常用开发库 - MapStruct工具库详解
常用开发库 - MapStruct工具库详解
MapStruct是一款非常实用Java工具,主要用于解决对象之间的拷贝问题,比如PO/DTO/VO/QueryParam之间的转换问题。区别于BeanUtils这种通过反射,它通过编译器编译生成常规方法,将可以很大程度上提升效率。@pdai
为什么会引入MapStruct这类工具
首先看下这类工具出现的背景。@pdai
JavaBean 问题引入
在开发的时候经常会有业务代码之间有很多的 JavaBean 之间的相互转化,比如PO/DTO/VO/QueryParam之间的转换问题。之前我们的做法是:
拷贝技术
- org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils.copyProperties
- org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils.copyProperties
- org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties
- net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanCopier
纯get/set
- 辅助IDE插件拷贝对象时可以自动set所有方法字段 (这种方式可能有些开发人员不清楚)
- 不仅看上去冗余添加新的字段时依然需要手动
- 开发效率比较低
MapStruct 带来的改变
MapSturct 是一个生成类型安全, 高性能且无依赖的 JavaBean 映射代码的注解处理器(annotation processor)。
工具可以帮我们实现 JavaBean 之间的转换, 通过注解的方式。
同时, 作为一个工具类,相比于手写, 其应该具有便捷, 不容易出错的特点。
MapStruct入门例子
这里展示最基本的PO转VO的例子,使用的是IDEA + Lombok + MapStruct
Pom.xml
注意:基于当前IDEA设置并不需要
mapstruct-processor的依赖
一般来说会加载两个包:
org.mapstruct:mapstruct: 包含Mapstruct核心,比如注解等;如果是mapstruct-jdk8会引入一些jdk8的语言特性;org.mapstruct:mapstruct-processor: 处理注解用的,可以根据注解自动生成mapstruct的mapperImpl类
如下示例基于IDEA实现,可以在build阶段的annotationProcessorPaths中配置mapstruct-processor的path。
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<org.mapstruct.version>1.4.0.Beta3</org.mapstruct.version>
<org.projectlombok.version>1.18.12</org.projectlombok.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok dependencies should not end up on classpath -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.71</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<!-- See https://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-compiler-plugin/compile-mojo.html -->
<!-- Classpath elements to supply as annotation processor path. If specified, the compiler -->
<!-- will detect annotation processors only in those classpath elements. If omitted, the -->
<!-- default classpath is used to detect annotation processors. The detection itself depends -->
<!-- on the configuration of annotationProcessors. -->
<!-- -->
<!-- According to this documentation, the provided dependency processor is not considered! -->
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
Entity
这里面假设基于一些业务需求采用的是MySQL,且将一些扩展的数据放在了config字段中,并以JSON转String存储。
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password; // 密码
private Integer sex; // 性别
private LocalDate birthday; // 生日
private LocalDateTime createTime; // 创建时间
private String config; // 其他扩展信息,以JSON格式存储
}
VO 类
最后真正展示的应该:
- 不显示密码;
- 将日期转换;
- config要转成对象的list;
