HDU 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again (最短路)
Problem Description
The Gorelians are a warlike race that travel the universe conquering new worlds as a form of recreation. Given their violent, fun-loving nature, keeping their leaders alive is of serious concern. Part of the Gorelian security plan involves changing the traffic patterns of their cities on a daily basis, and routing all Gorelian Government Officials to the Government Building by the fastest possible route.
Fortunately for the Gorelian Minister of Traffic (that would be you), all Gorelian cities are laid out as a rectangular grid of blocks, where each block is a square measuring 2520 rels per side (a rel is the Gorelian Official Unit of Distance). The speed limit between two adjacent intersections is always constant, and may range from 1 to 9 rels per blip (a blip, of course, being the Gorelian Official Unit of Time). Since Gorelians have outlawed decimal numbers as unholy (hey, if you're the dominant force in the known universe, you can outlaw whatever you want), speed limits are always integer values. This explains why Gorelian blocks are precisely 2520 rels in length: 2520 is the least common multiple of the integers 1 through 9. Thus, the time required to travel between two adjacent intersections is always an integer number of blips.
In all Gorelian cities, Government Housing is always at the northwest corner of the city, while the Government Building is always at the southeast corner. Streets between intersections might be one-way or two-way, or possibly even closed for repair (all this tinkering with traffic patterns causes a lot of accidents). Your job, given the details of speed limits, street directions, and street closures for a Gorelian city, is to determine the fastest route from Government Housing to the Government Building. (It is possible, due to street directions and closures, that no route exists, in which case a Gorelian Official Temporary Holiday is declared, and the Gorelian Officials take the day off.)
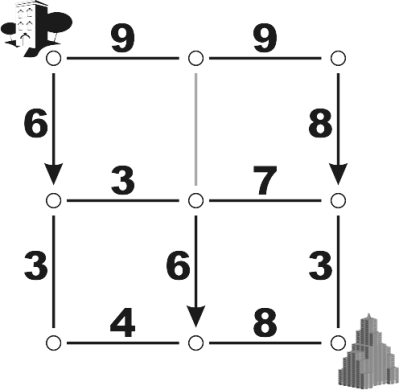
The picture above shows a Gorelian City marked with speed limits, one way streets, and one closed street. It is assumed that streets are always traveled at the exact posted speed limit, and that turning a corner takes zero time. Under these conditions, you should be able to determine that the fastest route from Government Housing to the Government Building in this city is 1715 blips. And if the next day, the only change is that the closed road is opened to two way traffic at 9 rels per blip, the fastest route becomes 1295 blips. On the other hand, suppose the three one-way streets are switched from southbound to northbound (with the closed road remaining closed). In that case, no route would be possible and the day would be declared a holiday.
Input
The input consists of a set of cities for which you must find a fastest route if one exists. The first line of an input case contains two integers, which are the vertical and horizontal number of city blocks, respectively. The smallest city is a single block, or 1 by 1, and the largest city is 20 by 20 blocks. The remainder of the input specifies speed limits and traffic directions for streets between intersections, one row of street segments at a time. The first line of the input (after the dimensions line) contains the data for the northernmost east-west street segments. The next line contains the data for the northernmost row of north-south street segments. Then the next row of east-west streets, then north-south streets, and so on, until the southernmost row of east-west streets. Speed limits and directions of travel are specified in order from west to east, and each consists of an integer from 0 to 9 indicating speed limit, and a symbol indicating which direction traffic may flow. A zero speed limit means the road is closed. All digits and symbols are delimited by a single space. For east-west streets, the symbol will be an asterisk '*' which indicates travel is allowed in both directions, a less-than symbol '<' which indicates travel is allowed only in an east-to-west direction, or a greater-than symbol '>' which indicates travel is allowed only in a west-to-east direction. For north-south streets, an asterisk again indicates travel is allowed in either direction, a lowercase "vee" character 'v' indicates travel is allowed only in a north-to-south directions, and a caret symbol '^' indicates travel is allowed only in a south-to-north direction. A zero speed, indicating a closed road, is always followed by an asterisk. Input cities continue in this manner until a value of zero is specified for both the vertical and horizontal dimensions.
