数据结构实验7:实现二分查找、二叉排序(查找)树和AVL树
实验7
学号: 姓名: 专业:
7.1实验目的
(1) 掌握顺序表的查找方法,尤其是二分查找方法。
(2) 掌握二叉排序树的建立及查找。
查找是软件设计中的最常用的运算,查找所涉及到的表结构的不同决定了查找的方法及其性能。二分查找是顺序表的查找中的最重要的方法,应能充分理解其实现方法和有关性能,并能借助其判定树结构来加深理解。二叉排序树结构在实验时具有一定的难度,可结合二叉树的有关内容和方法来实现。
7.2 实验任务
编写算法实现下列问题的求解。
(1) 对下列数据表,分别采用二分查找算法实现查找,给出查找过程依次所比较的元素(的下标),并以二分查找的判定树来解释。
第一组测试数据:
数据表为 (1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,17,18,19,20,24,25,26,30,35,40,45,50,100)
查找的元素分别为: 2,8,20, 30,50,5,15,33,110
第二组数据:
数据表为 (2,3,5,7,8,10,12,15,18,20,22,25,30,35,40,45,50,55,60, 80,100)
查找的元素分别为: 22,8,80,3,100,1,13,120
(2) 设计出在二叉排序树中插入结点的算法,在此基础上实现构建二叉排序树的算法。
测试数据:构建二叉排序树的输入序列如下:
第一组数据:
100,150,120,50,70,60,80,170,180,160,110,30,40,35,175
第二组数据:
100,70,60,80,150,120,50,160,30,40,170,180,175,35
(3) 设计算法在二叉排序树中查找指定值的结点。
测试数据:在任务<1>中第一组测试数据所构造的二叉排序树中,分别查找下列元素: 150,70,160,190,10,55,175
(4) 设计算法在二叉排序树中删除特定值的结点。
测试数据:在任务(1)中第一组测试数据所构造的二叉排序树中,分别删除下列元素:30,150,100
(5) 已知整型数组A[1..26]递增有序,设计算法以构造一棵平衡的二叉排序树来存放该数组中的所有元素。
测试数据:数组元素分别为:
第一组数据:
(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26)
第二组数据:
(1,3,6,10,15,21,28,36,45,55,66,78,91,105,120,136,153,171,190,210,231,253,277,302,328)
7.3实验数据要求
自我编写测试样例,要求每个功能函数的测试样例不少于两组
7.4 运行结果截图及说明
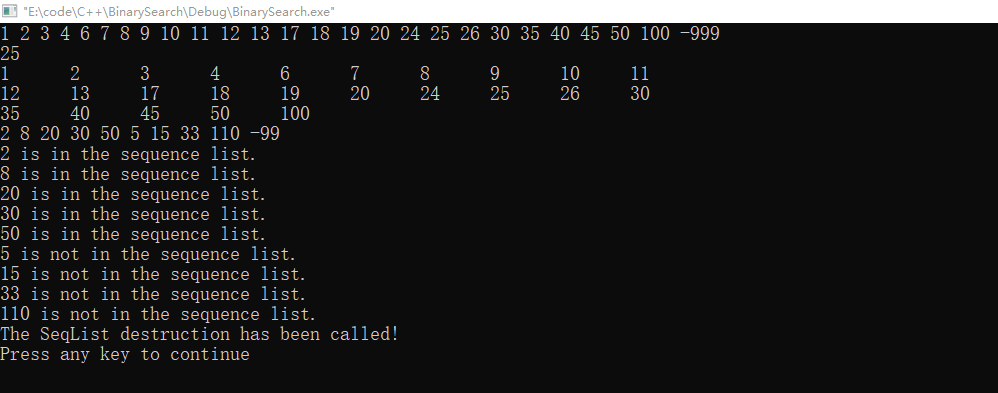
图1 测试(1)①
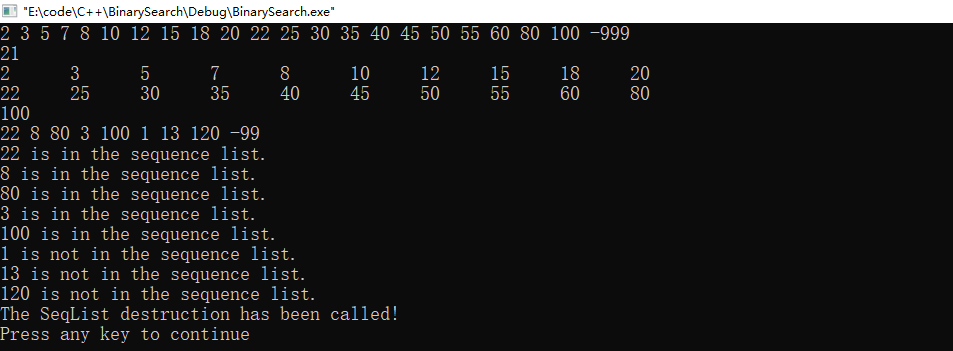
图2 测试(1)②
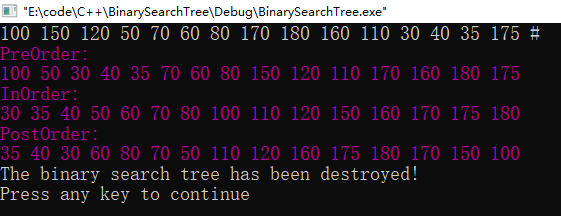
图3 测试(2)①
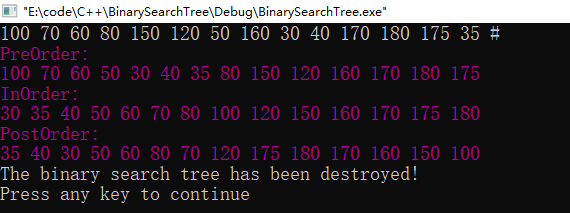
图4 测试(2)②
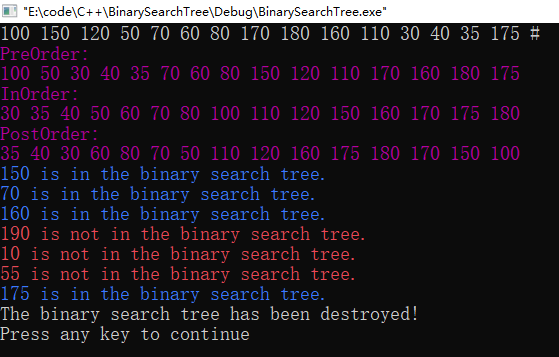
图5 测试(3)
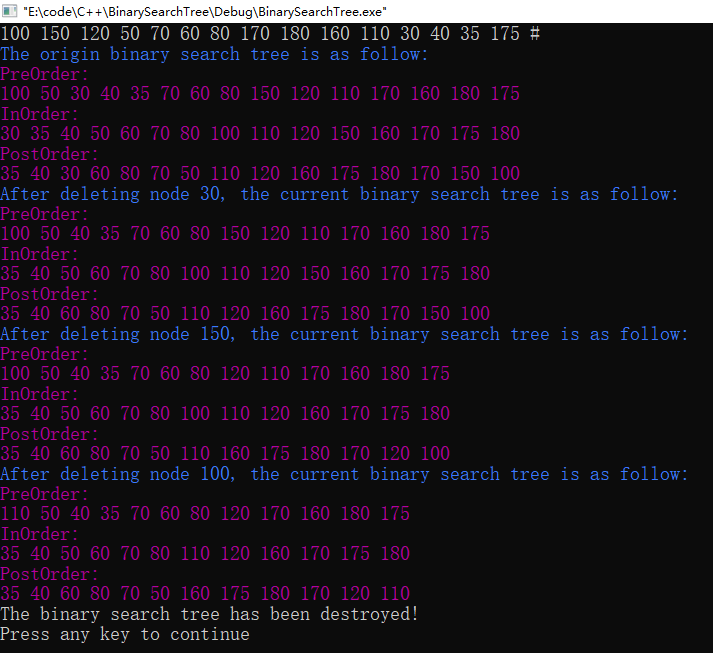
图6 测试(4)
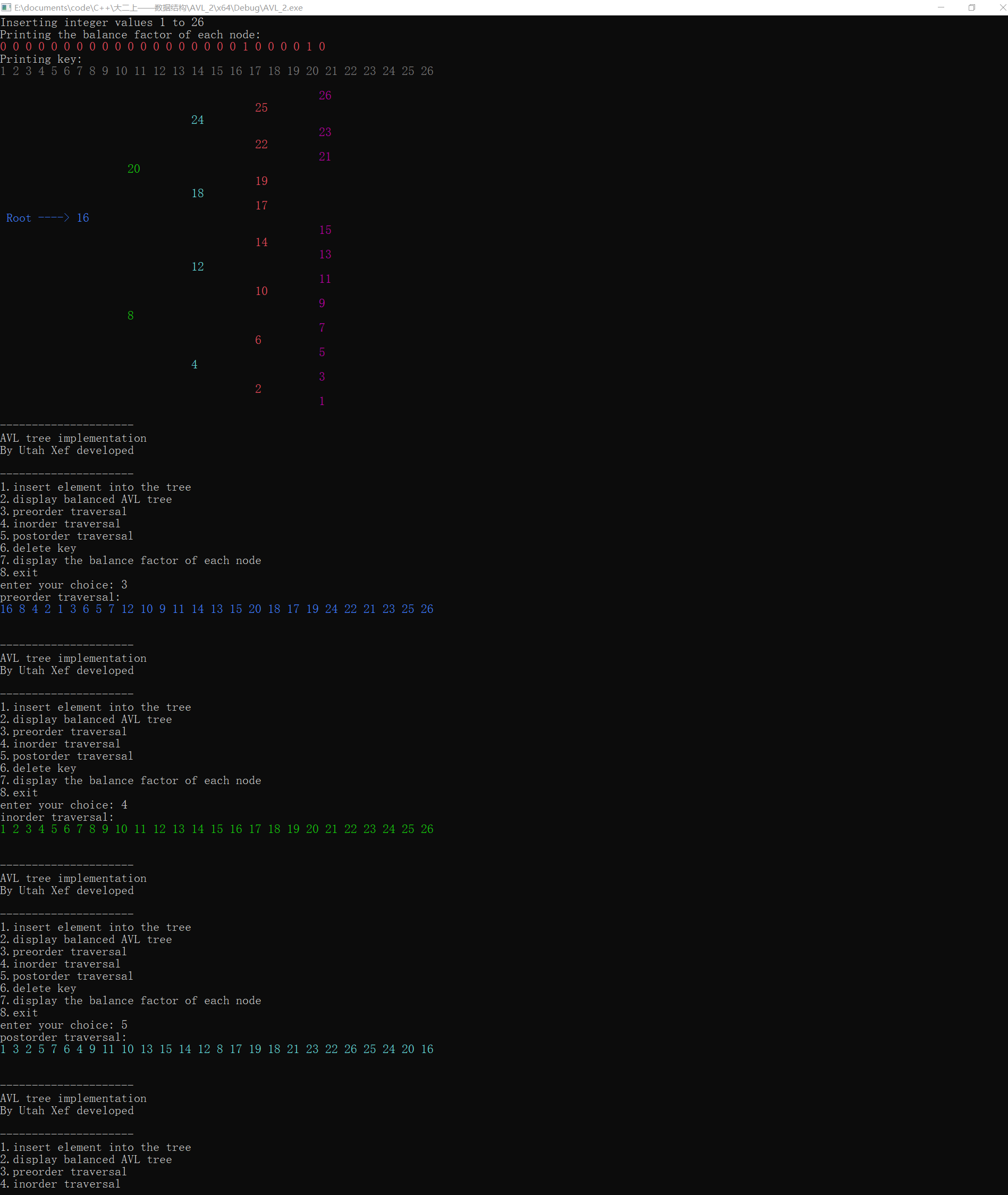
图7 测试(5)①
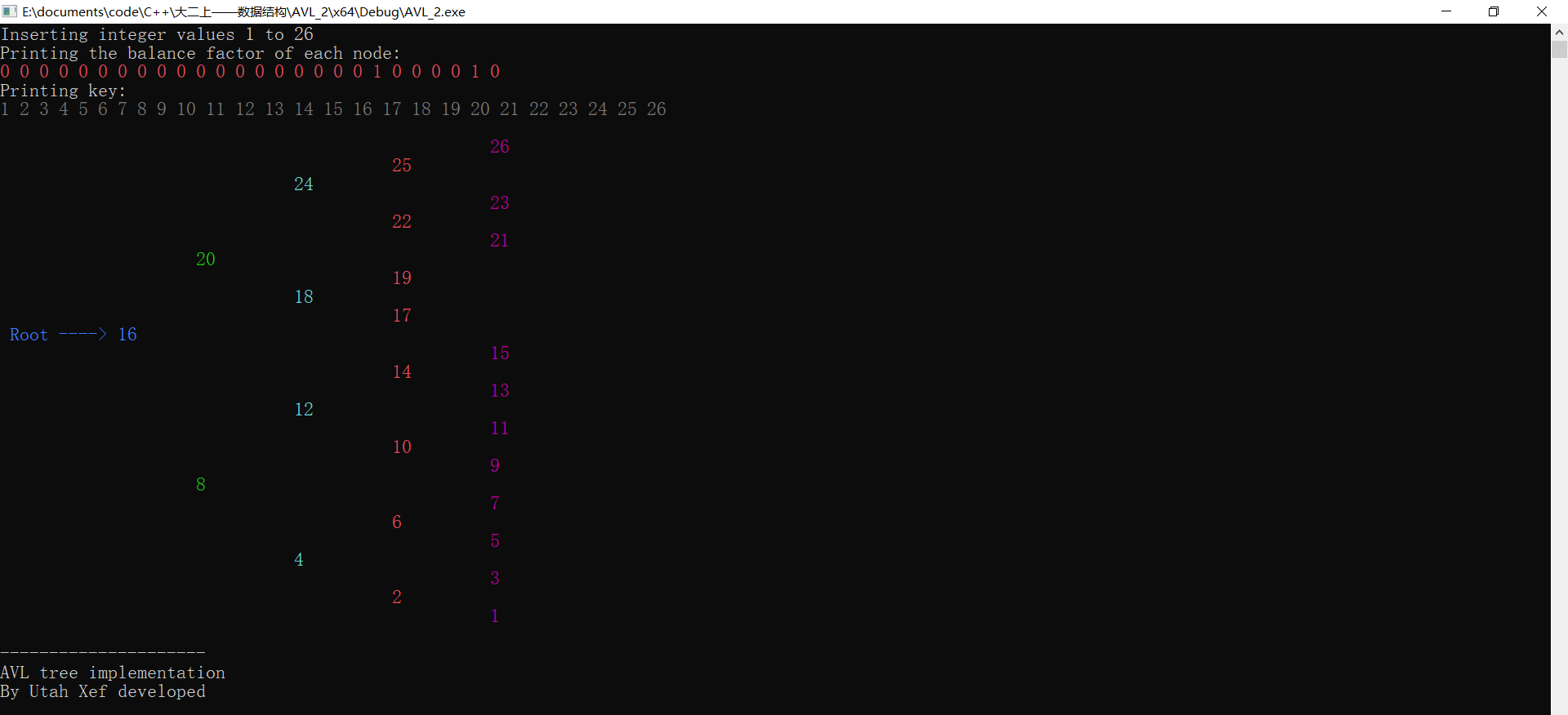
图8 测试(5)①
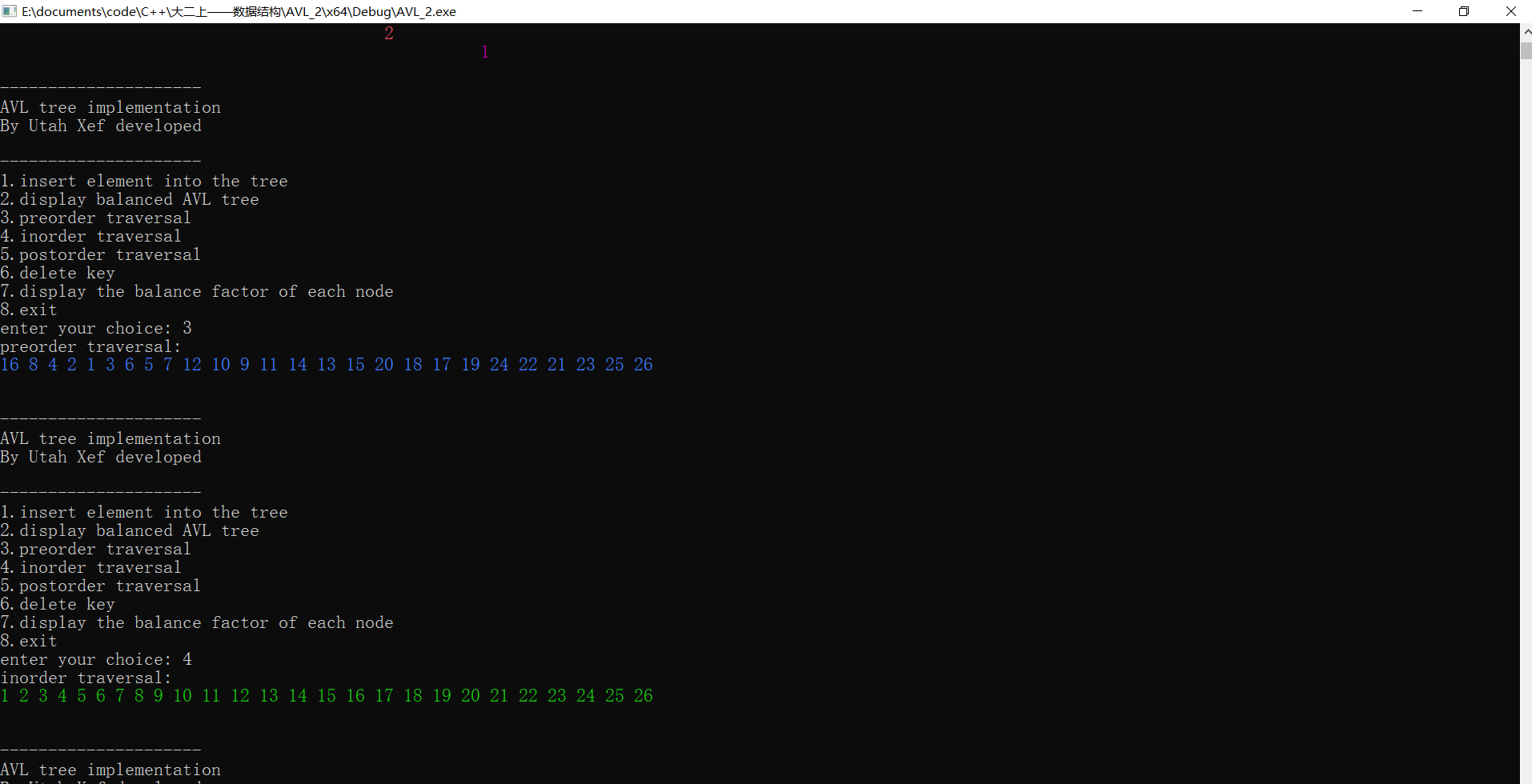
图9 测试(5)①
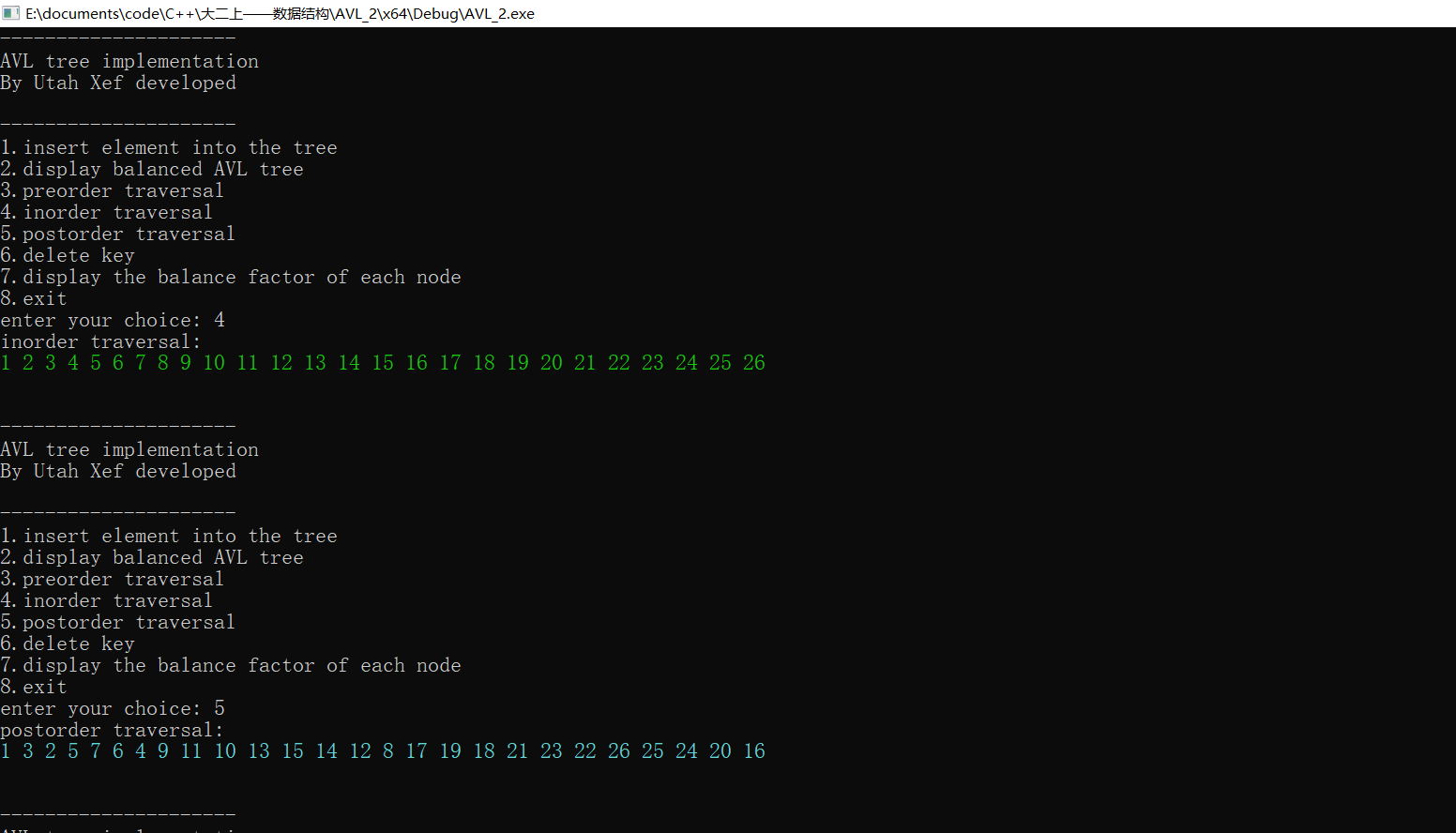
图10 测试(5)①
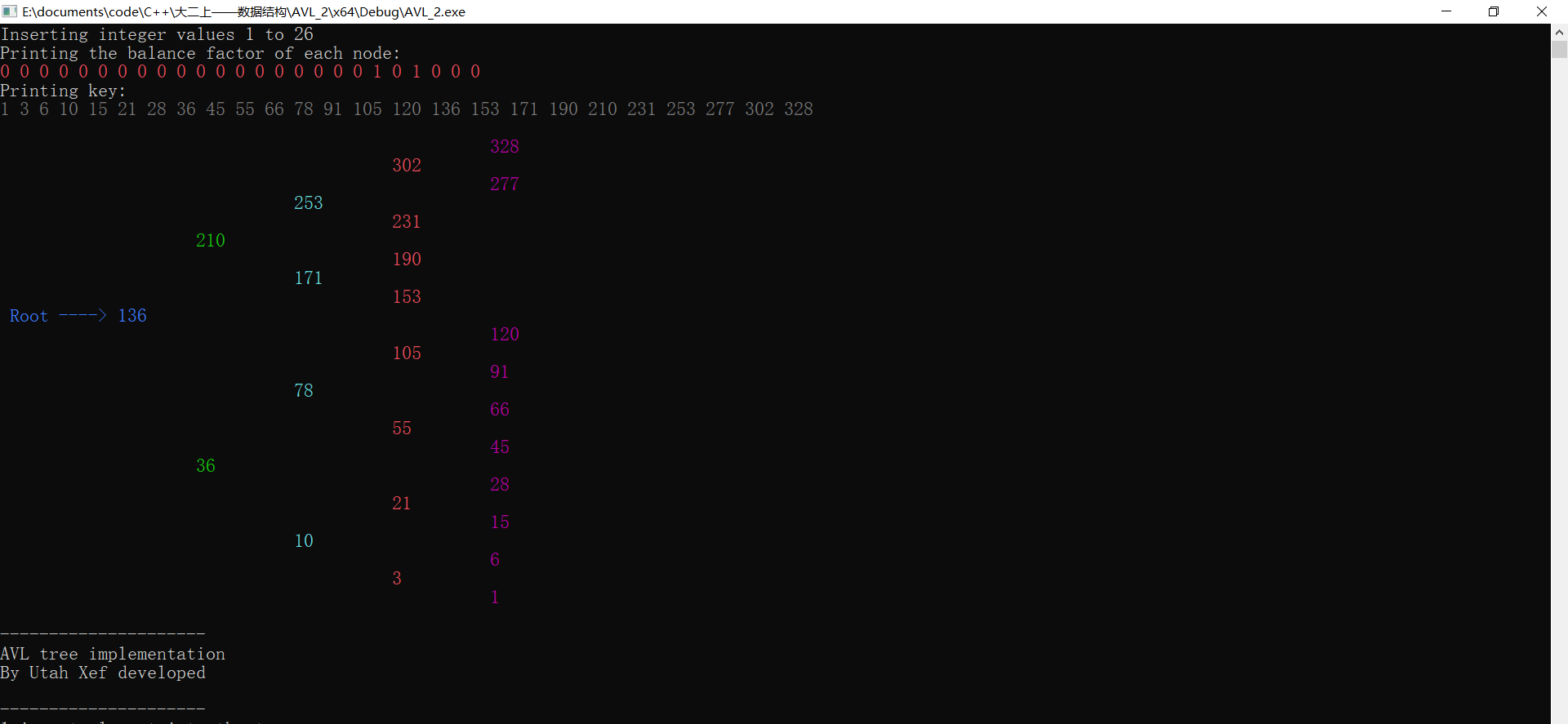
图11 测试(5)②
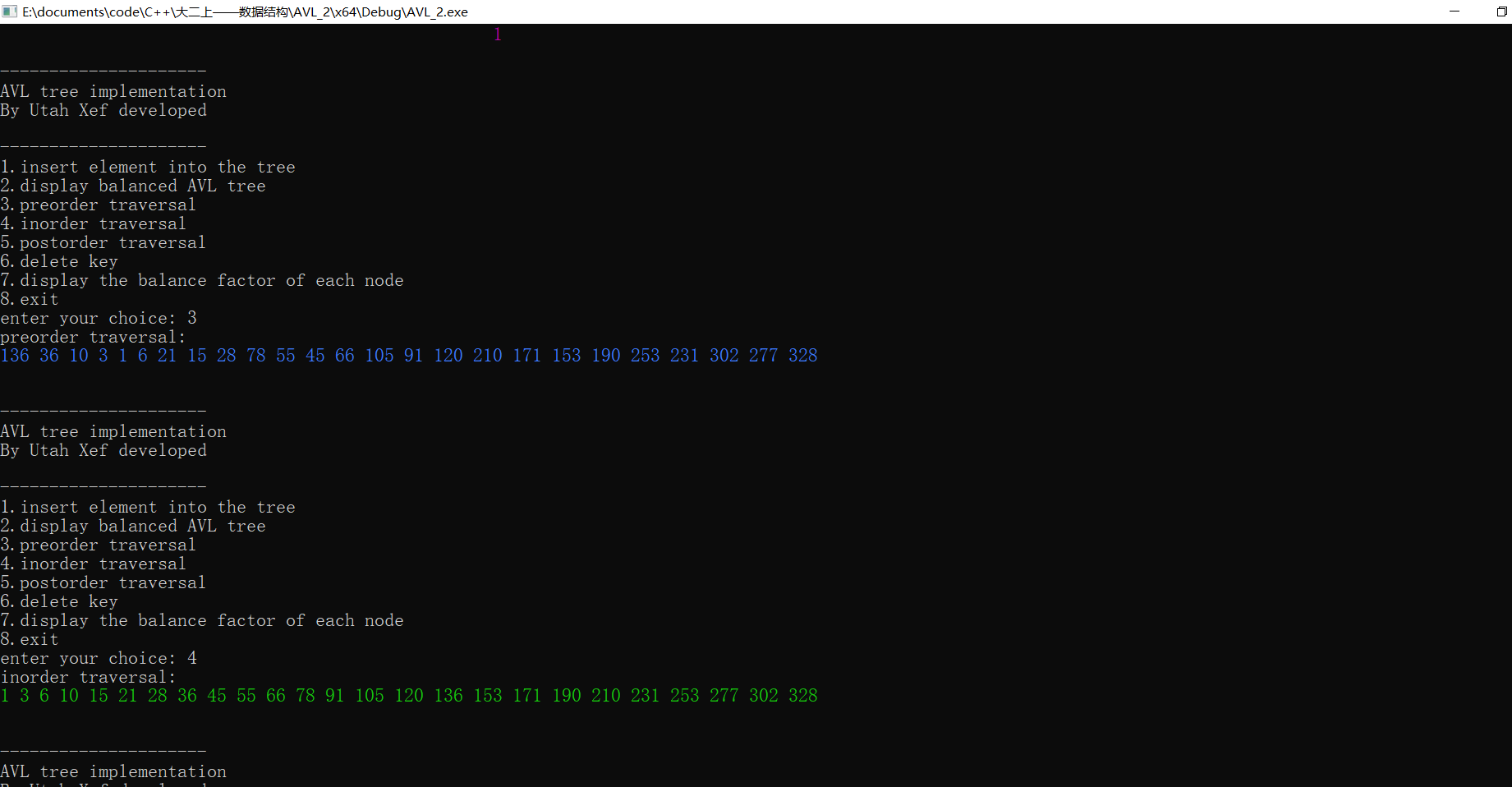
