201871010132--张潇潇--《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十一周学习总结
博文正文开头格式:(2分)
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11435127.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
|
第一部分:总结第八章关于泛型程序设计理论知识(25分)
8.1 为什么要使用泛型程序设计
从Java1.0版发布以来,变化最大的就是泛型。使用泛型机制编写的程序代码要比那些杂乱的使用object变量,然后再进行强制类型转换的代码具有更好的安全性和可读性
泛型程序设计意味着编写的代码可以被很多不同类型的对象所重用。
在Java中增加泛型类之前,泛型程序设计是用继承实现的。但是有两个问题:
当获取一个值时必须进行强制类型转换
这里没有错误检查,可以向数组列表中添加任何类的对象
类型参数的魅力在于:使得程序具有更好的可读性和安全性
JDK开发人员已经做出了很大的努力,为所有的集合类提供类类型参数!!!
8.2 定义简单泛型类
类型变量使用大写形式,且比较短,这是很常见的。在Java库中,使用变量E来表示集合的元素类型,K和V来表示关键字与值的类型。T表示“任意类型”
8.3 泛型方法
实际上,还可以定义一个带有类型参数的简单方法:
class ArrayAlg{
public static<T> T getMiddle(T...a) {
return a[a.lengtyh / 2];
}
}
类型变量放在修饰符的后面,返回类型的前面。当调用一个泛型方法时,在方法名钱的尖括号中放入具体的类型:
String middle = ArrayAlg.<String>getMiddle("John", "Holk");
1
8.4 类型变量的限定
有时,类或方法需要对类型变量加以约束
class ArrayAlg{
public static<T> T min(T[] a) {
if(a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T smallest = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < a.length;i++)
if(smallest.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) smallest = a[i]
return smallest;
}
}
这里有·问题,解决问题的方法是实现Comparator接口
public static <T extends Comparator> T min(T[] a)...
1
一个类型变量或通配符可以有多个限定,例如:
T extends Comparator & Serializable
限定类型用&分割,逗号用来分割类型变量
在Java的继承中,可以根据需要拥有多个接口超类型,但限定类只能有一个。如果用一个类做限定,必须把这个类写在限定列表的第一个
8.5 泛型代码和虚拟机
原始类型用一个限定类型变量来替换,如果没有限定就替换成Object(类型擦除)
关于Java泛型转换的事实:
虚拟机中没有泛型,只有普通的类或方法
所有类型参数都用它们的限定类型替换
桥方法被合成来保持多态
为保持类型安全性,必要时加入强制类型转换
8.6 约束和局限性
不能用基本类型实例化类型参数
运行时类型查询只适用于原始类型
不能创建参数化类型的数组
Varargs警告
不能实例化类型变量
不能构造泛型数组
泛型类的静态上下文中类型变量无效
不能抛出或捕获泛型类的实例
可以消除对受查异常的检查
注意擦除后的冲突
8.7通配符:“?”符号表明参数的类型可以是任何一种类型,而T表示一种未知类型。
通配符的一般用法:a.?:用于表示任何类型;
b.? extends type,表示带有上界;
c.? super type,表示带有下界。
二:实验部分。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解泛型概念;
(2) 掌握泛型类的定义与使用;
(3) 掌握泛型方法的声明与使用;
(4) 掌握泛型接口的定义与实现;
(5)了解泛型程序设计,理解其用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第8章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、调试、运行教材311、312页 代码,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型类定义及使用代码处添加注释;
l 掌握泛型类的定义及使用。
程序如下:
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] words = { "Mary", "had", "a", "little", "lamb" };//初始化一个String对象数组
Pair<String> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(words);//一对字符串:min,max
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
* Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of strings.
* @param a an array of strings
* @return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is null or empty
*/
public static Pair<String> minmax(String[] a)//普通方法,定义minmax为字符串类型
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
String min = a[0];
String max = a[0];
//将元素的泛型具体声明 for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)//length:数组属性值
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}//实现字符串比较大小
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T>//类型变量(放在类名后面)
{
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
运行结果如下:

测试程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材315页 PairTest2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在泛型程序设计代码处添加相关注释;
l 掌握泛型方法、泛型变量限定的定义及用途。
程序如下:
import java.time.*; /**
* @version 1.02 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LocalDate[] birthdays =
{
LocalDate.of(1906, 12, 9), // G. Hopper
LocalDate.of(1815, 12, 10), // A. Lovelace
LocalDate.of(1903, 12, 3), // J. von Neumann
LocalDate.of(1910, 6, 22), // K. Zuse
};
Pair<LocalDate> mm = ArrayAlg.minmax(birthdays);
System.out.println("min = " + mm.getFirst());
System.out.println("max = " + mm.getSecond());
}
} class ArrayAlg
{
/**
Gets the minimum and maximum of an array of objects of type T.
