Handling events in an MVVM WPF application
Posted: June 30, 2013 | Filed under: MVVM, WPF, XAML |1 Comment
In a WPF application that uses the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) design pattern, the view model is the component that is responsible for handling the application’s presentation logic and state. This means that the view’s code-behind file should contain no code to handle events that are raised from any user interface (UI) element such as a Button or a ComboBox nor should it contain any domain specific logic.
Ideally, the code-behind of a view – typically a Window or a UserControl – contains only a constructor that calls the InitializeComponent method and perhaps some additional code to control or interact with the view layer that is difficult or inefficient to express in XAML, e.g. complex animations.
In other words, an MVVM application should not have any code like this where a button’s click event is handled in the code-behind of the view:
<Button Content="Click here!" Click="btn_Click"/>
protected void btn_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
/* This is not MVVM! */
}
Commands
Instead, in addition to providing properties to expose data to be displayed or edited in the view, the view model defines actions that can be performed by the user and typically expose these as commands. A command is an object that implements theSystem.Windows.Input.ICommand interface and encapsulates the code for the action to be performed. It can be data bound to a UI control in the view to be invoked as a result of a mouse click, key press or any other input event. As well as the command being invoked as the user interacts with the UI, a UI control can be automatically enabled or disabled based on the command.
The Execute method of the ICommand interface encapsulates the operation itself while the CanExecute method indicates whether the command can be invoked at a particular time or not. The interface also defines a CanExecuteChanged event that is raised on the UI thread to cause every invoking control to requery to check if the command can execute.
WPF provides two implementations of the ICommand interface; the System.Windows.Input.RoutedCommand andSystem.Windows.Input.RoutedUICommand where the latter is a subclass of the former that simply adds a Text property that describes the command. However, neither of these implementations are especially suited to be used in a view model as they search the visual tree from the focused element and up for an element that has a matchingSystem.Windows.Input.CommandBinding object in its CommandBindings collection and then executes the Execute delegate for this particular CommandBinding. Since the command logic should reside in the view model, you don’t want to setup aCommandBinding in the view in order to connect the command to a visual element. Instead, you can create your own command by creating a class that implements the ICommand. The below implementation is a common one that invokes delegates for the Execute and CanExecute methods. If you are using Prism, the framework for building composite WPF and Silverlight applications from the Microsoft Patterns and Practices Team, there is a similar Microsoft.Practices.Prism.Commands.DelegateCommand class available.
public class DelegateCommand<T> : System.Windows.Input.ICommand
{
private readonly Predicate<T> _canExecute;
private readonly Action<T> _execute;
public DelegateCommand(Action<T> execute)
: this(execute, null)
{
}
public DelegateCommand(Action<T> execute, Predicate<T> canExecute)
{
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
if (_canExecute == null)
return true;
return _canExecute((parameter == null) ? default(T) : (T)Convert.ChangeType(parameter, typeof(T)));
}
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute((parameter == null) ? default(T) : (T)Convert.ChangeType(parameter, typeof(T)));
}
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()
{
if (CanExecuteChanged != null)
CanExecuteChanged(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
}
The view model will then expose properties of this type for the view to bind to. Below is a sample implementation of a view model that exposes a ButtonClickCommand that will disable any UI control that is bound to it if the private string field _input, which is in turn exposed through a string property called Input, is empty. If you only pass a single delegate to the constructor of the DelegateCommand<T> class, it will assume that the command should always by available and the CanExecute method will always return true. Also note that when the value of the string property changes, a RaiseCanExecuteChanged method is called to raise the CanExecuteChanged event in order to update the status of any control in the view that is bound to the command.
public class ViewModel
{
private readonly DelegateCommand<string> _clickCommand;
public ViewModel()
{
_clickCommand = new DelegateCommand<string>(
(s) => { /* perform some action */ }, //Execute
(s) => { return !string.IsNullOrEmpty(_input); } //CanExecute
);
}
public DelegateCommand<string> ButtonClickCommand
{
get { return _clickCommand; }
}
private string _input;
public string Input
{
get { return _input; }
set
{
_input = value;
_clickCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
}
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.DataContext = new ViewModel();
}
}
<StackPanel Margin="10">
<TextBox Text="{Binding Input, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}"/>
<Button Content="Click here!" Command="{Binding ButtonClickCommand}"
Margin="0 5 0 0"/>
</StackPanel>
With this approach you have now moved the presentation logic from the view to the view model. Instead of hooking up the button’s click handler, its Command property is now bound to the command defined in the view model and when the user clicks on the button the command’s Execute method will be invoked.
