑
b、可用性由服务管理者觉定,若服务管理者发送故障则所有的客户端将不可用;同时,所有的调用及存储都有服务管理者来完成,这样服务管理者可能会负载过高
c、服务端上下线客户端无感知
SpringCloud Netflix Eureka应用:
1、Eureka服务端
)添加Eureka Server依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
)启动类加上@EnableEurekaServer注解
)配置properties
## Eureka注册中心实例名
spring.application.name=eureka-server
## Eureka注册中心端口
server.port=9090 ## 关闭Actuator验证开关
management.security.enabled=false ## 不向注册中心获取服务列表
## eureka服务端的eureka.client.fetch-registry配置必须为false让他不要去找server节点,因为它本身就是server节点
eureka.client.fetch-registry=false
## 不注册到注册中心上
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=false ## 配置 注册中心的 地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9090/eureka
启动后可通过http://localhost:9090/eureka查看服务端情况
2、Eureka客户端
)添加Eureka Client依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
)启动类加上@EnableEurekaClient或@EnableDiscoveryClient
二者的共同点是:都是能够让注册中心能够发现,扫描到该服务。
不同点:@EnableEurekaClient只适用于Eureka作为注册中心,而@EnableDiscoveryClient可以是其他的注册中心。
)配置properties
## Eureka服务提供者实例名
spring.application.name=eureka-provider
## Eureka服务提供者端口
server.port=8070 ## 关闭Actuator验证开关
