scikit-learn机器学习(三)多项式回归(二阶,三阶,九阶)
我们仍然使用披萨直径的价格的数据
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=[u'simHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures X_train = [[6],[8],[10],[14],[18]]
y_train = [[7],[9],[13],[17.5],[18]]
X_test = [[6],[8],[11],[16]]
y_test = [[8],[12],[15],[18]] LR = LinearRegression()
LR.fit(X_train,y_train) xx = np.linspace(0,26,100)
yy = LR.predict(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
plt.plot(xx,yy)
二阶多项式回归
# In[1] 二次回归,二阶多项式回归
#PolynomialFeatures转换器可以用于为一个特征表示增加多项式特征
quadratic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
X_train_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_quadratic = LinearRegression()
regressor_quadratic.fit(X_train_quadratic,y_train) xx_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_quadratic = regressor_quadratic.predict(xx_quadratic)
plt.plot(xx,yy_quadratic,c='r',linestyle='--')
# In[2] 图参数,输出结果
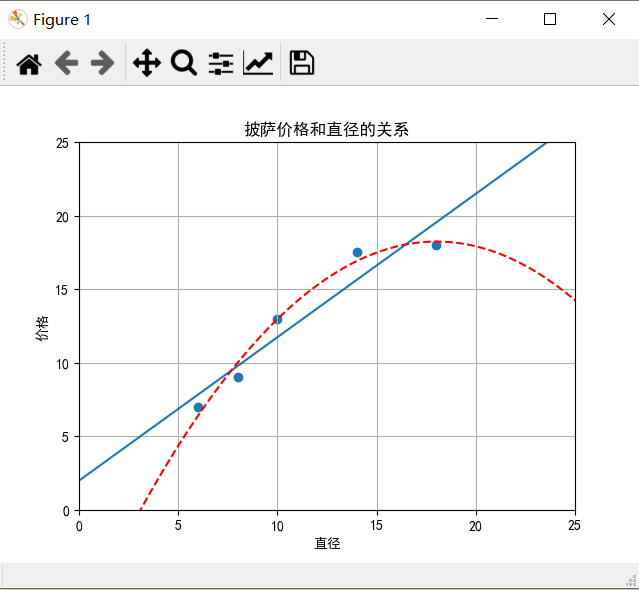
plt.title("披萨价格和直径的关系")
plt.xlabel("直径")
plt.ylabel("价格")
plt.axis([0,25,0,25])
plt.grid(True)
plt.scatter(X_train,y_train) print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_quadratic\n",X_train_quadratic)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_quadratic\n",X_test_quadratic)
print("简单线性规划R方",LR.score(X_test,y_test))
print("二阶多项式回归R方",regressor_quadratic.score(X_test_quadratic,y_test))
X_train
[[6], [8], [10], [14], [18]]
X_train_quadratic
[[ 1. 6. 36.]
[ 1. 8. 64.]
[ 1. 10. 100.]
[ 1. 14. 196.]
[ 1. 18. 324.]]
X_test
[[6], [8], [11], [16]]
X_test_quadratic
[[ 1. 6. 36.]
[ 1. 8. 64.]
[ 1. 11. 121.]
[ 1. 16. 256.]]
简单线性规划R方 0.809726797707665
三阶多项式回归
# In[3] 尝试三阶多项式回归
cubic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)
X_train_cubic = cubic_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_cubic = LinearRegression()
regressor_cubic.fit(X_train_cubic,y_train) xx_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_cubic = regressor_cubic.predict(xx_cubic)
plt.plot(xx,yy_cubic,c='g',linestyle='--')
plt.show() print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_cubic\n",X_train_cubic)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_cubic\n",X_test_cubic)
print("三阶多项式回归R方",regressor_cubic.score(X_test_cubic,y_test))

X_train
[[6], [8], [10], [14], [18]]
X_train_cubic
[[1.000e+00 6.000e+00 3.600e+01 2.160e+02]
[1.000e+00 8.000e+00 6.400e+01 5.120e+02]
[1.000e+00 1.000e+01 1.000e+02 1.000e+03]
[1.000e+00 1.400e+01 1.960e+02 2.744e+03]
[1.000e+00 1.800e+01 3.240e+02 5.832e+03]]
X_test
[[6], [8], [11], [16]]
X_test_cubic
[[1.000e+00 6.000e+00 3.600e+01 2.160e+02]
[1.000e+00 8.000e+00 6.400e+01 5.120e+02]
[1.000e+00 1.100e+01 1.210e+02 1.331e+03]
[1.000e+00 1.600e+01 2.560e+02 4.096e+03]]
三阶多项式回归R方 0.8356924156036954
九阶多项式回归
# In[4] 尝试九阶多项式回归
nine_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=9)
X_train_nine = nine_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_nine = nine_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_nine = LinearRegression()
regressor_nine.fit(X_train_nine,y_train) xx_nine = nine_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_nine = regressor_nine.predict(xx_nine)
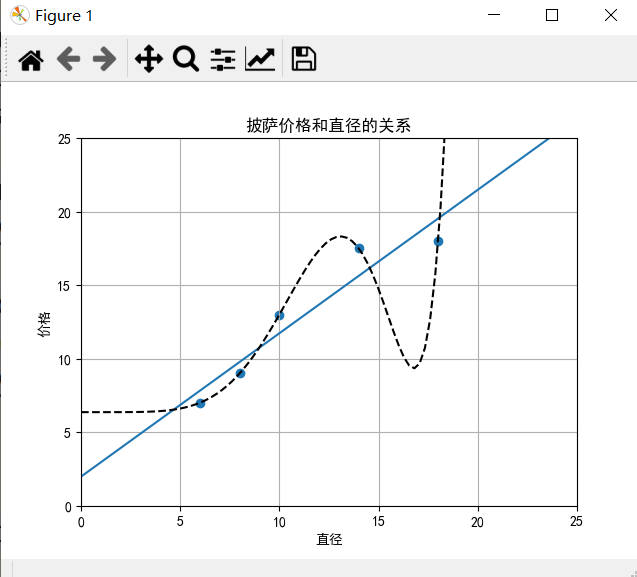
plt.plot(xx,yy_nine,c='k',linestyle='--')
plt.show() print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_nine\n",X_train_nine)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_nine\n",X_test_nine)
