STL杂记
STL介绍:
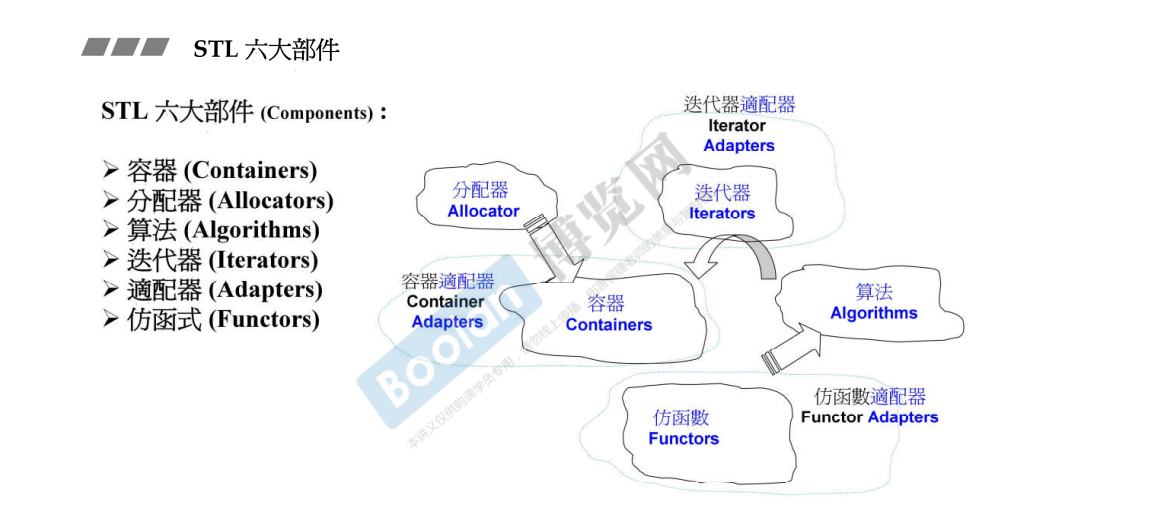
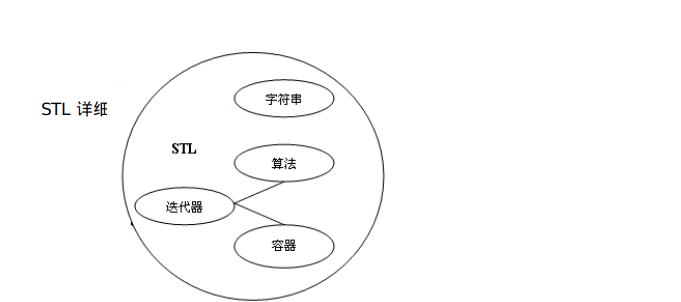
我所理解的stl:
容器: 是一种数据结构,如list,vector,和deques ,以模板类的方法提供。为了访问容器中的数据,可以使用由容器类输出的迭代器;
算法: 是用来操作容器中的数据的模板函数。例如,STL用sort()来对一个vector中的数据进行排序,用find()来搜索一个list中的对象,函数本身与他们操作的数据的结构和类型无关,因此他们可以在从简单数组到高度复杂容器的任何数据结构上使用;
迭代器: 提供了访问容器中对象的方法。例如,可以使用一对迭代器指定list或vector中的一定范围的对象。迭代器就如同一个指针。事实上,C++的指针也是一种迭代器。但是,迭代器也可以是那些定义了operator*()以及其他类似于指针的操作符地方法的类对象;
仿函数: 就是一个类里面重载() 所创建出来的对象,叫做函数对象,或者仿函数
迭代适配器(Adaptor):
空间配制器(allocator): 分配内存的, 偏底层
算法的使用介绍
在stl的算法中分为两大块:一个是全局(泛化)的,一个是容器本身所有的
在使用一个算法时首先看你使用的容器中是否有这个算法,如果有的话,就用容器本身有的
(注意不能使用泛化的,因为泛化的可能不能用这个容器,或者没有容器自带的效率高)
如果没有的话,就使用泛化的
注意这几个例子:图片左边是算法的实现,右边是哪个容器本身有这个算法


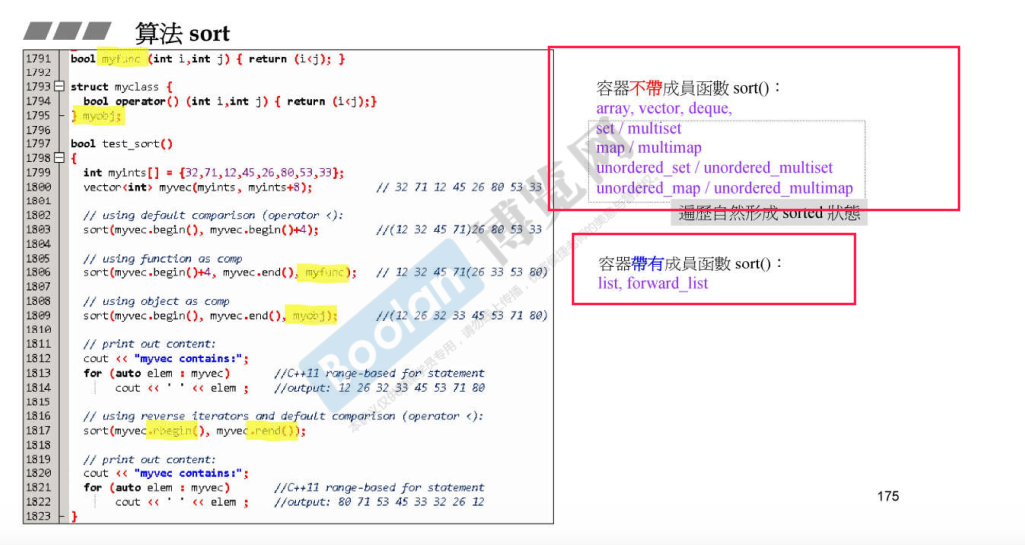
count和count_if使用
源码:
/**对谓词为真的序列的元素进行计数。
* @brief Count the elements of a sequence for which a predicate is true.
* @ingroup non_mutating_algorithms
* @param __first An input iterator.
* @param __last An input iterator.
* @param __pred A predicate.
* @return The number of iterators @c i in the range @p [__first,__last)
* for which @p __pred(*i) is true.
*/
template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Predicate>
inline typename iterator_traits<_InputIterator>::difference_type