management.security.enabled=false ## 配置 注册中心的 地址
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9090/eureka/
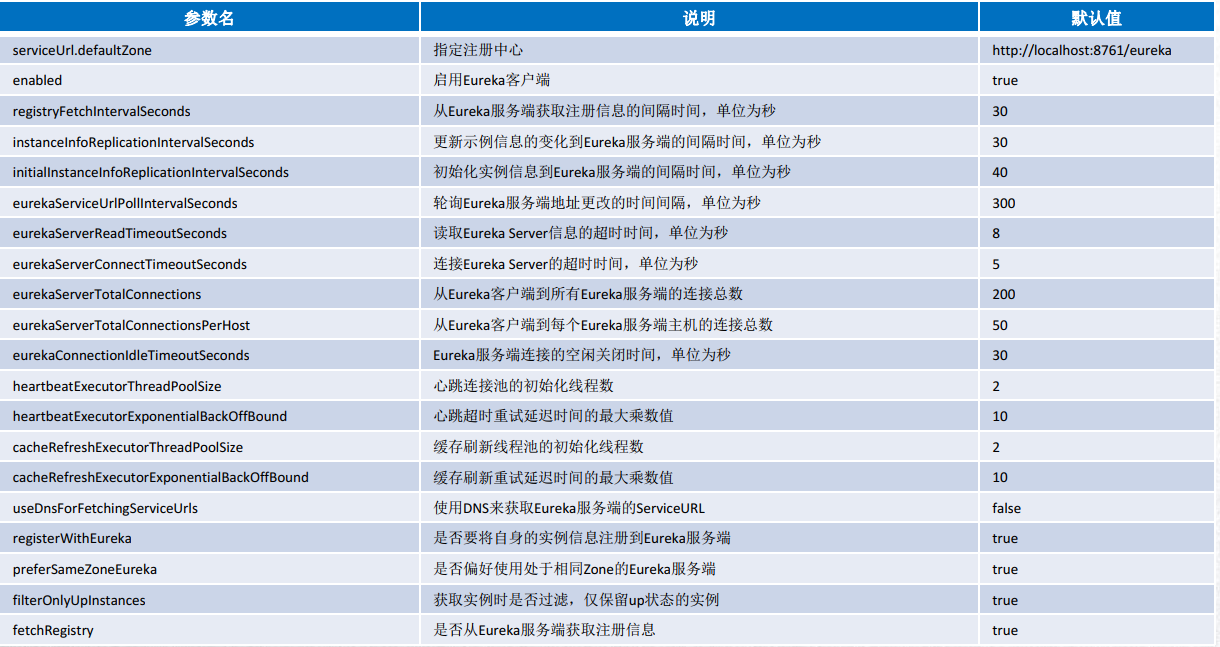
3、一些常用的配置
)客户端配置
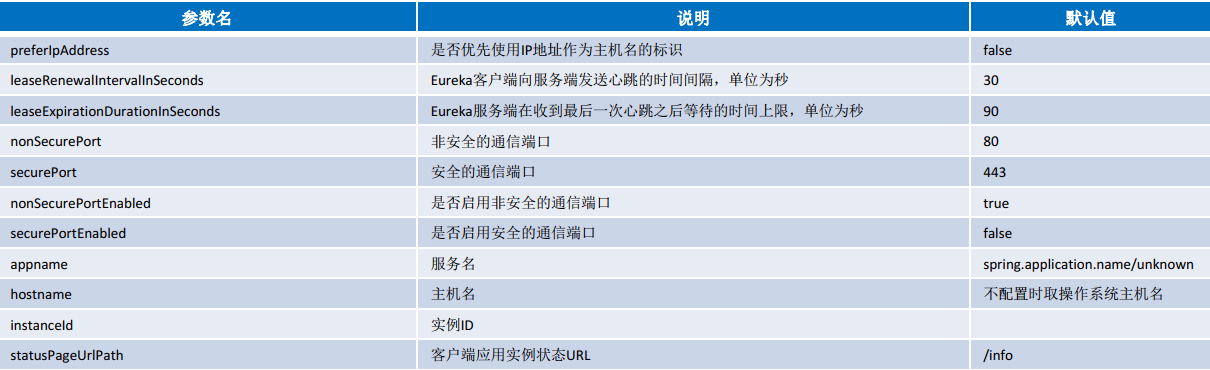
)服务实例配置
Eureka高可用:
我们都知道Eureka分为服务端和客户端,所以搭建高可用的Eureka时二者都需要高可用。
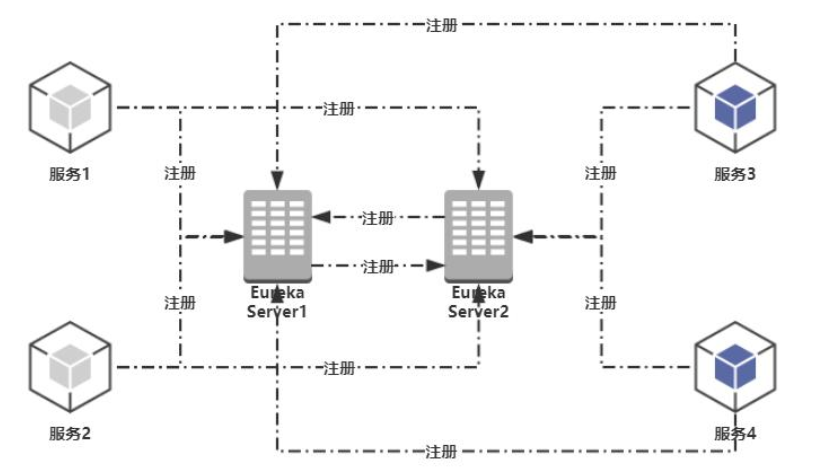
1、服务端
服务端的高可用其实就是让客户端获取服务列表时尽可能的少失败,所以我们只需要启动两个Eureka Server,让他们相互复制服务列表即可
server.port=9091
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9092/eureka
server.port=9092
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9091/eureka
2、客户端
客户端的高可用就是在获取服务列表时尽可能的少失败,所以我们只需要配置多个注册中心即可
eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:9091/eureka,http://localhost:9092/eureka
Eureka Client初始化:
首先我们知道若想将一个应用程序注册为Eureka的客户端那最主要的便是在启动类上加上@EnableDiscoveryClient这个注解,这便是Eureka Client的初始化。
阅读目的:为什么加上@EnableDiscoveryClient注解后且配置eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http后,就能将此服务注册到eureka,且能够让其它注册的服务发现此服务。
1、首先以@EnableDiscoveryClient注解来分析
从注解的字面意思来看就是启动DiscoveryClient,我们来大胆的猜测下 φ(>ω<*)
emmmmm,程序中应该有DiscoveryClient这个类吧,Ctrl + n,(⊙o⊙)…果真有这个类!