print("九阶多项式回归R方",regressor_nine.score(X_test_nine,y_test))
X_train
[[6], [8], [10], [14], [18]]
X_train_nine
[[1.00000000e+00 6.00000000e+00 3.60000000e+01 2.16000000e+02
1.29600000e+03 7.77600000e+03 4.66560000e+04 2.79936000e+05
1.67961600e+06 1.00776960e+07]
[1.00000000e+00 8.00000000e+00 6.40000000e+01 5.12000000e+02
4.09600000e+03 3.27680000e+04 2.62144000e+05 2.09715200e+06
1.67772160e+07 1.34217728e+08]
[1.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+01 1.00000000e+02 1.00000000e+03
1.00000000e+04 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+06 1.00000000e+07
1.00000000e+08 1.00000000e+09]
[1.00000000e+00 1.40000000e+01 1.96000000e+02 2.74400000e+03
3.84160000e+04 5.37824000e+05 7.52953600e+06 1.05413504e+08
1.47578906e+09 2.06610468e+10]
[1.00000000e+00 1.80000000e+01 3.24000000e+02 5.83200000e+03
1.04976000e+05 1.88956800e+06 3.40122240e+07 6.12220032e+08
1.10199606e+10 1.98359290e+11]]
X_test
[[6], [8], [11], [16]]
X_test_nine
[[1.00000000e+00 6.00000000e+00 3.60000000e+01 2.16000000e+02
1.29600000e+03 7.77600000e+03 4.66560000e+04 2.79936000e+05
1.67961600e+06 1.00776960e+07]
[1.00000000e+00 8.00000000e+00 6.40000000e+01 5.12000000e+02
4.09600000e+03 3.27680000e+04 2.62144000e+05 2.09715200e+06
1.67772160e+07 1.34217728e+08]
[1.00000000e+00 1.10000000e+01 1.21000000e+02 1.33100000e+03
1.46410000e+04 1.61051000e+05 1.77156100e+06 1.94871710e+07
2.14358881e+08 2.35794769e+09]
[1.00000000e+00 1.60000000e+01 2.56000000e+02 4.09600000e+03
6.55360000e+04 1.04857600e+06 1.67772160e+07 2.68435456e+08
4.29496730e+09 6.87194767e+10]]
九阶多项式回归R方 -0.09435666704291412
所有代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=[u'simHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures X_train = [[6],[8],[10],[14],[18]]
y_train = [[7],[9],[13],[17.5],[18]]
X_test = [[6],[8],[11],[16]]
y_test = [[8],[12],[15],[18]] LR = LinearRegression()
LR.fit(X_train,y_train) xx = np.linspace(0,26,100)
yy = LR.predict(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
plt.plot(xx,yy) # In[1] 二次回归,二阶多项式回归
#PolynomialFeatures转换器可以用于为一个特征表示增加多项式特征
quadratic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
X_train_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_quadratic = LinearRegression()
regressor_quadratic.fit(X_train_quadratic,y_train) xx_quadratic = quadratic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_quadratic = regressor_quadratic.predict(xx_quadratic)
plt.plot(xx,yy_quadratic,c='r',linestyle='--') # In[2] 图参数,输出结果
plt.title("披萨价格和直径的关系")
plt.xlabel("直径")
plt.ylabel("价格")
plt.axis([0,25,0,25])
plt.grid(True)
plt.scatter(X_train,y_train) print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_quadratic\n",X_train_quadratic)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_quadratic\n",X_test_quadratic)
print("简单线性规划R方",LR.score(X_test,y_test))
print("二阶多项式回归R方",regressor_quadratic.score(X_test_quadratic,y_test)) # In[3] 尝试三阶多项式回归
cubic_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)
X_train_cubic = cubic_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_cubic = LinearRegression()
regressor_cubic.fit(X_train_cubic,y_train) xx_cubic = cubic_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_cubic = regressor_cubic.predict(xx_cubic)
plt.plot(xx,yy_cubic,c='g',linestyle='--')
plt.show() print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_cubic\n",X_train_cubic)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_cubic\n",X_test_cubic)