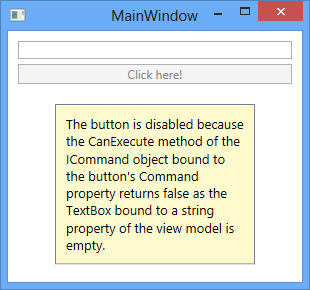
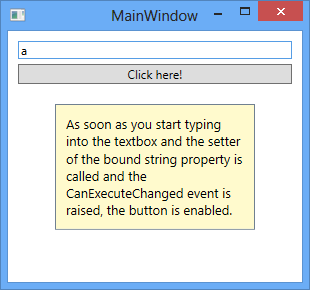
EventTriggers
There is an alternative way of associating a control in the view with a command object exposed by the view model. Only some controls can actually bind to a command through the Command property, notably those derived fromSystem.Windows.Controls.Primitives.ButtonBase or System.Windows.Controls.MenuItem. If you want to attach a command to some other control or when you want to invoke a command on an event other than the click event for a button, you can use Expression Blend interaction triggers and the System.Windows.Interactivity.InvokeCommandAction class. Below is an example on how you would execute a command object called MouseEnterCommand in the view model when the user moves the mouse pointer over a Rectangle element in the view. You specify the event for which the command will be executed in the EventName property of the EventTrigger. Remember to add a reference to System.Windows.Interactivity.dll for this to compile.
Also note that using the InvokeCommandAction doesn’t automatically enable or disable the control based on the command’s CanExecute method, unlike controls that have a Command property and can be bound directly to a command.
<Window x:Class="Mm.HandlingEventsMVVM.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:i="clr-namespace:System.Windows.Interactivity;assembly=System.Windows.Interactivity"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525">
<StackPanel>
<Rectangle Fill="Yellow" Stroke="Black" Width="100" Height="100">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseEnter" >
<i:InvokeCommandAction Command="{Binding MouseEnterCommand}" />
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</Rectangle>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
CommandParameters
If you wish to pass a parameter to a command from the view you do so by using the CommandParameter property. The type argument of the generic DelegateCommand<T> class specifies the type of the command parameter that gets passed to the Execute and CanExecute methods. The CommandParameter property exists in both the ButtonBase and MenuItem derived controls as well as in the InvokeCommandAction class:
<Button Content="Click here!" Command="{Binding ButtonClickCommand}"
CommandParameter="some string to be passed..."
Margin="0 5 0 0"/>
<i:InvokeCommandAction Command="{Binding MouseEnterCommand}"
CommandParameter="some string to be passed..."/>
CallMethodAction
Besides the InvokeCommandAction class, there is also another class named CallMethodAction that can be used to invoke a method in the view model from the view without using commands. It has a MethodName property for specifying the name of the method to call and a TargetObject property that needs to be bound to an instance of the class containing the method, i.e. the view model:
<Window x:Class="Mm.HandlingEventsMVVM.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:i="clr-namespace:System.Windows.Interactivity;assembly=System.Windows.Interactivity"
xmlns:ei="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/2010/interactions"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525">
<StackPanel>
<Rectangle Fill="Yellow" Stroke="Black" Width="100" Height="100">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseEnter" >
<!-- Execute a method called 'SomeMethod' defined in the view model -->
<ei:CallMethodAction TargetObject="{Binding}" MethodName="SomeMethod"/>
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</Rectangle>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
public void SomeMethod()
{
/* do something ... */
}
Note that the CallMethodAction class is defined in another assembly and namespace and you will need to add a reference to Microsoft.Expressions.Interactions.dll to be able to use it. Also note that it doesn’t support parameters.