图12 测试(5)②
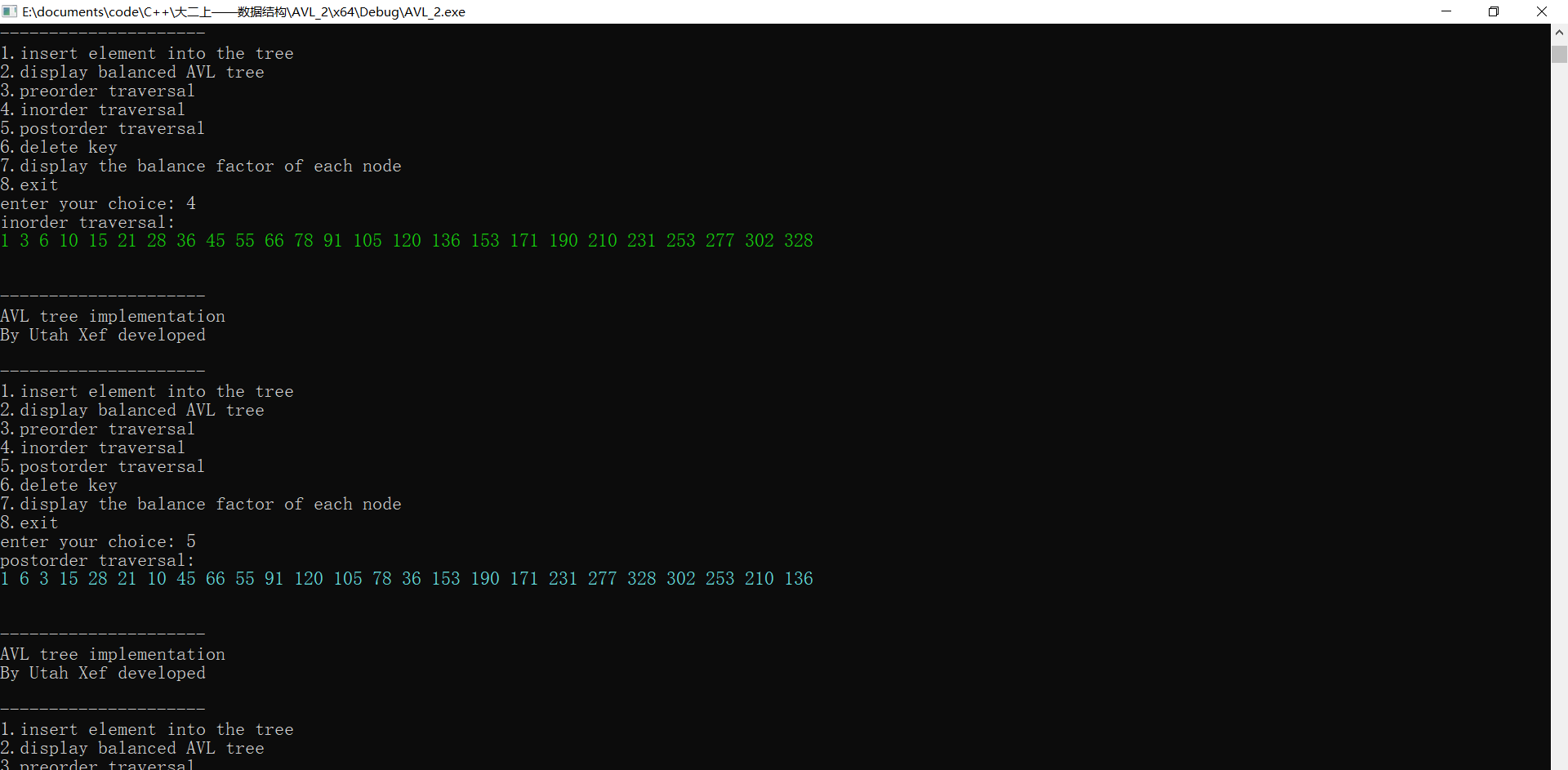
图13 测试(5)②
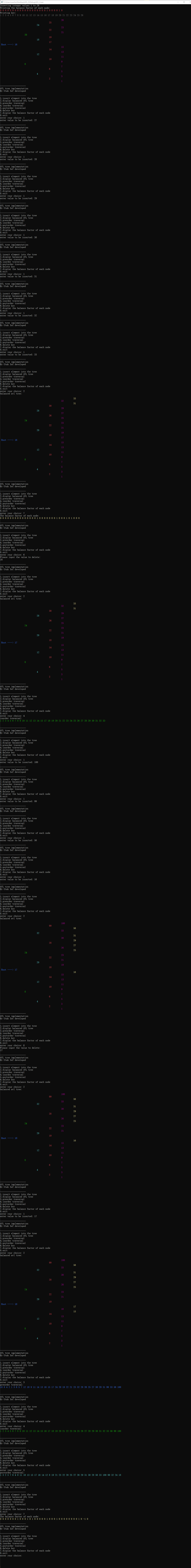
图14 测试(5)①(全)
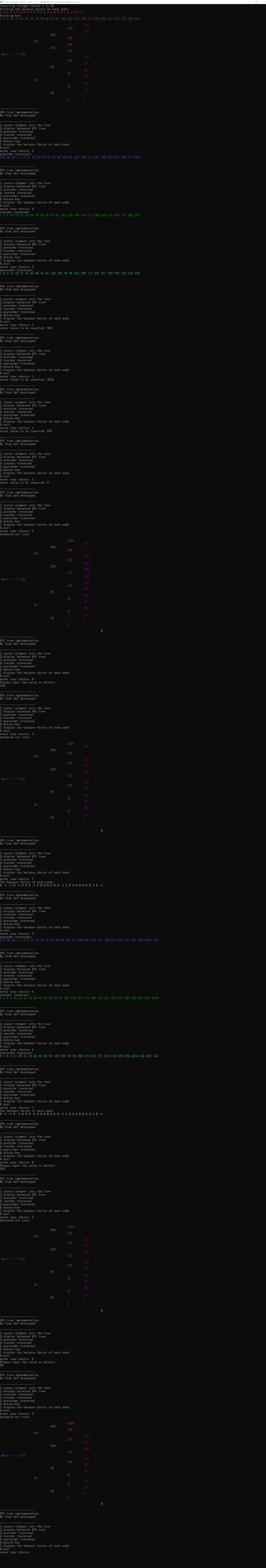
图15 测试(5)②(全)
7.5 附源代码
二分查找:
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
// #if !defined(AFX_STDAFX_H__940FF418_5647_412A_8B4F_3C89C07F8CA5__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_STDAFX_H__940FF418_5647_412A_8B4F_3C89C07F8CA5__INCLUDED_ #if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000 #include <stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long elementType; const long maxn = + ; // TODO: reference additional headers your program requires here //{{AFX_INSERT_LOCATION}}
// Microsoft Visual C++ will insert additional declarations immediately before the previous line. #endif // !defined(AFX_STDAFX_H__940FF418_5647_412A_8B4F_3C89C07F8CA5__INCLUDED_)
// SeqList.h: interface for the SeqList class.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #if !defined(AFX_SEQLIST_H__58D90762_85EC_4BBB_94EA_068A582CCD81__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_SEQLIST_H__58D90762_85EC_4BBB_94EA_068A582CCD81__INCLUDED_ #if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000 class SeqList
{
public:
SeqList();
virtual ~SeqList();
bool seqListFull();
bool seqListEmpty();
void randomInsert( elementType number );
void insert( elementType value );
void showLength();
elementType binarySearch( elementType value );
friend ostream &operator<<( ostream &os, SeqList &SL )
{
if( SL.length == - )
{
return os;
}
int column = ;
for( int i = ; i <= SL.length; i ++ )
{
os << setw() << setiosflags( ios::left ) << SL.Arr[i] << " ";
column ++;
if( column % == )
os << endl;
}
os << endl;
} private:
elementType Arr[maxn];
int length; }; #endif // !defined(AFX_SEQLIST_H__58D90762_85EC_4BBB_94EA_068A582CCD81__INCLUDED_)