print("三阶多项式回归R方",regressor_cubic.score(X_test_cubic,y_test)) # In[4] 尝试九阶多项式回归
nine_featurizer = PolynomialFeatures(degree=9)
X_train_nine = nine_featurizer.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_nine = nine_featurizer.transform(X_test) regressor_nine = LinearRegression()
regressor_nine.fit(X_train_nine,y_train) xx_nine = nine_featurizer.transform(xx.reshape(xx.shape[0],1))
yy_nine = regressor_nine.predict(xx_nine)
plt.plot(xx,yy_nine,c='k',linestyle='--')
plt.show() print("X_train\n",X_train)
print("X_train_nine\n",X_train_nine)
print("X_test\n",X_test)
print("X_test_nine\n",X_test_nine)
print("九阶多项式回归R方",regressor_nine.score(X_test_nine,y_test))

scikit-learn机器学习(三)多项式回归(二阶,三阶,九阶)的更多相关文章
- (原创)(三)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的线性回归模型初探
一.Scikit Learn中使用estimator三部曲 1. 构造estimator 2. 训练模型:fit 3. 利用模型进行预测:predict 二.模型评价 模型训练好后,度量模型拟合效果的 ...
- Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/175377/blog/84420#OSC_h2_23 Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习 Warning 警告:有些没能理解的 ...
- (原创)(四)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的Logistic回归初探
目录 5.3 使用LogisticRegressionCV进行正则化的 Logistic Regression 参数调优 一.Scikit Learn中有关logistics回归函数的介绍 1. 交叉 ...
- scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类 (python代码)
scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类数据集 fetch_20newsgroups #-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import ...
- TensorFlow 便捷的实现机器学习 三
TensorFlow 便捷的实现机器学习 三 MNIST 卷积神经网络 Fly Overview Enabling Logging with TensorFlow Configuring a Vali ...
- 【机器学习】多项式回归sklearn实现
[机器学习]多项式回归原理介绍 [机器学习]多项式回归python实现 [机器学习]多项式回归sklearn实现 使用sklearn框架实现多项式回归.使用框架更方便,可以少写很多代码. 使用一个简单 ...
- 【机器学习】多项式回归python实现
[机器学习]多项式回归原理介绍 [机器学习]多项式回归python实现 [机器学习]多项式回归sklearn实现 使用python实现多项式回归,没有使用sklearn等机器学习框架,目的是帮助理解算 ...
- Scikit Learn
Scikit Learn Scikit-Learn简称sklearn,基于 Python 语言的,简单高效的数据挖掘和数据分析工具,建立在 NumPy,SciPy 和 matplotlib 上.
- 机器学习框架Scikit Learn的学习
一 安装 安装pip 代码如下:# wget "https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/p/pip/pip-1.5.4.tar.gz#md5=83 ...
随机推荐
- 页面Header自适应屏幕
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8& ...
- c++对象模型和RTTI(runtime type information)
在前面已经探讨过了虚继承对类的大小的影响,这次来加上虚函数和虚继承对类的大小的影响. 先来回顾一下之前例子的代码: #include <iostream> using namespace ...
- MySQl 进阶一 基本查询及练习
知识点及练习 USE myemployees; #.查询表中的单个字段 SELECT last_name FROM employees; #.查询表中多个字段 #.查询全部 SELECT * FROM ...
- 0008SpringBoot中的spring.config.location对于运维的用处
在工作过程中,若项目已经打好包,application.properties中的配置文件已经不能修改,但是还是需要修改一些参数或者新增一些参数的情况下怎么办? 可以单独再定义一个配置文件,比如定义名称 ...
- 实例化Vue时的两种挂载方式el与$mount
el 与mount 都是挂载. el vue官网的介绍https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#el mount vue官网的介绍 https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/ap ...
- linux mint安装mysql-8.0.16
1.使用通用二进制文件在Unix / Linux上安装MySQL 下载的文件:mysql-8.0.16-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz 注意: 如果您以前使用操作系统本机程 ...
- Python 10--模块
可以在模块中,直接使用__file__,识别出该模块文件的路径. print __file__
- list,tuple,set,dict基础
list # @Auther : chen # @Time : 2018/4/26 19:55 # @File : list_ex.py # @SoftWare : PyCharm # list1 = ...
- yii 查询垃圾分类接口
public function actionGarbage() { // $param = \Yii::$app->request->post('rubbish', ''); // 接收j ...
- python以下划线开头的变量和函数的作用
在python中,我们经常能看到很多变量名以_下划线开头,而且下划线的数量还不一样,那么这些变量的作用到底是什么? 变量名分类: # 以数字.字母开头: 正常的公有变量名a = 1def aa(): ...