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class UserVo {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer gender;
private LocalDate birthday;
private String createTime;
private List<UserConfig> config;
@Data
public static class UserConfig {
private String field1;
private Integer field2;
}
}
mapper(或者converter)
注意:
- 这里没用@Mappings,且看最后编译出的类文件,会自动加
- 密码需要ignore
@Mapper
public interface UserConverter {
UserConverter INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(UserConverter.class);
@Mapping(target = "gender", source = "sex")
@Mapping(target = "createTime", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
UserVo do2vo(User var1);
@Mapping(target = "sex", source = "gender")
@Mapping(target = "password", ignore = true)
@Mapping(target = "createTime", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
User vo2Do(UserVo var1);
List<UserVo> do2voList(List<User> userList);
default List<UserVo.UserConfig> strConfigToListUserConfig(String config) {
return JSON.parseArray(config, UserVo.UserConfig.class);
}
default String listUserConfigToStrConfig(List<UserVo.UserConfig> list) {
return JSON.toJSONString(list);
}
}
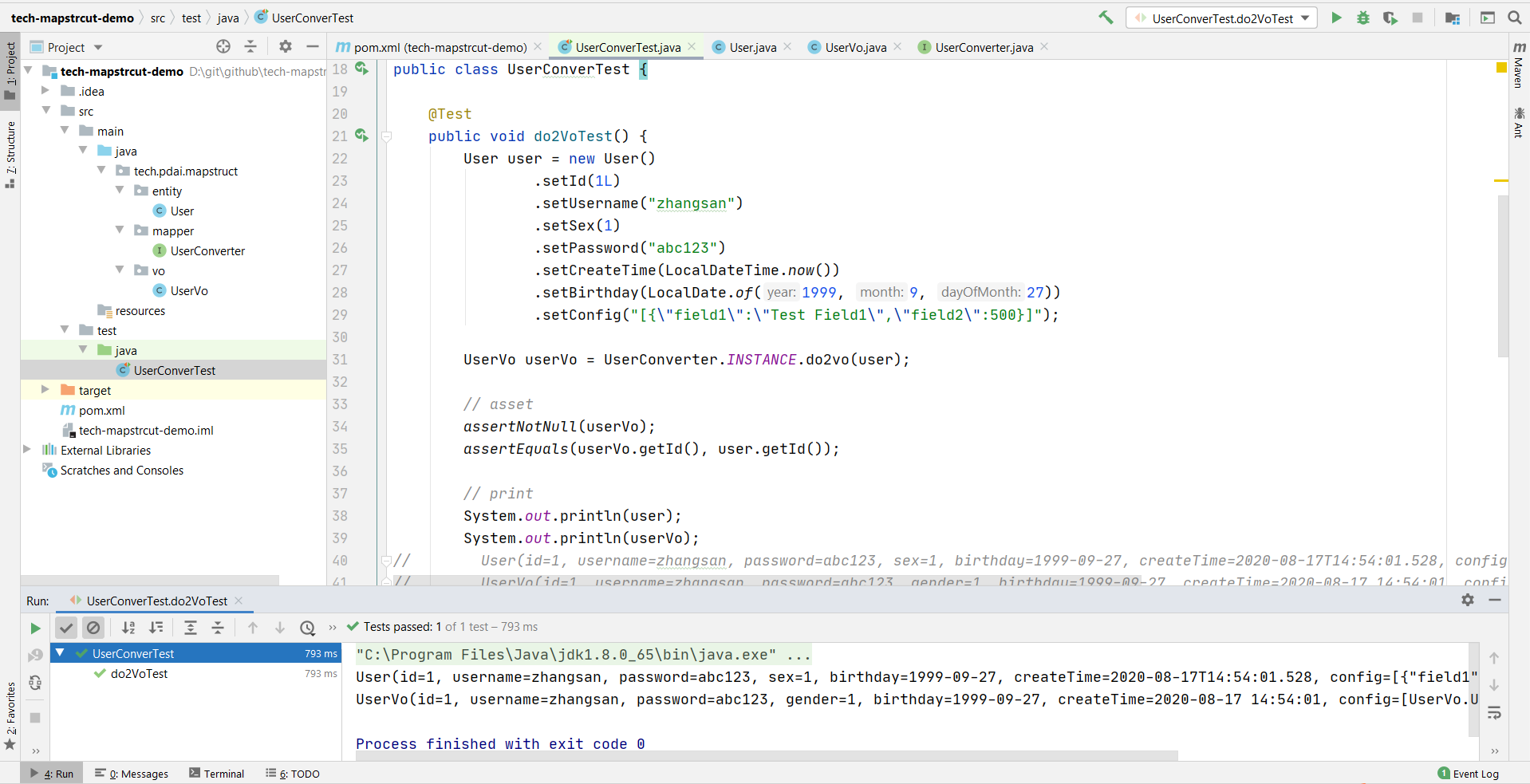
测试类
@Test
public void do2VoTest() {
User user = new User()
.setId(1L)
.setUsername("zhangsan")
.setSex(1)
.setPassword("abc123")
.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now())
.setBirthday(LocalDate.of(1999, 9, 27))
.setConfig("[{\"field1\":\"Test Field1\",\"field2\":500}]");
UserVo userVo = UserConverter.INSTANCE.do2vo(user);
// asset
assertNotNull(userVo);
assertEquals(userVo.getId(), user.getId());
// print
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(userVo);
// User(id=1, username=zhangsan, password=abc123, sex=1, birthday=1999-09-27, createTime=2020-08-17T14:54:01.528, config=[{"field1":"Test Field1","field2":500}])
// UserVo(id=1, username=zhangsan, password=abc123, gender=1, birthday=1999-09-27, createTime=2020-08-17 14:54:01, config=[UserVo.UserConfig(field1=Test Field1, field2=500)])
}
@Test
public void vo2DoTest() {
UserVo.UserConfig userConfig = new UserVo.UserConfig();
userConfig.setField1("Test Field1");
userConfig.setField2(500);
UserVo userVo = new UserVo()
.setId(1L)
.setUsername("zhangsan")
.setGender(2)
.setCreateTime("2020-01-18 15:32:54")
.setBirthday(LocalDate.of(1999, 9, 27))
.setConfig(Collections.singletonList(userConfig));
User user = UserConverter.INSTANCE.vo2Do(userVo);
// asset
assertNotNull(userVo);
assertEquals(userVo.getId(), user.getId());
// print
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(userVo);
}
MapStrcut实现的原理?
