OpenGL.Tutorial03_Matrices_测试
1、
2、
- // ZC: 工程-->右键-->属性--> 配置属性:
- // ZC: C/C++ -->常规-->附加包含目录,里面添加:
- // ZC: E:\OpenGL_something\glfw-3.2.1.bin.WIN32\include
- // ZC: E:\OpenGL_something\glm-0.9.8.5
- // ZC: E:\OpenGL_something\glew-2.1.0\include
- // ZC: 链接器-->输入-->附加依赖项,里面添加:
- // ZC: E:\OpenGL_something\glfw-3.2.1.bin.WIN32\lib-vc2010\glfw3.lib 这个应该是静态链接的lib(动态的貌似是glfw3dll.lib[ZC:我是看文件大小判断的...])
- // ZC: E:\OpenGL_something\glew-2.1.0\lib\Release\Win32\glew32.lib
- // ZC: opengl32.lib
- // ZC: glu32.lib
- // ZC: kernel32.lib
- // ZC: user32.lib
- // ZC: gdi32.lib
- // ZC: winspool.lib
- // ZC: shell32.lib
- // ZC: ole32.lib
- // ZC: oleaut32.lib
- // ZC: uuid.lib
- // ZC: comdlg32.lib
- // ZC: advapi32.lib
- // ZC: 关于使用glew32.lib还是glew32s.lib:
- // ZC: 看文件大小判断 静态链接的lib应该是glew32s.lib,但是我在编译的时候,发现无法定位函数grewInit(...)... 于是只能使用动态的glew32s.lib
- // ZC: 于是还要将"E:\OpenGL_something\glew-2.1.0\bin\Release\Win32\glew32.dll"复制到项目的"E:\Project_VS10\OpenGL_Console_zz\Test\Test"中
- // Include standard headers
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- // Include GLEW
- #include <GL/glew.h>
- // Include GLFW
- #include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
- extern GLFWwindow* window;
- // Include GLM
- #include <glm/glm.hpp>
- #include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
- using namespace glm;
- #include <common/shader.hpp>
- int mainTutorial03Matrices( void )
- {
- // Initialise GLFW
- if( !glfwInit() )
- {
- fprintf( stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW\n" );
- getchar();
- return -;
- }
- glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, );
- glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, );
- glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, );
- glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed
- glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); //We don't want the old OpenGL
- // Open a window and create its OpenGL context
- /*window = glfwCreateWindow( 1024, 768, "Tutorial 03 - Matrices", NULL, NULL);*/
- window = glfwCreateWindow( , , "Tutorial 03 - Matrices", NULL, NULL);
- if( window == NULL ){
- fprintf( stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.\n" );
- getchar();
- glfwTerminate();
- return -;
- }
- glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
- // Initialize GLEW
- glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile
- if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW\n");
- getchar();
- glfwTerminate();
- return -;
- }
- // Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below
- glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE);
