《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 3.1
先写DTFT子函数:
function [X] = dtft(x, n, w) %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Computes DTFT (Discrete-Time Fourier Transform)
%% of Finite-Duration Sequence
%% Note: NOT the most elegant way
% [X] = dtft(x, n, w)
% X = DTFT values computed at w frequencies
% x = finite duration sequence over n
% n = sample position vector
% w = frequency location vector M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; X = x * (exp(-j*pi/M)) .^ (n'*k);
% X = x * exp(-j*n'*pi*k/M) ;
下面开始利用上函数开始画图。结构都一样,先显示序列x(n),在进行DTFT,画出幅度响应和相位响应。
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 3.1 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ % ----------------------------------
% x1(n)
% ----------------------------------
n1_start = -11; n1_end = 13;
n1 = [n1_start : n1_end]; x1 = 0.6 .^ (abs(n1)) .* (stepseq(-10, n1_start, n1_end)-stepseq(11, n1_start, n1_end)); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 x1(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n1, x1);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x1');
title('x1(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X1] = dtft(x1, n1, w); magX1 = abs(X1); angX1 = angle(X1); realX1 = real(X1); imagX1 = imag(X1); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, magX1); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX1/pi); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi');
subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX1); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX1); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT of x1(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX1); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX1); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x2(n)