count_if(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Predicate __pred)
{
return std::__count_if(__first, __last,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__pred_iter(__pred));
}
使用:
//
// Created by lk on 18-6-4.
//
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std; bool myfun(int i){return i > ;}
struct myClasss{
bool operator()(int i){return i > ;}
}myObjj; int main()
{ // 泛化的
vector<int> vec = {,,,,,,,,};
auto num = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), );
cout << "vec中3的个数为"<< num << endl; auto t = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myfun); auto t2 = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myObjj);
cout << t << " " << t2 << endl; // 结果为3 3 // 容器本身自带的函数
set<int> s1 = {,,,,};
auto s_num = s1.count();
cout << s_num << endl; //
return ; }
使用方法
find方法:
template<typename _IIter, typename _Tp>
_IIter
find(_IIter, _IIter, const _Tp&); template<typename _FIter1, typename _FIter2>
_FIter1
find_first_of(_FIter1, _FIter1, _FIter2, _FIter2); template<typename _FIter1, typename _FIter2, typename _BinaryPredicate>
_FIter1
find_first_of(_FIter1, _FIter1, _FIter2, _FIter2, _BinaryPredicate); template<typename _IIter, typename _Predicate>
_IIter
find_if(_IIter, _IIter, _Predicate);
find源码
//
// Created by lk on 18-6-4.
