Notes on Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA)
转自:http://www.hongliangjie.com/2010/01/04/notes-on-probabilistic-latent-semantic-analysis-plsa/
I highly recommend you read the more detailed version of http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.3900
Formulation of PLSA
There are two ways to formulate PLSA. They are equivalent but may lead to different inference process.
Let’s see why these two equations are equivalent by using Bayes rule.
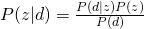
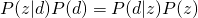
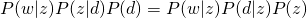
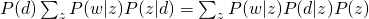
The whole data set is generated as (we assume that all words are generated independently):
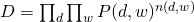
The Log-likelihood of the whole data set for (1) and (2) are:
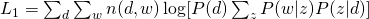
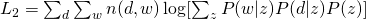
EM
For 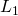 or
or 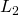 , the optimization is hard due to the log of sum. Therefore, an algorithm called Expectation-Maximization is usually employed. Before we introduce anything about EM, please note that EM is only guarantee to find a local optimum (although it may be a global one).
, the optimization is hard due to the log of sum. Therefore, an algorithm called Expectation-Maximization is usually employed. Before we introduce anything about EM, please note that EM is only guarantee to find a local optimum (although it may be a global one).
First, we see how EM works in general. As we shown for PLSA, we usually want to estimate the likelihood of data, namely 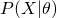 , given the paramter
, given the paramter 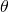 . The easiest way is to obtain a maximum likelihood estimator by maximizing
. The easiest way is to obtain a maximum likelihood estimator by maximizing 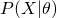 . However, sometimes, we also want to include some hidden variables which are usually useful for our task. Therefore, what we really want to maximize is
. However, sometimes, we also want to include some hidden variables which are usually useful for our task. Therefore, what we really want to maximize is 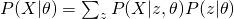 , the complete likelihood. Now, our attention becomes to this complete likelihood. Again, directly maximizing this likelihood is usually difficult. What we would like to show here is to obtain a lower bound of the likelihood and maximize this lower bound.
, the complete likelihood. Now, our attention becomes to this complete likelihood. Again, directly maximizing this likelihood is usually difficult. What we would like to show here is to obtain a lower bound of the likelihood and maximize this lower bound.
We need Jensen’s Inequality to help us obtain this lower bound. For any convex function 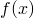 , Jensen’s Inequality states that :
, Jensen’s Inequality states that :
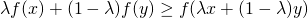
Thus, it is not difficult to show that :
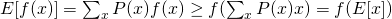
and for concave functions (like logarithm), it is :
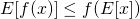
Back to our complete likelihood, we can obtain the following conclusion by using concave version of Jensen’s Inequality :
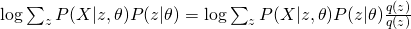
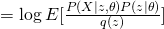
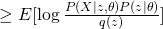
Therefore, we obtained a lower bound of complete likelihood and we want to maximize it as tight as possible. EM is an algorithm that maximize this lower bound through a iterative fashion. Usually, EM first would fix current 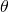 value and maximize
value and maximize 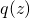 and then use the new
and then use the new 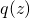 value to obtain a new guess on
value to obtain a new guess on 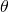 , which is essentially a two stage maximization process. The first step can be shown as follows:
, which is essentially a two stage maximization process. The first step can be shown as follows:
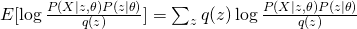
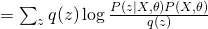
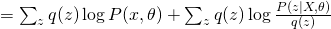
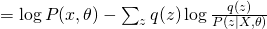
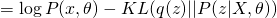
The first term is the same for all  . Therefore, in order to maximize the whole equation, we need to minimize KL divergence between
. Therefore, in order to maximize the whole equation, we need to minimize KL divergence between 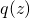 and
and 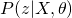 , which eventually leads to the optimum solution of
, which eventually leads to the optimum solution of 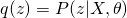 . So, usually for E-step, we use current guess of
. So, usually for E-step, we use current guess of 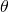 to calculate the posterior distribution of hidden variable as the new update score. For M-step, it is problem-dependent. We will see how to do that in later discussions.
to calculate the posterior distribution of hidden variable as the new update score. For M-step, it is problem-dependent. We will see how to do that in later discussions.