- // Dark blue background
- glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f);
- GLuint VertexArrayID;
- glGenVertexArrays(, &VertexArrayID);
- glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
- // Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders
- GLuint programID = LoadShaders( "../Test/shaders/SimpleTransform_03.vertexshader", "../Test/shaders/SingleColor_03.fragmentshader" );
- // Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform
- GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP");
- // Projection matrix : 45?Field of View, 4:3 ratio, display range : 0.1 unit <-> 100 units
- //glm::mat4 Projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(45.0f), 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
- glm::mat4 Projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(45.0f), 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
- // Or, for an ortho camera :
- //glm::mat4 Projection = glm::ortho(-10.0f, 10.0f, -10.0f, 10.0f, 0.0f, 100.0f); // In world coordinates
- // Camera matrix
- //glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
- // glm::vec3(4,3,3), // Camera is at (4,3,3), in World Space
- // glm::vec3(0,0,0), // and looks at the origin
- // glm::vec3(0,1,0) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
- // );
- glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
- glm::vec3(,,),// Camera is at (4,3,3), in World Space
- glm::vec3(,,), // and looks at the origin
- glm::vec3(,,) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
- );
- // ZC: 上面的参数的理解:
- // ZC: 第一个参数:摄像机所在的位置(世界坐标系)
- // ZC: 第二个参数:摄像机往哪个点看过去(摄像机往哪个点的方向看去) (ZC: 这个应该是参与计算的)
- // ZC: 第三个参数:头的位置(这里的"头" 实际就是指"摄像机"): (ZC: 这个稍微测试了一下,发现 应该就是指方向[即 其次坐标的"w"是0])
- // ZC: (0,1,0):就是正常的人类头顶朝上的样子,
- // ZC: (1,0,0):就是头往X轴正方向倒90°,
- // ZC: (0,0,1):应该就是头朝Z轴正方向倒90°(也就是往后倒,稍微验证了一下,应该就是这样子的)
- // Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
- glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(
- // 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("\n");
- // Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
- glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("\n");
- static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
- -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
- };
- //static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
- // -2.0f, -2.0f, 0.0f,
- // 2.0f, -2.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- //};
- GLuint vertexbuffer;
- glGenBuffers(, &vertexbuffer);
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
- glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_vertex_buffer_data), g_vertex_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
- do{
- // Clear the screen
- glClear( GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT );
- // Use our shader
- glUseProgram(programID);
- // Send our transformation to the currently bound shader,
- // in the "MVP" uniform
- glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, , GL_FALSE, &MVP[][]);
- // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
- glEnableVertexAttribArray();
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
- glVertexAttribPointer(
- , // attribute. No particular reason for 0, but must match the layout in the shader.
- , // size
- GL_FLOAT, // type
- GL_FALSE, // normalized?
- , // stride
- (void*) // array buffer offset
- );
- // Draw the triangle !
- glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, , ); // 3 indices starting at 0 -> 1 triangle
- glDisableVertexAttribArray();
- // Swap buffers
- glfwSwapBuffers(window);
- glfwPollEvents();
- } // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed
- while( glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE ) != GLFW_PRESS &&
- glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == );
- // Cleanup VBO and shader
- glDeleteBuffers(, &vertexbuffer);
- glDeleteProgram(programID);
- glDeleteVertexArrays(, &VertexArrayID);
- // Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW
- glfwTerminate();
- return ;
- }
3、改变中间的一段代码 用于测试:
3.1、上面的代码执行的现象:
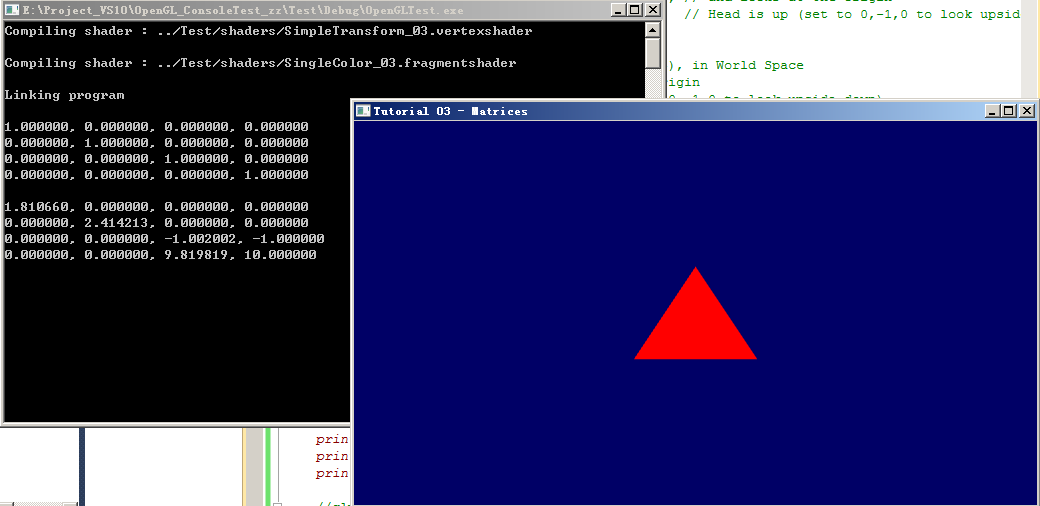
3.2、放大2倍(方式1):
- // Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f); // ZC: 变化的是这里,把X/Y/Z坐标都扩大了2倍
- glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(
- 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("\n");
- // Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
- glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("\n");
- static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
- -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
- };
现象:

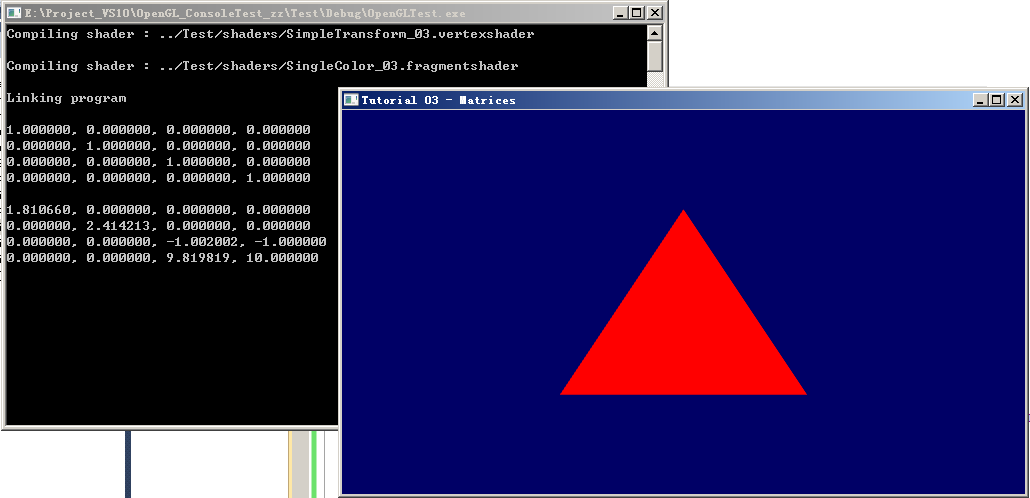
3.3、放大2倍(方式2):
- // Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
- glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f); // ZC: 这里没改变
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(
- // 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("\n");
- // Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
- glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("\n");//static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
- // -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- // 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