MapStruct 来生成的代码, 其类似于人手写。 速度上可以得到保证。
前面例子中生成的代码可以在编译后看到, 在 target/generated-sources/annotations 里可以看到; 同时真正在代码包执行的可以在target/classes包中看到。
编译后的类
- 编译后的class位置

- 编译后的内容
public class UserConverterImpl implements UserConverter {
@Override
public UserVo do2vo(User var1) {
if ( var1 == null ) {
return null;
}
UserVo userVo = new UserVo();
userVo.setGender( var1.getSex() );
if ( var1.getCreateTime() != null ) {
userVo.setCreateTime( DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern( "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ).format( var1.getCreateTime() ) );
}
userVo.setId( var1.getId() );
userVo.setUsername( var1.getUsername() );
userVo.setPassword( var1.getPassword() );
userVo.setBirthday( var1.getBirthday() );
userVo.setConfig( strConfigToListUserConfig( var1.getConfig() ) );
return userVo;
}
@Override
public User vo2Do(UserVo var1) {
if ( var1 == null ) {
return null;
}
User user = new User();
user.setSex( var1.getGender() );
if ( var1.getCreateTime() != null ) {
user.setCreateTime( LocalDateTime.parse( var1.getCreateTime(), DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern( "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" ) ) );
}
user.setId( var1.getId() );
user.setUsername( var1.getUsername() );
user.setBirthday( var1.getBirthday() );
user.setConfig( listUserConfigToStrConfig( var1.getConfig() ) );
return user;
}
@Override
public List<UserVo> do2voList(List<User> userList) {
if ( userList == null ) {
return null;
}
List<UserVo> list = new ArrayList<UserVo>( userList.size() );
for ( User user : userList ) {
list.add( do2vo( user ) );
}
return list;
}
}
这里面用了什么机制?
这和Lombok实现机制一致。
核心之处就是对于注解的解析上。JDK5引入了注解的同时,也提供了两种解析方式。
- 运行时解析
运行时能够解析的注解,必须将@Retention设置为RUNTIME, 比如@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME),这样就可以通过反射拿到该注解。java.lang,reflect反射包中提供了一个接口AnnotatedElement,该接口定义了获取注解信息的几个方法,Class、Constructor、Field、Method、Package等都实现了该接口,对反射熟悉的朋友应该都会很熟悉这种解析方式。
- 编译时解析
编译时解析有两种机制,分别简单描述下:
1)Annotation Processing Tool
apt自JDK5产生,JDK7已标记为过期,不推荐使用,JDK8中已彻底删除,自JDK6开始,可以使用Pluggable Annotation Processing API来替换它,apt被替换主要有2点原因:
- api都在com.sun.mirror非标准包下
- 没有集成到javac中,需要额外运行
2)Pluggable Annotation Processing API
JSR 269: Pluggable Annotation Processing API自JDK6加入,作为apt的替代方案,它解决了apt的两个问题,javac在执行的时候会调用实现了该API的程序,这样我们就可以对编译器做一些增强,这时javac执行的过程如下:

Lombok本质上就是一个实现了“JSR 269 API”的程序。在使用javac的过程中,它产生作用的具体流程如下:
- javac对源代码进行分析,生成了一棵抽象语法树(AST)
- 运行过程中调用实现了“JSR 269 API”的Lombok程序
- 此时Lombok就对第一步骤得到的AST进行处理,找到@Data注解所在类对应的语法树(AST),然后修改该语法树(AST),增加getter和setter方法定义的相应树节点
- javac使用修改后的抽象语法树(AST)生成字节码文件,即给class增加新的节点(代码块)
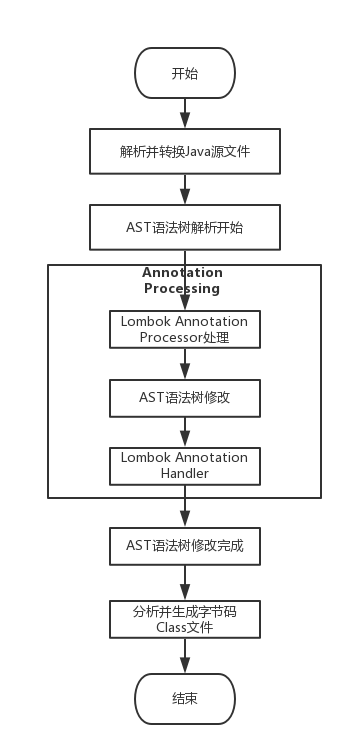
