android双进程守护,让程序崩溃后一定可以重启
由于我们做的是机器人上的软件,而机器人是24小时不间断服务的,这就要求我们的软件不能退出到系统桌面。当然最好是能够做到程序能够不卡顿,不崩溃,自己不退出。由于我们引用了很多第三方的开发包,也不能保证他们的稳定性,所以,要做到完全不崩溃也是不可能的。
退而求其次,如果崩溃了我们就要保证程序能够被拉起来,期间也看过很多保活的方案,比如service前台的方法,比如jni里写守护进程,比如接收系统广播唤醒,比如用alarmmanager唤醒等等,感觉不是效率底,就是被系统屏蔽了。经过不断筛选,我认为使用aidl进行双进程守护其实是效率很好的一个解决方案。
其实这个原理也很简单,简单的说就是创建两个service,其中一个再程序主进程,另外一个在其他进程,这两个进程通过aidl通信,一旦其中一个进程断开连接,那么就重启该服务,两个程序互相监听,就能够做到一方被杀死,另一方被启动了。当然,如果使用 adb shell force-stop packageName的方法杀死程序,肯定是不能够重启的。这种方式仅仅是为了避免ndk层崩溃,java抓不到从而不能使用java层重启应用的一种补充方式。要想做到完全不被杀死,那就太流氓了。
说了这么多,看代码吧
两个service,localservice和remoteservice
LocalService.java
package guide.yunji.com.guide.processGuard; import android.app.Application;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast; import guide.yunji.com.guide.MyApplication;
import guide.yunji.com.guide.activity.MainActivity;
import guide.yunji.com.guide.testFace.IMyAidlInterface; public class LocalService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = LocalService.class.getName();
private MyBinder mBinder; private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
Log.e("LocalService", "connected with " + iMyAidlInterface.getServiceName());
//TODO whh 本地service被拉起,检测如果mainActivity不存在则拉起
if (MyApplication.getMainActivity() == null) {
Intent intent = new Intent(LocalService.this.getBaseContext(), MainActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
getApplication().startActivity(intent);
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} @Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Toast.makeText(LocalService.this, "链接断开,重新启动 RemoteService", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.e(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected: 链接断开,重新启动 RemoteService");
startService(new Intent(LocalService.this, RemoteService.class));
bindService(new Intent(LocalService.this, RemoteService.class), connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
}
}; public LocalService() {
} @Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
} @Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "onStartCommand: LocalService 启动");
Toast.makeText(this, "LocalService 启动", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
startService(new Intent(LocalService.this, RemoteService.class));
bindService(new Intent(LocalService.this, RemoteService.class), connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
return START_STICKY;
} @Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mBinder = new MyBinder();
return mBinder;
} private class MyBinder extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub { @Override
public String getServiceName() throws RemoteException {
return LocalService.class.getName();
} @Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException { }
}
}
RemoteService.java
