Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”01之 线程池架构
概要
前面分别介绍了"Java多线程基础"、"JUC原子类"和"JUC锁"。本章介绍JUC的最后一部分的内容——线程池。内容包括:
线程池架构图
线程池示例
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3509903.html
线程池架构图
线程池的架构图如下:
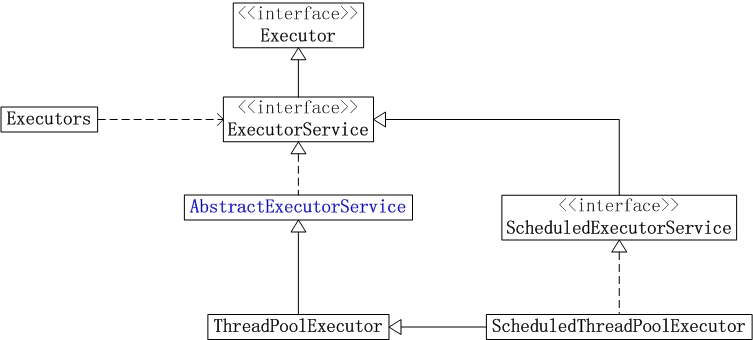
1. Executor
它是"执行者"接口,它是来执行任务的。准确的说,Executor提供了execute()接口来执行已提交的 Runnable 任务的对象。Executor存在的目的是提供一种将"任务提交"与"任务如何运行"分离开来的机制。
它只包含一个函数接口:
void execute(Runnable command)
2. ExecutorService
ExecutorService继承于Executor。它是"执行者服务"接口,它是为"执行者接口Executor"服务而存在的;准确的话,ExecutorService提供了"将任务提交给执行者的接口(submit方法)","让执行者执行任务(invokeAll, invokeAny方法)"的接口等等。
ExecutorService的函数列表
// 请求关闭、发生超时或者当前线程中断,无论哪一个首先发生之后,都将导致阻塞,直到所有任务完成执行。
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成时,返回保持任务状态和结果的 Future 列表。
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
// 执行给定的任务,当所有任务完成或超时期满时(无论哪个首先发生),返回保持任务状态和结果的 Future 列表。
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 执行给定的任务,如果某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
// 执行给定的任务,如果在给定的超时期满前某个任务已成功完成(也就是未抛出异常),则返回其结果。
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 如果此执行程序已关闭,则返回 true。
boolean isShutdown()
// 如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回 true。
boolean isTerminated()
// 启动一次顺序关闭,执行以前提交的任务,但不接受新任务。
void shutdown()
// 试图停止所有正在执行的活动任务,暂停处理正在等待的任务,并返回等待执行的任务列表。
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
// 提交一个返回值的任务用于执行,返回一个表示任务的未决结果的 Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
// 提交一个 Runnable 任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的 Future。
Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
// 提交一个 Runnable 任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的 Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result)
3. AbstractExecutorService
AbstractExecutorService是一个抽象类,它实现了ExecutorService接口。
AbstractExecutorService存在的目的是为ExecutorService中的函数接口提供了默认实现。
AbstractExecutorService函数列表
由于它的函数列表和ExecutorService一样,这里就不再重复列举了。
4. ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor就是大名鼎鼎的"线程池"。它继承于AbstractExecutorService抽象类。
ThreadPoolExecutor函数列表
// 用给定的初始参数和默认的线程工厂及被拒绝的执行处理程序创建新的 ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue)
// 用给定的初始参数和默认的线程工厂创建新的 ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
// 用给定的初始参数和默认被拒绝的执行处理程序创建新的 ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 用给定的初始参数创建新的 ThreadPoolExecutor。
ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) // 基于完成执行给定 Runnable 所调用的方法。
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t)
// 如果在保持活动时间内没有任务到达,新任务到达时正在替换(如果需要),则设置控制核心线程是超时还是终止的策略。
void allowCoreThreadTimeOut(boolean value)
// 如果此池允许核心线程超时和终止,如果在 keepAlive 时间内没有任务到达,新任务到达时正在替换(如果需要),则返回 true。
boolean allowsCoreThreadTimeOut()
// 请求关闭、发生超时或者当前线程中断,无论哪一个首先发生之后,都将导致阻塞,直到所有任务完成执行。
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
// 在执行给定线程中的给定 Runnable 之前调用的方法。
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r)
// 在将来某个时间执行给定任务。
void execute(Runnable command)
// 当不再引用此执行程序时,调用 shutdown。
protected void finalize()
// 返回主动执行任务的近似线程数。
int getActiveCount()
// 返回已完成执行的近似任务总数。
long getCompletedTaskCount()
// 返回核心线程数。
int getCorePoolSize()
// 返回线程保持活动的时间,该时间就是超过核心池大小的线程可以在终止前保持空闲的时间值。
long getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit unit)
// 返回曾经同时位于池中的最大线程数。
int getLargestPoolSize()
// 返回允许的最大线程数。
int getMaximumPoolSize()
// 返回池中的当前线程数。
int getPoolSize()
// 返回此执行程序使用的任务队列。
BlockingQueue<Runnable> getQueue()
// 返回用于未执行任务的当前处理程序。
RejectedExecutionHandler getRejectedExecutionHandler()
// 返回曾计划执行的近似任务总数。
long getTaskCount()
// 返回用于创建新线程的线程工厂。
ThreadFactory getThreadFactory()
// 如果此执行程序已关闭,则返回 true。
boolean isShutdown()
// 如果关闭后所有任务都已完成,则返回 true。
boolean isTerminated()
