python基础练习题
购物车程序
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/3/6 21:01
# @Author : hyang
# @Site :
# @File : shop_cart.py
# @Software: PyCharm """
购物车程序
数据结构:
goods = [
{"name": "电脑", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠标", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "美女", "price": 998},
......
] 功能要求:
基础要求: 1、启动程序后,输入用户名密码后,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表 2、允许用户根据商品编号购买商品 3、用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒 4、可随时退出,退出时,打印已购买商品和余额 5、在用户使用过程中, 关键输出,如余额,商品已加入购物车等消息,需高亮显示 扩展需求: 1、用户下一次登录后,输入用户名密码,直接回到上次的状态,即上次消费的余额什么的还是那些,再次登录可继续购买 2、允许查询之前的消费记录
"""
import os # 商品列表
goods = [
{"name": "电脑", "price": 1999},
{"name": "鼠标", "price": 10},
{"name": "游艇", "price": 20},
{"name": "IPAD", "price": 1998},
{"name": "手机", "price": 998},
{"name": "玩具", "price": 50},
{"name": "教科书", "price": 100}
] last_shop = [] # 上次购买数据
last_bal = [] # 得到每次购买余额 def is_shop(user):
"""
判断该用户是否已消费数据
:param user:
:return:
"""
flg = False
if os.path.exists(r"user_shop.txt"):
# 查询用户有购买记录
with open(r"user_shop.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
if line.find(user) != -1:
flg = True
break
else: # 创建空文件
with open(r"user_shop.txt", "w", encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("")
return flg def login():
"""
用户登录
:return:
"""
err_cnt = 0
suc_user = '' # 返回成功登录用户
# 判断锁标志
while err_cnt < 3:
user = input('输入用户名: ')
pwd = input('输入密码: ')
if user == 'alex' and pwd == '':
print('登录成功')
suc_user = user
break
else:
print('登录失败')
err_cnt += 1
else:
print('您登录失败已超过3次')
return suc_user def check_salary():
"""
检查收入
:return:
"""
while True:
salary = input('输入工资: ')
if salary.isdigit():
break
else:
print('工资输入错误,请重新输入!')
