洛谷——P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
题目描述
The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food.
The ant hill has nn chambers and n-1n−1 corridors connecting them.
We know that each chamber can be reached via a unique path from every other chamber.
In other words, the chambers and the corridors form a tree.
There is an entrance to the ant hill in every chamber with only one corridor leading into (or out of) it.
At each entry, there are gg groups of m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg ants respectively.
These groups will enter the ant hill one after another, each successive group entering once there are no ants inside.
Inside the hill, the ants explore it in the following way:
Upon entering a chamber with dd outgoing corridors yet unexplored by the group,the group divides into dd groups of equal size. Each newly created group follows one of the d corridors.If d=0d=0, then the group exits the ant hill.
- If the ants cannot divide into equal groups, then the stronger ants eat the weaker until a perfect division is possible.Note that such a division is always possible since eventually the number of ants drops down to zero.Nothing can stop the ants from allowing divisibility - in particular, an ant can eat itself, and the last one remaining will do so if the group is smaller than dd.
The following figure depicts mm ants upon entering a chamber with three outgoing unexplored corridors, dividing themselves into three (equal) groups of \left \lfloor m/3 \right \rfloor⌊m/3⌋ ants each.
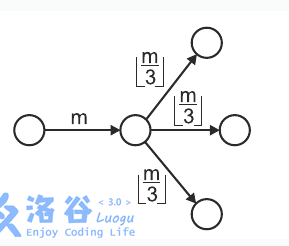
A hungry anteater dug into one of the corridors and can now eat all the ants passing through it.
However, just like the ants, the anteater is very picky when it comes to numbers.
It will devour a passing group if and only if it consists of exactly kk ants.
We want to know how many ants the anteater will eat.
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
输入输出格式
输入格式:
The first line of the standard input contains three integers nn, gg, kk(2\le n,g\le 1\ 000\ 0002≤n,g≤1 000 000, 1\le k\le 10^91≤k≤109), separated by single spaces.
These specify the number of chambers, the number of ant groups and the number of ants the anteater devours at once. The chambers are numbered from 1 to nn.
The second line contains gg integers m_1,m_2,\cdots,m_gm1,m2,⋯,mg (1\le m_i\le 10^91≤mi≤109), separated by single spaces, where m_imi gives the number of ants in the ii-th group at every entrance to the ant hill. The n-1n−1 lines that follow describe the corridors within the ant hill;the ii-th such line contains two integers a_iai,b_ibi (1\le a_i,b_i\le n1≤ai,bi≤n), separated by a single space, that indicate that the chambers no. a_iai and b_ibi are linked by a corridor. The anteater has dug into the corridor that appears first on input.