从上面的Lombok执行的流程图中可以看出,在Javac 解析成AST抽象语法树之后, Lombok 根据自己编写的注解处理器,动态地修改 AST,增加新的节点(即Lombok自定义注解所需要生成的代码),最终通过分析生成JVM可执行的字节码Class文件。使用Annotation Processing自定义注解是在编译阶段进行修改,而JDK的反射技术是在运行时动态修改,两者相比,反射虽然更加灵活一些但是带来的性能损耗更加大。
MapStruct更多例子
:::tip
一般特性和例子最好直接参考官网例子, 这里会差异化的体现一些常见的用法。@pdai
:::
自定义属性的转化
注意在不同的JDK版本中做法不太一样。@pdai
- JDK 8以上版本
一般常用的类型字段转换 MapStruct都能替我们完成,但是有一些是我们自定义的对象类型,MapStruct就不能进行字段转换,这就需要我们编写对应的类型转换方法,笔者使用的是JDK8,支持接口中的默认方法,可以直接在转换器中添加自定义类型转换方法。
上述例子中User对象的config属性是一个JSON字符串,UserVo对象中是List类型的,这需要实现JSON字符串与对象的互转。
default List<UserConfig> strConfigToListUserConfig(String config) {
return JSON.parseArray(config, UserConfig.class);
}
default String listUserConfigToStrConfig(List<UserConfig> list) {
return JSON.toJSONString(list);
}
- JDK 8 以下版本
如果是 JDK8以下的,不支持默认方法,可以另外定义一个 转换器,然后再当前转换器的 @Mapper 中通过 uses = XXX.class 进行引用。
定义好方法之后,MapStruct当匹配到合适类型的字段时,会调用我们自定义的转换方法进行转换。
转为多个对象
比如上面例子中User可以转为UserQueryParam, 业务功能上比如通过UserQueryParam里面的参数进行查找用户的。
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class UserQueryParam {
private Long id;
private String username;
}
添加转换方法
UserQueryParam vo2QueryParam(User var1);
Spring中使用MapStruct
除了UserConverter.INSTANCE这种方式还可以注入Spring容器中使用。
- componentModel
当添加componentModel="spring"时,它会在实现类上自动添加@Component注解,这样就能被Spring记性component scan,从而加载到springContext中,进而被@Autowird注入使用。(其它还有jsr330和cdi标准,基本上使用componentModel="spring"就够了)。
@Mapper(componentModel="spring")
public interface UserConverter {
}
- 引入和测试
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserConverterTest {
@Resource
private UserConverter userConverter;
// test methods
}
多个对象转一个对象
比如上述例子中User购买了东西,需要邮寄到他的地址Address,这时需要展示UserWithAddress的信息:
- Address
@Data
public class Address {
private String street;
private Integer zipCode;
private Integer houseNo;
private String description;
}
- UserWithAddressVo
@Data
public class UserWithAddressVo {
private String username;
private Integer sex;
private String street;
private Integer zipCode;
private Integer houseNumber;
private String description;
}
- converter方法
@Mapping(source = "person.description", target = "description")
@Mapping(source = "address.houseNo", target = "houseNumber")
UserWithAddressVo userAndAddress2Vo(User user, Address address);
注意:在多对一转换时, 遵循以下几个原则
- 当多个对象中, 有其中一个为 null, 则会直接返回 null
- 如一对一转换一样, 属性通过名字来自动匹配。 因此, 名称和类型相同的不需要进行特殊处理
- 当多个原对象中,有相同名字的属性时,需要通过 @Mapping 注解来具体的指定, 以免出现歧义(不指定会报错)。 如上面的 description
属性也可以直接从传入的参数来赋值。
@Mapping(source = "person.description", target = "description")
@Mapping(source = "hn", target = "houseNumber")
UserWithAddressVo userAndAddressHn2Vo(User user, Integer hn);
MapStruct再深入理解
:::tip
在了解基本的MapStruct使用之后,我们将从多个角度来深入理解MapStruct这个工具。@pdai
:::
IntelliJ IDEA 中对MapStruct的支持如何?
