C++设计模式——迭代器模式
前言
最近非常感伤,总是怀念大学的日子,做梦的时候也常常梦到。梦到大学在电脑前傻傻的敲着键盘,写着代码,对付着数据结构与算法的作业;建立一个链表,遍历链表,打印链表。现在把那个时候声明的链表的头文件拿出来看看:
typedef struct tagNode
{
int value;
tagNode *pPre;
tagNode *pNext;
}Node; class CList
{
public:
CList();
CList(size_t n);
~CList(); bool PushBack(int value);
bool PopBack(int &value);
bool Insert(int pos, int value);
bool Delete(int pos);
bool IsEmpty();
int GetLength(); void Print(); // To iterate the list
bool HasNext();
int Next(); private:
int m_iLength;
Node *m_pCurrent;
Node *m_pHead;
Node *m_pTail;
};
再回头看看,自己写的代码都有点不认识了。是的,那个时候,就是直接将链表的创建和遍历都放在一类中,就是为了方便,直到那天看了迭代器设计模式,让我有了一次回过头来重新审视自己写过的代码,认识自己的不足的机会。
迭代器模式
在GOF的《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》一书中对迭代器模式是这样说的:提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示。
一个聚合对象,就是所谓的对象容器了;作为一个容器,都应该提供一种方法来让别人可以访问它的元素;但是,有的时候,我是不希望遍历容器的人知道我的容器是如何实现的;那该怎么办?就像我在大学那样实现的链表,只提供了从头到尾的遍历,如果我需要从尾到头的遍历呢?是不是我又要添加对应的方法了呢!!!容器的遍历方式千变万化,我们不知道需求是如何的,如果需求变了,那么我们的代码就会发生很大的改动,所以,我们需要去改变;对于上面的代码,当我对同一个链表对象进行多次遍历时,是不是就出现了m_pCurrent对象混乱的局面呢?是的,这一切的一切,都说明,我们必须去将一个容器的内部结构与它的遍历进行解耦,要是出现上面的情况时,我们就无法面对。就好比STL中的容器,它将容器中对象的实现和遍历很好的解耦了,所以,我们就无法知道它的内部是如何组织对象数据的,同时,我们也可以按照我们自己的想法去遍历容器,而不会出现任何差错。在我们的项目中使用迭代器模式就能很好的将容器对象的内部表示与对它的遍历进行解耦。接下来,我们再来详细的总结迭代器模式。
UML类图
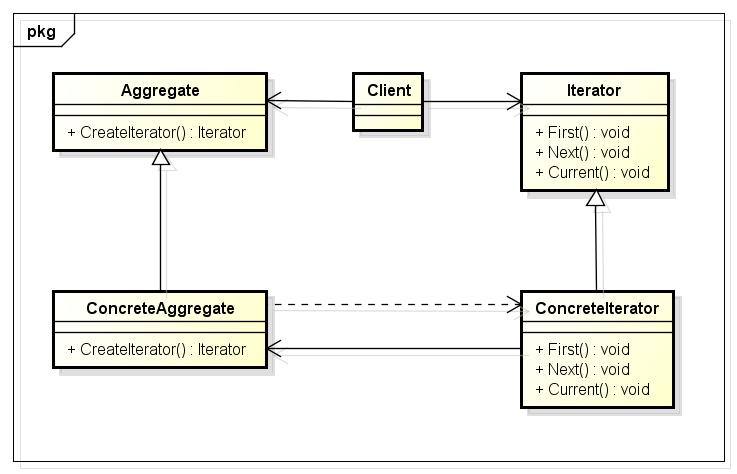
Iterator:定义迭代器访问和遍历元素的接口;
ConcreteIterator:实现具体的迭代器;
Aggregate:定义的容器,创建相应迭代器对象的接口;
ConcreteAggregate:具体的容器实现创建相应迭代器的接口,该操作返回ConcreteIterator的一个适当的实例。
使用场合
- 访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示;
- 支持对聚合对象的多种遍历(从前到后,从后到前);
- 为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口,即支持多态迭代。
作用
- 它支持以不同的方式遍历一个聚合,甚至都可以自己定义迭代器的子类以支持新的遍历;
- 迭代器简化了聚合的接口,有了迭代器的遍历接口,聚合本身就不再需要类似的遍历接口了。这样就简化了聚合的接口;
- 在同一个聚合上可以有多个遍历,每个迭代器保持它自己的遍历状态;因此,我们可以同时进行多个遍历。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; typedef struct tagNode
{
int value;
tagNode *pNext;
}Node; class JTList
{
public:
JTList() : m_pHead(NULL), m_pTail(NULL){};
JTList(const JTList &);
~JTList();
JTList &operator=(const JTList &); long GetCount() const;
Node *Get(const long index) const;
Node *First() const;
Node *Last() const;
bool Includes(const int &) const; void Append(const int &);
void Remove(Node *pNode);
void RemoveAll(); private:
Node *m_pHead;
Node *m_pTail;
long m_lCount;
}; class Iterator
{
public:
virtual void First() = ;
virtual void Next() = ;
virtual bool IsDone() const = ;
virtual Node *CurrentItem() const = ;
}; class JTListIterator : public Iterator
{
public:
JTListIterator(JTList *pList) : m_pJTList(pList), m_pCurrent(NULL){} virtual void First();
virtual void Next();
virtual bool IsDone() const;
virtual Node *CurrentItem() const; private:
JTList *m_pJTList;
Node *m_pCurrent;
}; JTList::~JTList()
{
Node *pCurrent = m_pHead;
Node *pNextNode = NULL;
while (pCurrent)
{
pNextNode = pCurrent->pNext;
delete pCurrent;
pCurrent = pNextNode;
}
} long JTList::GetCount()const
{
return m_lCount;
} Node *JTList::Get(const long index) const
{
// The min index is 0, max index is count - 1
if (index > m_lCount - || index < )
{
return NULL;
} int iPosTemp = ;
Node *pNodeTemp = m_pHead;
while (pNodeTemp)
{
if (index == iPosTemp++)
{
return pNodeTemp;
}
pNodeTemp = pNodeTemp->pNext;
}
return NULL;
} Node *JTList::First() const
{
return m_pHead;
} Node *JTList::Last() const
{
return m_pTail;
} bool JTList::Includes(const int &value) const
{
Node *pNodeTemp = m_pHead;
while (pNodeTemp)
{
if (value == pNodeTemp->value)
{
return true;
}
pNodeTemp = pNodeTemp->pNext;
}
return false;
} void JTList::Append(const int &value)
{
// Create the new node
Node *pInsertNode = new Node;
pInsertNode->value = value;
pInsertNode->pNext = NULL; // This list is empty
if (m_pHead == NULL)
{
m_pHead = m_pTail = pInsertNode;
}
else
{
m_pTail->pNext = pInsertNode;
m_pTail = pInsertNode;
}
++m_lCount;
} void JTList::Remove(Node *pNode)
{
if (pNode == NULL || m_pHead == NULL || m_pTail == NULL)
{
return;
} if (pNode == m_pHead) // If the deleting node is head node
{
Node *pNewHead = m_pHead->pNext;
m_pHead = pNewHead;
}
else
{
// To get the deleting node's previous node
Node *pPreviousNode = NULL;
Node *pCurrentNode = m_pHead;
while (pCurrentNode)
{
pPreviousNode = pCurrentNode;
pCurrentNode = pCurrentNode->pNext;
if (pCurrentNode == pNode)
{
break;
}
} // To get the deleting node's next node
Node *pNextNode = pNode->pNext; // If pNextNode is NULL, it means the deleting node is the tail node, we should change the m_pTail pointer
if (pNextNode == NULL)
{
m_pTail = pPreviousNode;
} // Relink the list
pPreviousNode->pNext = pNextNode;
} // Delete the node
delete pNode;
pNode = NULL;
--m_lCount;
} void JTList::RemoveAll()
{
delete this;
} void JTListIterator::First()
{
m_pCurrent = m_pJTList->First();
} void JTListIterator::Next()
{
m_pCurrent = m_pCurrent->pNext;
} bool JTListIterator::IsDone() const
{
return m_pCurrent == m_pJTList->Last()->pNext;
} Node *JTListIterator::CurrentItem() const
{
return m_pCurrent;
} int main()
{