% -------------------------------------
n2_start = -1; n2_end = 22;
n2 = [n2_start : n2_end]; x2 = (n2 .* (0.9 .^ n2)) .* (stepseq(0, n2_start, n2_end) - stepseq(21, n2_start, n2_end)); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 x2(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n2, x2);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x2');
title('x2(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X2] = dtft(x2, n2, w); magX2 = abs(X2); angX2 = angle(X2); realX2 = real(X2); imagX2 = imag(X2); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT of x2(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX2); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX2); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x3(n)
% -------------------------------------
n3_start = -1; n3_end = 52;
n3 = [n3_start : n3_end]; x3 = (cos(0.5*pi*n3) + j * sin(0.5*pi*n3)) .* (stepseq(0, n3_start, n3_end) - stepseq(51, n3_start, n3_end)); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 x3(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n3, x3);
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x3');
title('x3(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X3] = dtft(x3, n3, w); magX3 = abs(X3); angX3 = angle(X3); realX3= real(X3); imagX3 = imag(X3); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT of x3(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX3); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX3); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x4(n)
% -------------------------------------
n4_start = 0; n4_end = 7;
n4 = [n4_start : n4_end]; x4 = [4:-1:1, 1:4]; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 x4(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n4, x4, 'r', 'filled');
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x4');
title('x4(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X4] = dtft(x4, n4, w); magX4 = abs(X4); angX4 = angle(X4); realX4= real(X4); imagX4 = imag(X4); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT of x3(n)');;
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX4); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX4); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians'); % -------------------------------------
% x5(n)
% -------------------------------------
n5_start = 0; n5_end = 7;
n5 = [n5_start : n5_end]; x5 = [4:-1:1, -1:-1:-4]; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 x5(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n5, x5, 'r', 'filled');
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x5');
title('x5(n) sequence'); grid on; M = 500;
k = [-M:M]; % [-pi, pi]
%k = [0:M]; % [0, pi]
w = (pi/M) * k; [X5] = dtft(x5, n5, w); magX5 = abs(X5); angX5 = angle(X5); realX5= real(X5); imagX5 = imag(X5); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 3.1 DTFT of x5(n)');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(w/pi, magX5); grid on;
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude');
subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, angX5); grid on;
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians');
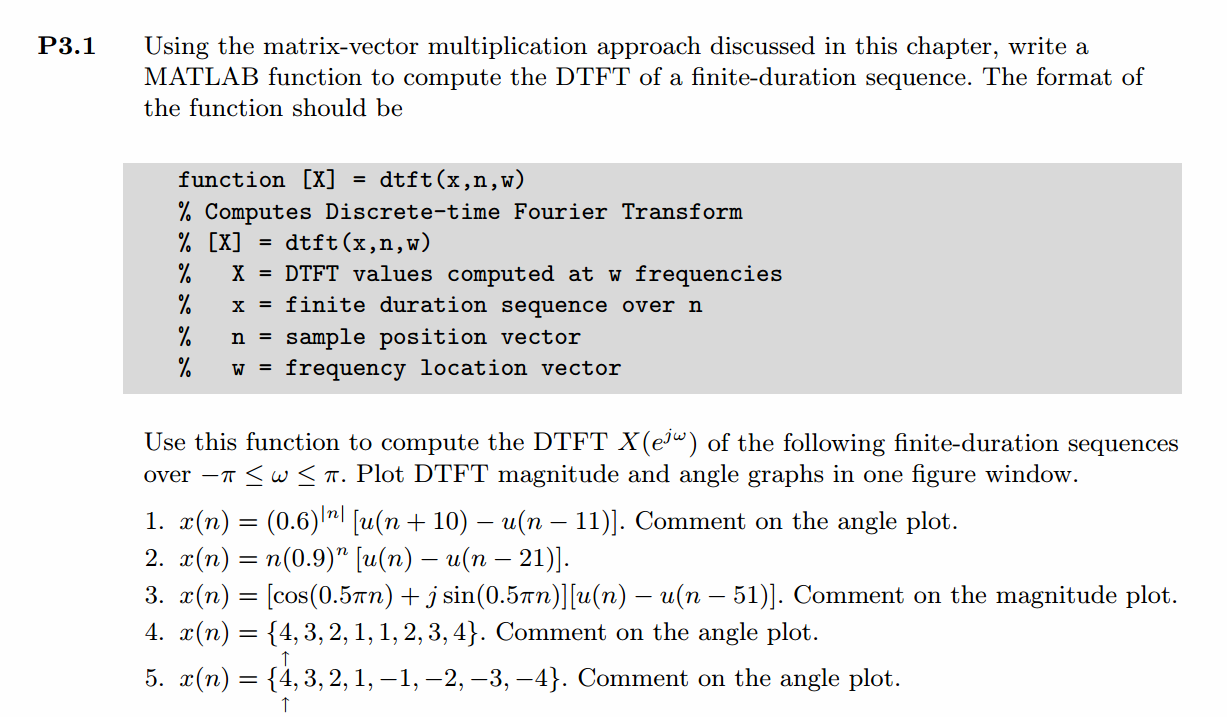
运行结果:
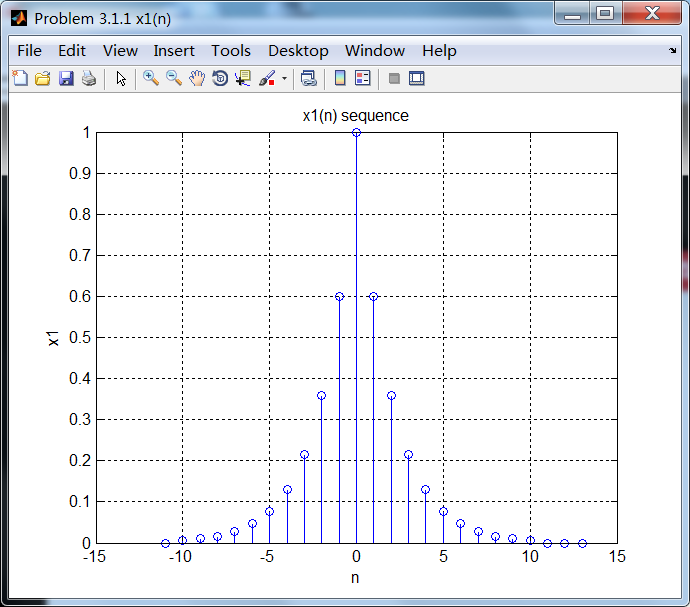

相位响应是关于ω=0偶对称的。
序列2:

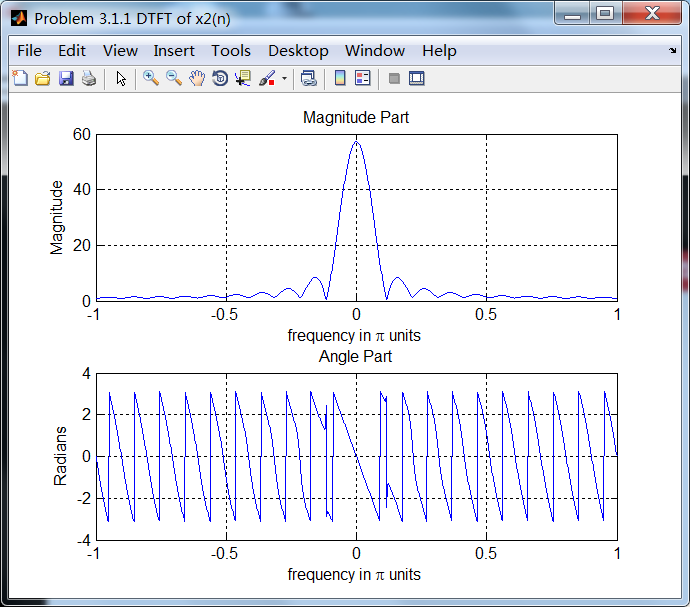
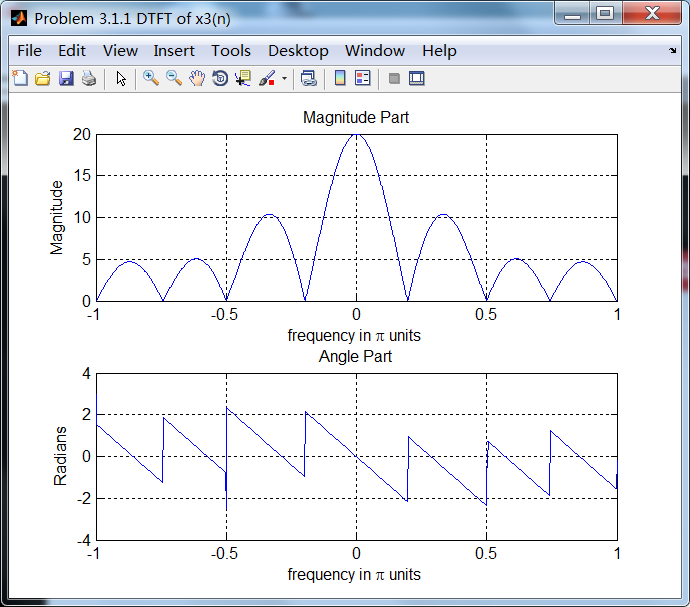
序列3:
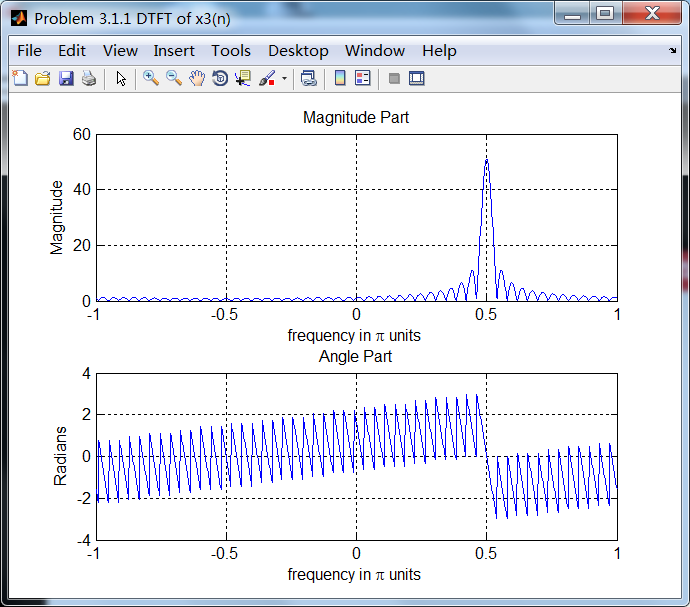
序列3的主要频率分量位于ω=0.5π。
序列4:
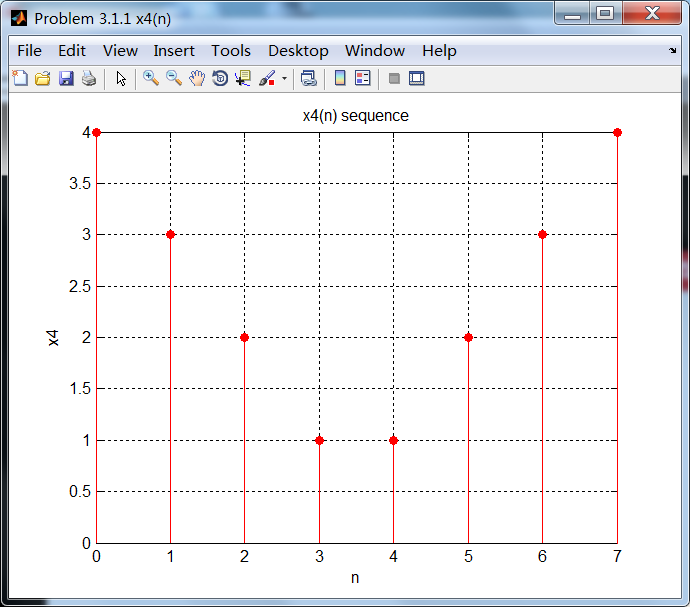
序列4的相位谱关于ω= 0奇对称。
序列5:

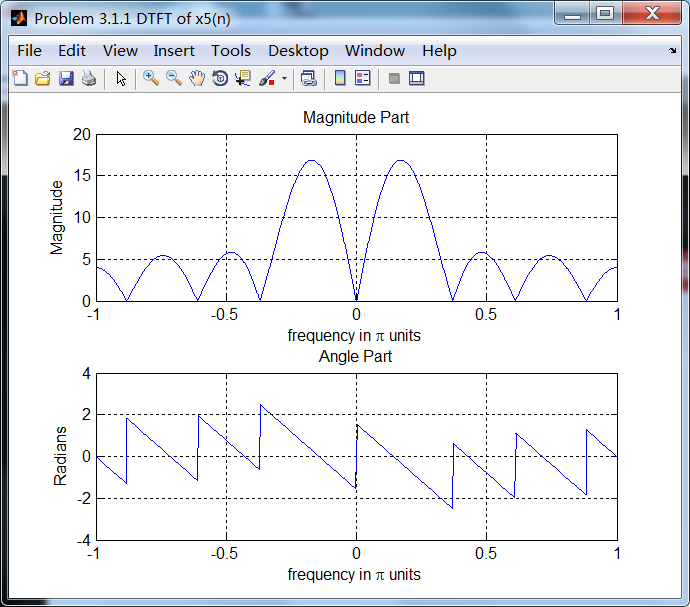