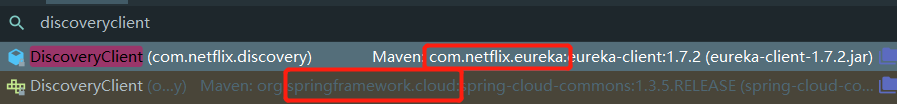
根据IDEA的检索结果,发现满足条件的有两个,一个是com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient,一个是org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient
看源码嘛,肯定先看结构咯~~~
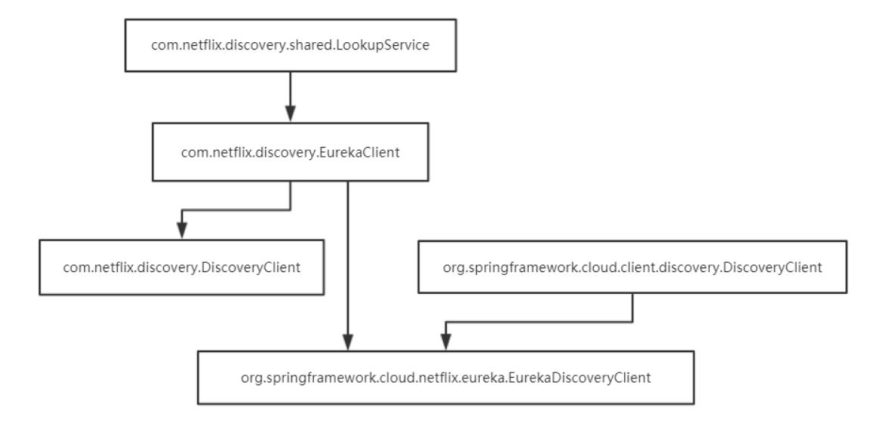
)com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient

)org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient是一个接口,其实现有很多,但Eureka的是org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClient

所以两个DiscoveryClient的逻辑结构便如下图:
2、了解结构后,我们再略读下这两个DiscoveryClient的实现
)首先从SpringCloud的看起,实现类org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClient
a、通过略读可以看出比较重要的public List<ServiceInstance> getInstances(String serviceId)、public List<String> getServices()两个方法都有使用一个eurekaClient的属性
b、而eurekaClient正是,Netflix的EurekaClient接口,所以我们可以得知SpringCloud应该仅是对Netflix的一个包装
c、所以我们直接看Netflix的EurekaClient接口(com.netflix.discovery.EurekaClient)的实现 >>> com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient
)com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient的实现
a、一般看类的实现是从构造函数入手,所以我们先找到最全的构造函数:DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider);
b、此构造一开始是大量的判断,这块就不看了,我们仅看最重要那部分(正常逻辑下,大量判断中的代码逻辑不是对bug的处理就是特殊情况的处理,所以我们先看那些不在if中的代码或者是少量if的代码) >>> initScheduledTasks()
c、initScheduledTasks():初始化定时器,其主要分为三大块 >>> 客户端定时获取服务列表、客户端定时发送心跳续约、客户端定时注册
客户端定时获取服务列表源码分析:
源码示例(客户端):
1 if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
2 // registry cache refresh timer
3 int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
4 int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
5 scheduler.schedule(
6 new TimedSupervisorTask(
7 "cacheRefresh",
8 scheduler,
9 cacheRefreshExecutor,
10 registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
11 TimeUnit.SECONDS,
12 expBackOffBound,
13 new CacheRefreshThread() // 定时获取服务列表thread
14 ),
15 registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
16 }
1、首先我们看第1行,clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() == true才会执行获取服务列表的job,我们点进去看,发现其实就是我们properties配置的eureka.client.fetch-registry,而默认值为true。
2、然后执行job的周期单位为秒(11行),执行周期为registryFetchIntervalSeconds,也就是第3行;第3行和第1行同理,为properties配置的eureka.client.registry-fetchInterval-seconds,而默认值为30
3、最后我们看看其核心线程(13行),可以看到其调用的函数其实是void refreshRegistry();函数最开始一大堆判断,最后一堆debug,这些都不用细究,我们直接看最核心的哪行代码boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified)
private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start();
try {
// If the delta is disabled or if it is the first time, get all
// applications
Applications applications = getApplications();
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta
{
logger.info("Disable delta property : {}", clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta());
logger.info("Single vip registry refresh property : {}", clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress());
logger.info("Force full registry fetch : {}", forceFullRegistryFetch);
logger.info("Application is null : {}", (applications == null));