@param a an array of objects of type T
@return a pair with the min and max value, or null if a is
null or empty
*/
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a) //泛型方法(comparable是T的上界约束)
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];//min和max与T的类型一致
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<>(min, max);
}
}
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T> //类型变量
{
private T first;
private T second; public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
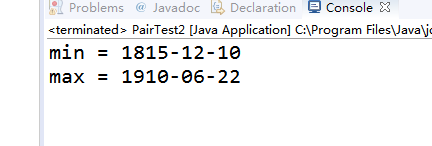
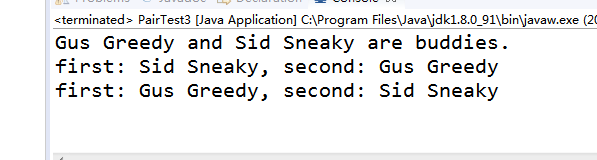
测试程序3:
l 用调试运行教材335页 PairTest3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解通配符类型的定义及用途。
程序如下:
/**
* @version 1.01 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PairTest3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Manager ceo = new Manager("Gus Greedy", 800000, 2003, 12, 15);
Manager cfo = new Manager("Sid Sneaky", 600000, 2003, 12, 15);
Pair<Manager> buddies = new Pair<>(ceo, cfo);
printBuddies(buddies); ceo.setBonus(1000000);
cfo.setBonus(500000);
Manager[] managers = { ceo, cfo }; Pair<Employee> result = new Pair<>(); minmaxBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
maxminBonus(managers, result);
System.out.println("first: " + result.getFirst().getName()
+ ", second: " + result.getSecond().getName());
} public static void printBuddies(Pair<? extends Employee> p)//通配符类型(带有上界)extends关键字所声明的上界既可以是一个类,也可以是一个接口。
{
Employee first = p.getFirst();
Employee second = p.getSecond();
System.out.println(first.getName() + " and " + second.getName() + " are buddies.");
} public static void minmaxBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//通配符类型(带有下界)必须是Manager的子类
{
if (a.length == 0) return;
Manager min = a[0];
Manager max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.getBonus() > a[i].getBonus()) min = a[i];
if (max.getBonus() < a[i].getBonus()) max = a[i];
}//比较大小值
result.setFirst(min);
result.setSecond(max);
} public static void maxminBonus(Manager[] a, Pair<? super Manager> result)//通配符类型(带有下界)
{
minmaxBonus(a, result);
PairAlg.swapHelper(result); //swapHelper捕获通配符类型
}
//无法编写公共静态< T超级管理器>
} class PairAlg
{
public static boolean hasNulls(Pair<?> p)//通过将hasNulls转换成泛型方法,避免使用通配符类型
{
return p.getFirst() == null || p.getSecond() == null;
} public static void swap(Pair<?> p) { swapHelper(p); } public static <T> void swapHelper(Pair<T> p)//使用辅助方法swapHelper(泛型方法),以在交换时临时保存第一个元素
{
T t = p.getFirst();
p.setFirst(p.getSecond());
p.setSecond(t);
}
}
/**
* @version 1.00 2004-05-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Pair<T>
{
private T first;
private T second;
//T是未知类型,不代表值
public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; } public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; } public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
}
import java.time.*; public class Employee//用户自定义类
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day);
} public String getName()
{
return name;
} public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
} public LocalDate getHireDay()
{
return hireDay;
} public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
public class Manager extends Employee//继承类
{
private double bonus; /**
@param name the employee's name
@param salary the salary
@param year the hire year
@param month the hire month
@param day the hire day
*/
public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day)
{
super(name, salary, year, month, day);
bonus = 0;
} public double getSalary()
