uiautomator设备和选择器~Python详解
1、设备对象
引入uiautomator,获取设备对象<所谓设备对象可理解为:Android模拟器或者真机>
语法:from uiautomator import device as d
d 即为设备对象
1.1、获取设备信息
语法:d.info
返回值:
{ u'displayRotation': 0,
u'displaySizeDpY': 640,
u'displaySizeDpX': 360,
u'currentPackageName': u'com.android.launcher',
u'productName': u'takju',
u'displayWidth': 720,
u'sdkInt': 18,
u'displayHeight': 1184,
u'naturalOrientation': True
}
返回值解释如下:
displayRotation 0 代表竖屏 1 代表横屏
currentPackageName 当前的Activity的Package名字
productName 当前设备名称
displayWidth 当前设备屏幕宽度 当 displayRotation 取值为 1 时,也就是说当前是横屏状态时,displayWidth 取值会和 displayHeight 互换
displayHeight 当前设备屏幕高度 当 displayRotation 取值为 1 时,也就是说当前是横屏状态时,displayHeight 取值会和 displayWidth 互换
sdkInt 当前SDK版本
naturalOrientation 当 displayRotation 取值为 1 时,也就是说当前是横屏状态时,取值为False,为竖屏状态时,取值为:True
1.2、点亮或熄灭屏幕(Turn on/off screen)
# Turn on screen
d.screen.on()
# Turn off screen
d.screen.off()
# wakeup the device
d.wakeup()
# sleep the device, same as turning off the screen.
d.sleep()
检查屏幕状态,关闭OR点亮?
if d.screen == "on": # of d.screen != "off"
# do something in case of screen on
pass
if d.screen == "off": # of d.screen != "on"
# do something in case of screen off
pass
1.3、系统常用按键
# press home key
d.press.home()
# press back key
d.press.back()
# the normal way to press back key
d.press("back")
# press keycode 0x07('0') with META ALT(0x02) on
d.press(0x07, 0x02)
下面的这些按键也是被支持的,如下:
Next keys are currently supported:
home #手机Home键back #手机返回键left #对应键盘上的向右键<-right #对应键盘上的向右键->up #对应键盘上的向上键down #对应键盘上的向下键center #选中?menu #菜单search #查找?enter #对应键盘上的Enter键delete(ordel) #对应键盘上的DEL键 用于删除recent(recent apps) #任务切换volume_up #声音向上调整volume_down #声音向下调整volume_mute #静音按键camera #拍照power #电源键
1.4、与设备交互(单击、长按、滑动(手势密码)、拖拽)
单击屏幕坐标点
# click (x, y) on screen
d.click(x, y)
长按屏幕坐标点
# long click (x, y) on screen
d.long_click(x, y)
在屏幕上滑动
# swipe from (sx, sy) to (ex, ey)
d.swipe(sx, sy, ex, ey)
# swipe from (sx, sy) to (ex, ey) with 10 steps
d.swipe(sx, sy, ex, ey, steps=10)
在屏幕上拖拽
# drag from (sx, sy) to (ex, ey)
d.drag(sx, sy, ex, ey)
# drag from (sx, sy) to (ex, ey) with 10 steps
d.drag(sx, sy, ex, ey, steps=10)
1.5、屏幕操作及屏幕方向获取与控制<上述:displayRotation 0 代表竖屏 1 代表横屏>,竖屏分为 natural(自然的,正常的竖屏) 和 upsidedown(倒过来的竖屏),横屏分为向左和向右两个方向,分别为:left 和 right
设备属性:orientation 可能取得值为:
naturalornleftorlrightorrupsidedownoru(can not be set)