Another explanation of EM is in terms of optimizing a so-called Q function. We devise the data generation process as 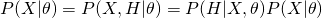 . Therefore, the complete likelihood is modified as:
. Therefore, the complete likelihood is modified as:
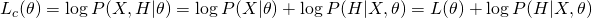
Think about how to maximize 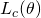 . Instead of directly maximizing it, we can iteratively maximize
. Instead of directly maximizing it, we can iteratively maximize 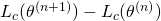 as :
as :
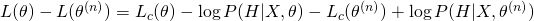
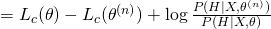
Now take the expectation of this equation, we have:

The last term is always non-negative since it can be recognized as the KL-divergence of 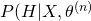 and
and 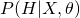 . Therefore, we obtain a lower bound of Likelihood :
. Therefore, we obtain a lower bound of Likelihood :
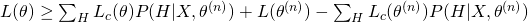
The last two terms can be treated as constants as they do not contain the variable 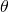 , so the lower bound is essentially the first term, which is also sometimes called as “Q-function”.
, so the lower bound is essentially the first term, which is also sometimes called as “Q-function”. 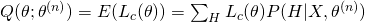
EM of Formulation 1
In case of Formulation 1, let us introduce hidden variables 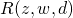 to indicate which hidden topic
to indicate which hidden topic  is selected to generated
is selected to generated 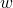 in
in 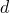 (
(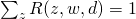 ). Therefore, the complete likelihood can be formulated as :
). Therefore, the complete likelihood can be formulated as :
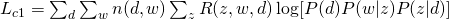
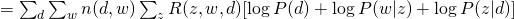
From the equation above, we can write our Q-function for the complete likelihood 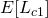 :
:
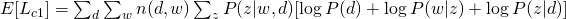
For E-step, simply using Bayes Rule, we can obtain:
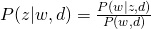
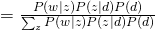
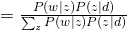
For M-step, we need to maximize Q-function, which needs to be incorporated with other constraints:
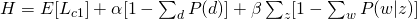

and take all derivatives:
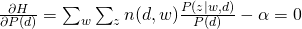
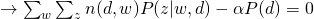
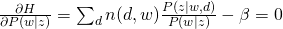
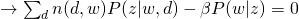
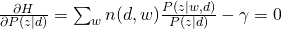
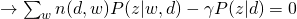
Therefore, we can easily obtain:
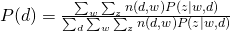
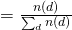
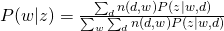
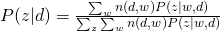
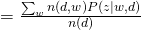
EM of Formulation 2
Use similar method to introduce hidden variables to indicate which  is selected to generated
is selected to generated 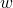 and
and 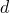 and we can have the following complete likelihood :
and we can have the following complete likelihood :
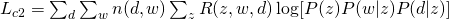
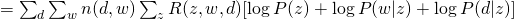
Therefore, the Q-function 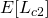 would be :
would be :
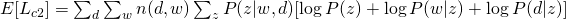
For E-step, again, simply using Bayes Rule, we can obtain:
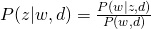
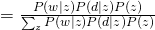
For M-step, we maximize the constraint version of Q-function:
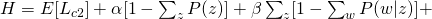
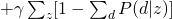
and take all derivatives:
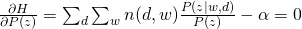
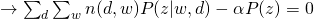
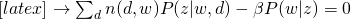
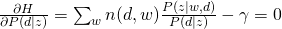
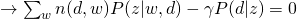
Therefore, we can easily obtain:
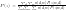
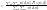
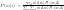
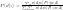
Notes on Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis (PLSA)的更多相关文章
- NLP —— 图模型(三)pLSA(Probabilistic latent semantic analysis,概率隐性语义分析)模型
LSA(Latent semantic analysis,隐性语义分析).pLSA(Probabilistic latent semantic analysis,概率隐性语义分析)和 LDA(Late ...