{
double baseSalary = super.getSalary();
return baseSalary + bonus;
} public void setBonus(double b)
{
bonus = b;
} public double getBonus()
{
return bonus;
}
}
实验2:结对编程练习(32分)
(1)编写一个泛型接口GeneralStack,要求类中方法对任何引用类型数据都适用。GeneralStack接口中方法如下:
push(item); //如item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。
pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。
peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty();//如为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量
(2)定义GeneralStack的子类ArrayListGeneralStack,要求:
ü 类内使用ArrayList对象存储堆栈数据,名为list;
ü 方法: public String toString()//代码为return list.toString();
ü 代码中不要出现类型不安全的强制转换。
(3)定义Car类,类的属性有:
private int id;
private String name;
方法:Eclipse自动生成setter/getter,toString方法。
(4)main方法要求
ü 输入选项,有quit, Integer, Double, Car 4个选项。如果输入quit,程序直接退出。否则,输入整数m与n。m代表入栈个数,n代表出栈个数。然后声明栈变量stack。
ü 输入Integer,打印Integer Test。建立可以存放Integer类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。入栈m次,出栈n次。打印栈的toString方法。最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
ü 输入Double ,打印Double Test。剩下的与输入Integer一样。
ü 输入Car,打印Car Test。其他操作与Integer、Double基本一样。只不过最后将栈中元素出栈,并将其name依次输出。
特别注意:如果栈为空,继续出栈,返回null
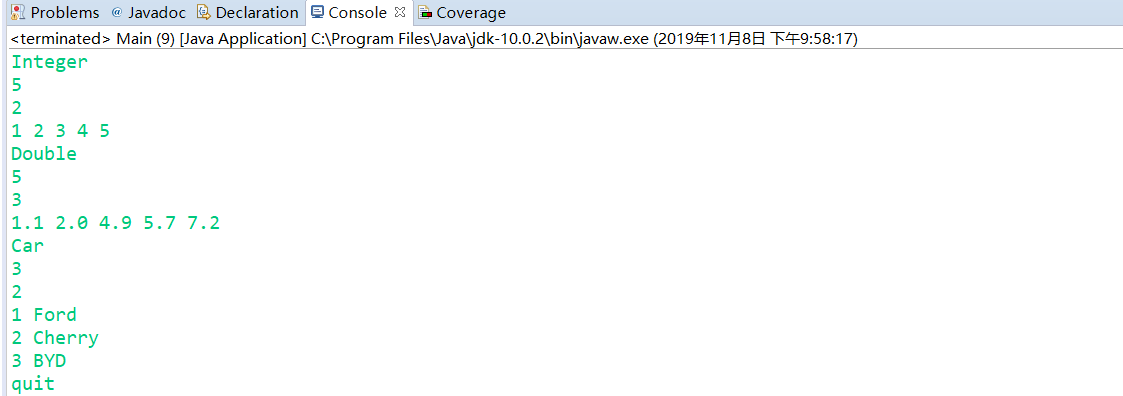
输入样例
Integer
5
2
1 2 3 4 5
Double
5
3
1.1 2.0 4.9 5.7 7.2
Car
3
2
1 Ford
2 Cherry
3 BYD
quit
输出样例
Integer Test
push:1
push:2
push:3
push:4
push:5
pop:5
pop:4
[1, 2, 3]
sum=6
interface GeneralStack
Double Test
push:1.1
push:2.0
push:4.9
push:5.7
push:7.2
pop:7.2
pop:5.7
pop:4.9
[1.1, 2.0]
sum=3.1
interface GeneralStack
Car Test
push:Car [id=1, name=Ford]
push:Car [id=2, name=Cherry]
push:Car [id=3, name=BYD]
pop:Car [id=3, name=BYD]
pop:Car [id=2, name=Cherry]
[Car [id=1, name=Ford]]
Ford
interface GeneralStack
实验代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner; interface GeneralStack<T>{
public T push(T item); //如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。
public T pop(); //出栈,如为栈为空,则返回null。
public T peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty(); //如为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素数量
}
class ArrayListGeneralStack implements GeneralStack{ //创建一个实现GeneralStack接口的类
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
@Override //重写toString方法
public String toString() {
return list.toString();
} @Override //重写压栈方法
public Object push(Object item) {
if (list.add(item)){
return item;
}else {
return false;
}
} @Override //重写出栈方法
public Object pop() {
if (list.size()==0){ //判断栈为空时,返回null
return null;
}
return list.remove(list.size()-1);
} @Override //重写获取栈顶元素的函数
public Object peek() {
return list.get(list.size()-1);
} @Override
public boolean empty() { //栈为空时,直接返回boolean值
if (list.size()==0){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
} @Override //重写得到栈中元素个数的函数
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
} class Car{ //定义一个Car类
private int id; //两个私有属性
private String name; @Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [" +
"id=" + id +
", name=" + name +
']';
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Car(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
String s=sc.nextLine();
//输入选项,有quit, Integer, Double, Car 4个选项。
if (s.equals("Double")){ //输入Double ,打印Double Test。
System.out.println("Double Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack();//建立可以存放Double类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(sc.nextDouble()));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //打印栈的toString方法
double sum=0;
