JavaScript数据结构与算法(七) 双向链表的实现
TypeScript方式实现源码
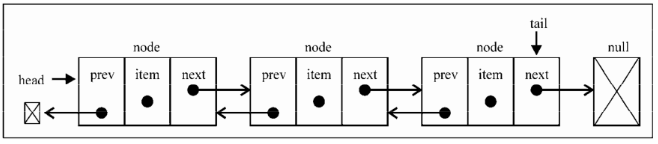
// 双向链表和普通链表的区别在于, 在链表中,
// 一个节点只有链向下一个节点的链接,而在双向链表中,链接是双向的:一个链向下一个元素,
// 另一个链向前一个元素,如下图所示:
//
// Node类里有prev属性(一个新指针) ,在DoublyLinkedList类里也有用来保存对列表最后一
// 项的引用的tail属性。 // 双向链表提供了两种迭代列表的方法:从头到尾,或者反过来。我们也可以访问一个特定节
// 点的下一个或前一个元素。在单向链表中,如果迭代列表时错过了要找的元素,就需要回到列表
// 起点,重新开始迭代。这是双向链表的一个优点。
// 代码角度
// 每个节点设置两个指针,关联相邻的前后节点.提供逆向遍历,链表篇提到,链表是针对大量删除与添加场景下使用的.因此双向链表是针对普通链表的功能为基础,强化了遍历的功能
// 抽象
// 想了很久找不到现实中的场景,还是拿火车来理解吧.早期火车就像普通链表,具有重组车厢的功能.而随着科技的进步,双向列车出来了,优势便是不用再每次脱离车头,开到转盘进行掉头
// 然后再行驶.双向链表便是双向列车,它弱化了车头的概念,前后皆可是车头.
// 总结
// 单向链表优势在于可执行大量删除、增加操作并不用像数组那样需要重新排序.劣势则是每次便利必须从头开始,无端增加许多系统开销.假如有这种场景,知道某个节点,我需要找到
// 该节点的爷爷,再找他爷爷的儿子,再找他儿子的孙子.我们大脑瞬间可以计算出,这不就是要找当前节点的儿子吗?的确!我们就是要程序能够这样做,但是单向链表就是一根筋,不具备
// 这样的智商,这时双向链表优势则非常明显
class Node {
element;
next;
prev; // 新增的
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
/**
* 双向链表
* @name DoublyLinkedList
*/
class DoublyLinkedList {
private length = ;
head = null;
tail = null; // 新增的
/**
* 向列表尾部添加一个新的项
* @param element
*/
public append(element) {
let node = new Node(element), current;
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
// 循环列表,知道找到最后一项
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// 找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立链接
current.next = node;
}
this.length++; // 更新列表长度
}
/**
* 向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项
* @param position
* @param element
*/
public insert(position, element) {
// 检查越界值
if (position >= && position <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element),
current = this.head,
previous,
index = ;
if (position === ) { // 在第一个位置添加
if (!this.head) { // 新增的
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node; // 新增的
this.head = node;
}
} else if (position === this.length) { // 最后一项 新增的
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node; // 新增的
node.prev = previous; // 新增的
}
this.length++; // 更新列表长度
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 从列表的特定位置移除一项
* @param position
*/
public removeAt(position) {
// 检查越界值
if (position > - && position < this.length) {
let current = this.head,
previous,
index = ;
// 移除第一项
if (position === ) {
this.head = current.next;
// 如果只有一项,更新tail // 新增的
if (this.length === ) {
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head.prev = null;
}
}
else if (position === this.length - ) { // 新增的
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将previous与current的下一项链接起来:跳过current,从而移除它
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous; // 新增的
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
} else {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 从列表中移除一项
* @param element
*/
public remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
/**
* :返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
* @param element
*/
public indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head,
index = -;
while (current) {
if (element === current.element) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -;
}
/**
* 如果链表中不包含任何元素, 返回true, 如果链表长度大于0则返回false
*/
public isEmpty() {
return this.length === ;
}
/**
* 返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似
*/
public size() {
return this.length;
}
/**
* 由于列表项使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的toString方法,让其只输出元素的值
*/
public toString() {
let current = this.head,
string = '';
while (current) {
string += current.element;
current = current.next;
}
return string;
}
public getHead() {
return this.head;
}
public print() {
console.log(this.toString());
}
}
var Node = (function () {
function Node(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
return Node;
}());
/**
* 双向链表
* @name DoublyLinkedList
*/
var DoublyLinkedList = (function () {
function DoublyLinkedList() {
this.length = ;
this.head = null;
this.tail = null; // 新增的
}
/**
* 向列表尾部添加一个新的项
* @param element
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.append = function (element) {
var node = new Node(element), current;
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
}
else {
current = this.head;
// 循环列表,知道找到最后一项
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// 找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立链接
current.next = node;
}
this.length++; // 更新列表长度
};
/**
* 向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项
* @param position
* @param element
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.insert = function (position, element) {
// 检查越界值
if (position >= && position <= this.length) {
var node = new Node(element), current = this.head, previous = void , index = ;
if (position === ) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node; // 新增的
this.head = node;
}
}
else if (position === this.length) {
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
}
else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node; // 新增的
node.prev = previous; // 新增的
}
this.length++; // 更新列表长度
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
};
/**
* 从列表的特定位置移除一项
* @param position
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function (position) {
// 检查越界值
if (position > - && position < this.length) {
var current = this.head, previous = void , index = ;
// 移除第一项
if (position === ) {
this.head = current.next;
// 如果只有一项,更新tail // 新增的
if (this.length === ) {
this.tail = null;
}
else {
this.head.prev = null;
}
}
else if (position === this.length - ) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}
else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 将previous与current的下一项链接起来:跳过current,从而移除它
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous; // 新增的
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
else {
return null;
}
};
/**
* 从列表中移除一项
* @param element
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.remove = function (element) {
var index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
};
/**
* :返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
* @param element
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (element) {
var current = this.head, index = -;
while (current) {
if (element === current.element) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -;
};
/**
* 如果链表中不包含任何元素, 返回true, 如果链表长度大于0则返回false
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
return this.length === ;
};
/**
* 返回链表包含的元素个数。与数组的length属性类似
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.size = function () {
return this.length;
};
/**
* 由于列表项使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的toString方法,让其只输出元素的值
*/
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.toString = function () {
var current = this.head, string = '';
while (current) {
string += current.element;
current = current.next;
}
return string;
};
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.getHead = function () {
return this.head;
};
DoublyLinkedList.prototype.print = function () {
console.log(this.toString());
};
return DoublyLinkedList;
}());
JavaScript数据结构与算法(七) 双向链表的实现的更多相关文章
- 为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第七章)—— 字典和散列表
本章学习使用字典和散列表来存储唯一值(不重复的值)的数据结构. 集合.字典和散列表可以存储不重复的值.在集合中,我们感兴趣的是每个值本身,并把它作为主要元素.而字典和散列表中都是用 [键,值]的形式来 ...