说明:在手机设备上,倒过来的屏幕很少见,因此:d.orientation 取值 upsidedown 的可能性几乎没有
# retrieve orientation, it may be "natural" or "left" or "right" or "upsidedown" 获取设备屏幕方向如下:
orientation = d.orientation
# set orientation and freeze rotation.
# notes: "upsidedown" can not be set until Android 4.3. 设置设备屏幕方向如下:
d.orientation = "l" # or "left"
d.orientation = "r" # or "right"
d.orientation = "n" # or "natural"
锁屏/解除锁屏
# freeze rotation
d.freeze_rotation() #锁屏
# un-freeze rotation
d.freeze_rotation(False) #解锁
截屏操作
# take screenshot and save to local file "home.png", can not work until Android 4.2.
d.screenshot("home.png")
打开通知或快速设置
# open notification, can not work until Android 4.3.
d.open.notification()
# open quick settings, can not work until Android 4.3.
d.open.quick_settings()
注意:(如果notification已经打开了,调用d.open.quick_settings()不会打开快速设置)
等待空闲或窗口更新(Wait for idle or window update)
# wait for current window to idle
d.wait.idle()
# wait until window update event occurs
d.wait.update()
2、uiautomator 选择器
选择器是在当前窗口中标识特定的UI对象。可理解为:UiObject对象
目前,在uiautomator中支持以下属性选择器:
text, textContains, textMatches, textStartsWith
className, classNameMatches
description, descriptionContains, descriptionMatches, descriptionStartsWith
