Spring in Action 4th 学习笔记 之 AOP
前提:本文中的AOP仅限于Spring AOP。
先说说为什么需要AOP
最简单的一个例子就是日志记录,如果想记录一些方法的执行情况,最笨的办法就是修改每一个需要记录的方法。但这,真的很笨。。。
好的方法,应该是通过反射获取方法,然后去匹配,如果需要记录日志,那就调用日志方法即可。
这就是AOP 的Weaving,俗称编织、织入,就是将需要添加的功能编织到现有功能中,而不需要修改现有代码。
另一个例子,不那么大众的需求:我想给一个对象添加方法,怎么实现?
如果有学过js、Python等动态语言,你肯定知道它们支持给对象添加方法,直接添加即可。
但是Java不行,因为Java的类型是封闭的。
Spring给出办法就是通过代理,拦截请求,然后去调用实际拥有该方法的对象的该方法!(略绕) 这就是Introduction,俗称引入。
如图:
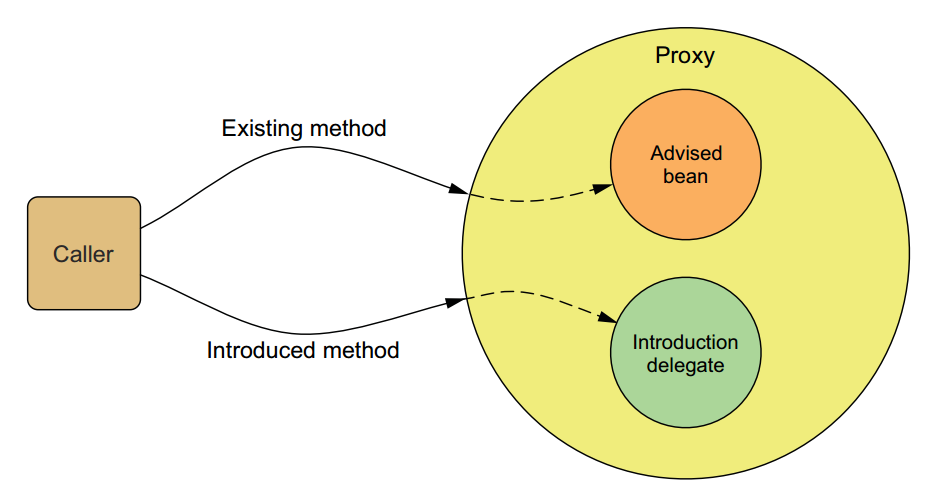
这是书中自带的图片,很形象。
如图所示,如果调用Advised bean的Existing method,那就是Weaving(织入);如果调用introduced method,那就是Introduction。
但是,无论那种,Spring都是通过其代理功能实现的。(如果你已经知道Spring的代理功能仅限于method,那你也可以想到Spring AOP仅限于method --- 稍后讨论)
以上,记住一点就行:Spring AOP中,给方法添加功能就是织入,给对象添加功能就是引入。
(至于为什么强调是Spring AOP,这是因为还有其他的AOP框架,稍后讨论。)
再列一下其他概念:
Weaving织入部分: Advice : 需要添加的功能,例如日志功能、权限功能等,以及什么时候添加(目标方法执行前、后、异常等时候)。 Join-point : 目标类中能够添加功能的地方! Pointcut : 指定目标类中添加功能的地方!因为不可能给所有Join-point织入Advice!(Spring AOP仅限于方法,因为它基于代理实现。其他的框架还可以针对字段添加功能!了解就行。) 需要注意的是,Advice定义了什么时候做、做什么,而Pointcut则定义了在哪里做。 Aspect = Advices + Pointcuts // Aspect可以认为是一堆Advice的类,且其中指定了每个Advice执行的Pointcut。
Introduction引入部分: 暂无
以上,Pointcut是关键,它决定了一个AOP框架的行为。
因为Pointcut意味着where(field?method?exception?)和when(编译时?加载时?运行时?)。
【】通常,使用class和method name来定义Pointcut,或者使用正则表达式匹配class和method name来定义Pointcut!!!