return int(salary) def shop(user, salary):
"""
用户购物
"""
shop_cart = [] # 购物车
while True:
print('-------商品列表--------')
for index, value in enumerate(goods):
print('商品编号:%s 商品名称:%s 商品价格:%s' % (index, value['name'], value['price'])) choice = input('输入商品编号:---输入q退出购买 ')
if choice.isdigit():
choice = int(choice)
if 0 <= choice < len(goods):
price = goods[choice]['price']
if (salary - price) > 0:
salary = salary - price
shop_cart.append(goods[choice])
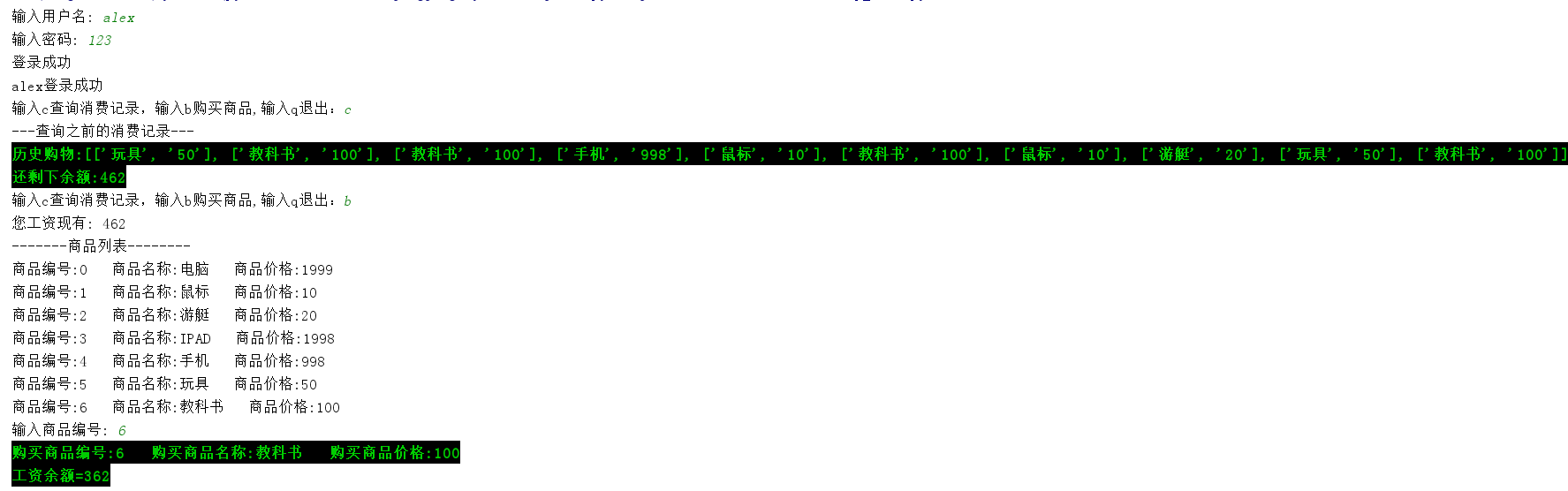
print('\033[1;32;40m购买商品编号:%s 购买商品名称:%s 购买商品价格:%s\033[0m'
% (choice, goods[choice]['name'], goods[choice]['price']))
print('\033[1;32;40m工资余额=%s\033[0m' % salary)
else:
print('余额不足')
continue
else:
print('商品编号不存在!') elif choice == 'q':
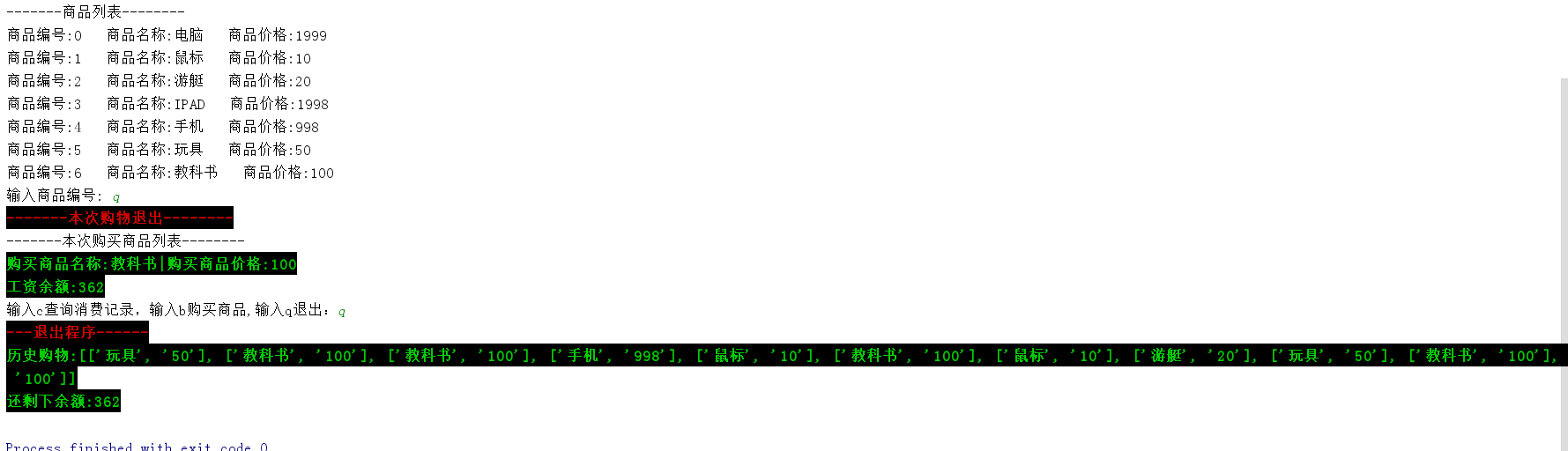
print('\033[1;31;40m-------本次购物退出--------\033[0m')
if len(shop_cart) > 0:
print('-------本次购买商品列表--------')
with open(r"user_shop.txt", "a+", encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("user:%s\n" % user)
for value in shop_cart:
shop_info = '购买商品名称:%s|购买商品价格:%s' % (value['name'], value['price'])
print('\033[1;32;40m%s\033[0m' % shop_info)
f.write(shop_info + "\n")
bal_info = '工资余额:%s' % salary
print('\033[1;32;40m%s\033[0m'% bal_info)
f.write(bal_info + "\n")
break def get_shop(user):
"""
读取文件得到用户已消费数据
:param user:
:return:
"""
flg = False
resume_goods = [] # 消费商品
with open(r"user_shop.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
if line.find("购买") != -1:
shop_li = line.split("|")
resume_goods.append([shop_li[0].split(":")[1].strip(), shop_li[1].split(":")[1].strip()])
elif line.find("余额") != -1:
last_bal.append(line.split(":")[1].strip())
print("\033[1;32;40m历史购物:%s\033[0m" % resume_goods) # 带绿色输出