checkable, checked, clickable, longClickable
scrollable, enabled,focusable, focused, selected
packageName, packageNameMatches
resourceId, resourceIdMatches
index, instance
下面依次进行解读:
2.1、text选择器(支持在uiautomator中Text属性不为空的元素)
例如:
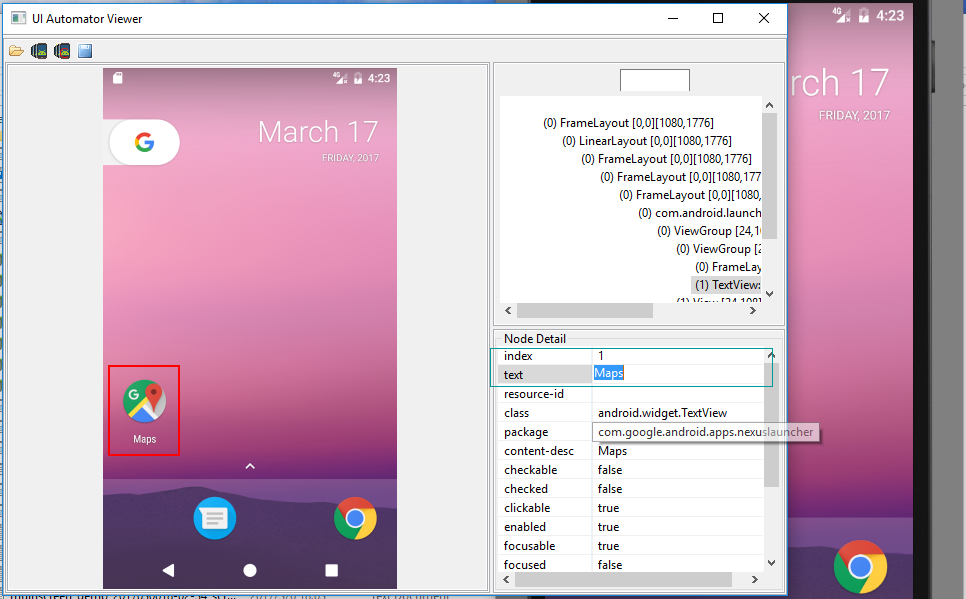
具体用法如下:
d(text="Maps").click()
#当然也可以多个属性在一块使用
d(text="Maps",className="android.widget.TextView").click()
#或者
d(text="Maps",className="android.widget.TextView",packageName="com.google.android.apps.nexuslauncher").click()
总之:要尽可能的使用选择器唯一确定一个被选择对象(UiObject)
除了可以进行选择UiObject对象以外,我们亦可以使用选择器设置某些元素的值,如下:
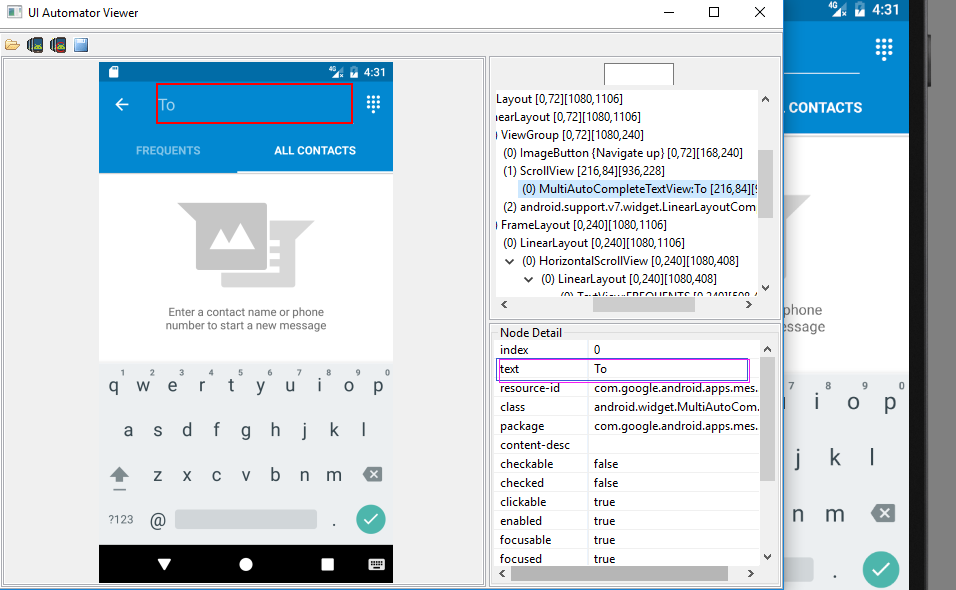
#输入短信目标手机号
d(text="To").set_text("")
#如果本窗口中有多个text为To的元素,我们也可以使用多属性选择
d(text="To",packageName="com.google.android.apps.messaging").set_text("").set_text("")
textContains,textMaches,textStartsWith 分别代表:包含,正则表达式,以XXX开头等
例如:
d(text="Name").set_text("John")
d(textContains="ame").set_text("John")
d(textStartsWith="Nam").set_text("John")
2.2、className,classNameMatches 类选择器 及 description, descriptionContains, descriptionMatches, descriptionStartsWith 描述选择器 及 packageName, packageNameMatches 包选择器 及 resourceId, resourceIdMatches ResId选择器用法和text选择器类似,都可以多属性选择器结合在一起使用。
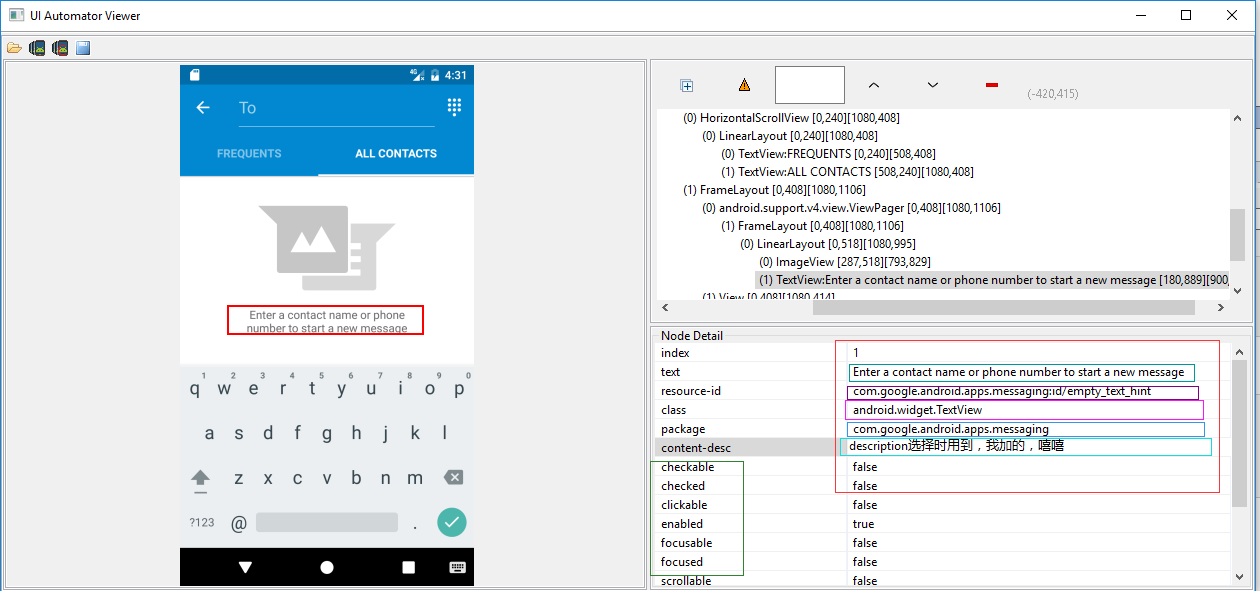
示例代码如下:
# To seleted the object ,text is 'Clock' and its className is 'android.widget.TextView'
d(text='Clock', className='android.widget.TextView')
d(description="add new contact").click()
d(descriptionContains="new contact").click()
d(descriptionStartsWith="add new").click()
#resourceid选择器
d(resourceId="com.android.contacts:id/menu_save").click()
#text选择器
d(textStartsWith="Nam").set_text("John")
#描述选择器
d(descriptionContains="new contact").click()
#多属性结合
d(text="Name",className="android.widget.EditText").set_text("John")
#index选择器和child选择器
d(resourceId="com.android.settings:id/list").child(className="android.widget.LinearLayout", index=2).child(resourceId="android:id/widget_frame").child(resourceId="android:id/switch_widget").click()
在此,说明下child、sibling选择器和index选择器及instance选择器(严格讲instance不是选择器,仅仅只是在输出多个结果的情况下,可以通过索引(下标)进行选择)
首先说明child选择器,sibling选择器:分别可理解为:子选择器(可嵌套),兄弟姐妹选择器
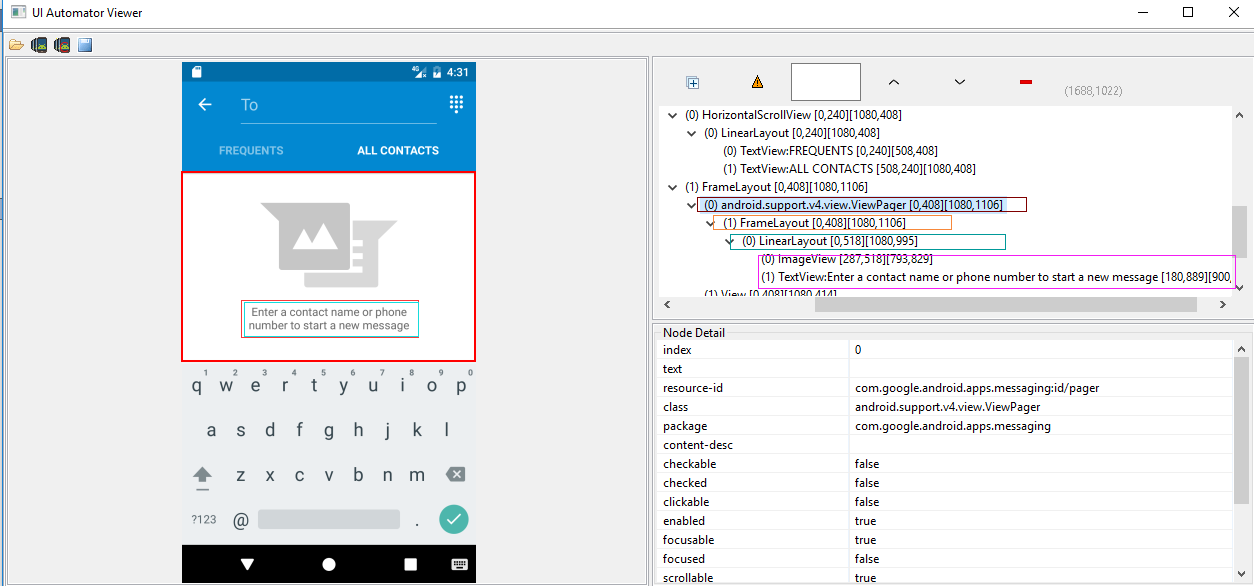
如上图右边部分,从上到下层次分为四层,最后一层的两个元素可理解为兄弟姐妹,在此,我们如果要选择最下面的那个元素就可以用到child选择器及sibling选择器,当然,本人不建议使用孩子,兄妹选择器,如果能用其他方法实现,建议用其他方法:
在此,我写的方法如下:<没有具体验证,仅仅只是演示>
#孩子选择器及兄弟姐妹选择器的用法:child/sibling
d(resourceId="id/pager").child(className="android.widget.FrameLayout").child(resourceId="id/empty_view").child(resourceId="id/empty_image_hint").sibling(packageName="com.google.android.apps.messaging")