Weaving应用部分
Spring AOP和AspectJ有很多协同。Spring AOP借鉴了AspectJ很多理念。
Spring对AOP的支持有四种形式:
① 经典的Spring基于代理的AOP。
② 纯POJO aspect。
③ @AspectJ注解驱动的aspect。
④ 注入的AspectJ aspect。
以上,前三种是Spring自有AOP的变体,由于都是基于代理,所以,仅限于方法拦截!!!
Spring AOP引用了AspectJ EL。
AspectJ EL表达式:核心就是execution,其他的都是用于限制各种参数的。【】【】
例如:
execution(* concert.Performance.perform(..)) && within(concert.*) // 这里就定义了一个pointcut,而且仅限于被concert包下的aspect使用。
上面的AspectJ EL是由两部分组成:execution定义切入点,within限定切入点。见下图:
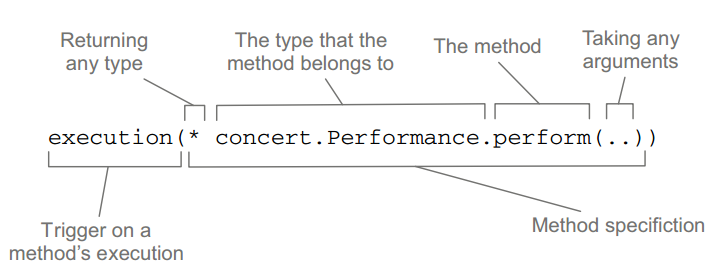

上面,可以使用&&或and、||或or、!或not。 类似EL或JSTL。
Spring还增加一个bean(),意思是仅限于该bean的Pointcut。
例如:execution(* concert.Performance.perform()) and bean('woodstock') 这里就定义了一个woodstock的pointcut。
例如:execution(* concert.Performance.perform()) and !bean('woodstock') 注意这里!!!很有意思的用法。
AspectJ 注解开发:
AspectJ 从 5 开始引入了注解开发,Spring AOP同样引入AspectJ的注解。
但是,Spring AOP仅仅是利用AspectJ的注解名词,底层仍然是Spring AOP的代理实现。
注解开发过程:
@Aspect注解到aspect所在的类上,然后@Before等注解到advice(aspect对应的方法)上。如下:
@Component // 这个是必须的!!
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") // 该注解声明了silenceCellPhones()需要应用到的Pointcut。
public void silenceCellPhones() {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones");
}
@Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void takeSeats() {
System.out.println("Taking seats");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void applause() {
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void demandRefund() {
System.out.println("Demanding a refund");
}
}
但是,上面这种写法很不方便,因为Pointcut是重复的。
解决办法:使用@Pointcut一次性定义好一个Pointcut。如下:
@Component // 这个是必须的!!!
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Pointcut("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void perform(){}; // 必须要定义一个方法,用于承载pointcut! // 其他的正常代码,略
}
但是,到目前为止,AOP仍然是无法执行的,因为Spring AOP不知道这些注解代表什么,所以需要先开启AspectJ自动代理。
开启方法:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解到JavaConfig上面。或者,如果使用XML,<aop:aspectj-autoproxy> 。注意导入名称空间。
现在,上面的内容可以直接进行测试了:
package aop.performance; /**
* 用这个演示join-point和pointcut。
* perform()就是join-point!