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
sum+=(double)arrayListGeneralStack.pop(); //最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("Integer")){ //输入Integer,打印Integer Test。
System.out.println("Integer Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack();//建立可以存放Integer类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(sc.nextInt()));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //打印栈的toString方法。
int sum=0;
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
sum+=(int)arrayListGeneralStack.pop(); //最后将栈中剩余元素出栈并累加输出。
}
System.out.println("sum="+sum);
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("Car")){ //输入Car,打印Car Test。
System.out.println("Car Test");
int count=sc.nextInt();
int pop_time=sc.nextInt();
ArrayListGeneralStack arrayListGeneralStack = new ArrayListGeneralStack(); //创建可以存放Car类型的ArrayListGeneralStack。
for (int i=0;i<count;i++){ //入栈次数
int id=sc.nextInt();
String name=sc.next();
Car car = new Car(id,name);
System.out.println("push:"+arrayListGeneralStack.push(car));
}
for (int i=0;i<pop_time;i++){ //出栈次数
System.out.println("pop:"+arrayListGeneralStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(arrayListGeneralStack.toString()); //定义toString方法
if (arrayListGeneralStack.size()>0){ //栈不为空
int size=arrayListGeneralStack.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++){
Car car=(Car) arrayListGeneralStack.pop();//将栈中元素出栈,并将其name依次输出。
System.out.println(car.getName());
}
}
System.out.println("interface GeneralStack");
}else if (s.equals("quit")){ //如果输入quit,程序直接退出。
break;
}
} }
}

三:实验总结。
这周主要学习了泛型程序,泛型类和泛型方法同时具备可重用性、类型安全和效率,泛型类不会强行对值类型进行装箱和拆箱,或对引用类型进行向下强制类型转换,所以是编程性能得到提高。在学习理论课时,听老师讲泛型类不算特别难,但在实验课上运行程序时,并不是太理解程序,经过老师和学长的讲解,对程序有了一定程度的理解,但是也只是基本能读懂程序,在自己编程时,还是有很大问题。在之后的学习中,我会多练习程序去了解这些知识,争取能够独立完整的编写程序。

201871010132--张潇潇--《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十一周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 20175227张雪莹 2018-2019-2 《Java程序设计》第十一周学习总结
20175227张雪莹 2018-2019-2 <Java程序设计>第十一周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第十三章 Java网络编程 URL类 一个URL对象通常包含最基本的三部分信息:协议 ...
随机推荐
- 快读&快写模板【附O2优化】
快读&快写模板 快读快写,顾名思义,就是提升输入和输出的速度.在这里简单介绍一下几种输入输出的优劣. C++ cin/cout 输入输出:优点是读入的时候不用管数据类型,也就是说不用背scan ...
- 【2019.7.22 NOIP模拟赛 T1】麦克斯韦妖(demon)(质因数分解+DP)
暴力\(DP\) 先考虑暴力\(DP\)该怎么写. 因为每个序列之后是否能加上新的节点只与其结尾有关,因此我们设\(f_i\)为以\(i\)为结尾的最长序列长度. 每次枚举一个前置状态,判断是否合法之 ...
- 调试九法: 软硬件错误的排查之道 (David J. Agans 著)
第1章 简介 (已看) 第2章 总体规则 (已看) 第3章 理解系统 (已看) 第4章 制造失败 第5章 不要想, 而要看 第6章 分而治之 第7章 一次只改一个地方 第8章 保持审计跟踪 第9章 检 ...
- 封装cookie的设置和获取
cookie的设置 function setCookie(key,value,options){ options=options||{}; var time=""; if(opti ...
- 【shell脚本】定时备份日志===logBackup.sh
定时备份日志 设置执行权限 [root@VM_0_10_centos shellScript]# chmod a+x logBackup,sh 脚本内容 [root@VM_0_10_centos sh ...
- Windows Terminal (Preview)治好了cmd,powershell的癌症
前言 话说n年前,我想开发一款powershell麻将游戏,但是发现命令行下无法显示麻将牌这种特殊符号. 经过研究发现,这是4字节的utf16le字符串.而powershell依赖的渲染引擎,只能渲染 ...
- Unsupervised Attention-guided Image-to-Image Translation
这是NeurIPS 2018一篇图像翻译的文章.目前的无监督图像到图像的翻译技术很难在不改变背景或场景中多个对象交互方式的情况下将注意力集中在改变的对象上去.这篇文章的解决思路是使用注意力导向来进行图 ...
- RFC的远程调用-异步
接上篇RFC的远程调用-同步(https://www.cnblogs.com/BruceKing/p/11169930.html). TABLES:USR21. DATA:A TYPE USR21-P ...
- mysql建表中auto_increment=21
CREATE TABLE `demo` ( `id` ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `img` ) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '大图', `status` ) ...
- C#,WPF,DataGrid,Excel,导出
private void btnExport_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw = n ...