package guide.yunji.com.guide.processGuard; import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast; import guide.yunji.com.guide.testFace.IMyAidlInterface; public class RemoteService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = RemoteService.class.getName();
private MyBinder mBinder; private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
IMyAidlInterface iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
Log.e(TAG, "connected with " + iMyAidlInterface.getServiceName());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} @Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.e(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected: 链接断开,重新启动 LocalService");
Toast.makeText(RemoteService.this, "链接断开,重新启动 LocalService", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
startService(new Intent(RemoteService.this, LocalService.class));
bindService(new Intent(RemoteService.this, LocalService.class), connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
}
}; public RemoteService() {
} @Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "onStartCommand: RemoteService 启动");
Toast.makeText(this, "RemoteService 启动", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
bindService(new Intent(this, LocalService.class), connection, Context.BIND_IMPORTANT);
return START_STICKY;
} @Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
mBinder = new MyBinder();
return mBinder;
} private class MyBinder extends IMyAidlInterface.Stub { @Override
public String getServiceName() throws RemoteException {
return RemoteService.class.getName();
} @Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException { }
}
}
注意,两个service要在不通的进程
<service
android:name=".processGuard.LocalService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true" />
<service
android:name=".processGuard.RemoteService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":RemoteProcess" />
两个service通过aidl连接,如下
// IMyAidlInterface.aidl
package guide.yunji.com.guide.testFace; // Declare any non-default types here with import statements interface IMyAidlInterface {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
double aDouble, String aString);
String getServiceName();
}
此外还要注意一点,程序的service初始化的时候如果在自定义的application的时候要注意多进程的问题,本来LocalService是在主进程中启动的,所以要做一下进程的判断,如下:
package com.honghe.guardtest; import android.app.ActivityManager;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent; public class MyApplication extends Application {
private static MainActivity mainActivity = null; public static MainActivity getMainActivity() {
return mainActivity;
} public static void setMainActivity(MainActivity activity) {
mainActivity = activity;
} @Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
if (isMainProcess(getApplicationContext())) {
startService(new Intent(this, LocalService.class));
} else {
return;
}
} /**
* 获取当前进程名
*/
public String getCurrentProcessName(Context context) {
int pid = android.os.Process.myPid();
String processName = "";