print('\033[1;32;40m还剩下余额:%s\033[0m' % last_bal[-1]) # 带绿色输出 if __name__ == '__main__':
user = login()
if user != '':
print('{}登录成功'.format(user))
while True:
action = input('输入c查询消费记录,输入b购买商品,输入q退出:')
if action == 'q':
print('\033[1;31;40m---退出程序------\033[0m') # 带红色输出
get_shop(user)
break
elif action == 'c':
if is_shop(user):
print("---查询之前的消费记录---")
get_shop(user)
else:
print("---查询之前无消费记录---")
elif action == 'b':
if not is_shop(user):
salary = check_salary()
else:
salary = int(last_bal[-1])
print('您工资现有:', salary)
shop(user, salary)
输出结果
三级菜单程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/3/1 9:38
# @Author : hyang
# @File : three_menu.py
# @Software: PyCharm
"""
可依次选择进入各子菜单
可从任意一层往回退到上一层
可从任意一层退出程序
"""
menu = {
'北京':{
'海淀':{
'五道口':{
'soho':{},
'网易':{},
'google':{}
},
'中关村':{
'爱奇艺':{},
'汽车之家':{},
'youku':{},
},
'上地':{
'百度':{},
},
},
'昌平':{
'沙河':{
'老男孩':{},
'北航':{},
},
'天通苑':{},
'回龙观':{},
},
'朝阳':{},
'东城':{},
},
'上海':{
'闵行':{
"人民广场":{
'炸鸡店':{}
}
},
'闸北':{
'火车站':{
'携程':{}
}
},
'浦东':{},
},
'山东':{},
} current_menu = menu # 当前菜单
last_menu = [] # 上层菜单
prompt = "输入菜单名,进入子菜单\n 输入'b',返回上层菜单\n 输入'q',退出程序\n"
while True:
if len(current_menu) == 0:
print('已经到最底层,该菜单下无节点')
else:
for k in current_menu:
print('菜单->', k)
input_str = input(prompt).strip()
if input_str == 'q':
print('退出程序')
break
elif input_str in current_menu:
last_menu.append(current_menu) # 保存上一层菜单
current_menu = current_menu[input_str] # 保存当前层
elif input_str == 'b':
if len(last_menu) != 0:
current_menu = last_menu.pop() # 弹出上一层菜单
else:
print('已经是顶层菜单')
else:
print('该节点菜单不存在')
continue
python基础练习题的更多相关文章
- python基础练习题1
深深感知python基础是有多么重要,Ljh说一定要多练题,so,我现在开始要每天打卡练习python.加油! 01:求‘1-100’的偶数和 #第一种解法: sum=0 num=0 while nu ...