2.3、index选择器及instance,比较容易混淆的两个,一个是选择器,一个代表索引,如下:
index选择器对应uiautomator的index属性,如下:
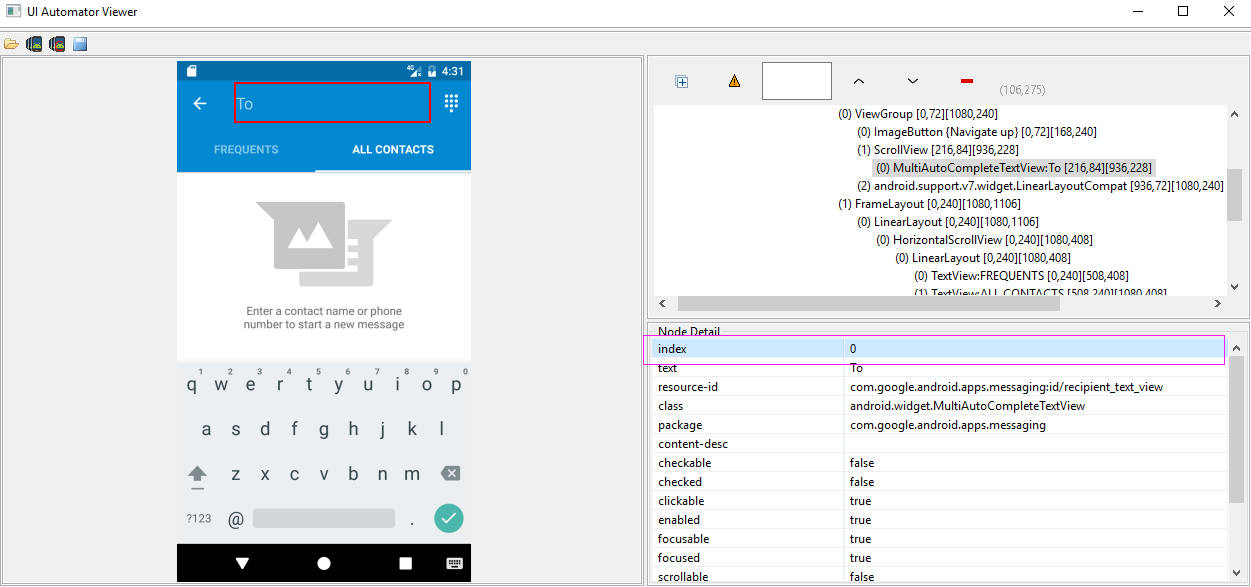
其用法和text选择器大同小异,不过在此需要指出的是,有些窗体中index取值会发生改变,因此,能不用index选择器的,尽可能不用!
#index选择器
d(className="android.widget.LinearLayout", index=2).click()
instance 的用法:当你的选择器返回的结果不是指向唯一元素时(两个或者多个),你可以通过instance进行选择。
贺晓聪原文:
Multiple instances
Sometimes the screen may contain multiple views with the same e.g. text, then you will have to use "instance" properties in selector like below:
d(text="Add new", instance=0) # which means the first instance with text "Add new"
However, uiautomator provides list like methods to use it.
# get the count of views with text "Add new" on current screen
d(text="Add new").count # same as count property
len(d(text="Add new")) # get the instance via index
d(text="Add new")[0]
d(text="Add new")[1]
... # iterator
for view in d(text="Add new"):
view.info # ...
2.4、获取选定的UI对象状态及其信息(Get the selected ui object status and its information)
检测特定的UI对象是否存在(Check if the specific ui object exists)
两种写法,如下:
d(text="Settings").exists # True if exists, else False
d.exists(text="Settings") # alias of above property.