JTList *pJTList = new JTList;
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append();
pJTList->Append(); Iterator *pIterator = new JTListIterator(pJTList); // Print the list by JTListIterator
for (pIterator->First(); !pIterator->IsDone(); pIterator->Next())
{
cout<<pIterator->CurrentItem()->value<<"->";
}
cout<<"NULL"<<endl; // Test for removing
Node *pDeleteNode = NULL;
for (pIterator->First(); !pIterator->IsDone(); pIterator->Next())
{
pDeleteNode = pIterator->CurrentItem();
if (pDeleteNode->value == )
{
pJTList->Remove(pDeleteNode);
break;
}
} // Print the list by JTListIterator
for (pIterator->First(); !pIterator->IsDone(); pIterator->Next())
{
cout<<pIterator->CurrentItem()->value<<"->";
}
cout<<"NULL"<<endl; delete pIterator;
delete pJTList; return ;
}
代码中实现了一个单向链表,将链表与迭代器解耦。对于多态迭代,添加抽象类AbstractJTList,声明如下:
class AbstractJTList
{
public:
virtual Iterator *GetIterator() const = ;
};
Iterator *JTList::GetIterator() const
{
return new JTListIterator(this);
}
好了,这样的话,在客户端就不用去new JTListIterator了,只需要这样:
Iterator *pIterator = pJTList->GetIterator();
这就完全好了;但是,这样又出现另外一个问题,我在GetIterator中new了一个JTListIterator,对于客户端来说,我并不知道这个new操作的存在,就会出现客户端不会去释放这个new开辟的内存,那么如何实现这个内存的自动释放呢。好了,就结合迭代器模式,再将之前总结的RAII机制再实际运用一次。
根据RAII机制,需要将这个迭代器进行封装,让它具有自动释放的功能,就得借助另一个类,如下:
class IteratorPtr
{
public:
IteratorPtr(Iterator *pIterator) : m_pIterator(pIterator){}
~IteratorPtr() { delete m_pIterator; } Iterator *operator->(){ return m_pIterator; }
Iterator &operator*() { return *m_pIterator; } private:
IteratorPtr(const IteratorPtr &);
IteratorPtr &operator=(const IteratorPtr &);
void *operator new(size_t size);
void operator delete(void *); private:
Iterator *m_pIterator;
};
我们在使用的时候,就像下面这样:
IteratorPtr pIterator(pJTList->GetIterator());
这样就省去了释放迭代器的麻烦了。
总结
迭代器模式是一个很经典的模式。但是,就是因为它太经典了,如果每次都要程序员去重复造轮子,就有点说不过去了,所以,现在基本成型的类库,都非常好的实现了迭代器模式,在使用这些类库提供的容器时,并不需要我们亲自去实现对应的迭代器;就好比STL了。但是话又说回来了,如此经典的东西,你不去学习是不是很可惜啊;是吧,在当今社会,技多不压身。好了,永远记住,设计模式是一种思想,并不是一层不变的,一种思想,你懂的。
C++设计模式——迭代器模式的更多相关文章
- 19. 星际争霸之php设计模式--迭代器模式
题记==============================================================================本php设计模式专辑来源于博客(jymo ...
- java设计模式——迭代器模式
一. 定义与类型 定义:提供一种方法,顺序访问一个集合对象中的各个元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示 类型:行为型. 二. 使用场景 (1) 访问一个集合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示 (2) 为遍 ...
- [Head First设计模式]生活中学设计模式——迭代器模式
系列文章 [Head First设计模式]山西面馆中的设计模式——装饰者模式 [Head First设计模式]山西面馆中的设计模式——观察者模式 [Head First设计模式]山西面馆中的设计模式— ...