// SeqList.cpp: implementation of the SeqList class.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "stdafx.h"
#include "SeqList.h" //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// SeqList::SeqList()
{
length = ;
} SeqList::~SeqList()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cout << "The SeqList destruction has been called!" << endl;
} bool SeqList::seqListFull()
{
return length == maxn - ;
} bool SeqList::seqListEmpty()
{
return length == ;
} void SeqList::randomInsert( elementType number )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if( seqListFull() )
{
cerr << "Inserting failed!The sequence list has been full.Error in void SeqList::randomInsert( int number )" << endl;
return;
} srand( time(NULL) );
elementType last = -;
for( int i = ; i < number; i ++ )
{
elementType key = rand() % ( - + ) + ;
if( key >= last )
{
length ++;
Arr[length] = key;
last = key;
}
else
{
i --;
}
}
} void SeqList::insert( elementType value )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if( seqListFull() )
{
cerr << "Inerting failed!The sequence list has been full.Error in void SeqList::insert( elementType value )" << endl;
return;
} length ++;
Arr[length] = value;
} elementType SeqList::binarySearch( elementType value )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if( seqListEmpty() )
{
cerr << "Searching failed!The sequence list is empty.Error in elementType SeqList::binarySearch( elementType value )" << endl;
return -;
}
elementType lower = , upper = length;
while( lower <= upper )
{
elementType mid = ( lower + upper ) >> ; //+ 1;
if( Arr[mid] == value )
{
return mid;
}
if( Arr[mid] >= value )
{
upper = mid - ;
}
else
{
lower = mid + ;
}
}
return -;