Output
For each input scenario, output a line specifying the integer number of blips of the shortest route, a space, and then the word "blips". For scenarios which have no route, output a line with the word "Holiday".
Sample Input
2 2
9 * 9 *
6 v 0 * 8 v
3 * 7 *
3 * 6 v 3 *
4 * 8 *
2 2
9 * 9 *
6 v 9 * 8 v
3 * 7 *
3 * 6 v 3 *
4 * 8 *
2 2
9 * 9 *
6 ^ 0 * 8 ^
3 * 7 *
3 * 6 ^ 3 *
4 * 8 *
0 0
Sample Output
1715 blips
1295 blips
Holiday
分析:
有个n*m大小的矩形,起点在矩形的左上角, 终点在右下角, 里面一个小矩形代表一个街区(block)。
每个小矩形的边长都是2520, 小矩形的边有一个速度限制,范围是0~9, 如果是0表示这条边不能行驶。
关于输入部分,由上到下,从左到右,按照上图的对应的位置方式给出数据,
每一条边是 "数字"+“空格”+“符号”的形式,
数字表示这条边的限速,符号表示这条路是单向(还分东西, 南北)的还是双向的。
其实主旨思想就是在求一个最从左上角到右下角的最短路,关键就在于确定每一个点对应的编号,以及每一条路所对应的起点和终点。
每行输入的奇数行肯定是表示的横向的路径,路径条数就是列数,偶数行表示的是竖向的路径,路径条数就是列数+1,这些就没必要解释了把。
然后是确定每一个点所对应的编号:
对于横向的路径,第i行的第j个点所对应的编号就是(m+1)(i/2)+j,所连接的另一个点编号就是该点的编号加1、减1
而对于纵向的路径,第i行的第j个点所对应的编号就是(m+1)(i/2-1)+j,所连接的另一个点编号就是该点的编号加m、减m。
这样就完全把路径给保存下来了。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,u,w;
int num;//一共涉及到的点的数目
char str[150];
const int vNum=445;
const int eNum=vNum*vNum/2;
int Count;
typedef pair<int,int>pii;
struct Node
{
int to,val;
int Next;
}node[eNum];
int head[vNum];
int dis[vNum];
struct Node1
{
int len,num;
};
void add(int u,int v,int w)
{
node[Count].to=v;
node[Count].val=w;
node[Count].Next=head[u];
head[u]=Count;
Count++;
}
void spfa(int src)
{
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++)
dis[i]=INF;
dis[src]=0;
queue<Node1>q;
Node1 Now,Next;
Now.len=dis[src];
Now.num=src;
q.push(Now);
while(!q.empty())
{
Now=q.front();
q.pop();
int u=Now.num;//得到点
if(dis[u]!=Now.len)continue;
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=node[i].Next)
{
int v=node[i].to;
int temp=dis[u]+node[i].val;
if(dis[v]>temp)
{
dis[v]=temp;
Next.len=dis[v];
Next.num=v;
q.push(Next);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n&&m)
{
getchar();
Count=0;
num=(n+1)*(m+1);//最后一个点的标号
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=1; i<=2*n+1; i++)//对于n行的图形,那么一共需要输入的路径就有2*n+1行
{
gets(str);
int len=strlen(str);
if(i&1)//输入的是行的信息
{
for(int j=0,k=1; j<len; j+=4,k++) //数字、空格、方向、空格四个一个循环
{
u=(m+1)*(i/2)+k;//一个点对应的一个编号
w=str[j]-'0';//获得速度
if(w==0) continue;
if(str[j+2]=='*')//双向的
{
add(u,u+1,2520/w);
add(u+1,u,2520/w);
}
else if(str[j+2]=='<')//单向的从右到左
{
add(u+1,u,2520/w);
}
else//单向的从左到右
{
add(u,u+1,2520/w);
}
}
}
else//输入的是列的信息
{
for(int j=0,k=1; j<len; j+=4,k+=1)
{
u=(m+1)*(i/2-1)+k;//每次上面的那个点代表的数字
w=str[j]-'0';
if(w==0)continue;
if(str[j+2]=='*')//双向的
{
add(u,u+m+1,2520/w);
add(u+m+1,u,2520/w);
}
else if(str[j+2]=='v')//从上到下
{
add(u,u+m+1,2520/w);
}
else if(str[j+2]=='^')//从下到上
{
add(u+m+1,u,2520/w);
}
}
}
}
spfa(1);
if(dis[num]!=INF)
printf("%d blips\n",dis[num]);
else
printf("Holiday\n");
}
return 0;
}
HDU 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again (最短路)的更多相关文章
- POJ 3653 & ZOJ 2935 & HDU 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again(最短路dijstra)
题目链接: PKU:http://poj.org/problem? id=3653 ZJU:problemId=1934" target="_blank">http ...