通常来说IDE对于MapStruct这类工具的支持体现在两方面,一个是Maven的集成,另一个是编辑时的提示(Hit); 相关的支持可以参考官网。@pdai
Maven支持
- 在IntelliJ 2018.1.1之前, 注意在早期的版本中
artifactId还需要加jdk版本,比如mapstruct-jdk8;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
- 在IntelliJ 2018.1.1之后是可以不添加
mapstruct-processor的
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<org.mapstruct.version>1.4.0.Beta3</org.mapstruct.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<!-- See https://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-compiler-plugin/compile-mojo.html -->
<!-- Classpath elements to supply as annotation processor path. If specified, the compiler -->
<!-- will detect annotation processors only in those classpath elements. If omitted, the -->
<!-- default classpath is used to detect annotation processors. The detection itself depends -->
<!-- on the configuration of annotationProcessors. -->
<!-- -->
<!-- According to this documentation, the provided dependency processor is not considered! -->
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
编辑器支持
- 编辑器支持:自动补全
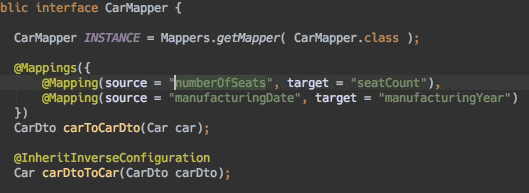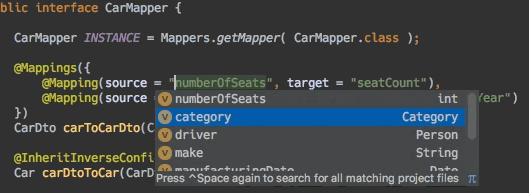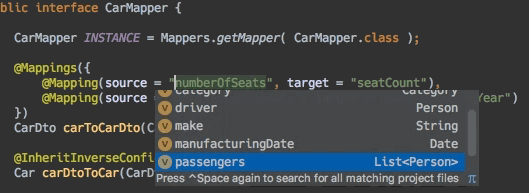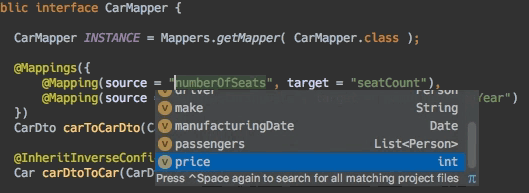
- 编辑器支持:连接跳转
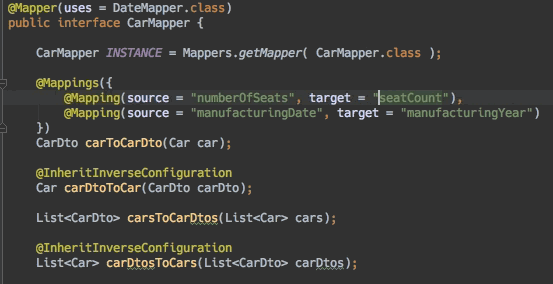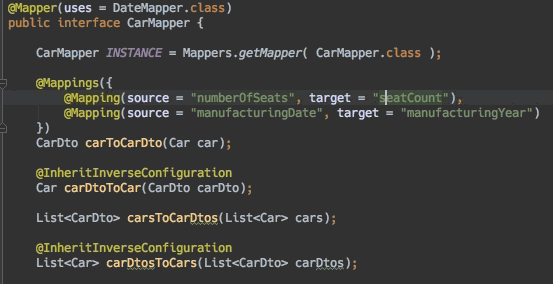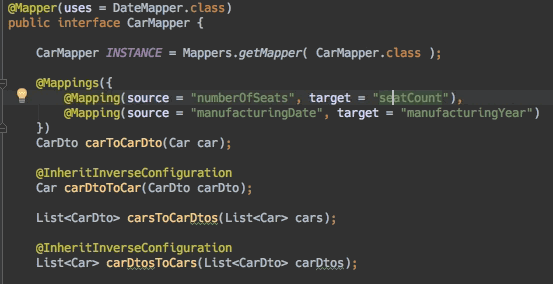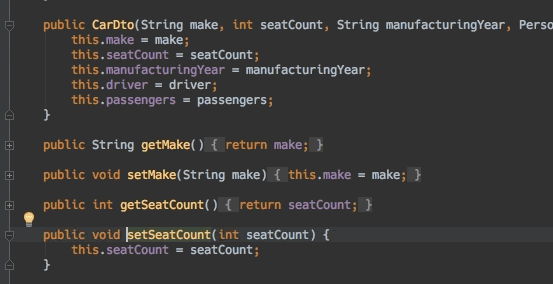