ActivityManager manager = (ActivityManager) context.getApplicationContext().getSystemService
(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
for (ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo process : manager.getRunningAppProcesses()) {
if (process.pid == pid) {
processName = process.processName;
}
}
return processName;
} public boolean isMainProcess(Context context) {
/**
* 是否为主进程
*/
boolean isMainProcess;
isMainProcess = context.getApplicationContext().getPackageName().equals
(getCurrentProcessName(context));
return isMainProcess;
}
}
然后LocalService重启后,可以判断是否要开启程序的主界面,上面的localService已经写了,就不多介绍了。
代码已经有了,我们怎么测试呢?
当然是伪造一个ndk的崩溃来验证程序的可行性了。
我们写一个jni,如下

写一个Jni的类
JniLoaderndk.cpp
#include <string.h>
#include <jni.h>
#include <stdio.h> //#include "yue_excample_hello_JniLoader.h"
//按照C语言规则编译。jni依照C的规则查找函数,而不是C++,没有这一句运行时会崩溃报错:
// java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: Native method not found:
extern "C"{ JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_honghe_guardtest_JniLoader_getHelloString
(JNIEnv *env, jobject _this)
{
int m=;
int n=;
int j=m/n;
printf("hello %d",j);
Java_com_honghe_guardtest_JniLoader_getHelloString(env,_this);
//return (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, "Hello world from jni)");//C语言格式,文件名应为xxx.c
return env->NewStringUTF((char *)("hello whh"));//C++格式,文件名应为xxx.cpp
} }
为什么这么写,因为我本来想通过除0来制造异常,但是ndk本身并不向上层因为除0崩溃,后来无奈只好使用递归来制造崩溃了。
android.mk
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS) # 要生成的.so库名称。java代码System.loadLibrary("firstndk");加载的就是它
LOCAL_MODULE := firstndk # C++文件
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := JniLoaderndk.cpp include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
application.mk
# 注释掉了,不写会生成全部支持的平台。目前支持:
APP_ABI := armeabi arm64-v8a armeabi-v7a mips mips64 x86 x86_64
#APP_ABI := armeabi-v7a
写完了ndk后需要到jni的目录下执行一个 ndk-build 的命令,这样会在main目录下生成libs文件夹,文件夹中有目标平台的so文件,但是android默认不会读取该目录的so文件,所以我们需要在app/build.gradle中加入路径,使程序能够识别so
sourceSets {
main {
jniLibs.srcDirs = ['src/main/libs']//默认为jniLibs
}
}
弄好后,就可以在安卓程序中找到ndk中的方法了。
创建调用类
JniLoader.java
package com.honghe.guardtest;
public class JniLoader {
static {
System.loadLibrary("firstndk");
}
public native String getHelloString();
}
调用该方法就能够发现程序在ndk影响下崩溃了,如图

看logcat
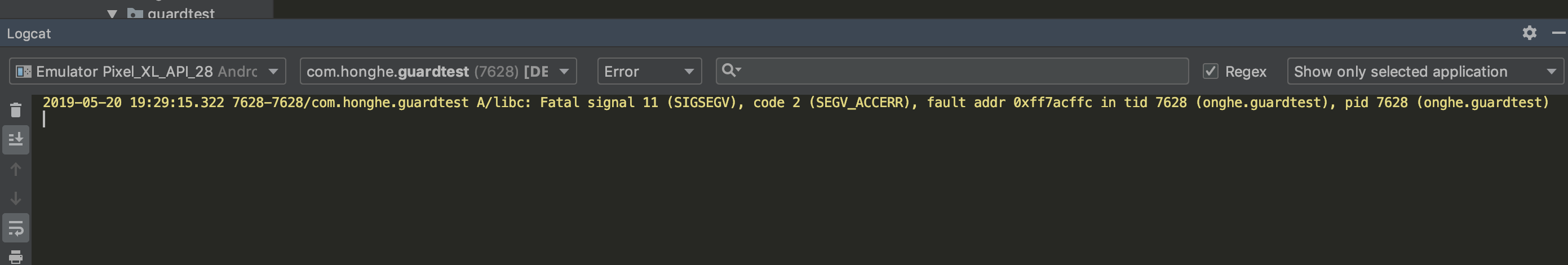
说明旧的进程由于ndk崩溃被杀死了,但是看界面里程序已经重启了,然后还多出了一个不通pid的同名进程,如下
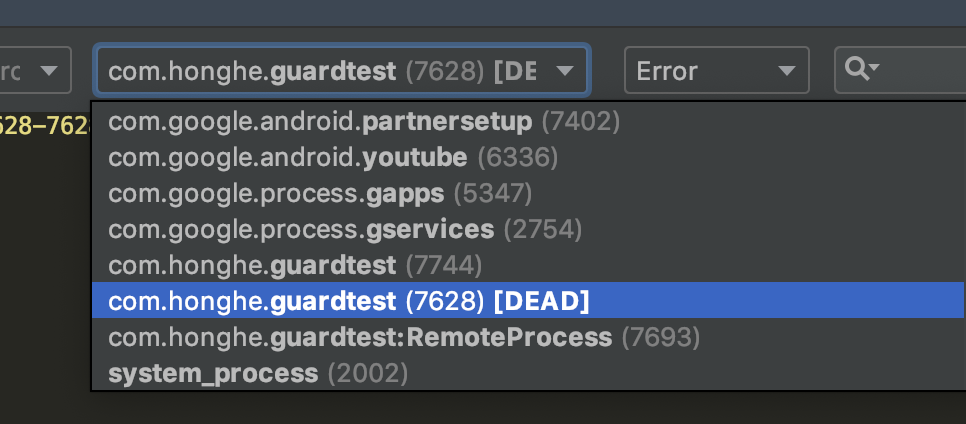
证明ndk崩溃后我们的软件重启成功了。
代码全部在github,如下
https://github.com/dongweiq/guardTest
我的github地址:https://github.com/dongweiq/study
欢迎关注,欢迎star o(∩_∩)o 。有什么问题请邮箱联系 dongweiqmail@gmail.com qq714094450
android双进程守护,让程序崩溃后一定可以重启的更多相关文章
- Android 保持Service不被Kill掉的方法--双Service守护 && Android实现双进程守护
本文分为两个部分,第一部分为双Service守护,第二部分为双进程守护 第一部分: 一.Service简介:Java.lang.Object ↳Android.content.Context ↳an ...
- Android实现双进程守护 (转)
做过android开发的人应该都知道应用会在系统资源匮乏的情况下被系统杀死!当后台的应用被系统回收之后,如何重新恢复它呢?网上对此问题有很多的讨论.这里先总结一下网上流传的各种解决方案,看看这些办法是 ...