*
* @author Larry
*/
public interface Performance {
void perform();
}
package aop.performance;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class PerformanceImpl implements Performance{
@Override
public void perform() {
System.out.println(this.getClass()+"正在演出~~~");
}
}
package aop; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 用Audience类来掩饰AspectJ 5的注解用法。
*
* @author Larry
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Audience {
@Before("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void takeSeat() {
System.out.println("演出之前要入座~");
} @Before("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void silenceCellPhones() {
System.out.println("演出之前要静音~");
} @After("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void applause() {
System.out.println("演出之后要鼓掌!");
} // TODO: 貌似不能这样用??而且会导致大BUG!!!阻止访问Pointcut!!!见下面
//@Around("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void greet() {
System.out.println("演出前后要致意~");
} @AfterReturning("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void leave() {
System.out.println("结束后,goodbye~");
} @AfterThrowing("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void demandRefund(){
System.out.println("退钱!!!");
} //上面,不好的地方是每次都要写相同的pointcut!解决办法如下:
@Pointcut("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))")
public void perform(){}
// 这样就定义了一个pointcut:performance(),然后就可以直接使用了!如下:
@Before("perform()")
public void wave(){
System.out.println("挥挥手~");
} // TODO: 务必注意,@Around必须手动调用Pointcut,否则会阻止对Pointcut的访问!!!
@Around("perform()")
public void greet2(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("演出前后要致意~A");
jp.proceed();//TODO:这里还可以调用带参数的!
System.out.println("演出前后要致意~B");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package aop; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import aop.performance.PerformanceImpl; @Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={ Audience.class,PerformanceImpl.class,AudienceB.class,IntroductionEncoreable.class })
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //激活AspectJ
public class JavaConfig { }
package aop.test; import java.util.Arrays; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import aop.JavaConfig;
import aop.performance.Performance; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = { JavaConfig.class })
public class PerformanceAOPTest {
@Autowired
Environment env;
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ac; @Autowired
Performance p; @Test
public void run() {
String[] activeProfiles = env.getActiveProfiles();
System.out.println("activeProfiles的长度"+activeProfiles.length);
for (String string : activeProfiles) {
System.out.println("activeProfiles:" + string);
} System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); String applicationName = ac.getApplicationName();
System.out.println("applicationName:"+applicationName);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
String beans = Arrays.toString(beanDefinitionNames);
System.out.println("applicationContext中的beans:"+beans); } @Test
public void run1() {
p.perform(); // 注意有没有激活AspectJ!
}
}
上面的代码就是一个测试的全过程,其中遇到的一个问题就是环绕通知@Around,这个注解要求必须手动调用Pointcut(方法),否则Spring代理会丢失该方法!
丢失该方法,就意味着后面的代理无法继续!!!(类似拦截器拦截请求,拦截之后还要手动放行,否则后面的程序无法接收到该请求,也就是 丢失请求!)
需要注意的是,还可以多次调用该方法!!!应用场景:异常后重新执行。
@Around("performance()")
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); // 相当于@Before
System.out.println("Taking seats"); // 相当于@Before
jp.proceed(); // 【】【】这个,就是调用pointcut。可能忘记调用,也可能重复调用。。。
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!"); // 相当于@After 【奇怪,那@AfterReturning呢】
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Demanding a refund"); // 相当于@AfterThrowing
}
}
到目前为止,介绍的都是无参数的Pointcut(是指Advice不使用Pointcut的参数),下面开始带参数的Pointcut。
带参数的Pointcut(Advice使用Pointcut的参数)
// 样式
execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber)
注意,需要在Pointcut中给定参数类型,以及形参名。然后,再给Advice添加相同的形参即可(类型和形参名)。如下:
/*
注意,这里实现的功能是统计trackNumber的播放次数!