} void SeqList::showLength()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cout << length << endl;
}
// BinarySearch.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// #include "stdafx.h"
#include "SeqList.h" void test1()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
SeqList SL1;
elementType number;
cin >> number;
SL1.randomInsert( number );
cout << SL1;
elementType value;
for( int i = ; i < number; i ++ )
{
cin >> value;
if( SL1.binarySearch(value) != - )
{
cout << value << " is in the sequence list." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << value << " is not in the sequence list." << endl;
}
}
} void test2()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
SeqList SL1;
elementType value;
while( cin >> value )
{
if( value == - )
{
break;
}
SL1.insert(value);
}
SL1.showLength();
cout << SL1; elementType key;
while( cin >> key )
{
//cin >> key;
if( key == - )
{
//break;
return;
}
if( SL1.binarySearch(key) != - )
{
cout << key << " is in the sequence list." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << key << " is not in the sequence list." << endl;
}
} } int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
test2(); return ;
}
二分查找(排序)树:
// stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
// or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
// are changed infrequently
// #if !defined(AFX_STDAFX_H__239FA301_F6C5_4AE4_BD82_5EB3365C7ECB__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_STDAFX_H__239FA301_F6C5_4AE4_BD82_5EB3365C7ECB__INCLUDED_ #if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000 #include <stdc++.h>
#include <graphics.h> using namespace std; //将 elementType 设为 int 可以顺利完成实验要求;而将其设为 string 则可以输入字符串等,
//此时的大小关系默认为为字典序
//typedef string elementType;
typedef int elementType; //为了图好玩,调用EasyX库把字体颜色改了一下
//这是EasyX的官方网站: https://www.easyx.cn/ typedef struct node