logger.info("Registered Applications size is zero : {}",
(applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0));
logger.info("Application version is -1: {}", (applications.getVersion() == -1));
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + appPathIdentifier + " - was unable to refresh its cache! status = " + e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
}
// Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status
onCacheRefreshed();
// Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
// registry was fetched successfully, so return true
return true;
}
从代码中我们可以看出要么是全量注册(23行)要么是增量注册(25行):
)全量注册
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
logger.info("Getting all instance registry info from the eureka server");
Applications apps = null;
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Response.Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (apps == null) {
logger.error("The application is null for some reason. Not storing this information");
} else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));
logger.debug("Got full registry with apps hashcode {}", apps.getAppsHashCode());
} else {
logger.warn("Not updating applications as another thread is updating it already");
}
}
)从中可以看出18行将apps从httpResponse获取,所以服务列表应该是从服务端获取的;故看下http调用,第8行调到其实现类com.netflix.discovery.shared.transport.jersey.AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient,看到其调用的http url是apps/
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(String... regions) {
return getApplicationsInternal("apps/", regions);
}
再点进去看,发现其实就是调用了http://服务端ip:服务端port/eureka/apps(GET请求),并且将结果放入Applications
)增量注册,增量注册与全量同理,但调用的是http://服务端ip:服务端port/eureka/apps/delta接口
全量增量注册讲完后我们来看看服务端的代码(着重看全量,增量与全量原理差不多)
源码示例(服务端):
我们知道全量注册调用的是http://服务端ip:服务端port/eureka/apps接口,我们找下这个接口的实现,com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationsResource#getContainers,并找到最重要的代码块
Response response;
if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
response = Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
return response;
进入responseCache.getZIP(cacheKey)后,我们可以知道代码很简单,就是从缓存中获取数据给客户端。
参数useReadOnlyCache也是客户端配置的,默认为true;6-12行很简单,缓存有取缓存,没有则从readWriteCacheMap拿到后再放入缓存。
@VisibleForTesting
ResponseCacheImpl.Value getValue(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) {
ResponseCacheImpl.Value payload = null;
try {
if (useReadOnlyCache) {
final ResponseCacheImpl.Value currentPayload = readOnlyCacheMap.get(key);
if (currentPayload != null) {
payload = currentPayload;
} else {
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, payload);
}
} else {
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Cannot get value for key :" + key, t);
}
return payload;
}
客户端定时发送心跳续约:
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
简单的地方我们就不一一看了,直接进入重点,发现第9行就是不断刷新lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp使之为当前时间戳(永不过期)
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
那我们再看看更新lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp的条件renew呗!