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class TrackCounter {
private Map<Integer, Integer> trackCounts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); // 定义Pointcut
@Pointcut("execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber)")
public void trackPlayed(int trackNumber) {}
// Advice
@Before("trackPlayed(trackNumber)") // trackNumber就是pointcut方法的形参名!!!
public void countTrack(int trackNumber) {
int currentCount = getPlayCount(trackNumber);
trackCounts.put(trackNumber, currentCount + 1);
}
// 普通的方法
public int getPlayCount(int trackNumber) {
return trackCounts.containsKey(trackNumber) ? trackCounts.get(trackNumber) : 0;
}
}
Introduction应用部分
Introduction就是给对象(Bean)引入需要的功能,而不修改原有代码。(例如你拿不到源代码的情况~)
Spring AOP的实现方法就是拦截请求,再转而调用实现了所需方法的对象即可。
示例:
现在需要给Performance引入一个performEncore功能(再来一个、加演、额外演出 的意思)。
根据Spring AOP的原理,我们需要一个拥有该方法的Bean,所以我们先定义一个接口,再去实现它。
package aop.performance; /**
* Encore,加演。延长演出的意思。
* @author Larry
*
*/
public interface Encoreable {
void performEncore();
}
package aop.performance; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class EncoreableImpl implements Encoreable{
@Override
public void performEncore() {
System.out.println("加演一场~~~");
}
}
package aop; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.DeclareParents;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import aop.performance.Encoreable;
import aop.performance.EncoreableImpl; /**
* AOP应用之Introduction,就是给对象(bean)添加功能,类似js之类的动态语言给对象添加方法。。
* @author Larry
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class IntroductionEncoreable { @DeclareParents(value="aop.performance.Performance+",defaultImpl=EncoreableImpl.class) // 稍后讲
public static Encoreable encoreable; // 先引入需要引入的方法所在的接口
}
package aop; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; import aop.performance.PerformanceImpl; @Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={ PerformanceImpl.class,IntroductionEncoreable.class })
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy //激活AspectJ
public class JavaConfig { }
package IntroductionEncoreable; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import aop.JavaConfig;
import aop.performance.Encoreable;
import aop.performance.Performance; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes={JavaConfig.class})
public class IntroductionAOPTest {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ac;
@Autowired
Performance p; @Test
public void run1(){
((Encoreable)p).performEncore(); // 通过类型强转调用Introduction的方法!!!
}
}
上面就是测试Introduction的全部代码。
需要注意两点:
① @DeclareParents Field,其value为Pointcut所在的类(这里是接口,+表示其所有实现类或子类),defaultImpl则是接口的默认实现类,而Field则是所需方法所在的接口。
② 通过类型强转,将目标Bean转成@DeclareParents Field类型,再去调用方法!
最后,XML中配置Weaving织入,懒得弄了,直接上图吧

在XML中,一样可以定义Pointcut,然后在其他地方引用:
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="silenceCellPhones"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applause"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
XML配置和注解配置类似,唯一需要注意的是环绕通知@Around,还是需要指定一个方法,该方法接收ProceedingJoinPoint对象。
就是说,实际上同@Aspect Class的@Around Method一样,只不过现在去掉@Aspect和@Around,改为XML配置。
package aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
public class Audience {
public void greet3(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("演出前后要致意~A");
jp.proceed(); // TODO:这里还可以调用带参数的!
System.out.println("演出前后要致意~B");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))" />
<aop:around pointcut-ref="performance" method="greet3"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
另外,XML配置中的带参数Pointcut,略。见Spring in Action, 4th Edition p147。
XML中Introduction引入配置
<aop:aspect>
<aop:declare-parents types-matching="aop.performance.Performance+" implement-interface="aop.performance.Encoreable" default-impl="aop.performance.DefaultEncoreable" />
</aop:aspect>
或者,不使用default-impl,而使用delegate-ref。
<bean id="encoreableDelegate" class="aop.performance.DefaultEncoreable" />
<aop:aspect>
<aop:declare-parents types-matching="aop.performance.Performance+" implement-interface="aop.performance.Encoreable" delegate-ref="encoreableDelegate" />
</aop:aspect>
未完待续
Spring in Action 4th 学习笔记 之 AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring in Action 4th 学习笔记
约定: 一.@Xxx Class 表示被@Xxx注解的类.同理还有@Xxx注解的字段或方法. 例如:@Bean Method. 二.@Component Class 同时代指 @Controller. ...