{
elementType data;
struct node *leftChidld, *rightChild;
}BSTNode, *_BSTree; // TODO: reference additional headers your program requires here //{{AFX_INSERT_LOCATION}}
// Microsoft Visual C++ will insert additional declarations immediately before the previous line. #endif // !defined(AFX_STDAFX_H__239FA301_F6C5_4AE4_BD82_5EB3365C7ECB__INCLUDED_)
// BSTree.h: interface for the BSTree class.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #if !defined(AFX_BSTREE_H__37E371A7_E165_4AC3_898B_DDF38B0F87D8__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_BSTREE_H__37E371A7_E165_4AC3_898B_DDF38B0F87D8__INCLUDED_ #if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000 class BSTree
{
public:
BSTree();
virtual ~BSTree();
BSTNode *search( _BSTree BST, elementType value );//递归查找
BSTNode *search( _BSTree BST, elementType value, _BSTree &father );//迭代查找
BSTNode *getRootNode();
bool insert( _BSTree BST, elementType value ); bool deleteNode1( _BSTree &BST, elementType value ); //删除指定结点,failed
void deleteNode2( _BSTree &BST, elementType value ); //递归删除指定结点
void deleteNode2_1( _BSTree &BST, elementType value ); //迭代删除指定结点,待调试!
void deleteNode3( _BSTree &BST, elementType value ); void removeNode1( _BSTree &BST );
void removeNode2( _BSTree &BST );
void removeNode3( _BSTree &BST ); void createBinarySearchTree( _BSTree BST, vector<elementType>VI/*elementType value*/ );
void destroy( _BSTree BST );
void preOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ );
void inOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ );
void postOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ );
private:
BSTNode *head;
}; #endif // !defined(AFX_BSTREE_H__37E371A7_E165_4AC3_898B_DDF38B0F87D8__INCLUDED_)
// BSTree.cpp: implementation of the BSTree class.