查看renew后可以得知,心跳续约调用了客户端的/apps/appName/id接口(PUT请求);然后我们卡卡客户端实现
1、首先接口在com.netflix.eureka.resources.InstanceResource#renewLease
2、我们想其核心代码boolean isSuccess = registry.renew(app.getName(), id, isFromReplicaNode)里跟进
public boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
RENEW.increment(isReplication);
// 还是一样的从registry中拿InstanceInfo
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);
Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToRenew = null;
if (gMap != null) {
leaseToRenew = gMap.get(id);
}
// 如果拿不到InstanceInfo就表示服务挂了,心跳续约失败
if (leaseToRenew == null) {
RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
logger.warn("DS: Registry: lease doesn't exist, registering resource: {} - {}", appName, id);
return false;
} else {
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToRenew.getHolder();
if (instanceInfo != null) {
// touchASGCache(instanceInfo.getASGName());
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = this.getOverriddenInstanceStatus(
instanceInfo, leaseToRenew, isReplication);
if (overriddenInstanceStatus == InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN) {
logger.info("Instance status UNKNOWN possibly due to deleted override for instance {}"
+ "; re-register required", instanceInfo.getId());
RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
return false;
}
if (!instanceInfo.getStatus().equals(overriddenInstanceStatus)) {
Object[] args = {
instanceInfo.getStatus().name(),
instanceInfo.getOverriddenStatus().name(),
instanceInfo.getId()
};
logger.info(
"The instance status {} is different from overridden instance status {} for instance {}. "
+ "Hence setting the status to overridden status", args);
instanceInfo.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
}
}
renewsLastMin.increment();
// 如果能拿到InstanceInfo就做一个续约
leaseToRenew.renew();
return true;
}
}
3、进一步看下续约leaseToRenew.renew()方法
public void renew() {
lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;
}
代码很简单,就是延长lastUpdateTimestamp的时间,duration则是通过构造传入的;若duration有执行则用构造指定的,若没有默认90秒
客户端定时注册:
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
进入InstanceInfoReplicator后会发现这个类实现Runnable接口,那既然是线程就去看run方法咯
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
然后我们看第7行,一步步根进去发现其实调用了"apps/" + info.getAppName()接口
接下来我们来看看"apps/" + info.getAppName()接口的实现
1、找到com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationResource的addInstance方法,找到其中的registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));根进去
2、找到com.netflix.eureka.registry.AbstractInstanceRegistry的register方法
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
read.lock();
// 根据实例名registrant.getAppName()获取InstanceInfo
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
if (gMap == null) {
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
// 若registry没有此实例时,注册一个空的示例
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
if (gMap == null) {
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// Retain the last dirty timestamp without overwriting it, if there is already a lease
if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();
Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp();
logger.debug("Existing lease found (existing={}, provided={}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
// this is a > instead of a >= because if the timestamps are equal, we still take the remote transmitted
// InstanceInfo instead of the server local copy.
// 若eureka服务器存在的示例的时间戳大于传入新实例的时间戳,则用已存在的(说明eureka server使用的实例都是最新的)
if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
logger.warn("There is an existing lease and the existing lease's dirty timestamp {} is greater" +
" than the one that is being registered {}", existingLastDirtyTimestamp, registrationLastDirtyTimestamp);
logger.warn("Using the existing instanceInfo instead of the new instanceInfo as the registrant");
registrant = existingLease.getHolder();
}
} else {
// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold
// (1