输出格式:
Your program should print to the standard output a single line containing a single integer: the number of ants eaten by the anteater.
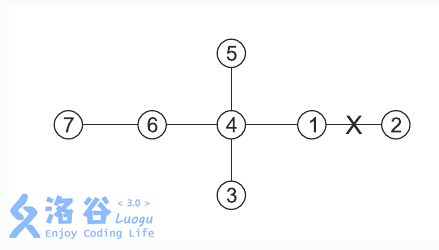
输入输出样例
7 5 3 3 4 1 9 11 1 2 1 4 4 3 4 5 4 6 6 7
21
说明
给一棵树,对于每个叶子节点,都有g群蚂蚁要从外面进来,每群蚂蚁在行进过程中只要碰到岔路,就将平均地分成岔路口数-1那么多份,然后平均地走向剩下的那些岔路口,余下的蚂蚁自动消失,树上有一个关键边,假如有一群蚂蚁通过了这条边且数量恰好为k,这k只蚂蚁就被吃掉,问一共有多少只蚂蚁被吃掉
树形dp
O(≧口≦)O做了一晚上、、、
我们会发现一个很严肃的问题,如果我们从子节点开始做的话会非常难处理(反正蒟蒻表示我不会、、、)
既然正着不会,我们就倒着搞吧、、其次他说的是通过一条边的数量为k,这k只蚂蚁都会被吃掉。然而我们如果直接用边来进行运算的话,既然这样我们直接将边改为这条边的两个节点,然后以这两个节点为根节点,将原来的树处理成两棵树。然后就可以在这两棵树上乱搞了
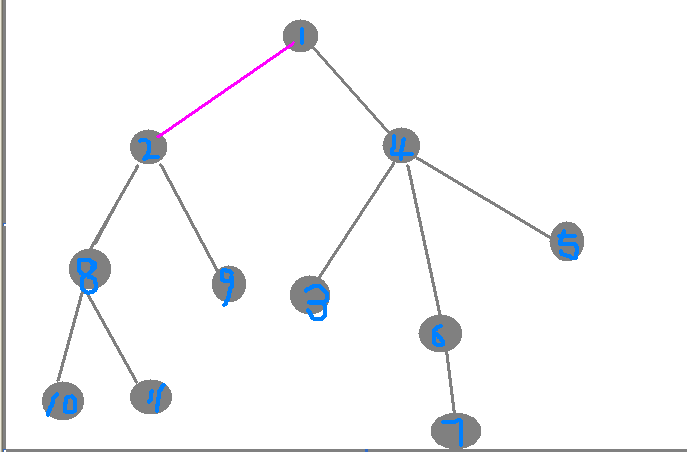 如图所示:在1~2这条边上如果有k只蚂蚁经过的时候这k只蚂蚁会被吃掉
如图所示:在1~2这条边上如果有k只蚂蚁经过的时候这k只蚂蚁会被吃掉
我们将上面的两棵树抽离成两颗一颗以1为根节点,一棵以2为根节点。
对于每一颗树我们从根节点开始往下进行搜索,更新每一个节点的父亲节点,如果这个点的父亲节点与他相连出去的节点不相同,那么将与他相连节点的父亲节点为当前节点。
我们看上面的图,如果要是蚂蚁经过1~2这条边上的时候蚂蚁的数量达到k时1号节点·与2好节点处的蚂蚁数量也就要为k。
然后我们在从这个各节点倒着计算他下面的节点蚂蚁的数量
我们知道进入蚂蚁的节点一定是子节点,然后每一个子节点往其他的分支那平分蚂蚁,他评分出来的蚂蚁一定是有一波要进入他的父亲节点。这样的话我们可以直接根据他的父亲节点的蚂蚁数目推出当前节点的蚂蚁数目,我们这个地方是不可能求出准确值的,因为他在平分的时候是下取整的。所以我们只能求出一个子节点的蚂蚁数目的范围。
子节点的蚂蚁的数目等于它的父节点的;连出去的边的条数*父节点的蚂蚁个数。
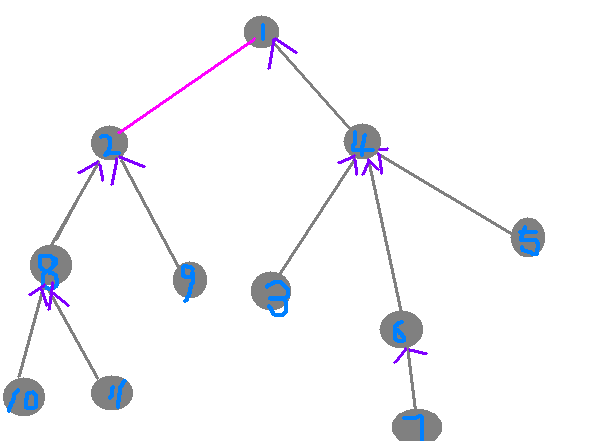 看这个图,你可以发现一个规律它的父节点连出去的边的条数正好等于它的父节点的入读。我们可以在进行dfs的时候处理处每一个点的父亲节点以及该点的入读、
看这个图,你可以发现一个规律它的父节点连出去的边的条数正好等于它的父节点的入读。我们可以在进行dfs的时候处理处每一个点的父亲节点以及该点的入读、
蚂蚁平分,子节点最少的蚂蚁的个数为他父亲节点的蚂蚁的数量*父亲节点的入读,也就是说没有蚂蚁被消灭。最多的蚂蚁的数量为还差一个蚂蚁就可以让每一个分支在多分一只蚂蚁了,极为maxn[t]=(sum[now]+1)*out[now]-1
然后dfs结束的条件的为他已经搜索到最后一层子节点了。当minn[to[i]]<=m[g]是说明还没有到达根节点。
然后我们可以处理处到达叶子节点的时候的蚂蚁的最多数量跟最少数量,然后在判断有多少组蚂蚁满足要求。
最后的可以吃到的蚂蚁的数量为k*满足条件的蚂蚁的组数
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define N 1100000
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n,g,k,x,y,sx,sy,tot;
int fa[N],in[N],head[N];
ll s[N],maxn[N],minn[N],ans;
int read()
{
,f=; char ch=getchar();
; ch=getchar();}
+ch-'; ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct Edge
{
int to,from,next;
}edge[N<<];
int add(int x,int y)
{
tot++;
edge[tot].to=y;
edge[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
int dfs(int now)
{
for(int i=head[now];i;i=edge[i].next)
{
int t=edge[i].to;
if(fa[now]!=t)
{
fa[t]=now;
in[now]++;
}
}
for(int i=head[now];i;i=edge[i].next)
{
int t=edge[i].to;
if(fa[now]!=t)
{
minn[t]=minn[now]*in[now];
maxn[t]=(maxn[now]+)*;
maxn[t]=min(maxn[t],s[g]);
if(minn[t]<=s[g]) dfs(t);
}
}
}
ll erfen(ll x)
{
,r=g,ans1=;
while(l<=r)
{
;
if(s[mid]<x)
{
ans1=mid;
l=mid+;
}
;
}
return ans1;
}
int main()
{
n=read(),g=read(),k=read();
;i<=g;i++) scanf("%lld",&s[i]);
sort(s+,s++g);
sx=read(),sy=read();
;i<n;i++)
{
x=read(),y=read();
add(x,y),add(y,x);
}
minn[sx]=minn[sy]=maxn[sx]=maxn[sy]=k;
dfs(sx),dfs(sy);
;i<=n;i++)
if(!in[i])
ans+=erfen(maxn[i]+)-erfen(minn[i]);
printf("%lld",ans*k);
;
}
洛谷——P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony的更多相关文章
- 洛谷 P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food. ...