检索特定UI对象的信息(Retrieve the info of the specific ui object)
d(text="Settings").info
(结果为列表List),如下:
{ u'contentDescription': u'',
u'checked': False,
u'scrollable': False,
u'text': u'Settings',
u'packageName': u'com.android.launcher',
u'selected': False,
u'enabled': True,
u'bounds': {u'top': 385,
u'right': 360,
u'bottom': 585,
u'left': 200},
u'className': u'android.widget.TextView',
u'focused': False,
u'focusable': True,
u'clickable': True,
u'chileCount': 0,
u'longClickable': True,
u'visibleBounds': {u'top': 385,
u'right': 360,
u'bottom': 585,
u'left': 200},
u'checkable': False
}
设置/清除字段或编辑文本
d(text="Settings").clear_text() # clear the text
d(text="Settings").set_text("My text...") # set the text
执行单击特定的UI对象
# click on the center of the specific ui object
d(text="Settings").click()
# click on the bottomright corner of the specific ui object 单击右下方
d(text="Settings").click.bottomright()
# click on the topleft corner of the specific ui object 单击左上方
d(text="Settings").click.topleft()
# click and wait until the new window update 单击并等待窗体响应
d(text="Settings").click.wait()
长时间点击特定的ui对象,双击?
# long click on the center of the specific ui object
d(text="Settings").long_click()
# long click on the bottomright corner of the specific ui object 右下角
d(text="Settings").long_click.bottomright()
# long click on the topleft corner of the specific ui object 左上角
d(text="Settings").long_click.topleft()
将UI对象拖动到另一点
# notes : drag can not be set until Android 4.3.
# drag the ui object to point (x, y)
d(text="Settings").drag.to(x, y, steps=100)
# drag the ui object to another ui object(center) 拖拽到text='Clock'的对象位置上
d(text="Settings").drag.to(text="Clock", steps=50)
滑动UI对象
滑动分为四个方向:left ,right,top ,bottom 即:左滑动 右滑动 上滑动 及向下滑动
d(text="Settings").swipe.right()
d(text="Settings").swipe.left(steps=10)
d(text="Settings").swipe.up(steps=10)
d(text="Settings").swipe.down()
Two point gesture from one point to another
d(text="Settings").gesture((sx1, sy1), (sx2, sy2)) .to((ex1, ey1), (ex2, ey2))
Two point gesture on the specific ui object
Supports two gestures:
In, from edge to centerOut, from center to edge
# notes : pinch can not be set until Android 4.3.
# from edge to center. here is "In" not "in"
d(text="Settings").pinch.In(percent=100, steps=10)
# from center to edge
d(text="Settings").pinch.Out()
3 point gesture
d().gestureM((sx1, sy1), (sx2, sy2),(sx3, sy3)) \
.to((ex1, ey1), (ex2, ey2),(ex3,ey3))
d().gestureM((100,200),(300,200),(600,200),(100,600),(300,600),(600,900))
等到特定的UI对象出现或消失
# wait until the ui object appears
d(text="Settings").wait.exists(timeout=3000)
# wait until the ui object gone
d(text="Settings").wait.gone(timeout=1000)
在具体的UI对象执行甩(滚动)Perform scroll on the specific ui object(scrollable)
Possible properties:
horizorvertforwardorbackwardortoBeginningortoEnd
# fling forward(default) vertically(default)
d(scrollable=True).fling()
# fling forward horizentally
d(scrollable=True).fling.horiz.forward()
# fling backward vertically
d(scrollable=True).fling.vert.backward()
# fling to beginning horizentally
d(scrollable=True).fling.horiz.toBeginning(max_swipes=1000)
# fling to end vertically
d(scrollable=True).fling.toEnd()
Perform scroll on the specific ui object(scrollable)-在具体的UI对象执行甩(滚动)
Possible properties:
horizorvertforwardorbackwardortoBeginningortoEnd, orto
# scroll forward(default) vertically(default)
d(scrollable=True).scroll(steps=10)
# scroll forward horizentally
d(scrollable=True).scroll.horiz.forward(steps=100)
# scroll backward vertically
d(scrollable=True).scroll.vert.backward()
# scroll to beginning horizentally
d(scrollable=True).scroll.horiz.toBeginning(steps=100, max_swipes=1000)
# scroll to end vertically
d(scrollable=True).scroll.toEnd()
# scroll forward vertically until specific ui object appears
d(scrollable=True).scroll.to(text="Security")
uiautomator设备和选择器~Python详解的更多相关文章
- 安卓自动化测试,贺晓聪之uiautomator设备和选择器~Python详解
1.设备对象 引入uiautomator,获取设备对象<所谓设备对象可理解为:Android模拟器或者真机> 语法:from uiautomator import device as d ...
- [转载]python 详解re模块
原文地址:python 详解re模块作者:Rocky 正则表达式的元字符有. ^ $ * ? { [ ] | ( ) .表示任意字符 []用来匹配一个指定的字符类别,所谓的字符类别就是你想匹配的一个字 ...