- 前端开发周报: CSS 布局方式方式与JavaScript数据结构和算法
前端开发周报:CSS 布局方式与JavaScript动画库 1.常见 CSS 布局方式详见: 一些常见的 CSS 布局方式梳理,涉及 Flex 布局.Grid 布局.圣杯布局.双飞翼布局等.http: ...
- 为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第八章)—— 树
之前介绍了一些顺序数据结构,介绍的第一个非顺序数据结构是散列表.本章才会学习另一种非顺序数据结构--树,它对于存储需要快速寻找的数据非常有用. 本章内容 树的相关术语 创建树数据结构 树的遍历 添加和 ...
- 为什么我要放弃javaScript数据结构与算法(第五章)—— 链表
这一章你将会学会如何实现和使用链表这种动态的数据结构,这意味着我们可以从中任意添加或移除项,它会按需进行扩张. 本章内容 链表数据结构 向链表添加元素 从链表移除元素 使用 LinkedList 类 ...
- JavaScript数据结构与算法-链表练习
链表的实现 一. 单向链表 // Node类 function Node (element) { this.element = element; this.next = null; } // Link ...
- javascript数据结构与算法 零(前记+前言)
前记 这本书Data Structure and Algorithm with Javascript 我将其翻译成<< javascript 数据结构和算法>> 为什么这么翻译 ...
- JavaScript 数据结构与算法之美 - 线性表(数组、栈、队列、链表)
前言 基础知识就像是一座大楼的地基,它决定了我们的技术高度. 我们应该多掌握一些可移值的技术或者再过十几年应该都不会过时的技术,数据结构与算法就是其中之一. 栈.队列.链表.堆 是数据结构与算法中的基 ...
- javascript数据结构与算法--高级排序算法
javascript数据结构与算法--高级排序算法 高级排序算法是处理大型数据集的最高效排序算法,它是处理的数据集可以达到上百万个元素,而不仅仅是几百个或者几千个.现在我们来学习下2种高级排序算法-- ...
- javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树
javascript数据结构与算法-- 二叉树 树是计算机科学中经常用到的一种数据结构.树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分成的方式存储数据,树被用来存储具有层级关系的数据,比如文件系统的文件,树还被用来存 ...
随机推荐
- SuSE的命令安装软件 zypper
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/s_k_yliu/article/details/6674079 SuSE的命令安装软件 zypper,yast2 redhat yum debain ...
- 【Spring源码深度解析学习系列】容器的基础XmlBeanFactory(二)
一.配置文件封装 Spring的配置文件读取是通过ClassPathResource进行封装的,如new ClassPathResource("test.xml"),那么Class ...
- tornado options
tornado.options.define() 用来定义options选项变量的方法,定义的变量可以在全局的tornado.options.options中获取使用,传入参数: name 选项变量名 ...
- vivado License导入方法与资源获取
前言 以下安装说明基于已经正确安装vivado 笔者操作环境:linux vivado版本:2015.2 vivado License导入方法: 点击菜单栏[Help],选择[Manage Licen ...
- 一个毕生难忘的BUG
记得以前接手过一个Java项目,服务器程序,直接让Jar在linux上跑的那种, 这个项目由两个web服务组成,也就是两条Java进程,主进程 xxx.jar,辅助进程 xxx_helper.jar. ...
- java克隆之深拷贝与浅拷贝
版权声明:本文出自汪磊的博客,转载请务必注明出处. Java深拷贝与浅拷贝实际项目中用的不多,但是对于理解Java中值传递,引用传递十分重要,同时个人认为对于理解内存模型也有帮助,况且面试中也是经常问 ...
- java中DelayQueue的一个使用陷阱分析
最近工作中有接触到DelayQueue,网上搜索资料的时候发现一篇文章谈到DelayQueue的坑.点击打开链接 文中已经总结了遇到坑的地方,还有解决方案.不过我第一眼看一下没弄明白为什么,所以翻了翻 ...
- python端口扫描用多线程+线程安全的队列+Thread类实现
用线程安全的队列Queue实现扫描端口数据存储 用多线程扫描端口 用Thread类实现程序组织 #coding:utf-8 import sys import socket import sys im ...
- 彻底搞懂shell的高级I/O重定向
本文目录: 1.1 文件描述符(file description,fd) 1.2 文件描述符的复制 1.3 重定向顺序很重要:">file 2>&1"和&quo ...
- Highcharts tooltip显示多条线的信息
直接上代码吧,简单粗暴点: tooltip: { shared: true, valueSuffix: '分', formatter: function () { let s = "&quo ...