- 洛谷P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony [二分答案,树形DP]
题目传送门 MRO-Ant colony 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in search of food. The ant h ...
- 洛谷—— P3576 [POI2014]MRO-Ant colony
https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=3576 题目描述 The ants are scavenging an abandoned ant hill in se ...
- 洛谷 P3580 - [POI2014]ZAL-Freight(单调队列优化 dp)
洛谷题面传送门 考虑一个平凡的 DP:我们设 \(dp_i\) 表示前 \(i\) 辆车一来一回所需的最小时间. 注意到我们每次肯定会让某一段连续的火车一趟过去又一趟回来,故转移可以枚举上一段结束位置 ...
- 洛谷 P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally 解题报告
P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally 题意: 给定一个\(N\)个点\(M\)条边的有向无环图,每条边长度都是\(1\). 请找到一个点,使得删掉这个点后剩余的图中的最长路径最短. 输入输 ...
- 洛谷P3572 [POI2014]PTA-Little Bird
P3572 [POI2014]PTA-Little Bird 题目描述 In the Byteotian Line Forest there are nn trees in a row. On top ...
- 2018.09.14 洛谷P3567 [POI2014]KUR-Couriers(主席树)
传送门 简单主席树啊. 但听说有随机算法可以秒掉%%%(本蒟蒻并不会) 直接维护值域内所有数的出现次数之和. 当这个值不大于区间总长度的一半时显然不存在合法的数. 这样在主席树上二分查值就行了. 代码 ...
- 洛谷P3567[POI2014]KUR-Couriers(主席树+二分)
题意:给一个数列,每次询问一个区间内有没有一个数出现次数超过一半 题解: 最近比赛太多,都没时间切水题了,刚好日推了道主席树裸题,就写了一下 然后 WA80 WA80 WA0 WA90 WA80 ?? ...
- 【刷题】洛谷 P3573 [POI2014]RAJ-Rally
题目描述 An annual bicycle rally will soon begin in Byteburg. The bikers of Byteburg are natural long di ...
随机推荐
- shell脚本,判断给出的字符串是否相等。
第一种方法[root@localhost wyb]# .sh #!/bin/bash #判断给出的字符串是否相等 read -p "Please Input a number:" ...
- 监控linux各主机系统时间是否一致
#!/bin/bashSTATE_OK=0 STATE_WARNING=1 STATE_CRITICAL=2 STATE_UNKNOWN=3PASSWD='**************'print_h ...
- PAT 乙级 1008
题目 题目地址:PAT 乙级 1008 思路 本题需要注意的一点是当 m > n 的时候会出现逻辑性的错误,需要在 m > n 情况下对m做模运算,即 m % n 代码 #include ...
- 自动化运维工具Ansible
一.简介 当下有许多的运维自动化工具( 配置管理 ),例如:Ansible.SaltStack.Puppet.Fabric 等. Ansible 一种集成 IT 系统的配置管理.应用部署.执行特定任务 ...
- C语言:哲学家吃饭问题
//五个哲学家围坐在一起,两人之间都放有一个叉子,意大利面需要2个叉子吃,哲学家吃饭时候叉子只能拿左右手,哲学家除了吃饭时间其他时间都在思考 #include <stdio.h> #inc ...
- 如何把握好 transition 和 animation 的时序,创作描边按钮特效
效果预览 在线演示 按下右侧的"点击预览"按钮可以在当前页面预览,点击链接可以全屏预览. https://codepen.io/comehope/pen/mKdzZM 可交互视频教 ...
- Lex与Yacc学习(二)之第一个Lex程序
用lex识别单词 构建一个识别不同类型英语单词的简单程序.先识别词性(名词,动词等),然后再扩展到处理符合简单英语语法的多个单词的句子. 先列出要识别的一组动词: is am are w ...
- C++中四种强制类型转换方式
类型转换有c风格的,当然还有c++风格的.c风格的转换的格式很简单(TYPE)EXPRESSION,但是c风格的类型转换有不少的缺点,有的时候用c风格的转换是不合适的,因为它可以在任意类型之间转换,比 ...
- Android开发工具——Gradle知识汇总
1.什么是构建工具 Eclipse大家都知道是一种IDE(集成开发环境),最初是用来做Java开发的,而Android是基于Java语言的,所以最初Google还是希望Android能在Eclipse ...
- tomcat 修改默认端口8080 为 80端口
首先,找到你的安装目录,如图: 打开server.xml文件,找到8080,如图: 将 8080 改成你想要的端口,如 80 即可.改完后,记得要重启tomcat! 将端口改成 80 后,访问就不需 ...