// for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)
this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin + 2;
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =
(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
}
logger.debug("No previous lease information found; it is new registration");
}
// 根据新的示例创建新的租约
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));
}
// This is where the initial state transfer of overridden status happens
if (!InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "
+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());
if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());
}
}
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());
if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);
registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);
}
// Set the status based on the overridden status rules
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);
registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
// If the lease is registered with UP status, set lease service up timestamp
if (InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();
}
registrant.setActionType(InstanceInfo.ActionType.ADDED);
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new AbstractInstanceRegistry.RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
logger.info("Registered instance {}/{} with status {} (replication={})",
registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getId(), registrant.getStatus(), isReplication);
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
服务下线:
若要将此客户端下线的话,要分两步走
)启动下线接口(配置properties)
# 启用下线功能
endpoints.shutdown.enabled=true
# 关闭下线功能的安全校验
endpoints.shutdown.sensitive=false
)调用下线接口(http://当前客户端ip/当前客户端port/shutdown)
1、客户端
客户端代码很简单,主要分为两步
)cancelScheduledTasks() >>> 停止客户端初始化的三个job(客户端定时获取服务列表、客户端定时发送心跳续约、客户端定时注册)
)unregister() >>> 注销(调用apps/appName/id接口,delete方式)
2、服务端
首先我们来找到客户端调的那个接口:com.netflix.eureka.resources.InstanceResource#cancelLease
@DELETE
public Response cancelLease(@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
boolean isSuccess = registry.cancel(app.getName(), id, "true".equals(isReplication)); if (isSuccess) {
logger.debug("Found (Cancel): " + app.getName() + " - " + id);
return Response.ok().build();
} else {
logger.info("Not Found (Cancel): " + app.getName() + " - " + id);
return Response.status(Status.NOT_FOUND).build();
}
}
我们看核心代码(第3行),并找到方法的实现com.netflix.eureka.registry.PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl#cancel
@Override
public boolean cancel(final String appName, final String id, final boolean isReplication) {
if (super.cancel(appName, id, isReplication)) {
replicateToPeers(PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.Action.Cancel, appName, id, null, null, isReplication);
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the threshold (1 for 30 seconds, 2 for a minute)
this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin = this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin - 2;
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold =
(int) (this.expectedNumberOfRenewsPerMin * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
看第三行,然后一步步跟进后找到其底层代码:
protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
try {
read.lock();
CANCEL.increment(isReplication);
// 还是同样的从registry中拿取数据
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName);
Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToCancel = null;
if (gMap != null) {
// 若拿到数据则移除该数据
leaseToCancel = gMap.remove(id);
}
synchronized (recentCanceledQueue) {
recentCanceledQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(System.currentTimeMillis(), appName + "(" + id + ")"));
}
InstanceInfo.InstanceStatus instanceStatus = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.remove(id);
if (instanceStatus != null) {
logger.debug("Removed instance id {} from the overridden map which has value {}", id, instanceStatus.name());
}
if (leaseToCancel == null) {