- 保持Service不被Kill掉的方法--双Service守护 && Android实现双进程守护
本文分为两个部分,第一部分为双Service守护,第二部分为双进程守护 第一部分: 一.Service简介:Java.lang.Object ↳Android.content.Context ↳an ...
- Android NDK(C++) 双进程守护
双进程守护如果从进程管理器观察会发现新浪微博.支付宝和QQ等都有两个以上相关进程,其中一个就是守护进程,由此可以猜到这些商业级的软件都采用了双进程守护的办法. 什么是双进程守护呢?顾名思义就是两个进程 ...
- Android实现双进程守护
做过android开发的人应该都知道应用会在系统资源匮乏的情况下被系统杀死!当后台的应用被系统回收之后,如何重新恢复它呢?网上对此问题有很多的讨论.这里先总结一下网上流传的各种解决方案,看看这些办法是 ...
- 结合程序崩溃后的core文件分析bug
引言 在<I/O的效率比较>中,我们在修改图1程序的BUF_SIZE为8388608时,运行程序出现崩溃,如下图1: 图1. 段错误 一般而言,导致程序段 ...
- Window提高_3.1练习_双进程守护
双进程守护 当打开一个进程A的时候,此进程检测是否存在进程B,如果不存在就创建进程B. 进程B的作用是检测进程A是否被关闭,如果被关闭了,就再创建一个进程A. 双进程守护A.exe代码如下: #inc ...
- jenkins结合supervisor进行python程序发布后的自动重启
jenkins结合supervisor进行python程序发布后的自动重启 项目背景: 通过jenkins发布kvaccount.chinasoft.com站点的python服务端程序,业务部门同事需 ...
- android程序崩溃后重启
有时候由于测试不充分或者程序潜在的问题而导致程序异常崩溃,这个是令人无法接受的,在android中怎样捕获程序的异常崩溃,然后进行一些必要的处理或重新启动 应用这个问题困恼了我很久,今天终于解决了该问 ...
随机推荐
- mysql-luster没有data目录
mysqld --initialize-insecure --user=mysql 直接复制上面这条命令 然后cmd进入到 mysql解压出来bin的目录中: 等待一会 就发发现data的这个目录了 ...
- windows jupyter notebook 切换默认环境
windows jupyter notebook 切换默认环境 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://blog ...
- 机器学习笔记6:K-Means
目录 目标函数 目标函数的表现函数 针对u和r求解: 最优解的表达式的意义: K-means聚类的形象化展示 聚类前 第一轮循环 第二轮循环 第三轮循环 最终结果 演示代码: 关于K-means的几个 ...
- Django之mysql数据库配置
在settings.py中配置 DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', # 数据库引擎 'NAME': 'my ...
- Docker 修改容器内的时区
利用docker发布服务,发现 程序用获取的系统时间比正常时间晚了8个小时 进入容器 docker exec -it /bin/sh 查询时间 date -R 发现时区为0时区 解决思路 1.复制相应 ...
- pip换源-换成国内的源
PyPI使用国内源 通过几次 pip 的使用,对于默认的 pip 源的速度实在无法忍受,于是便搜集了一些国内的pip源,如下: 阿里云 http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi ...
- moya与网络编程思想:网络请求的生命周期
请求数据管理的集中化: 请求配置的标注化: 请求管理的函数式参量化: 几个端点: target代表应用端的原始数据; endpoint代表应用端到网络端的中间数据,这个数据可以编辑公用数据header ...
- react 沉思录
react = Virtual DOM + component + data flow + jsx 核心是Virtual DOM结构的状态维护.渲染机制及UI系统的DOM组织功能: 基于Virtual ...
- Linux yum 包 下载地址
yum包网址: http://www.rpmfind.net/linux/rpm2html/search.php?query=yum
- 8-ESP8266 SDK开发基础入门篇--编写串口上位机软件
https://www.cnblogs.com/yangfengwu/p/11087558.html 咱用这个编写 ,版本都无所谓哈,只要自己有就可以,不同版本怎么打开 https://www.cnb ...