- 33 Python 详解命令解析 - argparse--更加详细--转载
https://blog.csdn.net/lis_12/article/details/54618868 Python 详解命令行解析 - argparse Python 详解命令行解析 - arg ...
- CSS系列(7)CSS类选择器Class详解
这一篇文章,以笔记形式写. 1, CSS 类选择器详解 http://www.w3school.com.cn/css/css_selector_class.asp 知识点: (1) 使用类选择 ...
- CSS 选择器【详解】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/polk6/archive/2013/07/19/3142142.html CSS 选择器及各样式引用方式介绍 一个好的界面,是一个Web吸引人们最 ...
- python 详解re模块
正则表达式的元字符有. ^ $ * ? { [ ] | ( ).表示任意字符[]用来匹配一个指定的字符类别,所谓的字符类别就是你想匹配的一个字符集,对于字符集中的字符可以理解成或的关系.^ 如果放在字 ...
- css所有选择器的详解
----------------------------------------css 选择器---------------------------------------- 1,组合选择器: 1)e ...
- 【经典案例】Python详解设计模式:策略模式
完成一项任务往往有多种方式,我们将其称之为策略. 比如,超市做活动,如果你的购物积分满1000,就可以按兑换现金抵用券10元,如果购买同一商品满10件,就可以打9折,如果如果购买的金额超过500,就可 ...
- USB HID设备报告描述符详解(转)
转自:http://group.ednchina.com/93/198.aspx. 参考:USB HID usage table 概述: 报告在这里意思是数据传输(data transfer),而 ...
随机推荐
- python之正则表达式和re模块一
摘要:正则表达式 re模块 一.正则表达式:只和字符串打交道,是一种用来约束字符串的规则 1.应用场景: 1,判断某一个字符串是否符合规则:注册页-判断手机号.身份证号 是否合法 注册某个账号的时候, ...
- Floyd算法——计算图中任意两点之间的最短路径
百度百科定义:传送门 一.floyd算法 说实话这个算法是用来求多源最短路径的算法. 算法原理: 1,从任意一条单边路径开始.所有两点之间的距离是边的权,如果两点之间没有边相连,则权为无穷大. 2,对 ...
- mysql 基本语句
求知若渴 虚心若愚 博客园 首页 新随笔 联系 管理 随笔-391 文章-0 评论-7 mysql sql常用语句大全 SQL执行一次INSERT INTO查询,插入多行记录 inser ...
- Linux内核参数
vm.overcommit_memory 0 - 表示内核将检查是否有足够的可用内存供应用进程使用:如果有足够的可用内存,内存申请允许:否则,内存申请失败,并把错误返回给应用进程. 1 - 表示内核允 ...
- pip install升级包
只需要python -m pip install --user --upgrade pip==9.0.3 只需要加一个--user
- Hbase 元数据一致性检查(转)
最近在学习HBase先关的知识,顺便做一下笔记,以加深知识的了解和掌握. Hbase常用工具 文件检测修复工具 hbase hbck -help 常用选项: -details 显示所有region检查 ...
- MongoDB3.6 一键化自动部署方案
1.系统基础配置 下面的命令默认都使用root用户进行操作,操作系统为Centos7,mongodb3.6.x以上版本 1.1 修改系统配置文件/etc/security/limits.conf和/e ...
- JavaScript 正则表达式基础语法
前言 正则表达式在人们的印象中可能是一堆无法理解的字符,但就是这些符号却实现了字符串的高效操作.通常的情况是,问题本身并不复杂,但没有正则表达式就成了大问题.javascript中的正则表达式作为相当 ...
- Consequence of Point-by-Point Bounds
设 $X$ 是完备距离空间, $\scrF$ 是 $X$ 上的实连续函数族且具有性质: 对于每一 $x\in X$, 存在常数 $M_x>0$, 使得对于每一 $F\in\scrF$, $$\b ...
- Leetcode#461. Hamming Distance(汉明距离)
题目描述 两个整数之间的汉明距离指的是这两个数字对应二进制位不同的位置的数目. 给出两个整数 x 和 y,计算它们之间的汉明距离. 注意: 0 ≤ x, y < 231. 示例: 输入: x = ...