- JAVA 设计模式 迭代器模式
用途 迭代器模式 (Iterator) 提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示. 迭代器模式是一种行为型模式. 结构
- 深入浅出设计模式——迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)
模式动机 一个聚合对象,如一个列表(List)或者一个集合(Set),应该提供一种方法来让别人可以访问它的元素,而又不需要暴露它的内部结构.针对不同的需要,可能还要以不同的方式遍历整个聚合对象,但是我 ...
- JavaScript设计模式 - 迭代器模式
迭代器模式是指提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示. 迭代器模式可以把迭代的过程从业务逻辑中分离出来,在使用迭代器模式之后,即使不关心对象的内部构造,也可以按顺 ...
- javascript设计模式-迭代器模式(Iterator)
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 设计模式 --迭代器模式(Iterator)
能够游走于聚合内的每一个元素,同时还可以提供多种不同的遍历方式. 基本概念: 就是提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而不是暴露其内部的表示. 使用迭代器模式的优点: 遍历集合或者数 ...
- js设计模式--迭代器模式
迭代器模式: 迭代器模式提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而又不需要暴露该方法中的内部表示.js中我们经常会封装一个each函数用来实现迭代器. 理解的意思:提供一个方法,去把对象的每一项按 ...
- javascript设计模式——迭代器模式
前面的话 迭代器模式是指提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各个元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示.迭代器模式可以把迭代的过程从业务逻辑中分离出来,在使用迭代器模式之后,即使不关心对象的内部构造,也 ...
随机推荐
- 关于wxpython多线程研究包括(import Publisher等错误研究)
作为一个自动化测试人员,开发基本的应用桌面程序是必须的!最近在研究wxpython相关知识,目前看到多线程一块,发现官方文档介绍说:"在线程中不能修改修改窗口属性!",但是实际情况 ...
- Golang 入门系列(九) 如何读取YAML,JSON,INI等配置文件
实际项目中,读取相关的系统配置文件是很常见的事情.今天就来说一说,Golang 是如何读取YAML,JSON,INI等配置文件的. 1. json使用 JSON 应该比较熟悉,它是一种轻量级的数据交换 ...
- 写论文时,使用word的一些技巧
目录 怎么设置文章里所有英文的字体.所有中文的字体样式 删除文章中的所有或者部分超链接 设置忽略英文的拼写检查 怎么设置文章里所有英文字体.所有中文字体样式 用鼠标选中需要更改的文章内容,如果是全文, ...
- jexus部署webapi或mvc报错处理
1路径错误:因为Windows和Linux的路径问题大小写问题. 解决: 修改jexus下的jws把export MONO_IOMAP=all注释去掉放出来. 2, 解决: 卸载
- MySql下实现先排序后分组
最近在工作中遇到一个先排序后分组的需求,发现MySql不同的版本有不同的结果,特此记录. 举例:要求在shop表中查询出各类型商店中价格最高的商品. --表结构-- create table `sho ...
- Shell命令-系统信息及显示之stat、du
文件及内容处理 - stat.du 1. stat:显示inode内容 stat命令的功能说明 stat 命令用于显示 inode 内容.stat 以文字的格式来显示 inode 的内容. stat命 ...
- Vue.js指令实例
v-if v-else v-show v-if 根据表达式的值的真假条件渲染元素. v-else 不需要表达式.前一兄弟元素必须有 v-if 或 v-else-if v-show 根据表达式之真假 ...
- nodejs开发辅助工具nodemon
前面的话 修改代码后,需要重新启动 Express 应用,所做的修改才能生效.若之后的每次代码修改都要重复这样的操作,势必会影响开发效率,本文将详细介绍Nodemon,它会监测项目中的所有文件,一旦发 ...
- rest framework 认证 权限 频率
认证组件 发生位置 APIview 类种的 dispatch 方法执行到 initial 方法 进行 认证组件认证 源码位置 rest_framework.authentication 源码内部需要 ...
- python 高阶函数之 reduce
1.正常写法 >>> from functools import reduce >>> def fn(x, y): ... return x * 10 + y .. ...