- python基础练习题(九九乘法表)
又把python捡起来了,动手能力偏弱,决定每日一练,把基础打好! ------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
- Python基础 练习题
DAY .1 1.使用while循环输出 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 n = 1 while n < 11: if n == 7: pass else: print(n) n ...
- Python基础练习题100例(Python 3.x)
1:题目:有四个数字:1.2.3.4,能组成多少个互不相同且无重复数字的三位数?各是多少? 程序分析:可填在百位.十位.个位的数字都是1.2.3.4.组成所有的排列后再去 掉不满足条件的排列. 程序源 ...
- python基础练习题30道
1.执行python脚本的两种方式 答:1>可以在python /home/xxxx.py 2>cd /home ./xxxx.py 因为py脚本里面指定了python解释器的位置 ...
- 08: python基础练习题
1.while循环实现输出2 - 3 + 4 - 5 + 6 ... + 100 的和 # 使用while循环实现输出2 - 3 + 4 - 5 + 6 ... + 100 的和 s = 0 i = ...
- 『Python基础练习题』day02
1.判断下列逻辑语句的True, False 1) 1 > 1 or 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6 2) ...
- Python学习【day03】- Python基础练习题(列表、元组、字典)
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- # 1.有两个列表 # l1 = [11,22,33] # l2 = [22,33,44] # a.获取内容相同 ...
- Python学习【day02】- Python基础练习题
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- # 执行Python 脚本的两种方式 # 答:①在windows的cmd窗口下 > D:/Python/p ...
随机推荐
- jQuery中animate()方法用法实例
本文实例讲述了jQuery中animate()方法用法.分享给大家供大家参考.具体分析如下: 此方法用于创建自定义动画,并且能够规定动画执行时长.擦除效果.动画完成后还可以地触发一个回调函数. ani ...
- zabbix安装步骤
第一步:安装环境 Zabbix要求的环境 组件 版本要求 Apache版本 1 .3.1 2 MySQL版本 5.0.3 PHP版本 5.4.0 本次安装的环境 组件 版本要求 操作系统 CentOS ...
- ★MySQL一些很重要的SQL语句
[mysqldumpslow] -s 排序选项:c 查询次数 r 返回记录行数 t 查询时间 -t 只显示top n条查询 mysqldumpslow -s r -t 10000 slow-que ...
- python学习:简单的wc命令实现
#!/usr/bin/python import sys import os try: fn = sys.argv[1] except IndexError: print &q ...
- 洛谷 P4016负载平衡问题【费用流】题解+AC代码
洛谷 P4016负载平衡问题 P4014 分配问题[费用流]题解+AC代码 负载平衡问题 题目描述 GG 公司有n个沿铁路运输线环形排列的仓库,每个仓库存储的货物数量不等.如何用最少搬运量可以使 n ...
- bzoj 3669: [Noi2014]魔法森林
bzoj 3669: [Noi2014]魔法森林 Description 为了得到书法大家的真传,小E同学下定决心去拜访住在魔法森林中的隐士.魔法森林可以被看成一个包含个N节点M条边的无向图,节点标号 ...
- C#实现七牛云存储
云存储,就是把本地的资源文件存放至网络上,可以公网访问.相当于网盘功能,感觉非常方便. 这里介绍的是七牛云存储.有兴趣的可以去官方网站详看 根据官网的介绍,本身是提供SDK的,下载地址,大家可以根据自 ...
- JavaScript 历史漫谈
话说 JavaScript 其实是诞生在一个特殊的时期,20世纪90年代,正值第三次科技革命时期,互联网刚开始进入人们的生活.设想一下,在网速只有几十比特的那个时代,在登录注册时要花上很长一段时间等待 ...
- Linux下 开启防火墙端口
命令行输入: vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables 将 -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 端口号 -j ACCEP ...
- DxPackNet 3.音频捕捉(录音)
用DxpackNet捕捉音频其实很简单 1.初始化控件 IDxMicrophCapture microphone; private void Form1_Load(object sender, Eve ...