序列5的相位谱关于ω=0奇对称。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 3.1的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.23
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info a ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15
用Kaiser窗方法设计一个台阶状滤波器. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.14
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.13
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.12
阻带衰减50dB,我们选Hamming窗 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
随机推荐
- VS2010/MFC编程入门之九(对话框:为控件添加消息处理函数)
创建对话框类和添加控件变量在上一讲中已经讲过,这一讲的主要内容是如何为控件添加消息处理函数. MFC为对话框和控件等定义了诸多消息,我们对它们操作时会触发消息,这些消息最终由消息处理函数处理.比如我们 ...
- uva11732 Trie转化
有40001 个单词每个单词长度不超过1000,每个两个单词之间都要比较求要比较次数 int strcmp(char *s,char *t){ int i; for(i = 0; s[i]==t[i] ...
- EF Code First 学习笔记:表映射(转)
多个实体映射到一张表 Code First允许将多个实体映射到同一张表上,实体必须遵循如下规则: 实体必须是一对一关系 实体必须共享一个公共键 观察下面两个实体: public class Per ...
- 20145311 《Java程序设计》第九周学习总结
20145311 <Java程序设计>第九周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第十六章 整合数据库 16.1JDBC 16.1.1JDBC简介 JDBC(Java DataBase Connec ...
- 日志自定义Tag
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /** * Crea ...
- Using SQLXML Bulk Load in the .NET Environment
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms171878.aspx 1.首先创建一张表 CREATE TABLE Ord ( OrderID ,) PRIMAR ...
- mis权限系统
在mis中开发,主要目的是有一个统一的权限管理(即r360.right表),以及一个统一的系统和界面供后台配置管理 1.数据库准备工作: mis后台涉及表: right表是权限操作表,role_rig ...
- ggplot2作图详解7(完):主题(theme)设置
凡是和数据无关的图形设置内容理论上都可以归为主题类,但考虑到一些内容(如坐标轴)的特殊性,可以允许例外的情况.主题的设置相当繁琐,很容易就占用了 大量的作图时间,应尽量把这些东西简化,把注意力主要放在 ...
- redis持久化策略
redis是内存数据库,它把数据存储在内存中,这样在加快读取速度的同时也对数据安全性产生了新的问题,即当redis所在服务器发生宕机后,redis数据库里的所有数据将会全部丢失. 为了解决这个问题,r ...
- Rails 5 Test Prescriptions 第6章Adding Data to Tests
bcreate the data quickly and easily.考虑测试运行的速度. fixtures and factories.以及下章讨论的test doubles,还有原生的creat ...