- spring in action 4 (学习笔记1)
1.spring两个核心性质 DI(依赖注入) AOP(面向切面编程) 2.bean的生命周期
- 1、Spring In Action 4th笔记(1)
Spring In Action 4th笔记(1) 2016-12-28 1.Spring是一个框架,致力于减轻JEE的开发,它有4个特点: 1.1 基于POJO(Plain Ordinary Jav ...
- Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3)
Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3) 1.0 静态代理模式的缺点: 1.在该系统中有多少的dao就的写多少的proxy,麻烦 2.如果目标接口有方法的改动,则proxy也需要改动. Person ...
- Spring实战第八章学习笔记————使用Spring Web Flow
Spring实战第八章学习笔记----使用Spring Web Flow Spring Web Flow是一个Web框架,它适用于元素按规定流程运行的程序. 其实我们可以使用任何WEB框架写流程化的应 ...
- Spring实战第一章学习笔记
Spring实战第一章学习笔记 Java开发的简化 为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采取了以下四种策略: 基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程: 通过依赖注入和面向接口实现松耦合: 基于切面 ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————09.利用PCA简化数据
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————09.利用PCA简化数据 关键字:PCA.主成分分析.降维作者:米仓山下时间:2018-11-15机器学习实战(Ma ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————08.使用FPgrowth算法来高效发现频繁项集
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————08.使用FPgrowth算法来高效发现频繁项集 关键字:FPgrowth.频繁项集.条件FP树.非监督学习作者:米 ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————07.使用Apriori算法进行关联分析
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————07.使用Apriori算法进行关联分析 关键字:Apriori.关联规则挖掘.频繁项集作者:米仓山下时间:2018 ...
随机推荐
- Mysql multi实现mysql双实例
Mysql multi实现mysql双实例 1.添加mysql用户 以root登录,新建mysql用户组 groupadd mysql useradd -d /data/mariadb -g mysq ...
- oracle Database link 创建
http://www.cnblogs.com/yhason/p/3735319.html
- PHPEXCEL导出excel表格中长数字文本自动转为科学计数法的解决办法
方法一:前面加空格 $objActSheet->setCellValue('A1', ' '.'330602198804224688'); 方法二: $objActSheet->setCe ...
- MongoDB创建索引(不锁库方法)
db.collection.createIndex( { a: 1 }, { background: true } )https://docs.mongodb.org/manual/tutorial/ ...
- hdu 5289 Assignment(给一个数组,求有多少个区间,满足区间内的最大值和最小值之差小于k)
1.区间是一段的,不是断开的哟 2.代码是看着标程写的 3.枚举左端点,二分右端点流程: watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQv/font/5a6L ...
- ssh-copy-id 安全地复制公钥到远程服务器上
[root@NB .ssh]# ssh-copy-id -i id_rsa.pub " -p22 root@150.57.38.226" root@150.57.38.226's ...
- 不同版本Lua介绍
luainterface.nlua.ulua.unilua.cstolua.slua luainterface:LuaInterface是开源的C#的lua桥接库,配合开源库luanet,能轻松实现L ...
- Linux Jenkins配置Git
1.卸载Centos自带的git1.7.1:通过git –version查看系统带的版本,Centos应该自带的是git版本是1.7.1 终端输入:yum remove git 2.安装所需软件包 终 ...
- Qt学习之路3---Qt中的坐标系统
-Qt使用统一的坐标系统定位窗口部件和位置大小 -Qt部件类提供成员函数在坐标系统中进行定位 -QWidget类提供了窗口部件所需的坐标系统成员函数 代码测试 #include "widge ...
- lambda续集——1
捕获列表,只用于局部非static变量,lambda可以直接使用局部static变量和它所在函数之外声明的名字. eg: #include<iostream> using namespac ...