//
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "stdafx.h"
#include "BSTree.h" //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// BSTree::BSTree()
{
//head = NULL;
//head = new BSTNode;
//head->leftChidld = head->rightChild = NULL;
} BSTree::~BSTree()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
destroy(head);
cout << "The binary search tree has been destroyed!" << endl;
} void BSTree::destroy( _BSTree BST )
{
if(BST)
{
destroy( BST->leftChidld );
destroy( BST->rightChild );
delete BST;
}
} void BSTree::preOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
/*
if(!BST)
{
cerr << "The binary search tree is empty.Error in void BSTree::preOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST )." << endl;
return;
}
*/
if(BST)
{
cout << BST->data << " ";
preOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld );
preOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild ); //for( int i = 0; i < space; i ++ )
// cout << " ";
//cout << BST->data << endl;
//preOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld, space + 5 );
//preOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild, space + 5 );
}
} void BSTree::inOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if(BST)
{
inOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld );
cout << BST->data << " ";
inOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild ); //inOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld, space + 5 );
//for( int i = 0; i < space; i ++ )
// cout << " ";
//cout << BST->data << endl;
//inOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild, space + 5 );
}
} void BSTree::postOrderTraversal( _BSTree BST/*, int space*/ )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if(BST)
{
postOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld );
postOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild );
cout << BST->data << " "; /*
postOrderTraversal( BST->leftChidld, space + 5 );
postOrderTraversal( BST->rightChild, space + 5 );
for( int i = 0; i < space; i ++ )
cout << " ";
cout << BST->data << endl;
*/
}
} void BSTree::createBinarySearchTree( _BSTree BST, /*elementType value*/vector<elementType>VI )
{
//BST = NULL;
head = NULL;
for( int i = ; i < VI.size(); i ++ )
{
insert( head, VI[i] );
}
return;
/*
while( cin >> value )
{
if( value == "#" )
{
return;
}
else
insert( head, value );
} for( int i = 0; i < value; i ++ )
{
elementType key;
cout << "input: ";
cin >> key;
insert( head, key );
}
*/
} BSTNode *BSTree::getRootNode()
{
return head;
} BSTNode *BSTree::search( _BSTree BST, elementType value )//递归查找
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if(!head)
{
cerr << "The binary search tree is empty.Error in BSTNode *BSTree::search( _BSTree BST, elementType value )." << endl;
return NULL;
}
else if( BST->data == value )
{
return BST;
}
else if( BST->data > value )
{
return search( BST->leftChidld, value );
}
else
{
return search( BST->rightChild, value );
}
} BSTNode *BSTree::search( _BSTree BST, elementType value, _BSTree &father )//迭代查找
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
/*
if(!head)
{
cerr << "The binary search tree empty.Error in BSTNode *BSTree::search( _BSTree BST, elementType value, _BSTree &father )." << endl;
return NULL;
}
*/
BSTNode *tmp = head;
father = NULL;
while( tmp && tmp->data != value )
{
father = tmp;
if( value < tmp->data )
{
tmp = tmp->leftChidld;
}
else
{
tmp = tmp->rightChild;
}
}
return tmp;
} bool BSTree::insert( _BSTree BST, elementType value )
{
//if(!head)
//{
// cerr << "The binary search tree does not exit.Error in bool BSTree::insert( _BSTree BST, elementType value )" << endl;
// return false;
//}
BSTNode *newNode, *target, *father; target = search( head, value, father );
if(target)
{
cerr << "Inserting failed!" << value << " has been exited in the binary search tree.\nError in bool BSTree::insert( _BSTree BST, elementType value )" << endl;
return false;
}
newNode = new BSTNode;
newNode->data = value;
newNode->leftChidld = newNode->rightChild = NULL;
if(!head)
{
head = newNode;
}
else if( value < father->data )
{
father->leftChidld = newNode;
}
else
{
father->rightChild = newNode;
}
return true;
} bool BSTree::deleteNode1( _BSTree &BST, elementType value )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
//if(!head)
if(!BST)
{
cerr << "The binary search tree does not exit.Error in bool BSTree::deleteNode( _BSTree BST, elementType value )" << endl;
return false;
}
BSTNode *newNode, *target, *father;
//target = search( head, value, father );
target = search( BST, value, father );
if( !target )//查找失败,不删除
{
cerr << "Node-deleting failed!\n" << value << " is not in the binary search tree.\n" << "Error in bool BSTree::deleteNode( _BSTree BST, elementType value )." << endl;
return false;
}
if( target->leftChidld && target->rightChild )//被删结点有两个 *target 孩子节点
{
newNode = target->rightChild; //找 target 的中序后继 newNode
father = target;
while( newNode->leftChidld )
{
father = newNode;
newNode = newNode->leftChidld;
}
target->data = newNode->data; //将 *newNode 的数据传給 *target
target = newNode; //找到的这个结点成为被删除结点
}
if( target->leftChidld ) //单孩子,记录非空孩子结点
{
newNode = target->leftChidld;
}
else
{
newNode = target->rightChild;
}
//if( target == head ) //被删结点是根结点
if( target == BST )
{
//head = newNode;
BST = newNode;
}
else if( newNode && ( newNode->data < father->data ) ) //重新链接,保持二叉排序树
{
father->leftChidld = newNode;
}
else
{
father->rightChild = newNode;
}
delete target;
return true;
} void BSTree::deleteNode2( _BSTree &BST, elementType value )
{
if(BST)
{
if( value < BST->data )
{
deleteNode2( BST->leftChidld, value );
}
else if( value > BST->data )
{
deleteNode2( BST->rightChild, value );
}
else
{
removeNode1(BST);
}
}
} void BSTree::deleteNode2_1( _BSTree &BST, elementType value ) //迭代删除指定结点,待调试!
{
BSTNode *target = NULL;
while( BST || BST->data != value )
{
target = BST;
if( value < target->data )
//if( value < BST->data )
BST = BST->leftChidld;
else
BST = BST->rightChild;
}
removeNode1(target);
//removeNode1(BST);
} void BSTree::deleteNode3( _BSTree &BST, elementType value )
{
if(BST)
{
if( value < BST->data )
{
deleteNode2( BST->leftChidld, value );
}
else if( value > BST->data )
{
deleteNode2( BST->rightChild, value );
}
else
{
removeNode2(BST);
}
}
}
/*
在二叉查找树中删除一个给定的结点p有三种情况 (1)结点p无左右子树,则直接删除该结点,修改父节点相应指针 (2)结点p有左子树(右子树),则把p的左子树(右子树)接到p的父节点上 (3)左右子树同时存在,则有三种处理方式 a.找到结点p的中序直接前驱结点s,把结点s的数据转移到结点p,然后删除结点s,
由于结点s为p的左子树中最右的结点,因而s无右子树,删除结点s可以归结到情况(2)。
严蔚敏数据结构P230-231就是该处理方式。
b.找到结点p的中序直接后继结点s,把结点s的数据转移到结点p,然后删除结点s,
由于结点s为p的右子树总最左的结点,因而s无左子树,删除结点s可以归结到情况(2)。
算法导论第2版P156-157该是该处理方式。
c.到p的中序直接前驱s,将p的左子树接到父节点上,将p的右子树接到s的右子树上,然后删除结点p。
*/
void BSTree::removeNode1( _BSTree &BST )
{
BSTNode *target = NULL;
if( !BST->leftChidld )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->rightChild;
delete target;
}
else if( !BST->rightChild )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->leftChidld;
delete target;
}
else
{
BSTNode *newNode = NULL;
target = BST;
newNode = BST->leftChidld; //左子树根结点
while( newNode->rightChild ) //寻找 BST 结点的中序前驱结点,即以 BST->leftChild为根结点的子树中的最右结点
{
target = newNode; //*target 指向 *BST 的父结点
newNode = newNode->rightChild; //*newNode 指向 *BST 的中序前驱结点
}
BST->data = newNode->data; //*newNode 的数据传給 *BST 的数据,然后删除结点 *newNode
if( target != BST ) //BST->leftChidld 的右子树非空,这句话等价于 if( !( target == BST ) )
{
target->rightChild = newNode->leftChidld; //*newNode 的左子树接到 *target 的右子树上
}
else
{
target->leftChidld = newNode->leftChidld; //*newNode 的左子树接到 *target 的左子树上
}
delete newNode; //删除结点 *newNode
}
} //注意 while 循环体:
//如果 BST 左子树为空,则 while 循环体不执行,那么 target 就不会发生改变。
//然而一开始 target == BST。
//反过来说,如果 BST 左子树不为空,则 while 执行,那么 target 就会发生改变。
//target 改变了,就和 BST 不一样。
//所以就可以表明 BST 左子树非空。 void BSTree::removeNode2( _BSTree &BST )
{
BSTNode *target = NULL;
if( !BST->leftChidld )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->rightChild;
delete target;
}
else if( !BST->rightChild )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->leftChidld;
delete target;
}
else
{
BSTNode *newNode = NULL;
target = BST;
newNode = BST->rightChild; //右子树根结点
while( newNode->leftChidld ) //寻找 BST 结点的中序前驱结点,即以 BST->leftChild为根结点的子树中的最左结点
{
target = newNode; //*target 指向 *BST 的父结点
newNode = newNode->leftChidld; //*newNode 指向 *BST 的中序后继结点
}
BST->data = newNode->data; //*newNode 的数据传給 *BST 的数据,然后删除结点 *newNode
if( target != BST ) //BST->leftChidld 的左子树非空,这句话等价于 if( !( target == BST ) )
{
target->leftChidld = newNode->rightChild; //*newNode 的右子树接到 *target 的左子树上
}
else
{
target->rightChild = newNode->rightChild; //*newNode 的右子树接到 *target 的右子树上
}
delete newNode; //删除结点 *newNode
}
} //注意 while 循环体:
//如果 BST 右子树为空,则 while 循环体不执行,那么 target 就不会发生改变。
//然而一开始 target == BST。
//反过来说,如果 BST 右子树不为空,则 while 执行,那么 target 就会发生改变。
//target 改变了,就和 BST 不一样
//所以就可以表明 BST 右子树非空。 void BSTree::removeNode3( _BSTree &BST )
{
BSTNode *target = NULL;
if( !BST->leftChidld )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->rightChild;
delete target;
}
else if( !BST->rightChild )
{
target = BST;
BST = BST->leftChidld;
delete target;
}
else
{
BSTNode *newNode = NULL;
target = BST;
newNode = BST->leftChidld; //左子树根结点
while( newNode->rightChild ) //寻找 BST 结点的中序前驱结点,即以 BST->leftChild为根结点的子树中的最右结点
{
//target = newNode;
newNode = newNode->rightChild;
}
newNode->rightChild = target->leftChidld; //*target 的左子树接到 *newNode 的左子树上
target = target->leftChidld; //*target 的左子树接到父结点上
delete target; //删除结点 *target
}
}
// BinarySearchTree.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// #include "stdafx.h"
#include "BSTree.h" //这是EasyX的官方网站: https://www.easyx.cn/ void test1()
{
HANDLE hOut; // 获取输出流的句柄
hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); BSTree BST1;
elementType value;
vector<elementType>VI;
while( cin >> value )
{
if( (char)value == '#' && value != /*-999*/ ) //细节处理:一定要加 && value != 35,因为 # 的ASCII码是35,
{ //不加的话在输入数字“35”而不是“#”时循环也会终止
break;
}
else
{
VI.push_back(value);
} }
BST1.createBinarySearchTree( BST1.getRootNode(), VI ); SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_BLUE |// 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY);// 加强 cout << "PreOrder:" << endl;
BST1.preOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "InOrder:" << endl;
BST1.inOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "PostOrder:" << endl;
BST1.postOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl; SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_GREEN | // 前景色_绿色
FOREGROUND_BLUE ); // 前景色_蓝色 return;
} void test2()
{
HANDLE hOut; // 获取输出流的句柄
hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); BSTree BST1;
elementType value;
vector<elementType>VI; while( cin >> value )
{
if( (char)value == '#' && value != /*-999*/ ) //细节处理:一定要加 && value != 35,因为 # 的ASCII码是35,
{ //不加的话在输入数字“35”而不是“#”时循环也会终止
break;
}
else
{
VI.push_back(value);
} } BST1.createBinarySearchTree( BST1.getRootNode(), VI ); _BSTree index = NULL; SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_BLUE |// 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY);// 加强 cout << "PreOrder:" << endl; BST1.preOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "InOrder:" << endl;
BST1.inOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "PostOrder:" << endl;
BST1.postOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl; //elementType key = ;// = 545;
//下面这句话不会运行
//cin >> key; elementType Arr[] = { , , , , , , }; for( int j = ; j < sizeof(Arr) / sizeof(elementType); j ++ )
{