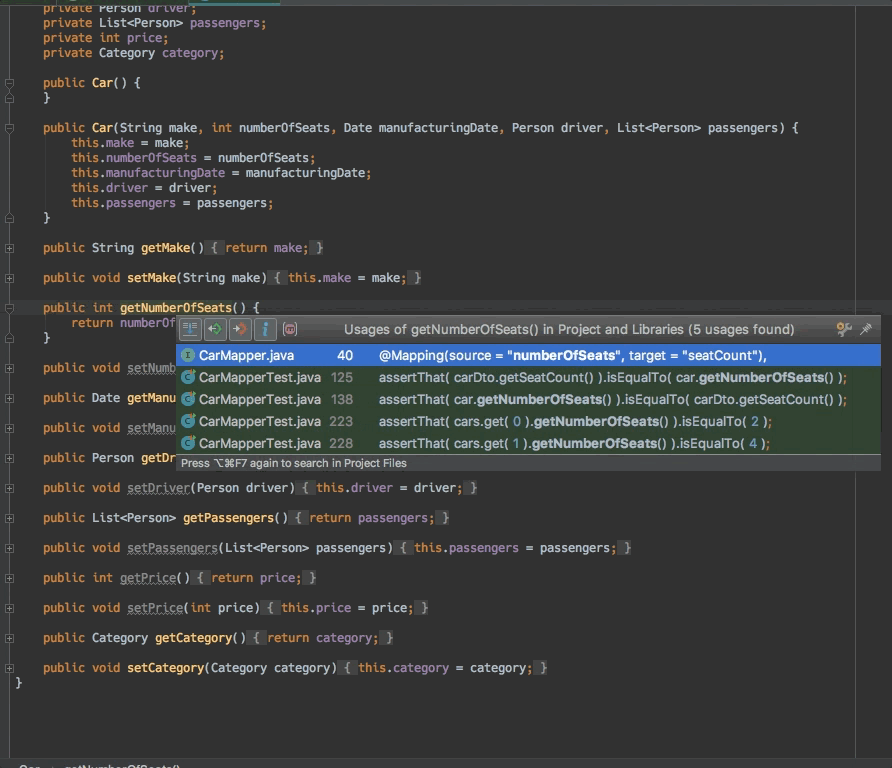
- 编辑器支持:查找使用方式
Eclipse 中对MapStruct的支持如何?
必须保证你使用的Eclipse中包含
m2e-apt插件,且尽可能的升级这个插件到最新的版本,这个插件主要用于自动应用annotation processor相关的配置。
Maven支持
同时在pom.xml中推荐你加入如下配置, 原因请看官方给的如下注释:
<properties>
<!-- automatically run annotation processors within the incremental compilation -->
<m2e.apt.activation>jdt_apt</m2e.apt.activation>
</properties>
编辑器支持
- 自动补全

- 快速修复

与其它属性拷贝框架性能到底相差多少?
基于我们对它原理的理解,我们知道mapstrcut最后执行时依然是get/set,所以性能是比较高的。同时我们也知道反射优化是可以解决一部分性能问题的,那么通过反射方式进行的属性拷贝和get/set这种性能相差多少呢?
有哪些属性拷贝方式呢?
综合我们前面的文章,常用的util包中有如下属性拷贝类:
- org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils.copyProperties
- org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils.copyProperties
- org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils.copyProperties
- net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanCopier
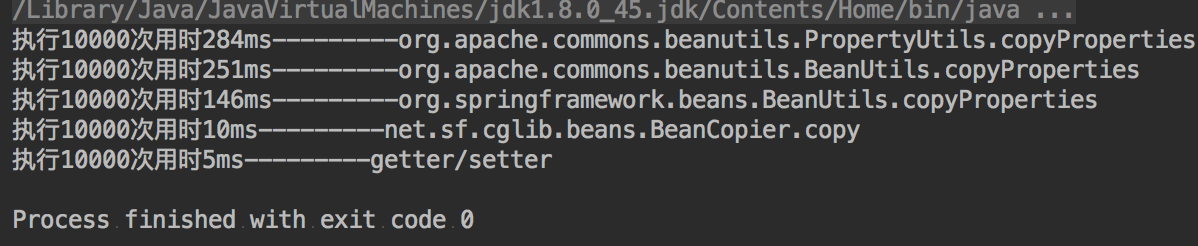
使用属性拷贝和set/get方式性能差异
- 10000次
- 1000次

- 10次
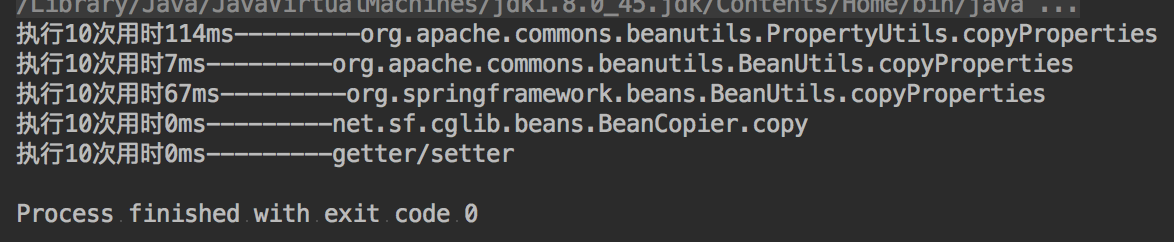
- 结论
- property少,写起来也不麻烦,就直接用传统的getter/setter,性能最好
- property多,转换不频繁,那就省点事吧,使用org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils.copyProperties
- property多,转换很频繁,为性能考虑,使用net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanCopier.BeanCopier,性能近乎getter/setter。但是BeanCopier的创建时消耗较大,所以不要频繁创建该实体,最好的处理方式是静态化或者缓存起来。
更多测试对比可以参考这里
和MapStruct类似框架的对比?