Handling events in an MVVM WPF application的更多相关文章
- 每天翻译一点点: WPF Application Framework (WAF)
ps:http://waf.codeplex.com/wikipage?title=Model-View-ViewModel%20Pattern&referringTitle=Document ...
- 【转】How to view word document in WPF application
How to view word document in WPF application (CSVSTOViewWordInWPF) Introduction The Sample demonstra ...
- Merging a WPF application into a single EXE(WPF应用程序合并成单个Exe文件)
I always dislike handing off little applications to people. Not because I can’t, but because of the ...
- C# WPF Application 下的文件操作
好气哦,电脑好烂,每天花大把的时间在等电脑反应上. 没有钱买新电脑,连组台式机的钱都没有.好气哦. 啊啊啊啊文件操作是什么鬼???C++下我都懵了,C#下好多东西要学!!!我不会!我不会!我不会!!! ...
- (4)事件处理——(1)事件处理(Handling Events)
JavaScript has several built-in ways of reacting to user interaction and other events. To make a pag ...
- WPF Application 类介绍以及怎样修改启动方式
因为想要修改wpf的启动方式,所以研究了下Application类,现把一些有用的属性与大家分享下: 属性: Current 获取当前 AppDomain的 Appl ...
- WPF——Application
Application类处于WPF应用程序的最顶端,main函数就在这个类中. Application类的作用: 截图连接 https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotne ...
- WPF Application
Application类作为启动的入口,在VS中,通常自动代码为我们继承了Application类,这样做的有点,我还没有理解到,但是我们先学到这个知识点. 为了能够更好的控制整个启动过程,包括得到A ...
- Eloquent JavaScript #12# Handling Events
索引 Notes onclick removeEventListener Event objects stopPropagation event.target Default actions Key ...
随机推荐
- MFC添加菜单事件
双击draw.rc,就能看到.
- error TRK0002
运行程序出现error TRK0002的原因是因为3ds max中打开了程序生成的模型,同时使用导致memory conflict,然后随之出现一些乱七八糟的问题. 只要将3ds max重置即可,即不 ...
- 数据结构之Dijkstra算法
基本思想 通过Dijkstra计算图G中的最短路径时,需要指定起点s(即从顶点s开始计算). 此外,引进两个集合S和U.S的作用是记录已求出最短路径的顶点(以及相应的最短路径长度),而U则是记录还未求 ...
- hdu 5018 Revenge of Fibonacci
大水题 #include<time.h> #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include<algorithm&g ...
- Linux内存性能指标、CPU性能指标
内存性能指标 内存基础概念 先执行一下 top 命令,看结果中关于内存的相关部分 # top 其中的 VIRT.RES.SWAP 都是什么呢? 分别是下面的3个概念: 物理内存 Resident - ...
- HTML5学习之拖放(十)
l元素可以用于拖拽必须设置draggable="true"属性,img和a标签除外,她们两个默认就可以被拖拽 想做拖拽处理,就需要在Dom元素上监听拖放的事件:dragstart, ...
- Shell编程基础教程7--脚本参数的传递
7.脚本参数的传递 7.1.shift命令 简介: shift n 每次将参数位置向左偏移n位 例子 #!/bin/bash us ...
- Pyqt 音视频播放器
在寻找如何使用Pyqt做一个播放器时首先找到的是openCV2 openCV2 貌似太强大了,各种关于图像处理的事情它都能完成,如 读取摄像头.图像识别.人脸识别. 图像灰度处理 . 播放视频等,强 ...
- 游戏主循环(Game Loop)
游戏主循环是游戏的心跳,一般使用while循环进行主动刷新. 一次循环由获取用户输入.更新游戏状态.处理AI.播放音乐和绘制画面组成. 这些行为可以分成两类: update_game(); // 更新 ...
- POJ2065 SETI(高斯消元 同模方程)
(a1 * 1^0 + a2 * 1^1 + ... an * 1^n - 1) % P = f1 .... (a1 * n^0 + a2 * n^1 + ... an - 1 * ...