// 如果此执行程序处于在 shutdown 或 shutdownNow 之后正在终止但尚未完全终止的过程中,则返回 true。
boolean isTerminating()
// 启动所有核心线程,使其处于等待工作的空闲状态。
int prestartAllCoreThreads()
// 启动核心线程,使其处于等待工作的空闲状态。
boolean prestartCoreThread()
// 尝试从工作队列移除所有已取消的 Future 任务。
void purge()
// 从执行程序的内部队列中移除此任务(如果存在),从而如果尚未开始,则其不再运行。
boolean remove(Runnable task)
// 设置核心线程数。
void setCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize)
// 设置线程在终止前可以保持空闲的时间限制。
void setKeepAliveTime(long time, TimeUnit unit)
// 设置允许的最大线程数。
void setMaximumPoolSize(int maximumPoolSize)
// 设置用于未执行任务的新处理程序。
void setRejectedExecutionHandler(RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
// 设置用于创建新线程的线程工厂。
void setThreadFactory(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 按过去执行已提交任务的顺序发起一个有序的关闭,但是不接受新任务。
void shutdown()
// 尝试停止所有的活动执行任务、暂停等待任务的处理,并返回等待执行的任务列表。
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
// 当 Executor 已经终止时调用的方法。
protected void terminated()
5. ScheduledExecutorService
ScheduledExecutorService是一个接口,它继承于于ExecutorService。它相当于提供了"延时"和"周期执行"功能的ExecutorService。
ScheduledExecutorService提供了相应的函数接口,可以安排任务在给定的延迟后执行,也可以让任务周期的执行。
ScheduledExecutorService函数列表
// 创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的 ScheduledFuture。
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的一次性操作。
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,后续操作具有给定的周期;也就是将在 initialDelay 后开始执行,然后在 initialDelay+period 后执行,接着在 initialDelay + 2 * period 后执行,依此类推。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,随后,在每一次执行终止和下一次执行开始之间都存在给定的延迟。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
6. ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承于ThreadPoolExecutor,并且实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口。它相当于提供了"延时"和"周期执行"功能的ScheduledExecutorService。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类似于Timer,但是在高并发程序中,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的性能要优于Timer。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor函数列表
// 使用给定核心池大小创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize)
// 使用给定初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
// 使用给定的初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 使用给定初始参数创建一个新 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) // 修改或替换用于执行 callable 的任务。
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(Callable<V> callable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task)
// 修改或替换用于执行 runnable 的任务。
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(Runnable runnable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task)
// 使用所要求的零延迟执行命令。
void execute(Runnable command)
// 获取有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下、是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略。
boolean getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy()
// 获取有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有延迟任务的策略。
boolean getExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy()
// 返回此执行程序使用的任务队列。
BlockingQueue<Runnable> getQueue()
// 从执行程序的内部队列中移除此任务(如果存在),从而如果尚未开始,则其不再运行。
boolean remove(Runnable task)
// 创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的 ScheduledFuture。
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行在给定延迟后启用的一次性操作。
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,后续操作具有给定的周期;也就是将在 initialDelay 后开始执行,然后在 initialDelay+period 后执行,接着在 initialDelay + 2 * period 后执行,依此类推。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit)
// 创建并执行一个在给定初始延迟后首次启用的定期操作,随后,在每一次执行终止和下一次执行开始之间都存在给定的延迟。
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit)
// 设置有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有定期任务的策略。
void setContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value)
// 设置有关在此执行程序已 shutdown 的情况下是否继续执行现有延迟任务的策略。
void setExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(boolean value)
// 在以前已提交任务的执行中发起一个有序的关闭,但是不接受新任务。
void shutdown()
// 尝试停止所有正在执行的任务、暂停等待任务的处理,并返回等待执行的任务列表。
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
// 提交一个返回值的任务用于执行,返回一个表示任务的未决结果的 Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
// 提交一个 Runnable 任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的 Future。
Future<?> submit(Runnable task)
// 提交一个 Runnable 任务用于执行,并返回一个表示该任务的 Future。
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result)
7. Executors
Executors是个静态工厂类。它通过静态工厂方法返回ExecutorService、ScheduledExecutorService、ThreadFactory 和 Callable 等类的对象。
Executors函数列表
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定特权的操作并返回其结果。
static Callable<Object> callable(PrivilegedAction<?> action)
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定特权的异常操作并返回其结果。
static Callable<Object> callable(PrivilegedExceptionAction<?> action)
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定的任务并返回 null。
static Callable<Object> callable(Runnable task)
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可运行给定的任务并返回给定的结果。
static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result)
// 返回用于创建新线程的默认线程工厂。
static ThreadFactory defaultThreadFactory()
// 创建一个可根据需要创建新线程的线程池,但是在以前构造的线程可用时将重用它们。
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool()
// 创建一个可根据需要创建新线程的线程池,但是在以前构造的线程可用时将重用它们,并在需要时使用提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程。
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
// 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池,以共享的无界队列方式来运行这些线程,在需要时使用提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 创建一个线程池,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
// 创建一个线程池,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,以无界队列方式来运行该线程。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor()
// 创建一个使用单个 worker 线程的 Executor,以无界队列方式来运行该线程,并在需要时使用提供的 ThreadFactory 创建新线程。
static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 创建一个单线程执行程序,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()
// 创建一个单线程执行程序,它可安排在给定延迟后运行命令或者定期地执行。
static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory)
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可在当前的访问控制上下文中执行给定的 callable 对象。
static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallable(Callable<T> callable)
// 返回 Callable 对象,调用它时可在当前的访问控制上下文中,使用当前上下文类加载器作为上下文类加载器来执行给定的 callable 对象。
static <T> Callable<T> privilegedCallableUsingCurrentClassLoader(Callable<T> callable)
// 返回用于创建新线程的线程工厂,这些新线程与当前线程具有相同的权限。
static ThreadFactory privilegedThreadFactory()
// 返回一个将所有已定义的 ExecutorService 方法委托给指定执行程序的对象,但是使用强制转换可能无法访问其他方法。
static ExecutorService unconfigurableExecutorService(ExecutorService executor)
// 返回一个将所有已定义的 ExecutorService 方法委托给指定执行程序的对象,但是使用强制转换可能无法访问其他方法。
static ScheduledExecutorService unconfigurableScheduledExecutorService(ScheduledExecutorService executor)
线程池示例
下面通过示例来对线程池的使用做简单演示。
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; public class ThreadPoolDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个可重用固定线程数的线程池
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 创建实现了Runnable接口对象,Thread对象当然也实现了Runnable接口
Thread ta = new MyThread();
Thread tb = new MyThread();
Thread tc = new MyThread();
Thread td = new MyThread();
Thread te = new MyThread();
// 将线程放入池中进行执行
pool.execute(ta);
pool.execute(tb);
pool.execute(tc);
pool.execute(td);
pool.execute(te);
// 关闭线程池
pool.shutdown();
}
} class MyThread extends Thread { @Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " is running.");
}
}
运行结果:
pool-1-thread-1 is running.
pool-1-thread-2 is running.
pool-1-thread-1 is running.
pool-1-thread-2 is running.
pool-1-thread-1 is running.