我们再看下是否有其它类似的框架呢?这里主要来源这篇文章
其它类似方案
- Dozer
Dozer 是一个映射框架,它使用递归将数据从一个对象复制到另一个对象。框架不仅能够在 bean 之间复制属性,还能够在不同类型之间自动转换。
更多关于 Dozer 的内容可以在官方文档中找到: http://dozer.sourceforge.net/documentation/gettingstarted.html ,或者你也可以阅读这篇文章:https://www.baeldung.com/dozer 。
- Orika
Orika 是一个 bean 到 bean 的映射框架,它递归地将数据从一个对象复制到另一个对象。
Orika 的工作原理与 Dozer 相似。两者之间的主要区别是 Orika 使用字节码生成。这允许以最小的开销生成更快的映射器。
更多关于 Orika 的内容可以在官方文档中找到:https://orika-mapper.github.io/orika-docs/,或者你也可以阅读这篇文章:https://www.baeldung.com/orika-mapping。
- ModelMapper
ModelMapper 是一个旨在简化对象映射的框架,它根据约定确定对象之间的映射方式。它提供了类型安全的和重构安全的 API。
更多关于 ModelMapper 的内容可以在官方文档中找到:http://modelmapper.org/ 。
- JMapper
JMapper 是一个映射框架,旨在提供易于使用的、高性能的 Java bean 之间的映射。该框架旨在使用注释和关系映射应用 DRY 原则。该框架允许不同的配置方式:基于注释、XML 或基于 api。
更多关于 JMapper 的内容可以在官方文档中找到:https://github.com/jmapper-framework/jmapper-core/wiki。
性能对比
对于性能测试,我们可以使用 Java Microbenchmark Harness,关于如何使用它的更多信息可以在 这篇文章:https://www.baeldung.com/java-microbenchmark-harness 中找到。
测试结果(某一种)
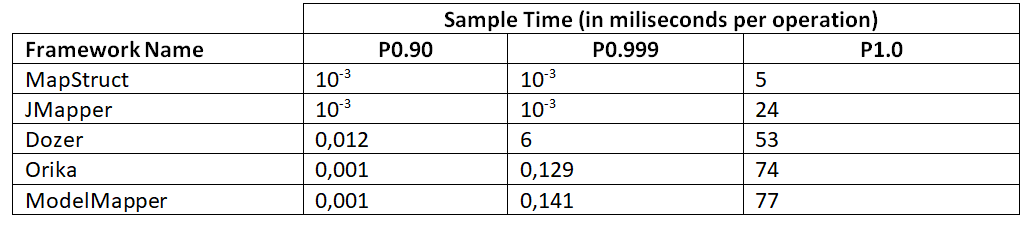
所有的基准测试都表明,根据场景的不同,MapStruct 和 JMapper 都是不错的选择,尽管 MapStruct 对 SingleShotTime 给出的结果要差得多。
其它常见问题?
当两个对象属性不一致时,比如User对象中某个字段不存在与UserVo当中时,在编译时会有警告提示,可以在@Mapping中配置 ignore = true,当字段较多时,可以直接在@Mapper中设置unmappedTargetPolicy属性或者unmappedSourcePolicy属性为 ReportingPolicy.IGNORE即可。
如果项目中也同时使用到了 Lombok,一定要注意 Lombok的版本要等于或者高于1.18.10,否则会有编译不通过的情况发生。
参考文章
https://mapstruct.org/documentation
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoyanghoo/p/5722113.html
https://www.baeldung.com/java-performance-mapping-frameworks
https://www.cnblogs.com/javaguide/p/11861749.html
常用开发库 - MapStruct工具库详解的更多相关文章
- 常用开发库 - 告別BeanUtils拷贝,MapStruct工具库最全详解
常用开发库 - MapStruct工具库详解 MapStruct是一款非常实用Java工具,主要用于解决对象之间的拷贝问题,比如PO/DTO/VO/QueryParam之间的转换问题.区别于BeanU ...