//
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std; namespace luck_count{
bool myfun(int i){return i > ;}
struct myClasss{
bool operator()(int i){return i > ;}
}myObjj; int test_count()
{ // 泛化的
vector<int> vec = {,,,,,,,,};
auto num = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), );
cout << "vec中3的个数为"<< num << endl; auto t = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myfun); auto t2 = count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myObjj);
cout << t << " " << t2 << endl; // 结果为3 3 // 容器本身自带的函数
set<int> s1 = {,,,,};
auto s_num = s1.count();
cout << s_num << endl; //
return ; }
}
namespace luck_find{
bool myFun(int i) {return i > ;}
struct MyClass{
bool operator()(int i) {return i > ;}
}myObj;
void test()
{
vector<int> vec = {,,,,,,,,}; auto it = find(vec.begin(), vec.begin()+, );
cout << "it是6的迭代器地址" << endl;
auto it2 = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myFun);
cout << "use custom functional" << endl;
cout << "it2是大于2的迭代器地址" << endl;
auto it3 = find_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), myObj);
cout << "use custom object" << endl;
cout << "it3是大于2的迭代器地址" << endl; }
}
int main()
{
luck_count::test_count();
luck_find:: test();
return ;
}
使用方法find和count
sort用法
包含仿函数
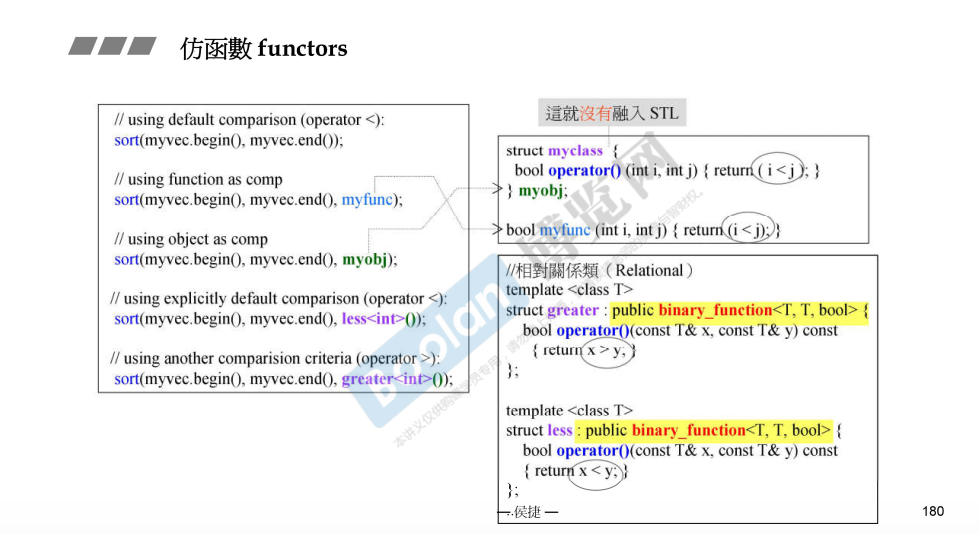
/**使用比较的谓词来排序序列的元素。
* @brief Sort the elements of a sequence using a predicate for comparison.
* @ingroup sorting_algorithms
* @param __first An iterator.
* @param __last Another iterator.
* @param __comp A comparison functor.
* @return Nothing.
*
* Sorts the elements in the range @p [__first,__last) in ascending order,
* such that @p __comp(*(i+1),*i) is false for every iterator @e i in the
* range @p [__first,__last-1).
*
* The relative ordering of equivalent elements is not preserved, use
* @p stable_sort() if this is needed.