- 主题模型之概率潜在语义分析(Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis)
上一篇总结了潜在语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis, LSA),LSA主要使用了线性代数中奇异值分解的方法,但是并没有严格的概率推导,由于文本文档的维度往往很高,如果在主题聚类 ...
- Latent semantic analysis note(LSA)
1 LSA Introduction LSA(latent semantic analysis)潜在语义分析,也被称为LSI(latent semantic index),是Scott Deerwes ...
- 主题模型之潜在语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis)
主题模型(Topic Models)是一套试图在大量文档中发现潜在主题结构的机器学习模型,主题模型通过分析文本中的词来发现文档中的主题.主题之间的联系方式和主题的发展.通过主题模型可以使我们组织和总结 ...
- Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Tutorial 潜语义分析LSA介绍 一
Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Tutorial 译:http://www.puffinwarellc.com/index.php/news-and-articles/a ...
- 潜语义分析(Latent Semantic Analysis)
LSI(Latent semantic indexing, 潜语义索引)和LSA(Latent semantic analysis,潜语义分析)这两个名字其实是一回事.我们这里称为LSA. LSA源自 ...
- 潜在语义分析Latent semantic analysis note(LSA)原理及代码
文章引用:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_62a9902f0101cjl3.html Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA)也被称为Latent S ...
- 海量数据挖掘MMDS week4: 推荐系统之隐语义模型latent semantic analysis
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49256457 海量数据挖掘Mining Massive Datasets(MMDs) -Jure Le ...
- Latent Semantic Analysis(LSA/ LSI)原理简介
LSA的工作原理: How Latent Semantic Analysis Works LSA被广泛用于文献检索,文本分类,垃圾邮件过滤,语言识别,模式检索以及文章评估自动化等场景. LSA其中一个 ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode Longest Common Prefix 最长公共前缀
题意:给多个字符串,返回这些字符串的最长公共前缀. 思路:直接逐个统计同一个位置上的字符有多少种,如果只有1种,那么就是该位是相同的,进入下一位比较.否则终止比较,返回前缀.可能有一个字符串会比较短, ...
- android SDK 快速更新配置(转)
http://blog.csdn.net/yy1300326388/article/details/45074447 1.强制使用http替换https链接 Tools>选择Options,勾选 ...
- nodejs开发阶段利器supervisor
在开始学习nodejs时,往往一般写代码,一边看效果.先停止node,再重新运行.非常耗时. 这时supervisor派上了用场. 安装 推荐使用npm,本人一直使用局部安装,这样可以将全部文件安装在 ...
- SAS Config文件 处理流程
Processing Options Specified by Additional CONFIG Options You can also specify additional –CONFIG op ...
- centos下安装xfce+vnc
首先安装桌面环境,我选择的是xfce,轻量级桌面,小巧实用不占太多内存,(占用内存方面,xfce少于kde,kde少于gnome). 安装xfce桌面一开始我以为第三方的软件源如rpmforge等应该 ...
- Linux makefile教程之概述一[转]
概述—— 什么是makefile?或许很多Winodws的程序员都不知道这个东西,因为那些 Windows的IDE都为你做了这个工作,但我觉得要作一个好的和professional的程序员,makef ...
- 常用的Oracle数据库语句 (待更新完毕)
一.常用的查询语句 1.1 常用查询 查表中有多少个字段 select count(*) from user_tab_columns where table_name=upper('表名') 或者 s ...
- SQL语句构建器类
问题 Java程序员面对的最痛苦的事情之一就是在Java代码中嵌入SQL语句.这么来做通常是由于SQL语句需要动态来生成-否则可以将它们放到外部文件或者存储过程中.正如你已经看到的那样,MyBatis ...
- new 动态分配数组空间 .xml
pre{ line-height:1; color:#3c3c3c; background-color:#d2c39b; font-size:16px;}.sysFunc{color:#627cf6; ...
- C++ 中类的构造函数理解(二)
C++ 中类的构造函数理解(二) 写在前面 上次的笔记中简要的探索了一下C++中类的构造函数的一些特性,这篇笔记将做进一步的探索.主要是复制构造函数的使用. 复制构造函数 复制构造函数也称拷贝构造函数 ...