- 【Android 应用开发】Ubuntu 下 Android Studio 开发工具使用详解 (旧版本 | 仅作参考)
. 基本上可以导入项目开始使用了 ... . 作者 : 万境绝尘 转载请注明出处 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/21035637 ...
- 【Android 应用开发】Ubuntu 下 Android Studio 开发工具使用详解
. 基本上可以导入项目开始使用了 ... . 作者 : 万境绝尘 转载请注明出处 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/21035637 ...
- 技巧:Linux 动态库与静态库制作及使用详解
技巧:Linux 动态库与静态库制作及使用详解 标准库的三种连接方式及静态库制作与使用方法 Linux 应用开发通常要考虑三个问题,即:1)在 Linux 应用程序开发过程中遇到过标准库链接在不同 L ...
- IE8“开发人员工具”使用详解上(各级菜单详解)
来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/JustinYoung/archive/2009/03/24/kaifarenyuangongju.html IE8“开发人员工具”使用详解上(各 ...
- (转)python标准库中socket模块详解
python标准库中socket模块详解 socket模块简介 原文:http://www.lybbn.cn/data/datas.php?yw=71 网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的 ...
- Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解
Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解 虽然Python的标准库中urllib2模块已经包含了平常我们使用的大多数功能,但是它的API使用起来让人实在感觉不好.它已经不适合现在的时代, ...
- IE8"开发人员工具"使用详解下(浏览器模式、文本模式、JavaScript调试、探查器)
来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/JustinYoung/archive/2009/04/03/kaifarenyuangongju2.html 在上一篇文章IE8“开发人员工具” ...
- 自动化运维工具——ansile详解
自动化运维工具——ansible详解(一) 目录 ansible 简介 ansible 是什么? ansible 特点 ansible 架构图 ansible 任务执行 ansible 任务执行模式 ...
随机推荐
- LOJ6283 数列分块入门 7 (分块 区间加/乘)题解
题意:区间加,区间乘,单点询问 思路:假设一个点为a,那么他可以表示为m * a + sum,所以区间加就变为m * a + sum + sum2,区间乘变为m * m2 * a + sum * m2 ...
- VP9 & AV1 & H.265
VP9 & AV1 & H.265 视频编码格式 AV1 https://caniuse.com/#search=AV1 VP9 https://caniuse.com/#search ...
- .gitignore规则不生效
.gitignore只能忽略那些原来没有被track的文件,如果某些文件已经被纳入了版本管理中,则修改.gitignore是无效的. 解决方法就是先把本地缓存删除(改变成未track状态),然后再提交 ...
- Flutter: redux简单使用
Pub redux flutter_redux import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:redux/redux.dart'; i ...
- C++算法代码——Tuna
这道题像个水题啊,可是在我做的这个OJ上就十几人做出来-- 题目来自:http://218.5.5.242:9018/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=2084 题目描述 渔民抓住 ...
- 死磕Spring之IoC篇 - 文章导读
该系列文章是本人在学习 Spring 的过程中总结下来的,里面涉及到相关源码,可能对读者不太友好,请结合我的源码注释 Spring 源码分析 GitHub 地址 进行阅读 Spring 版本:5.1. ...
- 2021 年学习 React 的所需要的 JavaScript 基础
在理想的情况中,您可以先了解所有有关 JavaScript 和 web 开发的知识,然后再深入了解React. 但是,我们没有办法这样,如果等你把所有 JavaScript 的知识都掌握了再去学习 R ...
- Vue学习笔记-Vue.js-2.X 学习(六)===>脚手架Vue-CLI(项目说明-Babel)
五 Vue学习-vue-cli脚手架学习(创建只选一个选项:Babel) 1. 项目目录说明 node_modules : 包管理文件夹 public : 静态资源 src : 源代码 gitign ...
- ubuntu系统共享桌面的使用和配置
内容转载自我的博客 目录 1. ubuntu共享桌面 2. 局域网登录远程桌面 2.1 ubuntu使用remmina登录远程桌面 2.2 在windows登录远程桌面 2.3 Android使用RD ...
- RabbitMQ-RPC版主机管理程序
一.作业需求 1.可以对指定机器异步的执行多个命令 例子: 请输入操作指令>>>:run ipconfig --host 127.0.0.0 in the call tack ...