*/
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_Mutable_RandomAccessIteratorConcept<
_RandomAccessIterator>)
__glibcxx_function_requires(_BinaryPredicateConcept<_Compare,
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type,
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last);
__glibcxx_requires_irreflexive_pred(__first, __last, __comp); std::__sort(__first, __last, __gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
sort源码
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <functional> namespace luck_sort{
void print(vector<int> &vec)
{
for (auto item : vec)
cout << item << " ";
cout << endl;
}
bool myfun(int i, int j){return i > j;}
struct myclass{
bool operator ()(int i, int j){return i < j;}
}myObj;
// 仿函数对象省略了
void test()
{
vector<int> vec = {,,,,,,,-};
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
cout << "use default 谓词"<<endl;
print(vec); cout << "use default functional"<<endl;
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), less<int>()); // greater<int>() 从大到小排序
print(vec); sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(), myfun);
cout << "use custom fun" << endl;
print(vec); sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(), myObj);
cout << "use custom object" << endl;
print(vec);
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
// luck_count::test_count();
// cout << endl;
// luck_find:: test();
// cout << endl;
luck_sort:: test();
return ;
}
sort用法
仿函数
仿函数:就是一个类里面重载() 所创建出来的对象,叫做函数对象,或者仿函数
有些功能的的代码,会在不同的成员函数中用到,想复用这些代码。
1)公共的函数,可以,这是一个解决方法,不过函数用到的一些变量,就可能成为公共的全局变量,再说为了复用这么一片代码,就要单立出一个函数,也不是很好维护。
2)仿函数,写一个简单类,除了那些维护一个类的成员函数外,就只是实现一个operator(),在类实例化时,就将要用的,非参数的元素传入类中
c和c++中的仿函数
1)c语言使用函数指针和回掉函数来实现仿函数,例如排序函数中使用仿函数:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//int sort_function( const void *a, const void *b);
int sort_function( const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int*)a-*(int*)b;
} int main()
{ int list[] = { , , , , };
qsort((void *)list, , sizeof(list[]), sort_function);//起始地址,个数,元素大小,回调函数 for (auto x = ; x < ; x++)
printf("%d\n", list[x]); return ;
}
2)在C++里,我们通过在一个类中重载括号运算符的方法使用一个函数对象而不是一个普通函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class display
{
public:
void operator()(const T &x)
{
cout<<x<<" ";
}
}; int main()
{
int ia[]={,,,,};
for_each(ia,ia+,display<int>()); //循环遍历数组 return ;
}
仿函数在STL中的定义
要使用STL内建的仿函数,必须包含<functional>头文件。而头文件中包含的仿函数分类包括
1)算术类仿函数
加:plus<T>
减:minus<T>
乘:multiplies<T>
除:divides<T>
模取:modulus<T>
否定:negate<T>
#include <iostream>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std; int main()
{
int ia[]={,,,,};
vector<int> iv(ia,ia+);
cout<<accumulate(iv.begin(),iv.end(),,multiplies<int>())<<endl; //加法 cout<<multiplies<int>()(,)<<endl; //乘法 modulus<int> modulusObj; //取模运算
cout<<modulusObj(,)<<endl; // 3
return ;
}
示例
2)关系运算类仿函数
等于:equal_to<T>
不等于:not_equal_to<T>
大于:greater<T>
大于等于:greater_equal<T>
小于:less<T>
小于等于:less_equal<T>
从大到小排序:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector> using namespace std; template <class T>