if( BST1.search( BST1.getRootNode(), Arr[j], index ) )
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_BLUE | // 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY ); // 前景色_加强
cout << Arr[j] << " is in the binary search tree." << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_GREEN | // 前景色_绿色
FOREGROUND_BLUE ); // 前景色_蓝色
}
else
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY ); // 前景色_加强
cout << Arr[j] << " is not in the binary search tree." << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_GREEN | // 前景色_绿色
FOREGROUND_BLUE ); // 前景色_蓝色
}
} //无法实现下面这样输入数值判断其是否存在
/*
BSTNode *father = NULL, *target = NULL; elementType key;
while( cin >> key )
{
//target = NULL;
if( (char)key == '#' && key != 35 )
{
break;
}
else
target = BST1.search( BST1.getRootNode(), key, father ); if(!target)
{
cout << "No!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Yes!" << endl;
} }
*/ return;
} void test3()
{
HANDLE hOut; // 获取输出流的句柄
hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE); BSTree BST1;
elementType value;
vector<elementType>VI; while( cin >> value )
{
if( (char)value == '#' && value != /*-999*/ ) //细节处理:一定要加 && value != 35,因为 # 的ASCII码是35,
{ //不加的话在输入数字“35”而不是“#”时循环也会终止
break;
}
else
{
VI.push_back(value);
} } BST1.createBinarySearchTree( BST1.getRootNode(), VI ); _BSTree index = NULL; SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_BLUE | // 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY ); // 前景色_加强
cout << "The origin binary search tree is as follow:" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_BLUE |// 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY);// 加强 cout << "PreOrder:" << endl; BST1.preOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "InOrder:" << endl;
BST1.inOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "PostOrder:" << endl;
BST1.postOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() ); cout << endl; elementType Arr[] = { , , };
for( int i = ; i < sizeof(Arr) / sizeof(elementType); i ++ )
{
_BSTree index = BST1.getRootNode();
//BST1.deleteNode1( index, Arr[i] );
BST1.deleteNode2( index, Arr[i] );
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_BLUE | // 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY ); // 前景色_加强
cout << "After deleting node " << Arr[i] << ", the current binary search tree is as follow:"<< endl; SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_BLUE |// 前景色_蓝色
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY);// 加强 cout << "PreOrder:" << endl; BST1.preOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "InOrder:" << endl;
BST1.inOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl;
cout << "PostOrder:" << endl;
BST1.postOrderTraversal( BST1.getRootNode() );
cout << endl; }
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut,
FOREGROUND_RED | // 前景色_红色
FOREGROUND_GREEN | // 前景色_绿色
FOREGROUND_BLUE ); // 前景色_蓝色
return;
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//test1();
//test2();
test3();
return ;
}
AVL树:
// Tips for Getting Started:
// 1. Use the Solution Explorer window to add/manage files
// 2. Use the Team Explorer window to connect to source control
// 3. Use the Output window to see build output and other messages
// 4. Use the Error List window to view errors
// 5. Go to Project > Add New Item to create new code files, or Project > Add Existing Item to add existing code files to the project
// 6. In the future, to open this project again, go to File > Open > Project and select the .sln file #ifndef PCH_H
#define PCH_H #include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <windows.h> using namespace std; // TODO: add headers that you want to pre-compile here #endif //PCH_H
#pragma once
/* AVL node */
template <class T>
class AVLNode
{
public:
T key;
int balance;
AVLNode *leftChild, *rightChild, *parent; AVLNode(T k, AVLNode *p) : key(k), balance(), parent(p),leftChild(NULL), rightChild(NULL) {}
~AVLNode();
};
#pragma once
/* AVL tree */ #include "AVLnode.h"
template <class T>
class AVLTree
{
public:
AVLTree(void);
~AVLTree(void);
bool insert(T key);
void deleteKey(const T key);
void printBalance();
void inOrderTraverse();
void preOrderTraverse();
void postOrderTraverse();
void display(); AVLNode<T>* RR_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB); //rotate left
//当在RR发生不平衡时需要进行左旋转
AVLNode<T>* LL_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB); //rotate right
//当在LL发生不平衡时需要进行右旋转
AVLNode<T>* LR_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB); //rotate left then right
AVLNode<T>* RL_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB); //rotate right then left
AVLNode<T>* getRootNode();
void reBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
int height(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void setBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void printBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void clearNode(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void inOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void preOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB);
void postOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB); void display(AVLNode <T>*AVLB, int space, int colour); private:
AVLNode<T> *root;
};
#include "pch.h"
#include "AVLnode.h" template <class T>
AVLNode<T>::~AVLNode()
{
delete leftChild;
delete rightChild;
}
#include "pch.h"
#include "AVLtree.h" template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::reBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
setBalance(AVLB); if (AVLB->balance == -)
{
if (height(AVLB->leftChild->leftChild) >= height(AVLB->leftChild->rightChild))
AVLB = LL_Rotate(AVLB);
else
AVLB = LR_Rotate(AVLB);
}
else if (AVLB->balance == )
{
if (height(AVLB->rightChild->rightChild) >= height(AVLB->rightChild->leftChild))
AVLB = RR_Rotate(AVLB);
else
AVLB = RL_Rotate(AVLB);
} if (AVLB->parent != NULL)
{
reBalance(AVLB->parent);
}
else
{
root = AVLB;
}
} template <class T>
AVLNode<T>* AVLTree<T>::RR_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
AVLNode<T> *tmp = AVLB->rightChild;
tmp->parent = AVLB->parent;
AVLB->rightChild = tmp->leftChild; if (AVLB->rightChild != NULL)
AVLB->rightChild->parent = AVLB; tmp->leftChild = AVLB;
AVLB->parent = tmp; if (tmp->parent != NULL)
{
if (tmp->parent->rightChild == AVLB)
{
tmp->parent->rightChild = tmp;
}
else
{
tmp->parent->leftChild = tmp;
}
} setBalance(AVLB);
setBalance(tmp);
return tmp;
} template <class T>
AVLNode<T>* AVLTree<T>::LL_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
AVLNode<T> *tmp = AVLB->leftChild;
tmp->parent = AVLB->parent;
AVLB->leftChild = tmp->rightChild; if (AVLB->leftChild != NULL)
AVLB->leftChild->parent = AVLB; tmp->rightChild = AVLB;
AVLB->parent = tmp; if (tmp->parent != NULL)
{
if (tmp->parent->rightChild == AVLB)
{
tmp->parent->rightChild = tmp;
}
else
{
tmp->parent->leftChild = tmp;
}
} setBalance(AVLB);
setBalance(tmp);
return tmp;
} template <class T>
AVLNode<T>* AVLTree<T>::LR_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
AVLB->leftChild = RR_Rotate(AVLB->leftChild);
return LL_Rotate(AVLB);
} template <class T>
AVLNode<T>* AVLTree<T>::RL_Rotate(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
AVLB->rightChild = LL_Rotate(AVLB->rightChild);
return RR_Rotate(AVLB);
} template <class T>
AVLNode<T>* AVLTree<T>::getRootNode()
{
return root;
} template <class T>
int AVLTree<T>::height(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
if (AVLB == NULL)
return -;
return + max(height(AVLB->leftChild), height(AVLB->rightChild));
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::setBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
AVLB->balance = height(AVLB->rightChild) - height(AVLB->leftChild);
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::printBalance(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if (AVLB != NULL)
{
printBalance(AVLB->leftChild);
cout << AVLB->balance << " ";
//std::cout << n->key << " ";
printBalance(AVLB->rightChild);
}
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::inOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if (AVLB)
{
inOrderTraverse(AVLB->leftChild);
cout << AVLB->key << " ";
inOrderTraverse(AVLB->rightChild);
}
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::preOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
if (AVLB)
{
cout << AVLB->key << " ";
preOrderTraverse(AVLB->leftChild);
preOrderTraverse(AVLB->rightChild);
}
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::postOrderTraverse(AVLNode<T> *AVLB)
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
if (AVLB)
{
postOrderTraverse(AVLB->leftChild);
postOrderTraverse(AVLB->rightChild);
cout << AVLB->key << " ";
}
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::display(AVLNode <T>*AVLB, int space, int colour )
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
HANDLE hConsole;
hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
if (AVLB)
{
display(AVLB->rightChild, space + , colour + );
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | colour);
//colour++;
cout << endl;
if (AVLB == root)
cout << " Root ----> ";
for (int i = ; i < space && AVLB != root; i++)
cout << " ";
cout << AVLB->key;
display(AVLB->leftChild, space + , colour + );
}
} template <class T>
AVLTree<T>::AVLTree(void) : root(NULL) {} template <class T>
AVLTree<T>::~AVLTree(void)
{
delete root;
} template <class T>
bool AVLTree<T>::insert(T key)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
root = new AVLNode<T>(key, NULL);
}
else
{
AVLNode<T> //这种风格我觉得不错
//I appreciate this style of code
*target = root,
*parent; while ()
{
if (target->key == key)
return false; parent = target; bool goLeft = target->key > key;
target = goLeft ? target->leftChild : target->rightChild; if (target == NULL)
{
if (goLeft)
{
parent->leftChild = new AVLNode<T>(key, parent);
}
else
{
parent->rightChild = new AVLNode<T>(key, parent);
} reBalance(parent);
break;
}
}
} return true;
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::deleteKey(const T delKey)
{
if (root == NULL)
return; AVLNode<T>
*target = root,
*parent = root,
*delNode = NULL,
*child = root; while (child != NULL)
{
parent = target;
target = child;
child = delKey >= target->key ? target->rightChild : target->leftChild;
if (delKey == target->key)
delNode = target;
} if (delNode != NULL)
{
delNode->key = target->key; child = target->leftChild != NULL ? target->leftChild : target->rightChild; if (root->key == delKey)
{
root = child;
}
else
{
if (parent->leftChild == target)
{
parent->leftChild = child;
}
else
{
parent->rightChild = child;
} reBalance(parent);
}
}
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::printBalance()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
printBalance(root);
cout << endl;
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::inOrderTraverse()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
inOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::preOrderTraverse()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
preOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::postOrderTraverse()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
postOrderTraverse(root);
cout << endl;
} template <class T>
void AVLTree<T>::display()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int color = ;
display(root, , color);
cout << endl;
}
// AVL_2.cpp : This file contains the 'main' function. Program execution begins and ends there.