结果说明:
主线程中创建了线程池pool,线程池的容量是2。即,线程池中最多能同时运行2个线程。
紧接着,将ta,tb,tc,td,te这3个线程添加到线程池中运行。
最后,通过shutdown()关闭线程池。
更多内容
Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”01之 线程池架构的更多相关文章
- Java多线程系列--“JUC原子类”01之 框架
根据修改的数据类型,可以将JUC包中的原子操作类可以分为4类. 1. 基本类型: AtomicInteger, AtomicLong, AtomicBoolean ;2. 数组类型: AtomicIn ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC原子类”04之 AtomicReference原子类
概要 本章对AtomicReference引用类型的原子类进行介绍.内容包括:AtomicReference介绍和函数列表AtomicReference源码分析(基于JDK1.7.0_40)Atomi ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC原子类”02之 AtomicLong原子类
概要 AtomicInteger, AtomicLong和AtomicBoolean这3个基本类型的原子类的原理和用法相似.本章以AtomicLong对基本类型的原子类进行介绍.内容包括:Atomic ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC原子类”03之 AtomicLongArray原子类
概要 AtomicIntegerArray, AtomicLongArray, AtomicReferenceArray这3个数组类型的原子类的原理和用法相似.本章以AtomicLongArray对数 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC原子类”05之 AtomicLongFieldUpdater原子类
概要 AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater, AtomicLongFieldUpdater和AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater这3个修改类的成员的原子类型的原理和用法 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”06之 Callable和Future
概要 本章介绍线程池中的Callable和Future.Callable 和 Future 简介示例和源码分析(基于JDK1.7.0_40) 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.co ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”02之 线程池原理(一)
概要 在上一章"Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”01之 线程池架构"中,我们了解了线程池的架构.线程池的实现类是ThreadPoolExecutor类.本章,我们通过分析Th ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”03之 线程池原理(二)
概要 在前面一章"Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”02之 线程池原理(一)"中介绍了线程池的数据结构,本章会通过分析线程池的源码,对线程池进行说明.内容包括:线程池示例参考代 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”04之 线程池原理(三)
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3509960.html 本章介绍线程池的生命周期.在"Java多线程系列--“基础篇”01之 基 ...
- Java多线程系列--“JUC线程池”05之 线程池原理(四)
概要 本章介绍线程池的拒绝策略.内容包括:拒绝策略介绍拒绝策略对比和示例 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3512947.html 拒绝策略 ...
随机推荐
- AndroidManifest.xml中<activity></activity>相关属性说明
虽说,从事android开发有一定时间了,对于Activity大家也都不陌生,但是具体的对于Activity中相关属性的含义有必要做一个系统的总结: intent-filteraction: 来指定响 ...
- STL练习题
//hdu_2717 //map 一对多映射,基于关键字快速查找,不允许重复值 //queue 队列 先进先出 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio& ...
- [转]Python数据挖掘
- 移动开发发展方向-----Hybird混合开发3大方案
移动开发发展方向-----Hybird混合开发3大方案
- phoenix 开发API系列 目录
phoenix 开发API系列(一)创建简单的http api phoenix 开发API系列(二)phoenix 各类 api 实现方式 phoenix 开发API系列(三)phoenix api ...
- 【腾讯Bugly干货分享】QQ电话适配iOS10 Callkit框架
本文来自于腾讯bugly开发者社区,非经作者同意,请勿转载,原文地址:http://dev.qq.com/topic/58009392302e4725036142fc Dev Club 是一个交流移动 ...
- s3c2440笔记1(启动)
s3c2440启动方式 1. 从nand flash 启动 1.1 上电后将nand flash中的前4KB数据复制到“Stepping Stone”: 1.2 CPU 执行“Stepping Sto ...
- Java虚拟机5:Java垃圾回收(GC)机制详解
哪些内存需要回收? 哪些内存需要回收是垃圾回收机制第一个要考虑的问题,所谓“要回收的垃圾”无非就是那些不可能再被任何途径使用的对象.那么如何找到这些对象? 1.引用计数法 这个算法的实现是,给对象中添 ...
- 【C语言学习】《C Primer Plus》第9章 函数
学习总结 1.函数有利于我们可以省去重复的代码,函数可以使程序更加模块化,从而有利于程序的阅读.修改和完善.我们在系统设计或架构设计的时候,往往追求的是模块化.组件化.松耦合,而函数就是其代码的表现. ...
- hadoop学习笔记:zookeeper学习(上)
在前面的文章里我多次提到zookeeper对于分布式系统开发的重要性,因此对zookeeper的学习是非常必要的.本篇博文主要是讲解zookeeper的安装和zookeeper的一些基本的应用,同时我 ...