- //};
- static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = { // ZC: 这里改变了,手动的将 三角形的3个点的坐标放大了
- -2.0f, -2.0f, 0.0f,
- 2.0f, -2.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- };
现象:
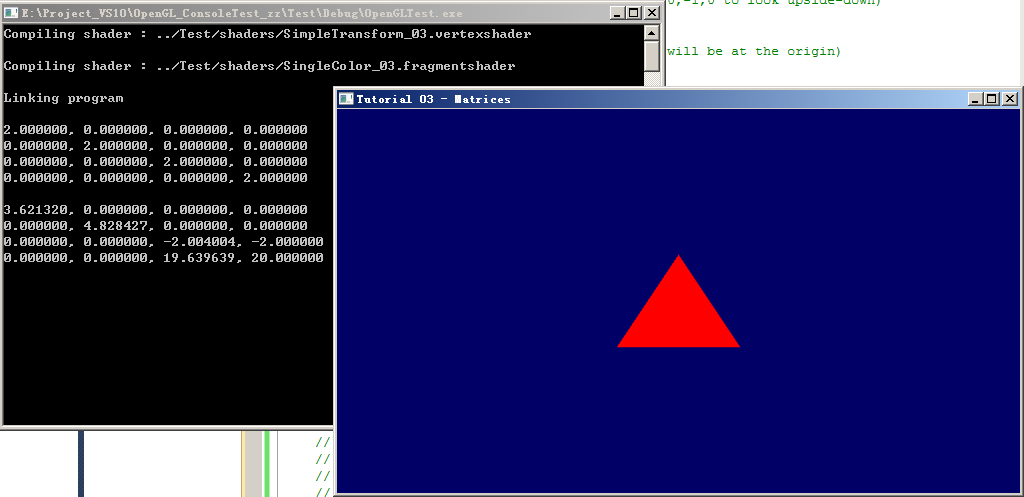
3.4、测试:刚开始 放大 是使用的 “glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(2.0f);”,实际这是没有 放大效果的(视觉上 大小没变化),原因寻找:Model的矩阵信息为:
- 2.0f 0.0f 0.0f 0.0f
- 0.0f 2.0f 0.0f 0.0f
- 0.0f 0.0f 2.0f 0.0f
- 0.0f 0.0f 0.0f 2.0f
∵ 它把 X/Y/Z轴的数据放大了,但是 它的最后一行数据“0.0f 0.0f 0.0f 2.0f” 实现了类似这样的功能:把摄像机拉远了一倍距离。这个的数学解释 我暂时还不太明白,只是做了一个实验 验证了一下
3.4.1、
- glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
- glm::vec3(,,),// Camera is at (4,3,3), in World Space
- glm::vec3(,,), // and looks at the origin
- glm::vec3(,,) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
- );
- // Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
- glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(2.0f); // ZC: 改了这里
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(
- // 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- // 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("\n");
- // Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
- glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("\n");
现象:
3.4.2、
- glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
- glm::vec3(,,),// ZC: 这里,手动将摄像机 拉远了一倍距离
- glm::vec3(,,), // and looks at the origin
- glm::vec3(,,) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
- );
- // Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
- //glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(2.0f);
- glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4( // ZC: 这里,将 X/Y/Z轴数据放大1倍
- 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 0.0f, 2.0f, 0.0f,
- 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", Model[].x, Model[].y, Model[].z, Model[].w);
- printf("\n");
- // Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
- glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("%f, %f, %f, %f\n", MVP[].x, MVP[].y, MVP[].z, MVP[].w);
- printf("\n");
现象:
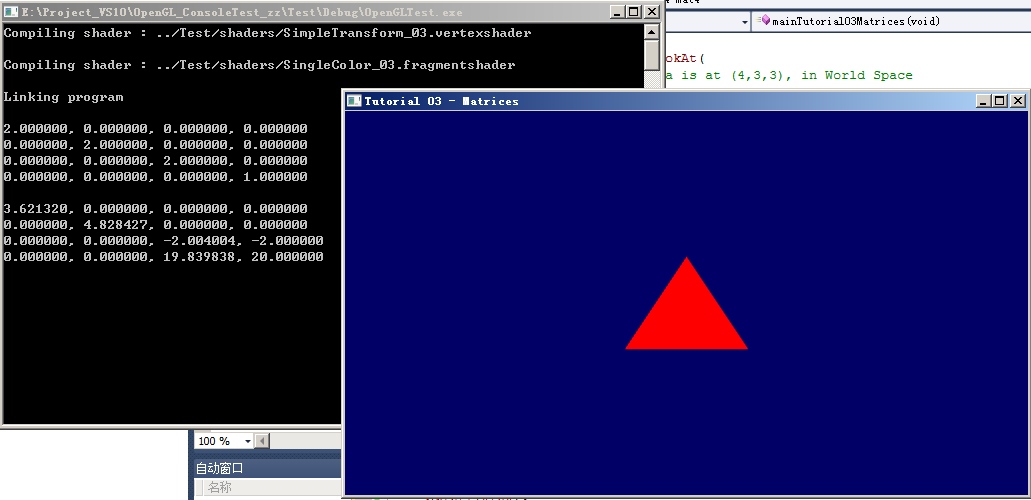
ZC:可以看到,虽然 矩阵Model 的信息不同,但是 最后的 矩阵MVP 的信息是一样的,∴ 肉眼看起来 效果一样...
4、尝试 C++中计算好位置,直接传入 GLSL(不要再在 GLSL中去做乘法计算)
ZC:貌似 这个例子中使用的 "glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);"的方式,暂时不支持实现 这个尝试,看后面会不会 学习到别的方式,或者 后面水平高了再来尝试吧...
5、
OpenGL.Tutorial03_Matrices_测试的更多相关文章
- OpenGL光照测试
OpenGL光照测试 花了大概半个月,研究了OpenGL的光照.请注意是固定管线渲染的光照,如果使用着色器的高手们请飘过.这个程序是通过光照对模型的照射,来研究OpenGL光照的性质.以后可以通过这个 ...
- Qt OpenGL裁剪测试
剪裁测试(Scissor Test)用于限制绘制区域. 我们可以指定一个矩形的剪裁窗口,当启用剪裁测试后,只有在这个窗口之内的像素才能被绘制,其它像素则会被丢弃. 换句话说,无论怎么绘制,剪裁窗口以外 ...