CANCEL_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
logger.warn("DS: Registry: cancel failed because Lease is not registered for: {}/{}", appName, id);
return false;
} else {
// 将此InstanceInfo移除
leaseToCancel.cancel();
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToCancel.getHolder();
String vip = null;
String svip = null;
if (instanceInfo != null) {
instanceInfo.setActionType(InstanceInfo.ActionType.DELETED);
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new AbstractInstanceRegistry.RecentlyChangedItem(leaseToCancel));
instanceInfo.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
vip = instanceInfo.getVIPAddress();
svip = instanceInfo.getSecureVipAddress();
}
invalidateCache(appName, vip, svip);
logger.info("Cancelled instance {}/{} (replication={})", appName, id, isReplication);
return true;
}
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
最后服务下单其实就是调用leaseToCancel.cancel(),通过更新evictionTimestamp来取消租赁
public void cancel() {
if (evictionTimestamp <= 0) {
evictionTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
SpringCloud学习笔记(三、SpringCloud Netflix Eureka)的更多相关文章
- SpringCloud学习笔记:SpringCloud简介(1)
1. 微服务 微服务具有的特点: ◊ 按照业务划分服务 ◊ 每个微服务都有独立的基础组件,如:数据库.缓存等,且运行在独立的进程中: ◊ 微服务之间的通讯通过HTTP协议或者消息组件,具有容错能力: ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(2):使用Ribbon负载均衡
简介 Spring Cloud Ribbon是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端负载均衡工具,在注册中心对Ribbon客户端进行注册后,Ribbon可以基于某种负载均衡算法,如轮询(默认 ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(4):Hystrix容错机制
简介 在微服务架构中,微服务之间的依赖关系错综复杂,难免的某些服务会出现故障,导致服务调用方出现远程调度的线程阻塞.在高负载的场景下,如果不做任何处理,可能会引起级联故障,导致服务调用方的资源耗尽甚至 ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(5):Hystrix Dashboard可视化监控数据
简介 上篇文章中讲了使用Hystrix实现容错,除此之外,Hystrix还提供了近乎实时的监控.本文将介绍如何进行服务监控以及使用Hystrix Dashboard来让监控数据图形化. 项目介绍 sc ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(6):使用Zuul构建服务网关
简介 Zuul是Netflix提供的一个开源的API网关服务器,SpringCloud对Zuul进行了整合和增强.服务网关Zuul聚合了所有微服务接口,并统一对外暴露,外部客户端只需与服务网关交互即可 ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(3):使用Feign实现声明式服务调用
简介 Feign是一个声明式的Web Service客户端,它简化了Web服务客户端的编写操作,相对于Ribbon+RestTemplate的方式,开发者只需通过简单的接口和注解来调用HTTP API ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(7):使用Spring Cloud Config配置中心
简介 Spring Cloud Config为分布式系统中的外部化配置提供了服务器端和客户端支持,服务器端统一管理所有配置文件,客户端在启动时从服务端获取配置信息.服务器端有多种配置方式,如将配置文件 ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记:服务支撑组件
SpringCloud学习笔记:服务支撑组件 服务支撑组件 在微服务的演进过程中,为了最大化利用微服务的优势,保障系统的高可用性,需要通过一些服务支撑组件来协助服务间有效的协作.各个服务支撑组件的原理 ...
- Oracle学习笔记三 SQL命令
SQL简介 SQL 支持下列类别的命令: 1.数据定义语言(DDL) 2.数据操纵语言(DML) 3.事务控制语言(TCL) 4.数据控制语言(DCL)
- [Firefly引擎][学习笔记三][已完结]所需模块封装
原地址:http://www.9miao.com/question-15-54671.html 学习笔记一传送门学习笔记二传送门 学习笔记三导读: 笔记三主要就是各个模块的封装了,这里贴 ...
随机推荐
- Python—导入自定义的模块和包(指定路径下的模块和包)
模块路径如下图: import sys sys.path.append(r"E:\project\path") print "===>", sys.arg ...
- JVM java内存区域的介绍
jvm虚拟机在运行时需要用到的内存区域.广泛一点就是堆和栈,其实不然,堆和栈只是相对比较笼统的说法,真正区分有如下几个 先上图一: 总的就是 java的内存模型 内存模型又分堆内存(heap)和方法区 ...
- ArrayList的输出以及一些问题
//首先需要创建一个ArrayList ArrayList arr=new ArrayList(); //然后往ArrayList里面插入一些值 arr.add("a"); arr ...
- <Matrix> 311 378
311. Sparse Matrix Multiplication 稀疏矩阵的计算.稀疏矩阵的特点是有大量的0,如果采用暴力算法则比然会有很多无意义的计算. C[ i ][ j ] += A[ i ] ...
- Vue STOP&SELF方法使用
stop属性:停止冒泡只执行到此处 self:只执行当前 代码: <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> ...
- 分布式SQL数据库中部分索引的好处
在优锐课的java学习分享中,探讨了分布式SQL数据库中部分索引的优势,并探讨了性能测试,结果等. 如果使用局部索引而不是常规索引,则在可为空的列上(其中只有一小部分行的该列不具有空值),然后可以大大 ...
- 06-Django视图
什么是视图? 视图就是应用中views.py文件中的函数,视图函数的第一个参数必须是request(HttpRequest)对象.返回的时候必须返回一个HttpResponse对象或子对象(包含Htt ...
- 学习 正则表达式 js java c# python 通用
正则表达式 js java c# python 学习网站 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Globa ...
- Java设计模式:Singleton(单例)模式
概念定义 Singleton(单例)模式是指在程序运行期间, 某些类只实例化一次,创建一个全局唯一对象.因此,单例类只能有一个实例,且必须自己创建自己的这个唯一实例,并对外提供访问该实例的方式. 单例 ...
- hive引擎的选择:tez和spark
背景 mr引擎在hive 2中将被弃用.官方推荐使用tez或spark等引擎. 选择 tez 使用有向无环图.内存式计算. spark 可以同时作为批式和流式的处理引擎,减少学习成本. 问题& ...