class display
{
public:
void operator()(const T &x)
{
cout<<x<<" ";
}
}; int main()
{
int ia[]={,,,,};
vector<int> iv(ia,ia+);
sort(iv.begin(),iv.end(),greater<int>());
for_each(iv.begin(),iv.end(),display<int>());
return ;
}
3)逻辑运算仿函数
逻辑与:logical_and<T>
逻辑或:logical_or<T>
逻辑否:logical_no<T>
bind和适配器

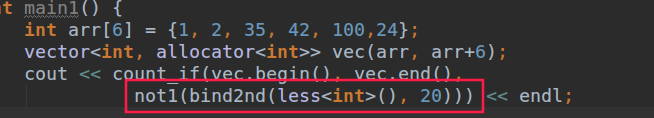
如果想要统计和比20大的数,用自带的仿函数不行,又不像自己写,或者自己写,要写很多,所以用适配器,绑定参数,这里是绑定less中的第二个参数, 原本less中是x>y 现在就变成x>20
这里的调用过程: 在vec的序列中,统计不满足后面的条件的数的个数
Less<int>()是一个临时的仿函数对象(class A ==> A a()) ,不是调用函数
但是现在bind2nd被改成bind bind的功能更加强大,绑定很多个参数
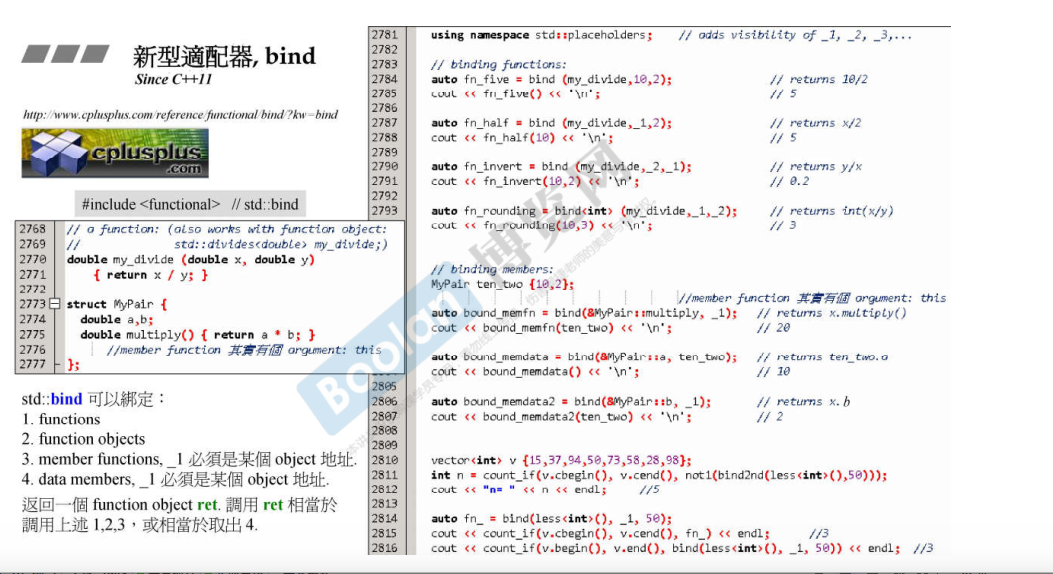
这里主要讲bind的使用
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <functional> namespace luck_bind{
// bind(函数对象,仿函数对象, 对象要的参数_1,_2,...) template<typename T>
void print(vector<T> &vec)
{
for (auto item : vec)
{
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} // a function: (also works with function object: std::divides<double> my_divide;)
double my_divide (double x, double y) {return x/y;} struct MyPair {
double a,b;
double multiply() {return a*b;}
}; void test() {
// 这句话必须写, 还有functional头文件
using namespace std::placeholders; // adds visibility of _1, _2, _3,... // binding functions:
auto fn_five = std::bind (my_divide,,); // returns 10/2
std::cout << fn_five() << '\n'; // auto fn_half = std::bind (my_divide,_1,); // returns x/2
std::cout << fn_half() << '\n'; // auto fn_invert = std::bind (my_divide,_2,_1); // returns y/x
std::cout << fn_invert(,) << '\n'; // 0.2 auto fn_rounding = std::bind<int> (my_divide,_1,_2); // returns int(x/y)
std::cout << fn_rounding(,) << '\n'; // MyPair ten_two {,}; // binding members:
auto bound_member_fn = std::bind (&MyPair::multiply,_1); // returns x.multiply()
std::cout << bound_member_fn(ten_two) << '\n'; // auto bound_member_data = std::bind (&MyPair::a,ten_two); // returns ten_two.a
std::cout << bound_member_data() << '\n'; // vector<int> vec = {,,,,,-,};
cout << "bind and bind2nd different"<<endl;
cout << count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), not1(bind2nd(less<int>(), ))) << endl; cout << "use bind of count_if"<<endl;
auto fn = bind(less<int>(), _1, );
cout << count_if(vec.begin(), vec.end(), fn); // 小于4的有几个 4个 cout << "\nbind sort" << endl;
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), less<int>()); print<int>(vec); // 模板函数
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), bind(less<int>(), _2, _1));
print<int>(vec);
}
} int main()
{
// luck_count::test_count();
// cout << endl;
// luck_find:: test();
// cout << endl;
// luck_sort:: test();
luck_bind::test(); return ;
}
测试_必看
STL杂记的更多相关文章
- 面试基础知识集合(python、计算机网络、操作系统、数据结构、数据库等杂记)
python python _.__.__xx__之间的差别 python中range.xrange和randrange的区别 python中 =.copy.deepcopy的差别 python 继承 ...
- 2016.6.19——C++杂记
C++杂记 补充的小知识点: 1.while(n--)和while(--n)区别: while(n--)即使不满足也执行一次循环后跳出. while(--n)不满足直接跳出循环,不执行语句. 用cou ...
- 详细解说 STL 排序(Sort)
0 前言: STL,为什么你必须掌握 对于程序员来说,数据结构是必修的一门课.从查找到排序,从链表到二叉树,几乎所有的算法和原理都需要理解,理解不了也要死记硬背下来.幸运的是这些理论都已经比较成熟,算 ...