// #include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "AVLtree.h"
#include "AVLnode.h"
#include "AVLnode.cpp"
#include "AVLtree.cpp" int main()
{
//std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
AVLTree<int> AVLBT;
HANDLE hConsole;
hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
cout << "Inserting integer values 1 to 26" << std::endl;
int Arr[] = { ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,, };
for (int i = ; i < sizeof(Arr) / sizeof(int); i++)
//for( int i = 0; Arr[i] != 0; i ++ )
//AVLBT.insert(i);
AVLBT.insert(Arr[i]); cout << "Printing the balance factor of each node: " << std::endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, );
AVLBT.printBalance();
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, );
cout << "Printing key: " << std::endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | );
AVLBT.inOrderTraverse();
AVLBT.display();
//AVLTree<int> *root = avl.getRootNode();
while ()
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, );
cout << "\n---------------------" << endl;
cout << "AVL tree implementation" << endl;
cout << "By Utah Xef developed" << endl;
cout << "\n---------------------" << endl;
cout << "1.insert element into the tree" << endl;
cout << "2.display balanced AVL tree" << endl;
cout << "3.preorder traversal" << endl;
cout << "4.inorder traversal" << endl;
cout << "5.postorder traversal" << endl;
cout << "6.delete key" << endl;
cout << "7.display the balance factor of each node" << endl;
cout << "8.exit" << endl;
cout << "enter your choice: ";
int choice;
cin >> choice; switch (choice) { case : cout << "enter value to be inserted: ";
int item;
cin >> item; AVLBT.insert(item); break; case : if (AVLBT.getRootNode() == nullptr) { cout << "tree is empty" << endl; continue; } cout << "balanced avl tree:" << endl; AVLBT.display(); break; case : cout << "preorder traversal:" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | );
AVLBT.preOrderTraverse(); cout << endl; break;
case : cout << "inorder traversal:" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | );
AVLBT.inOrderTraverse(); cout << endl; break; case : cout << "postorder traversal:" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | );
AVLBT.postOrderTraverse(); cout << endl; break; case :
int value;
cout << "Please input the value to delete:" << endl;
cin >> value;
AVLBT.deleteKey(value);
break; case :
cout << "The balance factor of each node:" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(hConsole, 0x0008 | );
AVLBT.printBalance();
break;
case :
exit(); break;
default: cout << "Wrong choice" << endl;
break;
} }
//std::cout << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
} // Run program: Ctrl + F5 or Debug > Start Without Debugging menu
// Debug program: F5 or Debug > Start Debugging menu // Tips for Getting Started:
// 1. Use the Solution Explorer window to add/manage files
// 2. Use the Team Explorer window to connect to source control
// 3. Use the Output window to see build output and other messages
// 4. Use the Error List window to view errors
// 5. Go to Project > Add New Item to create new code files, or Project > Add Existing Item to add existing code files to the project
// 6. In the future, to open this project again, go to File > Open > Project and select the .sln file
数据结构实验7:实现二分查找、二叉排序(查找)树和AVL树的更多相关文章
- 数据结构-查找-二叉排序查找(平衡二叉树,B树,B+树概念)
0.为什么需要二叉排序树 1)数组存储方式: 优点:通过下标访问元素,速度快,对于有序数组,可以通过二分查找提高检索效率: 缺点:如果检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按一定顺序)会整体移动,效率较低: 2 ...
- 第七章 二叉搜索树(d4)AVL树:(3+4)-重构
- 第七章 二叉搜索树 (d3)AVL树:删除
- 第七章 二叉搜索树 (d2)AVL树:插入
- 第七章 二叉搜索树 (d1)AVL树:重平衡
- 数据结构:JAVA_二叉数查找树基本实现(中)
数据结构:二叉数查找树基本实现(JAVA语言版) 1.写在前面 二叉查找树得以广泛应用的一个重要原因是它能保持键的有序性,因此我们可以把它作为实现有序符号表API中的众多方法的基础. 也就是说我们构建 ...
- 二叉平衡查找树AvlTree(C实现)
二叉平衡查找树即是一棵树中所有节点的左右子树高度差不超过1的查找树 头文件—————————————————————————————— #ifndef _AVLTREE_H_ #define _AVL ...
- SDUT-2132_数据结构实验之栈与队列二:一般算术表达式转换成后缀式
数据结构实验之栈与队列二:一般算术表达式转换成后缀式 Time Limit: 1000 ms Memory Limit: 65536 KiB Problem Description 对于一个基于二元运 ...
- [PTA] 数据结构与算法题目集 6-12 二叉搜索树的操作集
唯一比较需要思考的删除操作: 被删除节点有三种情况: 1.叶节点,直接删除 2.只有一个子节点,将子节点替换为该节点,删除该节点. 3.有两个子节点,从右分支中找到最小节点,将其值赋给被删除节点的位置 ...
随机推荐
- C++ 的浅拷贝和深拷贝(结构体)
关于浅拷贝和深拷贝这个问题遇上的次数不多,这次遇上整理一下,先说这样一个问题,关于浅拷贝的问题,先从最简单的说起. 假设存在一个结构体: struct Student { string name; i ...
- System.Web.Mvc 和 using System.Net.Http 的 Filter
在尝试给webapi增加 ExceptionFilter时,出现了错误,经查询区别如下: System.Web.Mvc.Filters 是给mvc用的 System.Web.Http.Filters ...
- Win7执行应用报CLR20r3错误处理记录
Windows7环境下运行应用报"CLR20r3"错误,错误信息如下: 问题详细信息: 问题签名: 问题事件名称: CLR20r3 问题签名 : qbbtools.exe 问题签名 ...
- PWA之push服务
转载: https://www.jishux.com/p/c5735af96c39bd4a https://www.jianshu.com/p/9970a9340a2d 系列文章参考:https:// ...
- bash 变量传递方法
###1.sh ##(该sh 目的是 将变量env传入env.sh, 同时让env.sh在当前事物生效,最后执行env.sh 定义的变量envs) export ENV=prepareecho ...
- storm的3节点集群详细启动步骤(非HA和HA)(图文详解)
前期博客 apache-storm-1.0.2.tar.gz的集群搭建(3节点)(图文详解)(非HA和HA) 启动storm集群(HA) 本博文情况是 master(主) nimbus slave1( ...
- [转]Android 如何监听返回键,弹出一个退出对话框
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sunnyfans/article/details/8094349 Android 如何监听返回键点击事件,并创建一个退出对话框, 防止自己写的应用 ...
- log4go折腾
导包 go get -u github.com/alecthomas/log4go log4go.xml配置 <logging> <filter enabled="true ...
- Ubuntu rar的坑
通过apt-get安装rar后,执行rar命令会有如下坑: rar: loadlocale.c:130: _nl_intern_locale_data: Assertion `cnt < (si ...
- AJPFX关于一维数组的声明与初始化
一维数组:可以理解为一列多行.类型相同的数据,其中每个数据被称为数组元素:一维数组的声明方式: type varName[]; 或 type[] varName;(推荐) ...