- opengl 模板测试 glStencilOp glStencilFunc
下面来设置蒙板缓存和蒙板测试. 首先我们启用蒙板测试,这样就可以修改蒙板缓存中的值. 下面我们来解释蒙板测试函数的含义: 当你使用glEnable(GL_STENCIL_TEST)启用蒙板测试之后,蒙 ...
- OpenGL(十四) 模板测试
启用模板测试时,OpenGL会在内存中开辟一块空间作为模板缓冲区,里边保存了每个像素的"模板值",模板测试的过程就是把每一个像素的模板值与一个设定的模板参考值进行比较,符合设定条件 ...
- opengl学习-利用模板测试勾画物体轮廓中出现的一个问题
我在学习OpenGL模板测试勾画物体轮廓的时候,出现了这个问题: 这个出现的原因就是,改变摄像机的时候,每次绘制,上次绘制中模板缓冲区的数据没有清除的原因.也就是在while循环开始的时候,glCle ...
- opengl入门学习
OpenGL入门学习 说起编程作图,大概还有很多人想起TC的#include <graphics.h>吧? 但是各位是否想过,那些画面绚丽的PC游戏是如何编写出来的?就靠TC那可怜的640 ...
- OpenGL入门学习(转)
OpenGL入门学习 http://www.cppblog.com/doing5552/archive/2009/01/08/71532.html 说起编程作图,大概还有很多人想起TC的#includ ...
- Android OpenGL ES .介绍
引自:http://blog.csdn.net/hgl868/article/details/6971624 1. OpenGL ES 简介 Android 3D引擎采用的是OpenGL ES. ...
- OpenGL理解
说起编程作图,大概还有很多人想起TC的#include <graphics.h>吧? 但是各位是否想过,那些画面绚丽的PC游戏是如何编写出来的?就靠TC那可怜的640*480分辨率.16色 ...
随机推荐
- JAVA8 中 LocalDateTime的使用小栗子
LocalDate givenDate = LocalDate.parse("2019-04-23",DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy- ...
- 在C#中,Windows Console控制台 设置控制台标题、禁用关闭按钮、关闭快速编辑模式、插入模式
设置控制台标题 禁用关闭按钮 关闭快速编辑模式 关闭插入模式 设置控制台标题.禁用关闭按钮 #region 设置控制台标题 禁用关闭按钮 [DllImport("user32.dll&quo ...
- Mybatis下的sql注入
以前只知道mybatis框架下,order by后面接的是列名是不能用#{},这样不起效果,只能用${},这样的话就可能产生sql注入.后来发现其实还有另外两种情况也是类似的: 1.order by ...
- PureMVC 官方文档翻译(一)
最近在学习PureMVC框架,感觉最权威的还是阅读官方文档,顺便翻译了下全当记笔记了. PureMVC概览 这篇文档他讨论PureMVC框架的类和接口,使用UML来阐述它们的角色.职责和协作. Pur ...
- 25 range打印100到0的连续整数
使用range打印100,99,98,...0for i in range(100,-1,-1): print(i)
- vuejs简单介绍特点
官网:https://cn.vuejs.org/ vue是一个渐进式的框架, 是一个轻量级的框架, 也不算是一个框架, 他核心只关注图层, 是一个构建数据驱动的web界面,易于上手, 还便于于第三方库 ...
- tiny6410 烧写uboot 转载
#烧录 参考: 03- Tiny6410刷机指南.pdf 假设拿到的Tiny6410开发板没有提前下载任何程序,包括Bootloader. ##Bootloader - Superboot Super ...
- git 使用过程中遇到的问题does not appear to be a git repository Could not read from remote respository
想把本地的git库上传到github上.github已经新建了一个public仓库,利用网站的命令 git Bash报错:does not appear to be a git repository ...
- redis知识点汇总
1. redis是什么 2. 为什么用redis 3. redis 数据结构 4. redis中的对象类型 5. redis都能做什么?怎么实现的的? 6. redis使用过程中需要注意什么 7. 数 ...
- Linux服务器---博客wordpress
Wordpress Wordpress是一个开源的博客平台,是搭建个人博客的首选,用户可以去wordpress中文网站寻找帮助资料 1.下载wordpress软件(https://cn.wordpre ...