- STL标准模板库(简介)
标准模板库(STL,Standard Template Library)是C++标准库的重要组成部分,包含了诸多在计算机科学领域里所常见的基本数据结构和基本算法,为广大C++程序员提供了一个可扩展的应 ...
- STL的std::find和std::find_if
std::find是用来查找容器元素算法,但是它只能查找容器元素为基本数据类型,如果想要查找类类型,应该使用find_if. 小例子: #include "stdafx.h" #i ...
- STL: unordered_map 自定义键值使用
使用Windows下 RECT 类型做unordered_map 键值 1. Hash 函数 计算自定义类型的hash值. struct hash_RECT { size_t operator()(c ...
- C++ STL简述
前言 最近要找工作,免不得要有一番笔试,今年好像突然就都流行在线笔试了,真是搞的我一塌糊涂.有的公司呢,不支持Python,Java我也不会,C有些数据结构又有些复杂,所以是时候把STL再看一遍了-不 ...
- [Erlang 0118] Erlang 杂记 V
我在知乎回答问题不多,这个问题: "对你职业生涯帮助最大的习惯是什么?它是如何帮助你的?",我还是主动回答了一下. 做笔记 一开始笔记软件做的不好的时候就发邮件给自己, ...
- codevs 1285 二叉查找树STL基本用法
C++STL库的set就是一个二叉查找树,并且支持结构体. 在写结构体式的二叉查找树时,需要在结构体里面定义操作符 < ,因为需要比较. set经常会用到迭代器,这里说明一下迭代器:可以类似的把 ...
随机推荐
- OSS文档1
简介: OSS 对象存储 用于单独存储文件视频音频类等文件 上传方式: 普通上传: 单文件普通上传 分片上传: 文件切片后上传,完成后组合,适合大文件,弱网络 追加上传: 流文件上传, ...
- Linux引导过程与服务控制
一:系统引导流程: 开机自检(BIOS)-->MBR引导-->GRUB菜单-->加载内核(kernel)-->init进程初始化 二:系统引导级别: 0 poweroff.t ...
- .Net Core 基于CAP框架的事件总线
.Net Core 基于CAP框架的事件总线 CAP 是一个在分布式系统中(SOA,MicroService)实现事件总线及最终一致性(分布式事务)的一个开源的 C# 库,她具有轻量级,高性能,易使用 ...
- luogu P5606 小 K 与毕业旅行 - 构造 - 多项式
题目传送门 传送门 先考虑 $a_i > 0$ 的情况.考虑构造这样一个顺序:$a_i$ 要么和后面的数的乘积都大于 $w$ 要么都小于等于 $w$. 这个构造可以这样做: vector< ...
- 推荐WEB 端批量移动设备管理控制工具STF
推荐WEB 端批量移动设备管理控制工具STF 1 官方网站 https://openstf.io/ 2 github https://github.com/openstf/stf 后面有时间了,抽空也 ...
- etcd v3 ssl 集群添加新节点
集群搭建 下面只用同一台服务器进行三个成员节点的开启 节点1 ./etcd --name cd0 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2380 ...
- C++ 类中的3种访问权限和继承方式
访问权限:public 可以被任意实体访问,protected 只允许子类(无论什么继承方式)及本类的成员函数访问,private 只允许本类的成员函数访问.三种继承方式分别是 public 继承,p ...
- html5手机端播放音效不卡的方法
html5手机端播放音效不卡的方法线下载http://wxserver.knowway.cn/solosea/js/audioEngine.js 这个是性能不错 然后直接播放音效就可以了 audioE ...
- Jenkins集成Sonar Quabe和权限配置
目录 安装Sonar Jenkins配置sonar Maven Jenkins Job配置 Pipeline Jenkins Job配置 Sonar权限管理 Sonar quality Gate通过阈 ...
- vue-v-xxx基于 Vue拓展的 v-xxx 库
君问归期未有期,巴山夜雨涨秋池. 何当共剪西窗烛,却话巴山夜雨时. 作为vue轻车熟路的老司机,经常会用到一些指令,vue官方提供的指令又太少,无法满足旺盛的欲望,而每次要写一遍,终日郁郁寡欢,从小就 ...