- HDU 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again (spfa)
Here We Go(relians) Again Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 32768/32768K (Java/ ...
- hdu 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again (最短路径)
Here We Go(relians) Again Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Jav ...
- HDU 2722 Here We Go(relians) Again
最短路,建图太麻烦,略过…… #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <queue> const int INF ...
- 【HDOJ】2722 Here We Go(relians) Again
根据矩阵建图,然后求最短路径. #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #define L ...
- hdu 5545 The Battle of Guandu spfa最短路
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5545 题意:有N个村庄, M 个战场: $ 1 <=N,M <= 10^5 $; 其中曹 ...
- HDU 3416 Marriage Match IV (求最短路的条数,最大流)
Marriage Match IV 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/122685#problem/Q Description Do not si ...
- hdu - 2586 How far away ?(最短路共同祖先问题)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2586 最近公共祖先问题~~LAC离散算法 题目大意:一个村子里有n个房子,这n个房子用n-1条路连接起 ...
- HDU 6071 Lazy Running (同余最短路 dij)
Lazy Running Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others)To ...
随机推荐
- ES6 常用1
( (1)交换变量的值 ) [x, y] = [y, x]; ( (2)从函数返回多个值 // 返回一个数组function example() { return [1, 2, 3]; } var [ ...
- 2013长沙网赛E题Travel by Bike
题目链接:http://acm.zju.edu.cn/changsha/showProblem.do?problemId=26 题意:一个人从一个地方到另一个地方,长度为L,每小时速度为speed,周 ...
- mysql 读写锁
1. 表读锁 lock table tablename read; 例如: 从上图中可以看到,当给表a加了读锁之后,该进程本身对表a是可读的,但是不可写,再看在另外一个进程中: 在另外一个进程中表a也 ...
- Python语言算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度
算法复杂度分为时间复杂度和空间复杂度. 其作用: 时间复杂度是指执行算法所需要的计算工作量: 而空间复杂度是指执行这个算法所需要的内存空间. (算法的复杂性体现在运行该算法时的计算机所需资源的多少上, ...
- 【bzoj3751】 Hnoi2014—画框
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3571 (题目链接) 题意 给出一个$2*N$个点的二分图,$N*N$条边,连接$i$和$j$的边有两 ...
- Java考试题之九
QUESTION 177 Given: 1. class TestException extends Exception { } 2. class A { 3. public ...
- BZOJ 1010 [HNOI2008]toy 玩具装箱
2017.6.9:经过我的不懈努力,终于把此题A掉了,但上凸和下凸总是那么让人费解…… P教授要去看奥运,但是他舍不下他的玩具,于是他决定把所有的玩具运到北京.他使用自己的压缩器进行压缩,其可以将任意 ...
- 01 C++ 多线程入门实例
1.可复用的完整实例 #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <mutex> using namespace ...
- 使用traefik作为kubernetes的ingress
目录 说明 部署 创建一个独立的命名空间 配置rbac授权 配置secret 创建一个configmap用于存放traefik的配置文件 配置traefik的deployment文件 配置服务 通过p ...
- K8S从私有仓库拉取镜像
通常来讲,我们在通过公共镜像仓库拉取docker镜像的时候,不需要任何的认证操作,但我们在构建了企业的私有镜像以后,就不得不在拉取镜像之前通过用户名密码来完成认证. 在docker单机环境中,我们可以 ...
